Week 6: The Nervous System
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
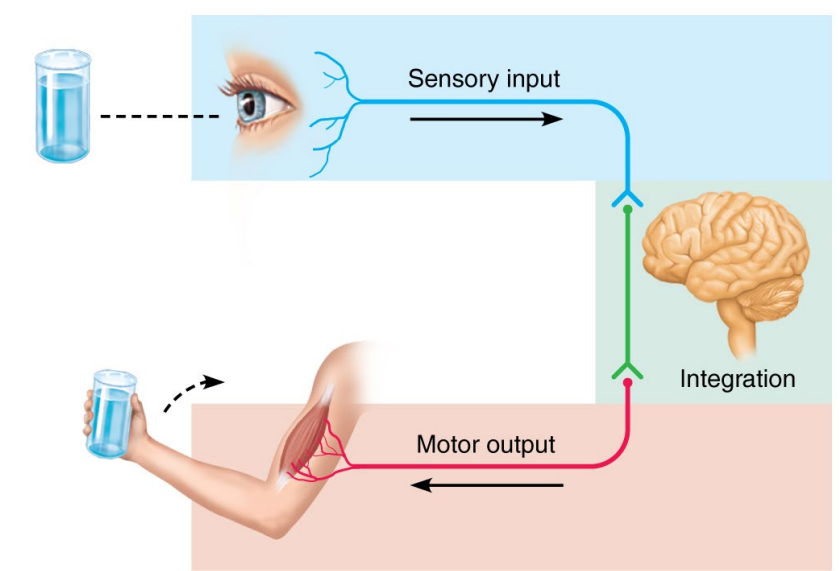
What are the 3 Basic Functions of the Nervous System?
Sensory - Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment.
Integration - Input is processed so that the system (brain) can decide on what to do.
Motor Output - Response initiated which then activates the body’s muscles and glands.
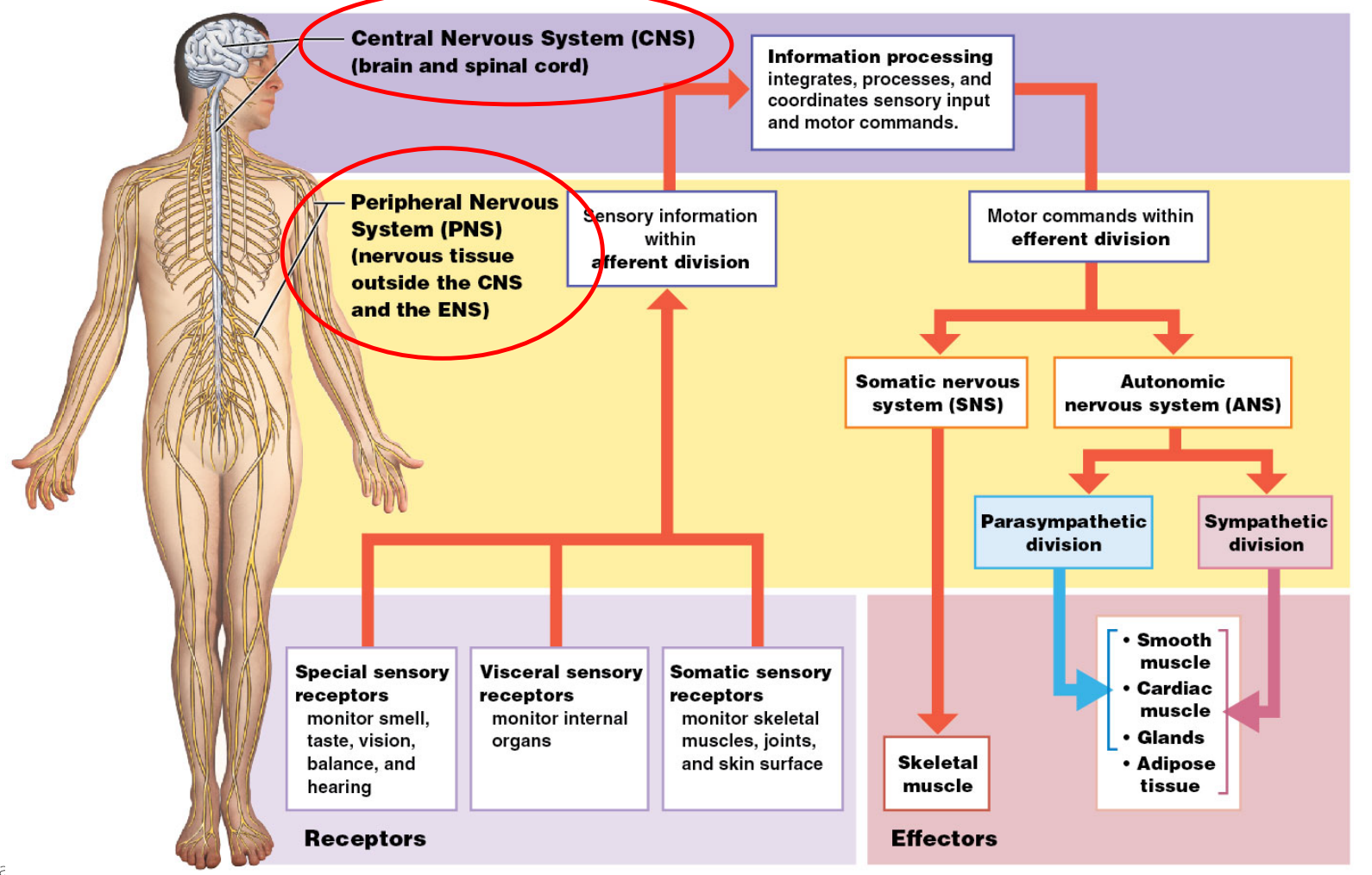
Name and describe the Divisions of the Nervous System:
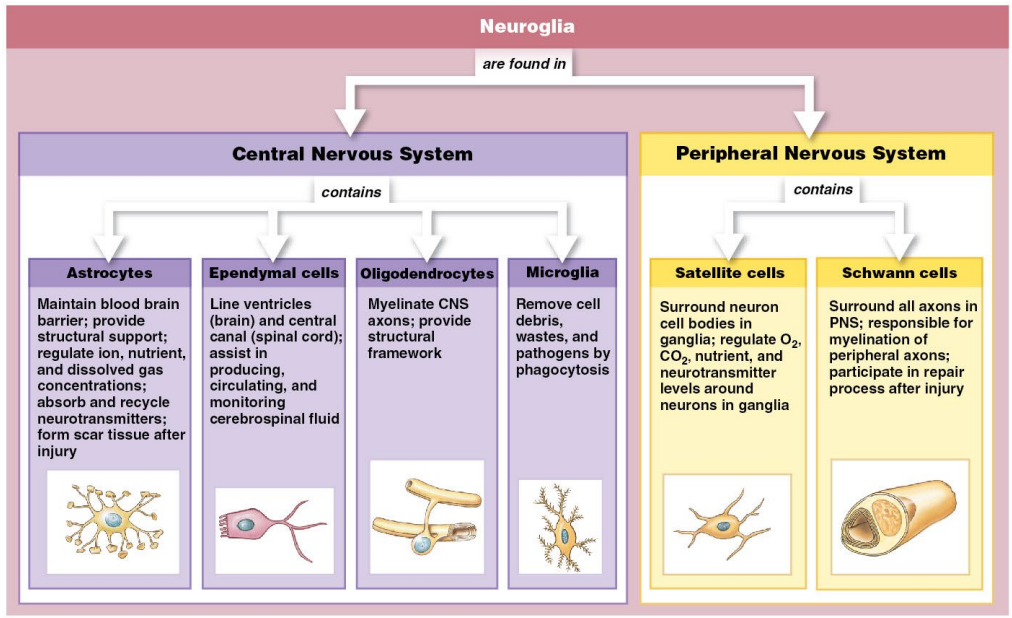
Name and Describe what the Nervous System is made of? Name the 3 Functional Neurons:
Neurons
Communication
Processes information
Control functions
Neuroglia (Glial Cells)
Supporting cells
Functional Neurons:
Motor Neurons - CNS sends signal to targeted muscles or glands.
