HA and Seizure
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anything italicized is from outside resources
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Acute HA
A pain to head or face that is rapid onset and severe intensity and is more likely an intracranial disorder
Vascular events, ICH, Malignant HTN, arterial dissection/aneurysm, infections (meningitis, encephalitis), CO poisoning, Intracranial Mass (elevated ICP)
Common causes of acute HA
OLDCARTS, Valsalva/cough/exertion/coitus/position changes (ICP increase), PMHx (HTN, pheo, HIV status (cryptococcal meningitis))
What do we need to find out in the hx for headaches?
Fever (infectious cause), BP (could be protective, ICP), CO oximeter reading (CO poisoning)
Which vital signs are important for acute HA?
Mental status, focal neuro deficits (motor, sensory, gait, pronator drift), visual acuity (glaucoma, temporal arteritis), Visual fields (venous sinus thrombosis, tumor, aneursym), Pupils (intracranial mass, optic neuritis, swinging light test), papilledema (increased ICP)
What are we looking for in the physical for acute HA?
Ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis (if present with HA think carotid artery dissection)
Horner’s Syndrome Triad
Systemic symptoms (illness, weight loss fever, etc), Neurological symptoms (confusion, AMS, seizures), New Onset (older than 50, thunderclap), Other features (trauma, drug use, toxic exposure), Previous Hx or pattern (change in frequency/severity)
Red flags for Acute HA - Yield to high care if necessary
Abnormal neuro exam, abnormal mental status, thunderclap, HIV with new type of HA
What are some signs we need emergent imaging for a HA
50+ yr old with new type of HA
What are some signs we need urgent imaging for a HA (with in 48 hours)
CT or MRI (contrast use depends)
Preferred imaging for HA
CSF (gram stain, CBC with diff, glucose, protein, culture, VDRL, cryptococcal antigen (HIV)), ESR (temporal arthritis, endocarditis), UA (HTN), CBC, CMP
What labs should we consider for a HA?
Haloperidol with NSAID (ketolac) + diphenhydramine (prevent akathisia)
Treatment plan for Acute HA (tbh just treat the underlying)
cluster, migraine, tension
Types of primary chronic HA
head injuries, cervical spondylosis, dental disease, eye disease, TMJ, sinusitis, depression
Types of Secondary chronic HA
Cluster HA
What type of HA is the MOST PAINFUL, more common in middle-age males, and often has a circadian/episodic rhythm?
diet, EtOH, stress, bright lights
Triggers for cluster HA
High flow O2 non-rebreather, Sumatriptan (Sc/nasally), zolmitriptan (nasal), dihydroergotamine (IM/IV), Viscous lidocaine (nasally)
35 y/o male presents to the ER for a HA. He states that they have been going on off and on since they woke him up last night. He reports that they only last for about 20 min at each time. He describes the pain as “stabbing him in the left eye” and his nose is stuffed up on the left. On a physical exam you note rhinorrhea, conjunctival injection, ptosis, miosis, and lacrimation. Labs and imaging are normal. What is your initial treatment?
oral medications, no beta blockers
What are we NOT going to do for our bros with cluster HA?
Verapamil bridged with prednisone (then taper the steroids); Lithium carbonate, galcanezumab, steroid injection (suboccipital/greater occipital nerve), electrical stimulation of vagal nerve, ergotamine tartrate
35 y/o male presents to the ER for a HA. He states that they have been going on off and on since they woke him up last night. He reports that they only last for about 20 min at each time. He describes the pain as “stabbing him in the left eye” and his nose is stuffed up on the left. On a physical exam you note rhinorrhea, conjunctival injection, ptosis, miosis, and lacrimation. Labs and imaging are normal. What are you sending him home with for prevention?
migraine, paroxysmal hemicrania, trigeminal neuraligia, temporal arteritis, carotid artery dissection, SAH
DDX for cluster HA
Migraines
Which type of HA is the leading cause of debilitating HAs that peak during the 4th decade and is more common in women?
