biochemistry -glycolysis
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
what does glycolosis result in
pyruvate formation
what are the 2 fates of pyruvate metabolisim
lactate and ACetyl CoA
what pathway results in lactate
anaerobic
what pathway results in ACa
aerobic
what converts pyruvate to lactate
lactate dehydrogenase
what does actate dehydrogenase require and where does it get it from
requires NADH
-supplied from glycolosis
what is the fate of glucose in yeast
pyruvate then either :
Ethanol of Acetyl coA
explain how ethanol is produces
pyruvate is converteed to acetaldehyde but pyruvate decarboxylase
aceta;dehyde is converted to ethanol via alcohol dehydrogenase
How many steps are in glycolysis?
10
what are the 2 phases of glycolosis
investment and pay off phase
step one in the investment phase
-what converted to what
-what enzyme used
-anything lost
glucose converted to Glucose-6-phosphate
enzyme is hexokinase
ATP converted toADP
step TWO in the investment phase
-what converted to what
-what enzyme used
-anything lost
glucose 6 phosphate is converted ti fructose -6- phosphate
enzyme :phosphoglucose isomerase
step three in the investment phase
-what converted to what
-what enzyme used
-anything lost
fructose-6-phosphate is converted to fructose1-6 biphosphate
enzyme used :phosphofructokinase
Atp is used in the reaction
step four in the investment phase
-what converted to what
-what enzyme used
-anything lost
fuctose1-6 biphosphate is converted to either dihydroxyacetone phosphate or Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
enzyme used :aldolase
note
dihydroxyacetone phosphate and Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate can be interchanged via the enzyme triose phosphate isomerase
what do we have at the end of the investment phase
2x glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate molecules
step one in the pay-off phase
-what converted to what
-what enzyme used
-anything lost
g;yceraldegyde3-phospahte is converted to 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate
enzyme used :Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase
NAD+ reduced to NADH
phosphate is added
step two in the pay-off phase
-what converted to what
-what enzyme used
-anything lost
1,3 bisphosphoglycerate converted to 3-phosphoglycerate
enzyme used
phosphoglycerate kinase
ADP converted to ATP
step 3 in the pay-off phase
-what converted to what
-what enzyme used
-anything lost
3-phosphoglycerate CONVERTED TO 2-PHOSPHOGLYCERATE
enzyme used
-phosphoglycerate mutase
step 4 in the pay-off phase
-what converted to what
-what enzyme used
-anything lost
2-PHOSPHOGLYCERATE converted to phosphoenolpyruvate
enzyme used
enolase
step 5 in the pay-off phase
-what converted to what
-what enzyme used
-anything lost
phosphoenolpyruvate converted to pyruvate
enzyme used
pyruvate kinase
ATP generated
what is the first key enzyne in the control of glycolytic flux
hexokinase
what is the size and shape of hexokinase
100kdA HOMODIMER
how many isoforms of hexokinase and what is the main isoform
4 isofoms
hexokinase II is the main isoform
what are all hexokinases inhibited by
All of the isoforms apart from4 are inhibited by their products(glucose -6-phosphate) in a negative feedback inhibition
why does the hexokinase 4 not experience negative feedback
Isoform 4 does not experience the inhibition and is therefore important in the liver and the brain as you always need this reaction to occur
explain how a high fat diet in a mouse contributes to obesitey
Give mice high fat diet
Increased expresseion of the glucokinase
Transmits a signal via the vagus nerve
The brown fat switches of in the body and brown fat thermogensis is decreased
what promoted glusocse consumption in rates
an increase in arcuate glucokinase
explain the increase in arcuate glucokinase increase
-fasting causises the following
increased glucokinase
decrease in the potassium ATP channel
increase in the calcium ions
increase in Neuropeptide Y release
increase in glucose consumption
what is the second key enzyme in the control of the glycolytic flux
phosphofructokinase
what is the phosphofructokinase enzyme size and structure
360kDa tetramer
how many isoforms of the phosphofructokinase enzyme
3
what are the 3 isoforms of the phosphofructokinase (PFK)enzyme
muscle
liver
platelet
what does a mutation in PFK-M enzyme lead to
tauris diseases
-muscle weakness and myopathy
what inhibits phosphofructoinase
ligh levels of ATP allosterically inhibit the enzyme
how does ATP inhibit phosphofructokinase
ATP binds to a specific regulatory site that is distinct from the catalytic site. The binding of ATP lowers the enzyme's affinity for fructose 6-phosphate.
what activates phosphofructokinase
F-2 and 6BP
fructose 2, 6 biphosphate
what is the enzyme that generates an allosteric effect of phosphofructokinase
phosphofructokinase 2 and fructose biphosphatatse 2
what is the structure of the phosphofructokinase 2 / fructose biphosphatatse 2 enzyme
110-220 kDa
-homodimer of 2 enzymes
-a kinase at the N-terminus and a phosphatase domain at the c terminus
how many isoforms of the phosphofructokinase 2 / fructose biphosphatatse 2 enzyme (PFK
4
liver muscle and fetal-PFKB1
cardiac-PFKB2
placental inducable brain PFKB3
testse -PFKB4
what regulates the phosphofructokinase 2 / fructose biphosphatatse 2 enzyme
glucagon and insulin
are the phosphofructokinase 2 / fructose biphosphatatse 2 enzyme the same thing
No, PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are not the same, but they are two enzymatic activities of the same bifunctional protein, known as 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (PFKFB).
what does phosphofructokinase 2 (PKK-2) do
Adds a phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate (F6P), converting it into fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6BP).
what si the result of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6BP). formation
Effect: Increases F2,6BP, which activates PFK-1 and enhances glycolysis.
what doesFructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase-2) do
Removes a phosphate from F2,6BP, converting it back to F6P.
what is a result of the activity of Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase-2)
Decreases F2,6BP, reducing PFK-1 activity and favoring gluconeogenesis.
explain the regulation of PFK-2 and FBPase-2 whith glucagon
Glucagon binds to the glucagon receptor when blood glucose levels are low.