Sensory Neurons - Send sensory information to the CNS.
Interneurons - Located in the CNS. They connect sensory neurons to motor neurons.
Name and describe the 6-Types of Neuroglia:
CNS
Astrocytes
Maintain blood-brain barrier.
Regulate nutrient and ion balance.
Provide structural support.
Repair damaged tissue (scar formation).
Ependymal Cells
Line brain ventricles and spinal cord central canal.
Produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheath around CNS axons.
Provide structural framework.
Microglia
Immune cells of the CNS.
Remove waste and pathogens (phagocytosis).
Activated during injury or disease.
PNS
Satellite Cells
Surround neuron cell bodies in PNS ganglia.
Regulate O2 and CO2, nutrient, and neurotransmitter levels around in ganglia.
Schwann Cells
Form myelin sheath around PNS axons.
Aid in axon regeneration.
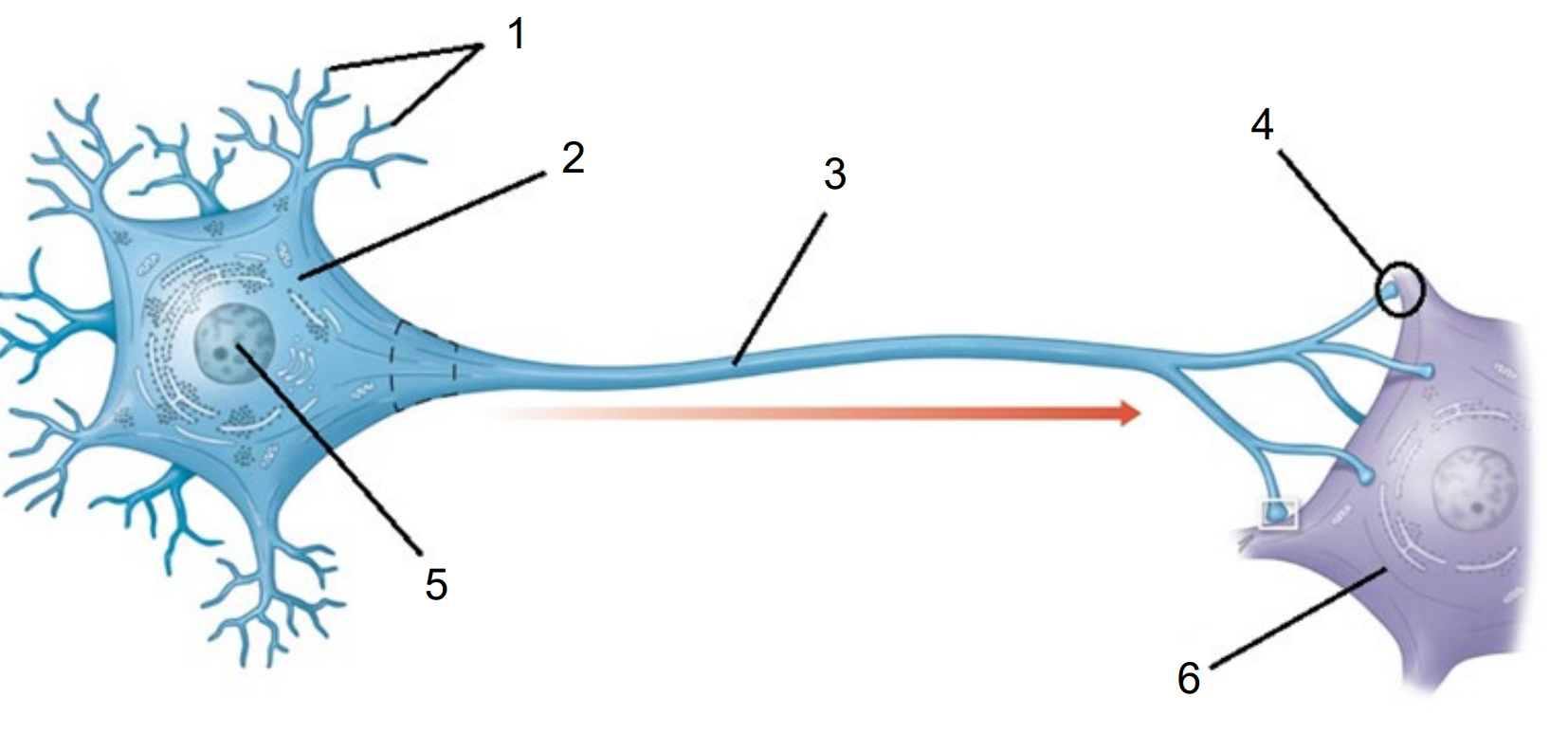