probably due to neuronal dysfunction in trigeminal system (calcitonin gene-related)
Pathophys for migraines
Aura
Cortical spreading depression wave of neuronal and glial depolarization across the cerebral cortex and occurs in 25% of migraine patients
emotional stress, hormones, fasting, sleep disturbances, menses, OCPs, weather changes
Triggers for migraine
Minimum of 5 attacks, last 4-72 hours untreated/unsuccessfully treated, At least 2 (unilateral, pulsating, moderate/severe, worsens with activity), At least 1 during the HA (N/V, photophobia AND phonophobia)
Criteria for migraine w/o aura (common - 80%)
1+ of fully reversible aura (visual, sensory, speech, langauge, motor, brainstem, retinal) 3+ of these (1 aura lasting longer than 5 min, 2+ symptoms in progressive, individual aura last 5-60 min, 1 symptom is unilateral, 1 aura symptom is positive, HA follows aura within 60 min)
Criteria for migraine w/ aura (classic - 20%)
sensory, hearing , dysphasic speech disturbance, scotoma, photopsia, scintillating scotoma
Characteristics of Auras in migraines
Prodrome
What stage of the migraine HA am I describing - euphoria, depression, irritability, food cravings, constipation, increased urination, muscle and neck stiffness, yawning (24-48 hrs before)
aura
What stage of the migraine HA am I describing - seeing bright flashing dots or lights, blind spots, numb/tingling skin, speech changes, temporary vision loss, tinnitus, seeing wavy lines, changes in smell or taste, “funny” feeling (5-60 min before)
HA
What stage of the migraine HA am I describing - photophobia, phonophobia, sensitivity to odors, N/V/D, abd pain, feeling warm, loss of appetite, pallor, fatigue, speech changes, tender scalp, blurred vision, fever - 4-72 hours?
Postdrome (hangover)
What stage of the migraine HA am I describing - being unable to concentrate, feeling depressed, fatigue, not being able to understand things, euphoria - 1-2 days after
Dark quiet room, laying flat, tylenol/NSAIDs taken at 1st warning, butalbital w/caffiene and acetaminophen (Fioricet), Triptans, dihydroergotamine (nasal spray, sc, IM, IV), ergotamine tartrate/caffeine (tablet, suppositories), dexamethasone IV/IM for HA recurrence
47 y/o female presents to the ER for a unilateral, throbbing HA that has been going on for the last 7 hours. She also notes neck pain and visual disturbances. Physical exam (including neuro), imaging, and lab work is normal. What is our symptomatic therapy?
avoid in pregnancy, hx of TIA/strokes, uncontrolled HTN; C/I with coronary/vascular disease, Prinzmetal angina
Rules for Triptans
Avoid in pregnancy, CVD, patients taking 3A4 inhibitors
Rules for dihydroergotamine
sumatriptan sc + metaclopramide IV/prochlorperzaine + dipherhydramine (prevent dystonia) + dexamethasone (decrease rebound)
47 y/o female presents to the ER for a unilateral, throbbing HA that has been going on for the last 7 hours. She also notes neck pain and visual disturbances, AND N/V. Family Hx is positive for migraines. Physical exam (including neuro), imaging, and lab work is normal. What is our symptomatic therapy?
Use simple analgesics less than 15 days per month, use combination analgesics less than 10 days per month
How to prevent Medication overuse
HA more than 2-3x/month, last longer than 12 hours, associated with significant disability
When should you consider preventative therapy for migraines - can taper when HA are managed?
NSAIDs, beta-blockers (propanolol, timolol), CCBs (verapamil), TCAs (amytriptyline, desipramine), anticonvulsants (topiramate, valproic acid, gabapentin)
47 y/o female presents to the ER for a unilateral, throbbing HA that has been going on for the last 7 hours. She also notes neck pain and visual disturbances, AND N/V. Family Hx is positive for migraines. Physical exam (including neuro), imaging, and lab work is normal. What is our preventative therapy?
botox, Mg, acupunctures, transcutaneous supraorbital nerve stimulation, occipitals nerve block/compression, biofeedback
What are the other ways to reduce/treat migraines?
Tension HA
Which type of primary HA is MOST COMMON and is more prevalent in adult females lasting minutes to days?
abnormal neuronal sensitivity
What is the current theory behind the pathophysiology of tension HA?
Infrequent episodic
Which type of tension HA occurs less than 1 day/month (30 min - 7 days in duration) for less than 12 days/year?
Frequent episodic
Which type of tension HA occurs between 1-14 days/month for at least 3 months (between 12-180 days/year)?
Chronic
Which type of tension HA occurs more than 15 days/month for more than 3 months lasting hours to days (unrelenting)?
mental tension, fatigue, missed meals, eye strain, light, noise, stress, anxiety, depression
Tension HA can be exacerbated by
NSAIDs, Tylenol, ASA, caffeine (65 mg) + analgesics
25 y/o female presents to the ER for generalized dull head pain that wraps around her forehead in a band-like pain. She notes that it is non-pulsating and is not worsened by physical exertion. On physical exam you note peri-cranial tenderness and No focal neurological symptoms. Everything is normal. What is your acute treatment plan?
bilateral, pressuring/tightening, mild-moderate, not aggravated by exertion, No N/V, photophobia or phonophobia (not together)
The international class of HA disorders Criteria for tension HA needs at least 2+
either Frequent episodic or chronic subtype
What are the rules for preventative therapy of tension HA?
exercise, diet, sleep, massage, stretching, electrical stimulation (tens), counseling, relaxation exercises, biofeedback
Preventative measures for Tension HA - best practice is meds and behavioral therapy
TCAs (amitryptylines, nortriptyline, doxepin), Venlafaxine
25 y/o female presents to the ER for generalized dull head pain that wraps around her forehead in a band-like pain. She notes that it is non-pulsating and is not worsened by physical exertion. On physical exam you note peri-cranial tenderness and No focal neurological symptoms. Everything is normal. What is your prophylatic treatment plan?