This activates adenylyl cyclase, which increases cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels.
cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA), which phosphorylates the PFK-2/FBPase-2 enzyme, activating FBPase-2 and inactivating PFK-2.
FBPase-2 reduces fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6BP) levels by converting it back to fructose-6-phosphate (F6P).
Since F2,6BP is an activator of PFK-1 (a key enzyme in glycolysis), its reduction inhibits glycolysis and promotes gluconeogenesis instead.
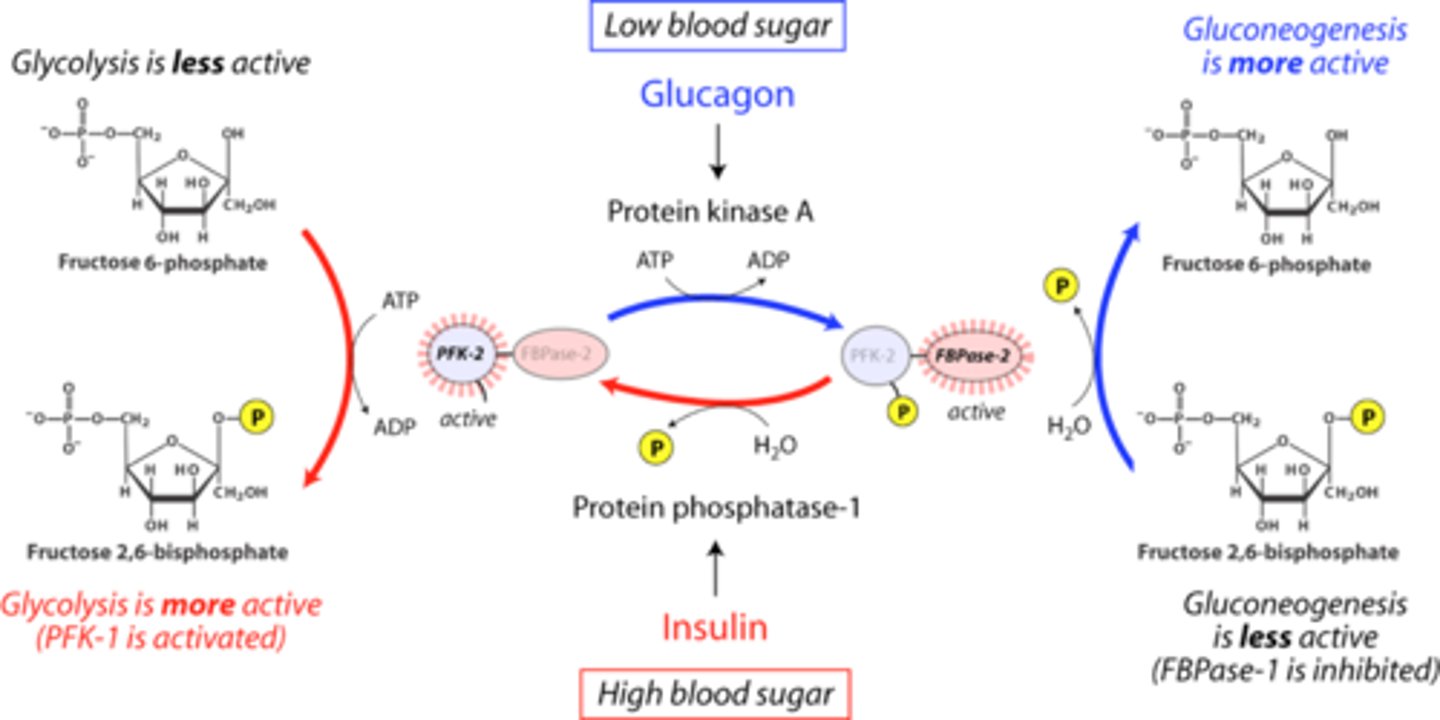
explain the regulation of PFK-2 and FBPase-2 whithinsulin
Insulin binds to the insulin receptor when blood glucose levels are high.
This activates a protein phosphatase, which dephosphorylates the PFK-2/FBPase-2 enzyme, activating PFK-2 and inactivating FBPase-2.
PFK-2 increases fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6BP) levels, which strongly activates PFK-1, stimulating glycolysis.
What is the 3rd key enzyme in the control of the glycoltic flux
pyruvate kinase
what is the structre and size of pyruvate kinase
228kDa tetramer
how many isoforms of pyruvate kinase
4
liver
erythrocyte
muscle
fetal
what regualtes pyruvate kinase
glucagon and insulin
explain the regulation of pyruvate kinase by glucagon
Glucagon binds to the glucagon receptor (when blood glucose is low).
This activates adenylyl cyclase, which increases cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels.
cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA), which phosphorylates pyruvate kinase, inhibiting it.
Inhibited pyruvate kinase means phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) is not converted to pyruvate, reducing glycolysis.
Instead, PEP can be used for gluconeogenesis, producing glucose.
Glycolysis is turned OFF.
explain the regulation of pyruvate kinase by insulin
Insulin binds to the insulin receptor (when blood glucose is high).
This activates pyruvate kinase phosphatase, which removes the phosphate group from pyruvate kinase, activating it.
Active pyruvate kinase converts PEP to pyruvate, producing ATP and promoting glycolysis.
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (F-1,6-BP) acts as an activator, ensuring the reaction proceeds efficiently.
Glycolysis is turned ON.