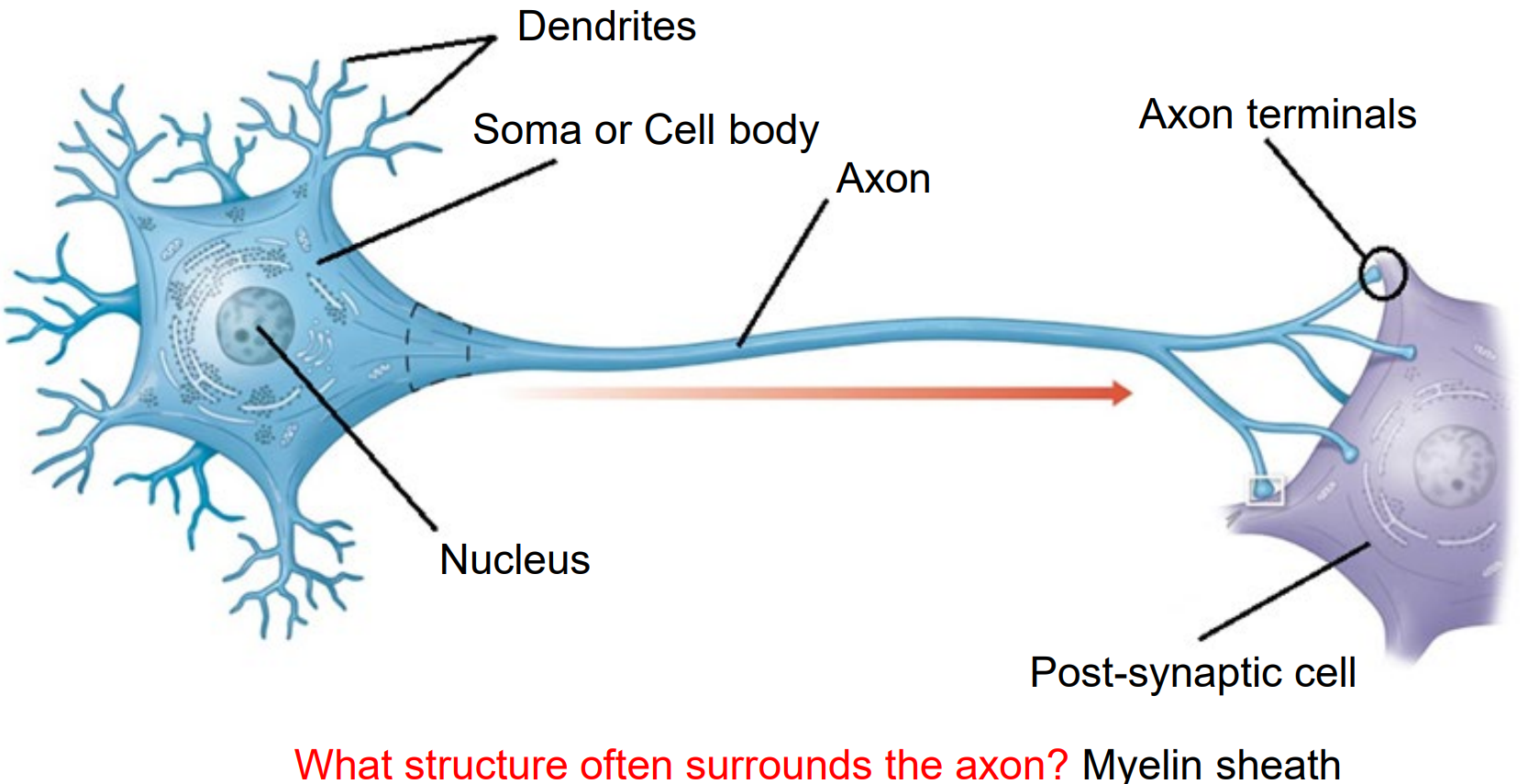
Name and describe the Structures of a Neuron:
Dendrites - Receives electrical signal from other neurons.
Soma (Cell Body) - Holds the Nucleus and supports cell function.
Nucleus - Holds DNA and controls function and repair.
Axon - Long fibre that transmits electrical signal.
Myelin Sheath - Insulates axon and speeds process. Made from Oligodendrocytes (CNS) and Schwann Cells (PNS).
Axon Terminal - Releases neurotransmitter to synapse.
Synapse - The gap between 2 neurons.
Post-Synaptic Cell - The neuron (muscle or gland) receives neurotransmitter. Has receptors to detect/respond to chemical message.
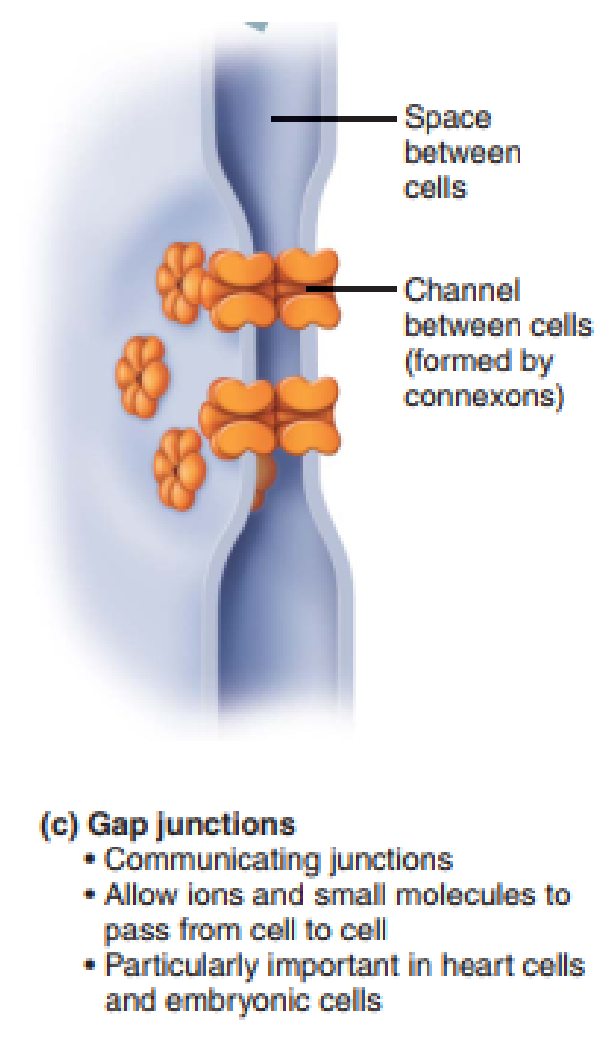
What is an Electrical Synapse?
Cytoplasmic continuity between two neurons (like a bridge). It’s called a Gap Junction (connexons).
Fast messaging
e.g., reflexes
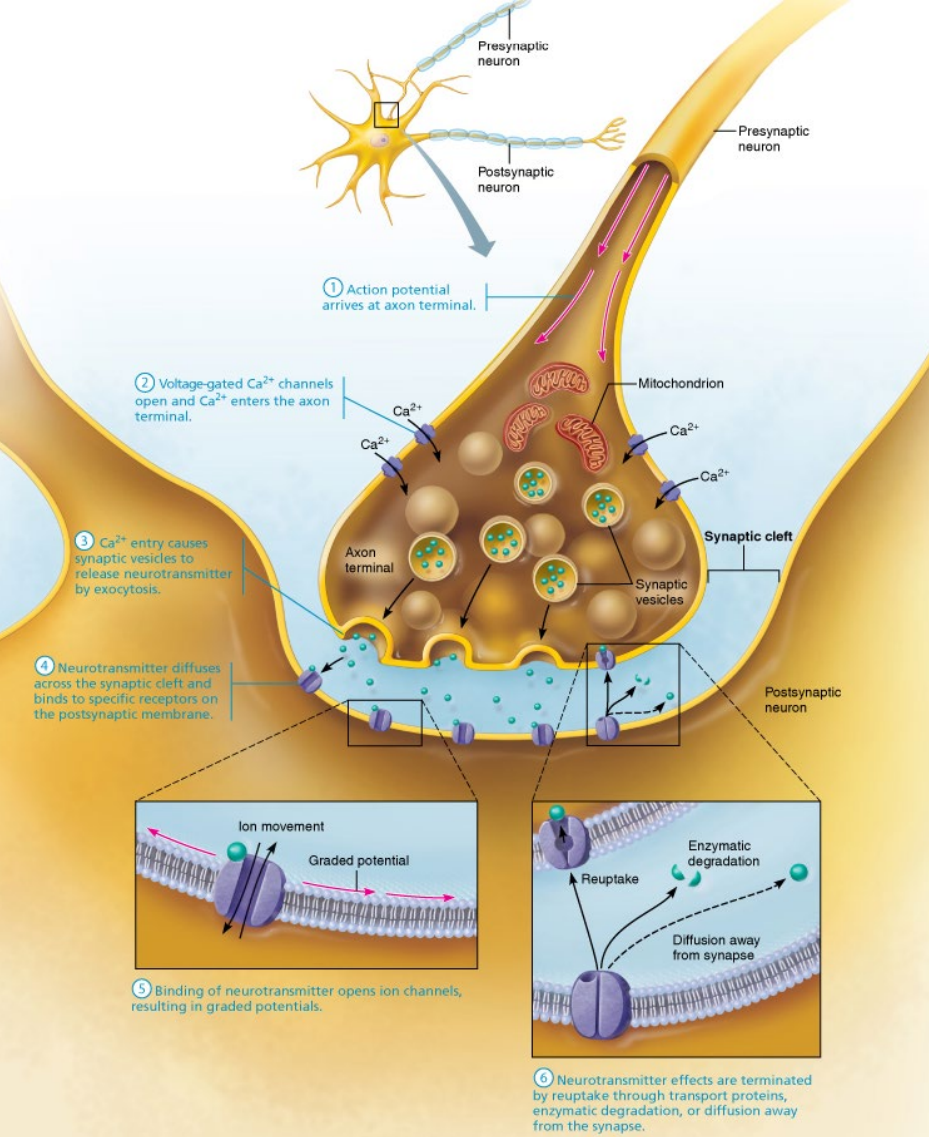
What is a Chemical Synapse?