2+ HA/week, lasts 4+ hours, does not respond to acute therapies, HA are disabling
Rules for prophylactic treatment of tension HA
provoked
Which type of seizures have an identifiable cause (25%)?
2 or more unprovoked seizures
Define epilepsy
congenital/perinatal injuries, Mesial temporal sclerosis (hippocampal), trauma, space-occupying lesions, vascular diseases, degenerative disorders, genetics, infection, metabolic (hypoglycemia, hyponatremia), immune, idiopathic
Causes of Seizures
Missed Meds, lack of sleep, flashing lights (epilepsy w/ photosensitivity), Stressors, EtOH (with and withdrawals), catamenial (menstrual), drugs, caffeine, OTC meds, abnormal labs, serotonin syndrome
Triggers for seizures
subtle
What type of seizure am I describing - brief halt in activity, regular/patterned eye blinking?
dramatic
What type of seizure am I describing - yelling and shaking of limbs
Focal (partial)
What type of seizure am I describing - from one area of the brain w/ or w/o spread (60%)
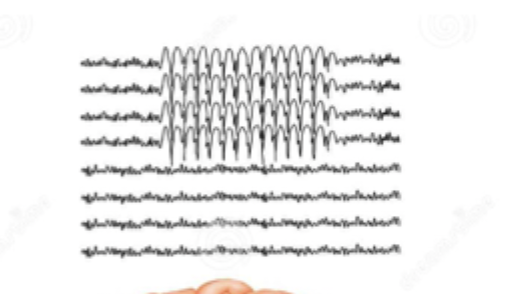
Generalized
What type of seizure am I describing - involves both sides of the brain at the same time
Prodrome (warning hour-days earlier), Aura (sec-min, EEG changes present), Seizure (ictal), Post-Ictal (slow return to awareness, HA, drowsiness), Interictal (breaks between serial seizures)
Stages of Seizures
automatism
Involuntary, repetitive movements or behaviors during a seizures (lip smacking/fumbling with clothes during a focal seizure)
Atonic
Sudden loss of muscle tone, causing a person to go limp or collapse (“drop attack”)
Clonic
Repeated, rhythmic jerking of muscles due to contractions and relaxations (arms and legs rhythmically jerk)
Tonic
Sustained stiffness or contraction (rigid)
myoclonic
Sudden brief, shock-like muscle jerks (quick-jolt that makes you drop something)
hyperkinetic
Sudden, excessive, uncontrollable movements during a seizures (wild, thrashing movements)
Epileptic spams
Brief sudden muscle contractions that usually occur in cluster (jackknife movement)
bland, quiet, deja vu, odd sensory sensations (taste, smell, tinnitus), abd pain
A seizure in the temporal lobe (most common) will look like…
Dramatic, nocturnal, brief (15-45 sec), loss of motor control, change in behavior or expression
A seizure in the Frontal lobe (2nd most common) will look like…
sudden visual changes, subtle/dramatic
A seizure in the occipital lobe will look like…
numbness, tingling, burning or cold sensation in the contralateral limb, vertigo
A seizure in the parietal lobe (uncommon) will look like…
Simple partial
Which type of focal seizure is awareness maintained and is characterized by the Jacksonian march
Complex partial
Which type of focal seizure is awareness impaired, lasts 1-2 min with no aura and can have a post ictal phase
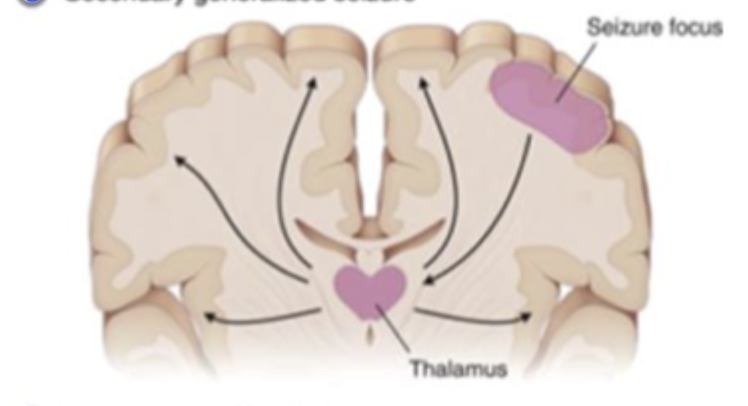
Secondary generalization
If a focal seizure progresses to bilateral tonic clonic and a loss of awareness, what is this known as
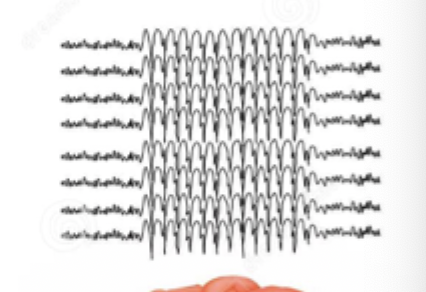
Tonic Clonic (Grand Mal)
Which generalized seizure (most commonly associated with epilepsy) type am I describing - sudden LOC (maybe aura/prodrome), patient becomes rigid and falls to the ground (tonic for 1 min), clonic for 2-3 min, followed by a flaccid coma
Absence (petit mals)
Which generalized seizure type am I describing - patient is unaware they are having a seizure and may miss a few words when speaking, these are very brief and have NO aura, children with these usually outgrow them and they can be elicited by hyperventilation?
