Unit 10- Mixtures and solutions
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What’s a mixture?
When two or more substances mix together but be able to sepeate into two pure substances.
Solution
Homogeneous mixture that has substances that are uniformly distributed. Can be gas, liquid, aqueous, or solid.
Suspension
Heterogeneous mixture that contains large particles that are unevenly distributed. Dispersed, settle, float, etc
Colloid
Heterogeneous mixture that has tiny particles that remain distributed throughout the water. Usually produce cloudy mixture
What’s homogeneous?
A mixture in which the particles are uniformly distributed and the particles are not visible.
What’s heterogenous?
A mixture in which you can see the particles and there are different visible parts. Particles are NOT uniformly distributed.
electrolyte
substance that dissolves in water and the solution conducts electricity. (ionic bonds, polar molecules, strong acids)
non-electrolyte
substance that dissolves in water but the solution does not conduct electricity (covalent bonds/weak acids)
alloy
a solid solution
concentration
The amount of solute in a given amount of solvent
What are 3 ways to express concentration?
Molarity, dilutions, and mole fraction!
Molarity formula:
Molarity = moles of solute / liters of solution
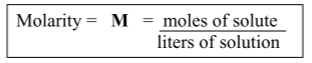
Dilutions formula
M1V1= M2V2 M= molarity (M) V= volume (L)
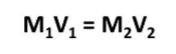
what does M1 mean in the formula?
stock solution or initial value
What is the formula for mole fraction?
mole fraction = moles of component / total moles of solution

solvent
thing doing the dissolving (most common is water)
solute
thing that’s dissolving
What are the 4 ways to classify mixtures?
Filtration, distillation, crystallization, and chromatography
What are the 3 factors that affect the solubility of a solute?
Surface area, stirring/shaking, and temperature
Does pressure affect liquids, solids, and gases?
It only affects gases, it increases the solubility