Instead of a Gap Junction it releases a chemical, ‘neurotransmitters’ into the Synaptic Cleft.
Neurotransmitters float across the Synaptic Cleft and enter a post-synaptic cell.
Slow/controlled
e.g., Neuromuscular Junction
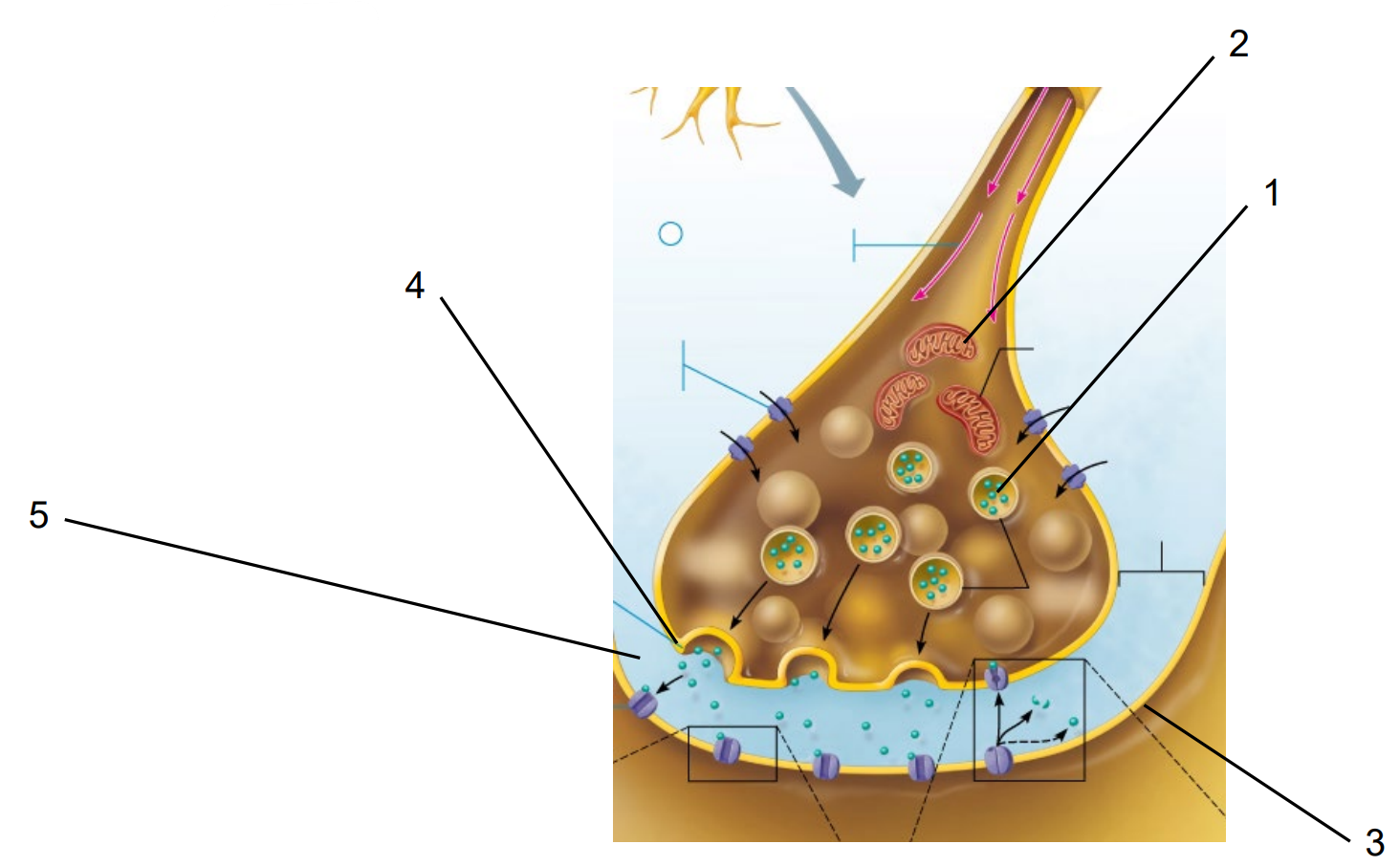
Name the Structures of the Chemical Synapse:
Pre-Synaptic Vesicle
Mitochondria
Post-Synaptic Neuron
Pre-Synaptic Vesicle (Pre-Synaptic Membrane)
Synaptic Cleft
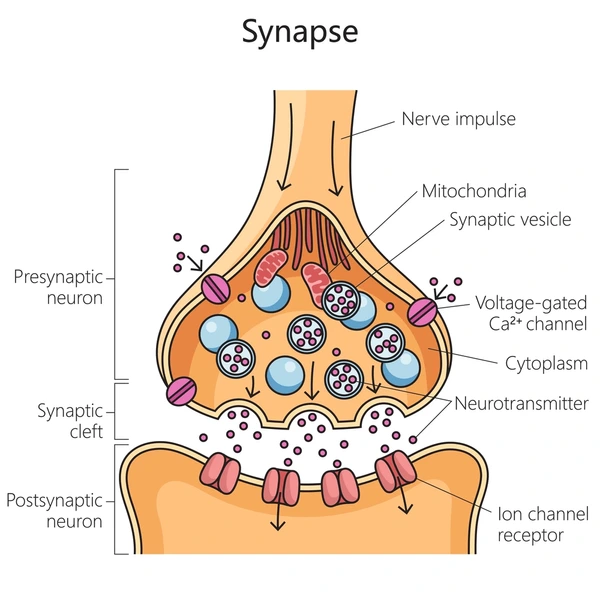
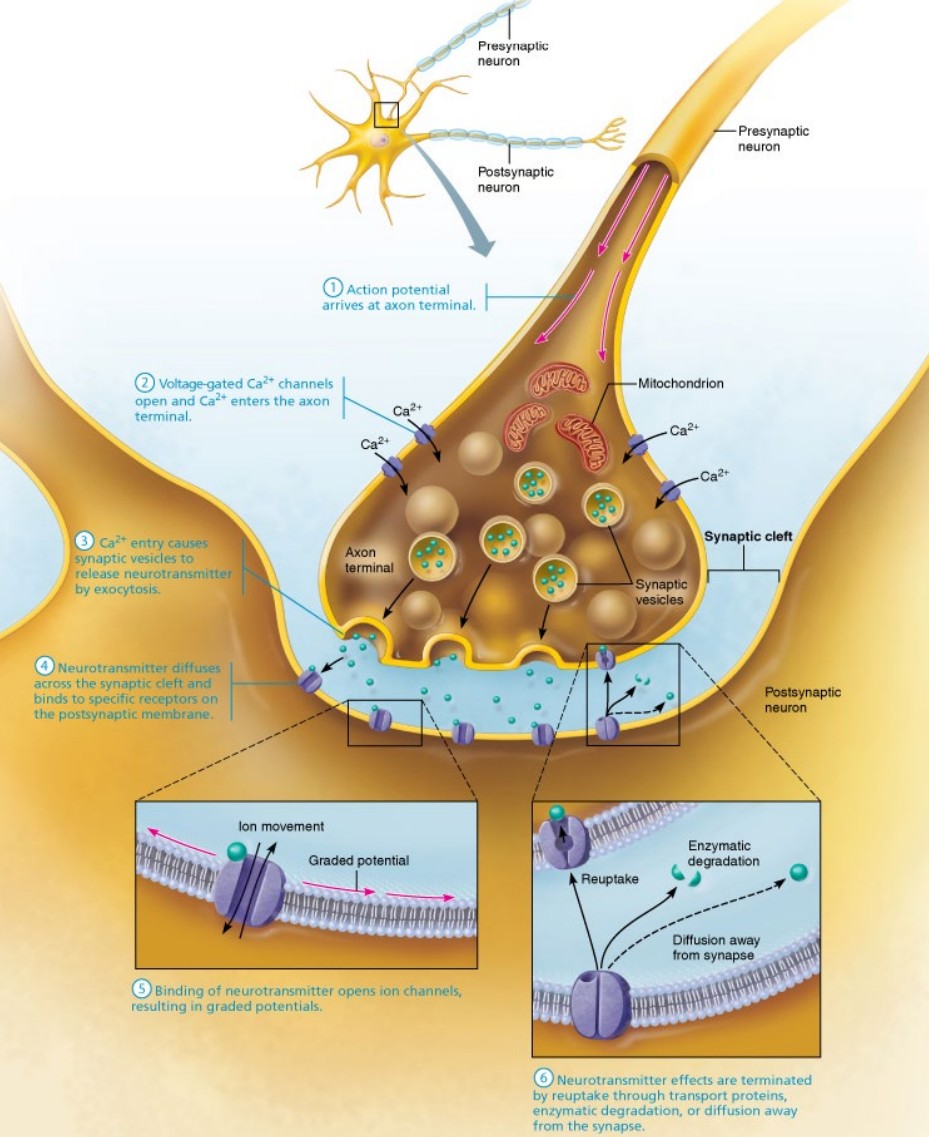
Describe the Process of Chemical Synapse and Name the Ion Channels:
In the pre-synaptic cell, the electrical signal travels via the axon to the axon terminals.
Action potential
The voltage charged Ca2+ (calcium) channels open (Active: Electrical - Voltage Channel).