bilateral synchronous and symmetric 3-Hz spike-wave pattern
EEG rhythm for petit mal seizure
Myoclonic
Which generalized seizure type am I describing - sudden, brief and flash-like movements w/o LOC and is associated with JME (episodes after waking - HALLMARK)
brief burst of high-amplitude, generalized spike OR polyspike and waves
EEG rhythm for myoclonic
tonic
Which generalized seizure type (uncommon) am I describing - a sudden LOC with rigid posture lasting for about 10-20 seconds, patient’s head and eyes may deviated to one side and may occur at night
low-amp, generalized, fast, discharge (less than 15 hertz or 15 cycles/sec)
EEG rhythm for tonic seizures
Atonic
Which generalized seizure type (uncommon) am I describing - sudden LOC for less than 15 seconds with a complete loss of postural tone, patient may present with falls and self-injury (prescribe a helmet)
generalized/mutlifocal spike OR polyspike and wave (interictal); burst of spike and wave followed by a brief flattening of the EEG (ictal)
EEG rhythm for atonic seizures
Description of before, after, during; triggers, previous evals, treatments, PHMx (Fam, meds, allergies, ROS), Normal physical, Labs to r/o other causes, EEG (Gold standard), Head CT, 3 Tesla MRI (Diagnostic imaging of choice)
Work-up for ANY seizure
after 2+ unprovoked (start low and slow - monitor levels)
The goal of seizure treatment is to prevent/reduce seizure, severity, improve mortality, decrease complications, when do we initiate treatment?
Lifestyle changes, anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs), refer to neuro, surgery, keto diet in kids
Treatment plan for seizures
carbamazepine, lamotrigine, levetiacetam, oxcarbazepine
Meds for focal seizures
Valporate, lacosamide, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, topiramate
Meds for generalized seizures
Ethosuximide
Meds for absence seizure
Lamotrigine/levetiracetam, folic acid - NO VAPORATE
Gameplan for pregnant peeps with seizures
Tx with prophylactically with phenytoin/fosphenytoin for up to 2 weeks
Gameplan for perioperative peeps with seizures
Vagal nerve stimulation, Brain surgery (70% cured)
Intractable epilepsy (failed medications) treatment plan
ABCs (intubate and cooling blanket), IV D50 (if the glucose is low - get a fingerstick), IV benzos, fospheytoin/phenytoin IV, EKG/EEG, IV phenobarb (watch for hypotension/respiratory depression), sedate with Midazolam, propofol, pentobarbital
16 y/o patient presents to the ER following a witnessed seizure lasting 5 min, while your nurse is triaging the patient begins to have another seizure - WHAT ARE YOU DOING?
sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP)
Electrical shut down of the brain resulting in changes in heart function and breathing (linked to grand mal)
Alcohol/drug withdrawal seizures
Grand mal seizure associated with the cessation of alcohol that is treated with acute benzos
refractory seizures (2+ med), uncertain seizure behavior, progressive neuro disorder, inpatient monitoring for surgical eval
When do you refer to the neurologist for seizures
status epilepticus, seizure characterization, surgical evaluation
When should seizure patients be admitted
Bects (rolandic epilepsy)
Most common epilepsy in childhood, usually onset 2-14 y/o but is typically outgrown by 16 and is characterized by by sensory/motor that can occur when asleep or awake (abnormal EEG spikes unilateral or bilateral)
Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome
Which epilepsy syndrome has an onset of 1-10 y/o and infantile spasms precede ____ in 10-25% (atypical absence, atonic, tonic, focal, tonic-clonic) characterized by 1-2.5 hz spike and wave complex
Infantile Spasms
Which epilepsy syndrome has an onset of 1-3 months and tuberous sclerosis is the most common cause - triad of infantile, developmental disabilities, and abnormal EEG