Ca2+ enters the channels and enter the axon terminal.
The Ca2+ enter pre-synaptic vesicles.
The vesicles hold neurotransmitters.
The vesicles fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane for exocytosis (exit).
The neurotransmitters travel through the synaptic cleft.
The neurotransmitters enter post-synaptic receptors and bind.
Ion channels (Active: Chemical - Ligand Channel) open.
Graded Potential
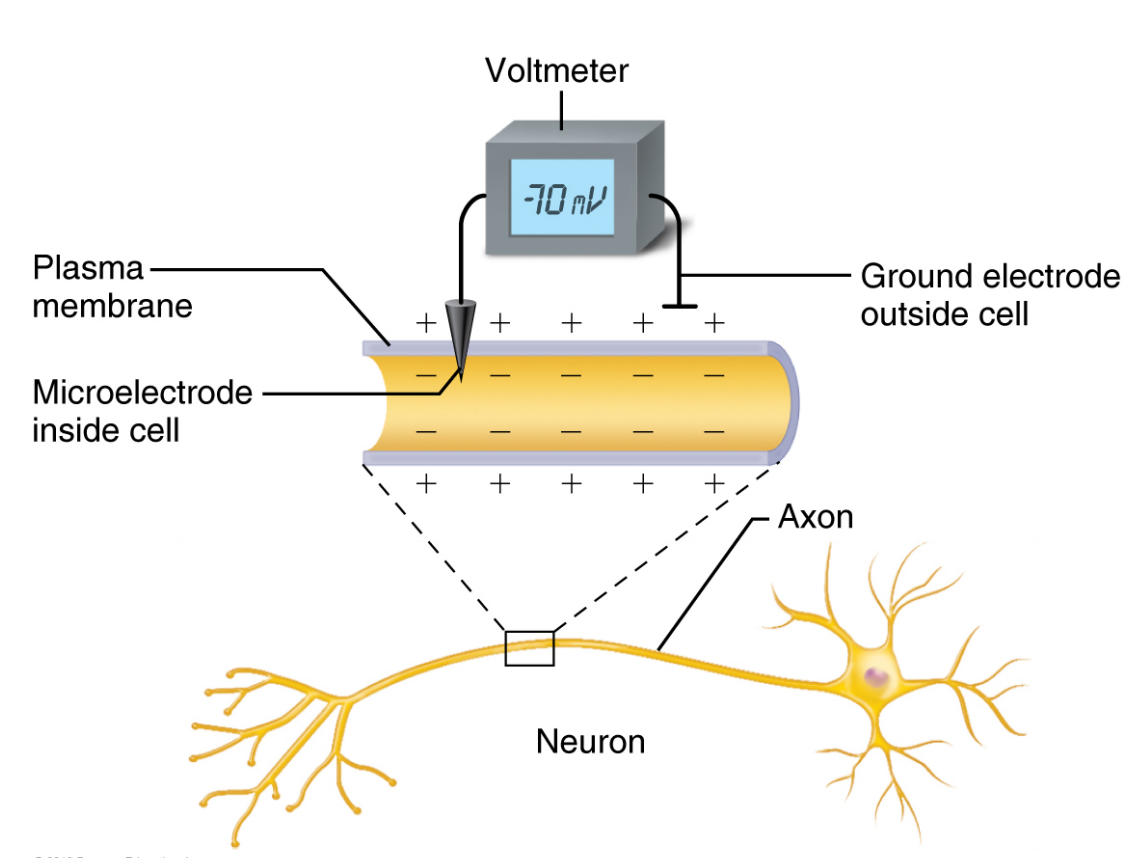
What does ‘Resting Membrane Potential’ Mean?
The neuron is at rest (not sending an electrical signal).
Polarised - Exterior is positively charged and interior is negatively charged.
Uneven distribution of ions (like Na⁺ and K⁺) and the work of the sodium-potassium pump.
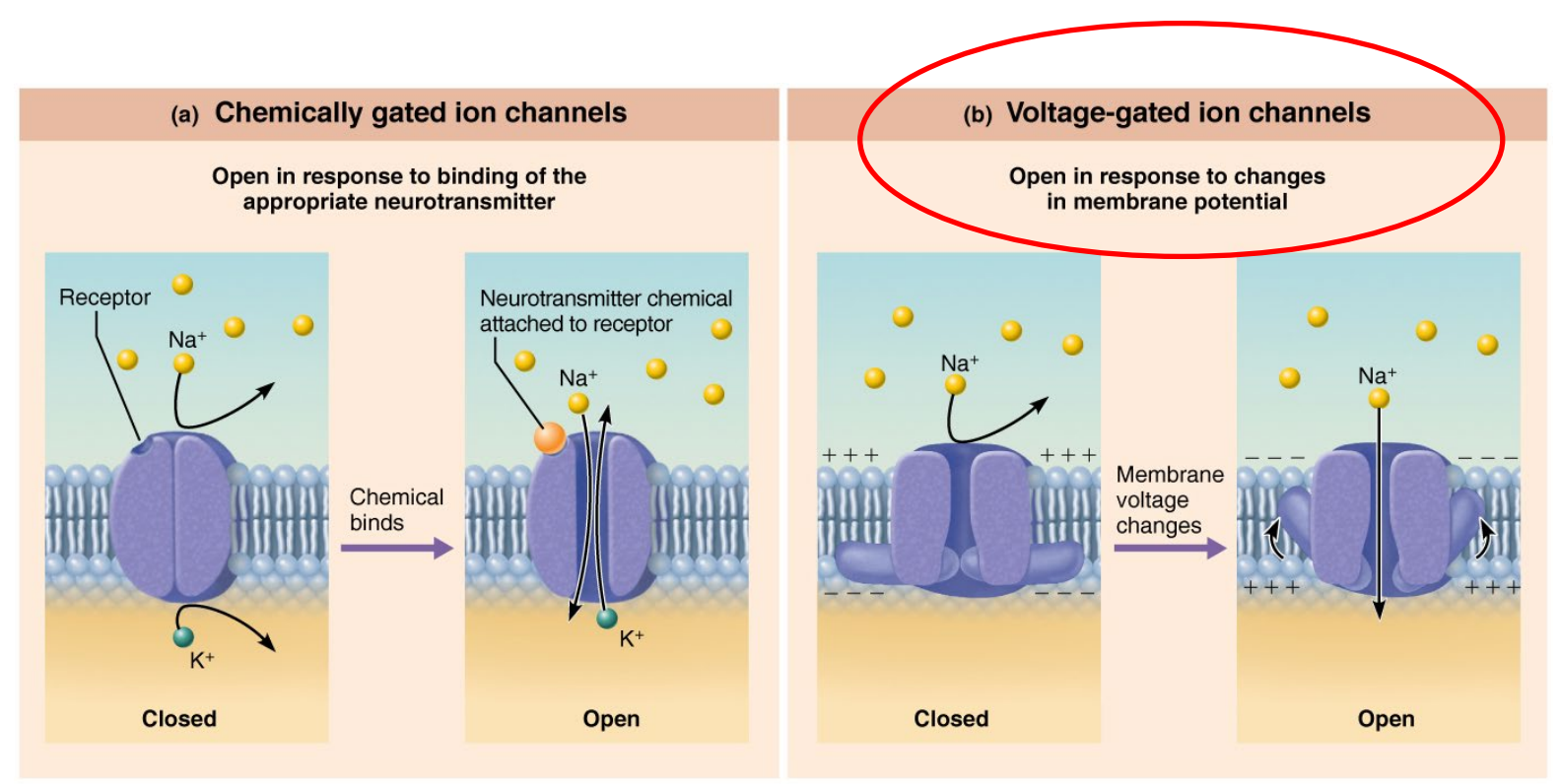
What are Ion Channels? Give examples:
Tiny gates in the neuron’s membrane.
They open and close ions like Na⁺ (sodium), K⁺ (potassium), or Ca²⁺ (calcium) pass in or out.
When they open, they can change the charge inside the neuron.
Passive channels
Active channels
Chemically gated (ligand gated)
Mechanically gated
Voltage gated (electrical signal)
e.g., Ca2+ Voltage Charged Channel
What does ‘Graded Potential’ Mean? Also, Name and Describe it’s Polarisation:
A small change in the neuron’s charge.
Happens when a few ion channels open, usually near the dendrites or cell body.
Can be strong or weak — the size of the signal depends on the strength of the stimulus.
If the graded potential is strong enough and reaches the axon hillock, it may trigger an action potential (e.g., a full nerve signal).
If a stimulus opens ion channels:
If Na⁺ enters → the inside becomes less negative → this is called depolarisation.
If Cl⁻ (chloride ion) enters or K⁺ leaves → the inside becomes more negative → this is hyperpolarisation.
These changes are temporary and vary in strength — hence the term graded.
What does ‘at rest’ Mean?
Polarised
The inside of the neuron is more negative than the outside.
Both Na+ and K+ channels are closed.
The neuron is ready to fire but not active (action potential).
What is Depolarisation?
The inside becomes less negative and more positive.
Na+ channels open allowing Na+ entry, K+ channels are closed.
Can lead to an action potential if it reaches the threshold.
What is Hyperpolarisation?
The inside becomes more negative than the resting state.
Caused by K+ leaving or Cl- entering the cell.
Makes the neuron less likely to fire.
What is Repolarisation?
The neuron returns to its resting state after depolarisation.
K+ leaves the cell to restore the negative charge inside.
Happens after an action potential to reset the membrane.
What are Ions? Give some Examples:
Positive charged particles.
Can change the charge of a neuron.
e.g.,
Na+ (Sodium)
K+ (Potassium)
Ca2+ (Calcium)
Name and Describe the Protective Mechanisms of the Brain?
Bone Exterior: Skull and Vertebral Column
Skull:
Hard
Boney
Encases the Brain.
Vertebral Column:
Protects Spinal Cord
Meninges (3-Layers)
Dura Mater
Tough and thick outer layer.
Attached to the inner surface of the skull.
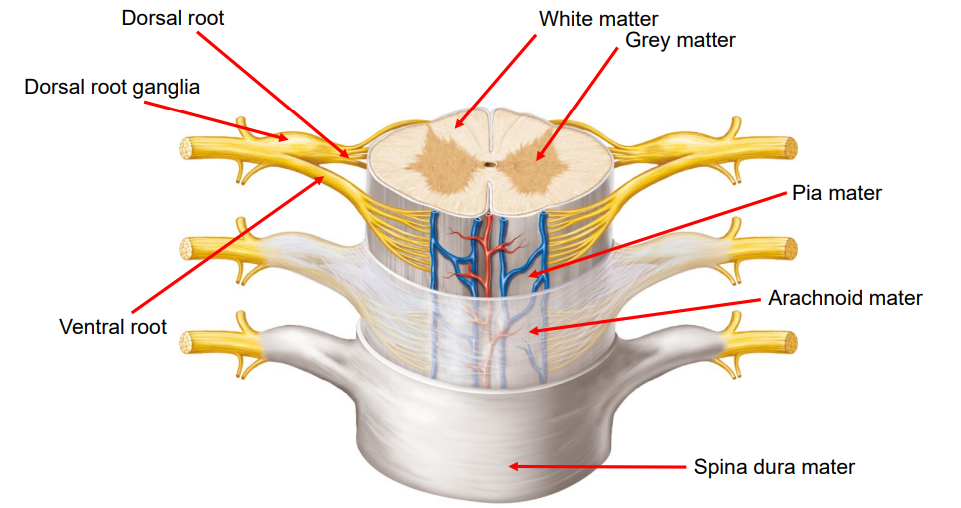
Arachnoid Mater
Web-like middle layer.
Contains spaces where (cerebrospinal fluid) CSF flows.
Pia Mater
Thin, delicate layer that clings tightly to the brain surface.
Carries blood vessels into brain tissue.
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Clear fluid that circulates the arachnoid and pia mater, and within the brain’s ventricles.
Cushions the brain.
Removes waste and delivers nutrients.
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
Selective filter made of tight junctions between brain capillary cells.
Protects the brain from pathogens.
Allows essential molecules to pass through (e.g., oxygen, glucose, medications).
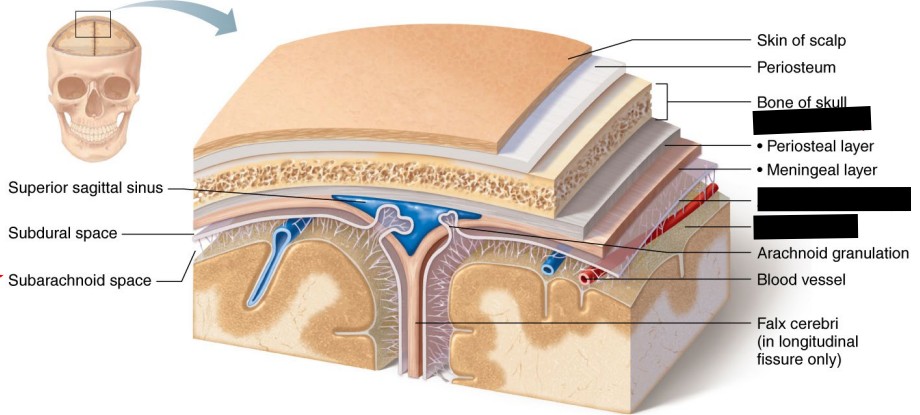
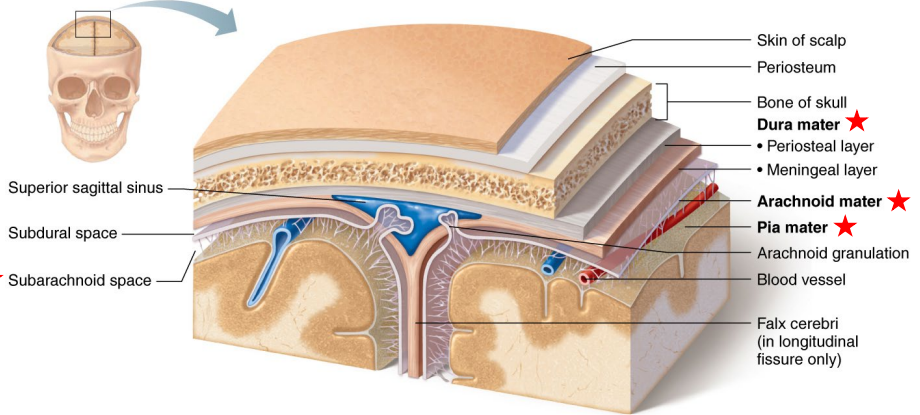
Identify and Describe the Meninges:
Meninges (3-Layers)
Dura Mater
Tough and thick outer layer.
Attached to the inner surface of the skull.
Arachnoid Mater
Web-like middle layer.
Contains spaces where (cerebrospinal fluid) CSF flows.
Pia Mater
Thin, delicate layer that clings tightly to the brain surface.
Carries blood vessels into brain tissue.
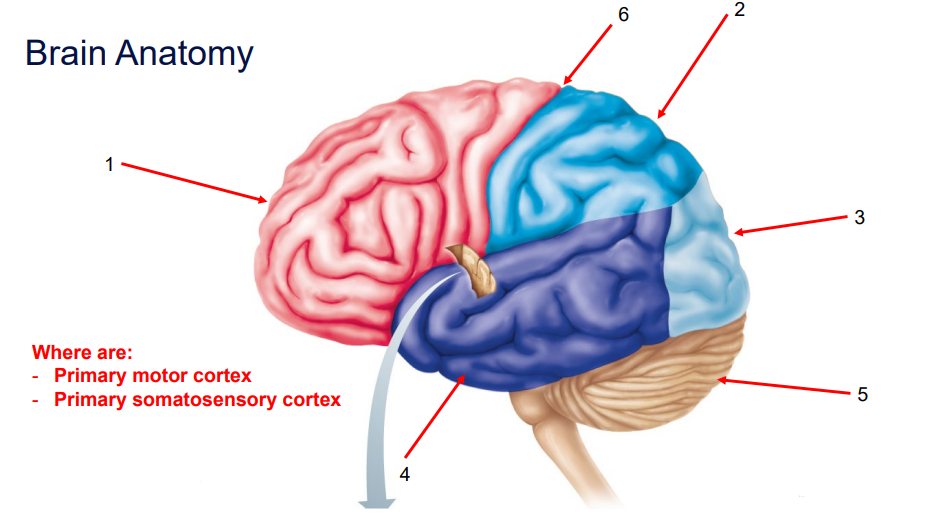
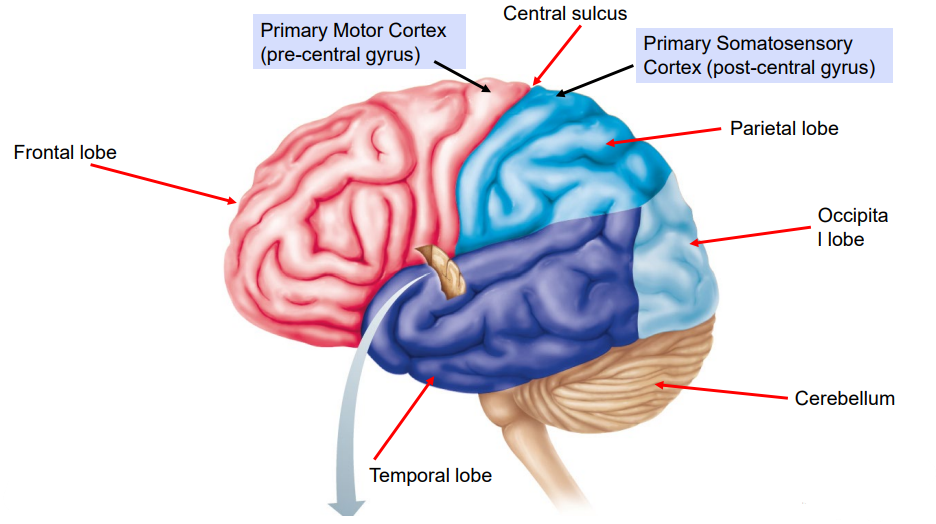
Identify and Describe (Positioning) the Structures of the Brain:
Frontal Lobe
Judgement
Reasoning
Personality
Voluntary Movement - contains Primary Motor Cortex
Anterior surface of the brain.
Anterior to Central Sulcus.
Parietal Lobe
Sensory information (e.g., pain ,touch, temperature).
Superior surface
Posterior to Frontal lobe.
Posterior to Central Sulcus.
Occipital Lobe
Interpretation of visual patterns (eyes).
Most posterior aspect of the cerebrum.
Temporal Lobe
Hearing
Language
Lateral surface of Cerebrum.
Inferior to Lateral Sulci.
Cerebellum
Coordinating movement
Balance
Posture
Inferior and posterior to the Occipital Lobe
Central Sulcus
Separates the Frontal and Parietal Lobes.
Defines the Primary Motor Cortex (skeletal muscle) and Primary Somatosensory Cortex (senses).
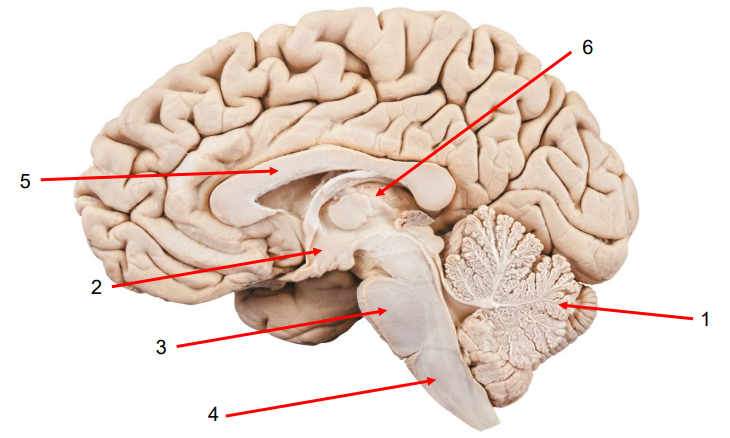
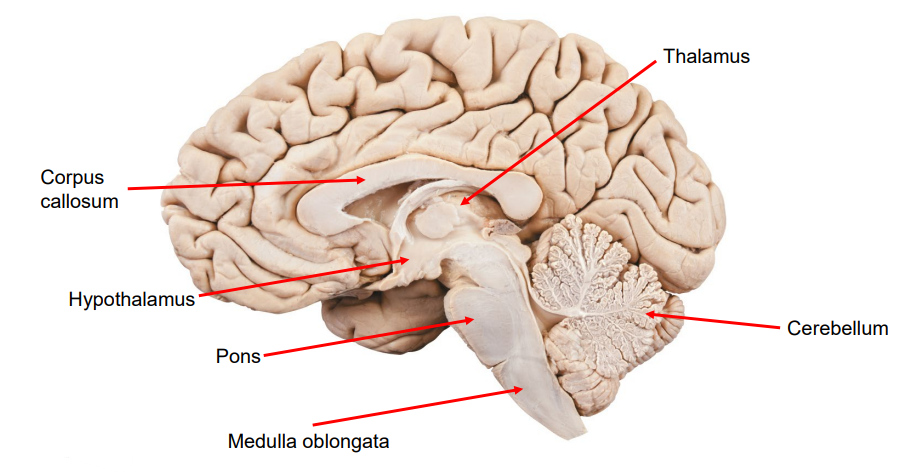
Name and Describe the Brain’s Structures:
Cerebellum: Balance, posture, and fine motor movement.
Hypothalamus: Homeostasis and links the Nervous System and Endocrine System via the Pituitary Gland.
Pons: Breathing regulation and communication between the cerebrum and cerebellum.
Medulla Oblongata: Vital automatic functions (e.g., heart rate, breathing).
Corpus Callosum: Thick band of fibres that connect the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
Thalamus: Sends sensory signals to the right areas of the cerebral cortex.
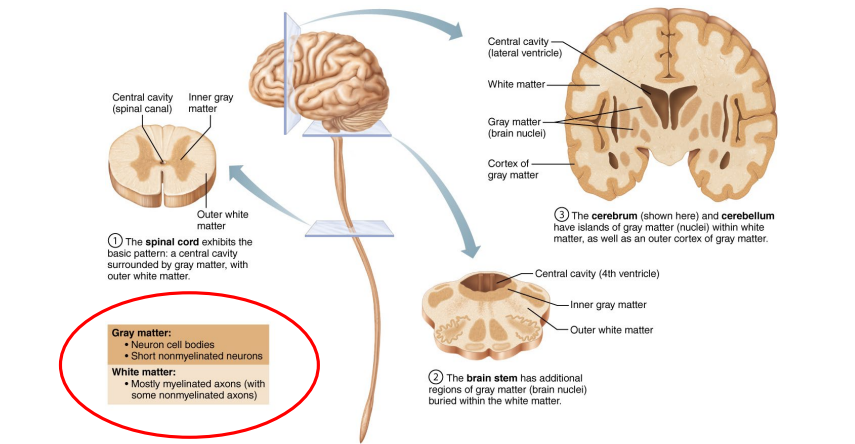
What is Grey and White Matter?
Grey Matter:
Made up of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses.
Processing and decision-making (e.g., thinking, memory, sensory input).
White Matter:
Made up of axons covered in myelin (makes it look white).
Carries signals between grey matter regions.
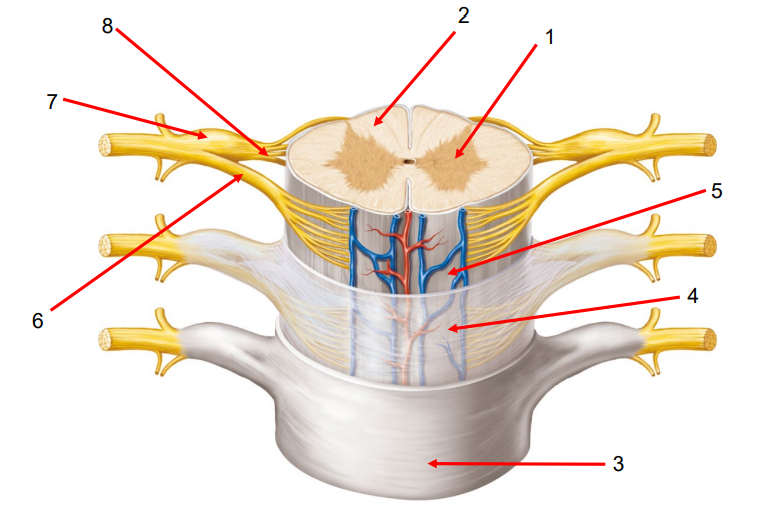
Name and Describe the Spinal Cord:
Dorsal Root Ganglia: Processes incoming sensory information (e.g., touch, pain).
Dorsal Root: Carries sensory information into the spinal cord.
Ventral Root: Carries motor information (voluntary) out of the spinal cord.
Classification of Neurons
Describe the Differences of the Somatic and Automatic System:
Somatic:
Voluntary
Motor Cortex
Skeletal muscle
Autonomic:
Involuntary
Hypothalamus, brain stem
Smooth, cardiac muscle, glands.