Understanding Bond Prices and Yields IM exam 2
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Bond
A security that obligates the issuer to make specified payments to the holder over a period of time
Bond indenture
The contract between an issuer and the bond holder
Par value (face value)
The payment to the bondholder at the maturity of the bond
Coupon payments
Per period payments of interest for the life of the bond
Coupon rate
A bond's annual interest payment per dollar of par value
Zero-coupon bonds
A bond paying no coupons that sells at a discount and provides only a payment of par value at maturity
Accrued interest
Annual coupon payment divided by Days separating coupon payments multiplied by Days since last coupon payment
Flat price
Net of accrued interest
Invoice price
Includes the accrued interest
Corporate Bonds
Thin market due to variety of issues along maturity, coupon rate, seniority, etc.
Straight bonds
Bond that pays a fixed coupon every period and repays its full face value at maturity
Callable bonds
Bond that may be repurchased by the issuer at a specified call price during the call period
Refunding
New bond issue pays for repurchase of higher-coupon callable bonds
Deferred callable bonds
Callable bonds with a period of call protection
Convertible bonds
Bond where the bondholder can exchange the bond for a specified number of stock
Market conversion value
The current value of the shares for which the bonds may be exchanged
Conversion premium
Excess of the bond price over its conversion value
Puttable bonds
Bond where investor can exchange for par value at some date or extend for a given period
Floating-rate bonds
Bond with coupon rates periodically reset according to a specified market rate
Preferred stock
Considered equity but functions like fixed-income
Floating-rate preferred stock
Pays dividend rate linked to a measure of current market interest rates
Maturity
Some firms issue 50 to 100 year bonds, whereas convention is 30
Inverse floater
Interest rate falls when general level of interest rate rises
Asset-backed bonds
Income from a specified group of assets servicing debt
Pay-in-kind bonds
Issuer may pay interest in either cash or additional bonds
Catastrophe bonds
Payments halted conditional on a catastrophe
Indexed bonds
Payments tied to a general price index or the price of a commodity
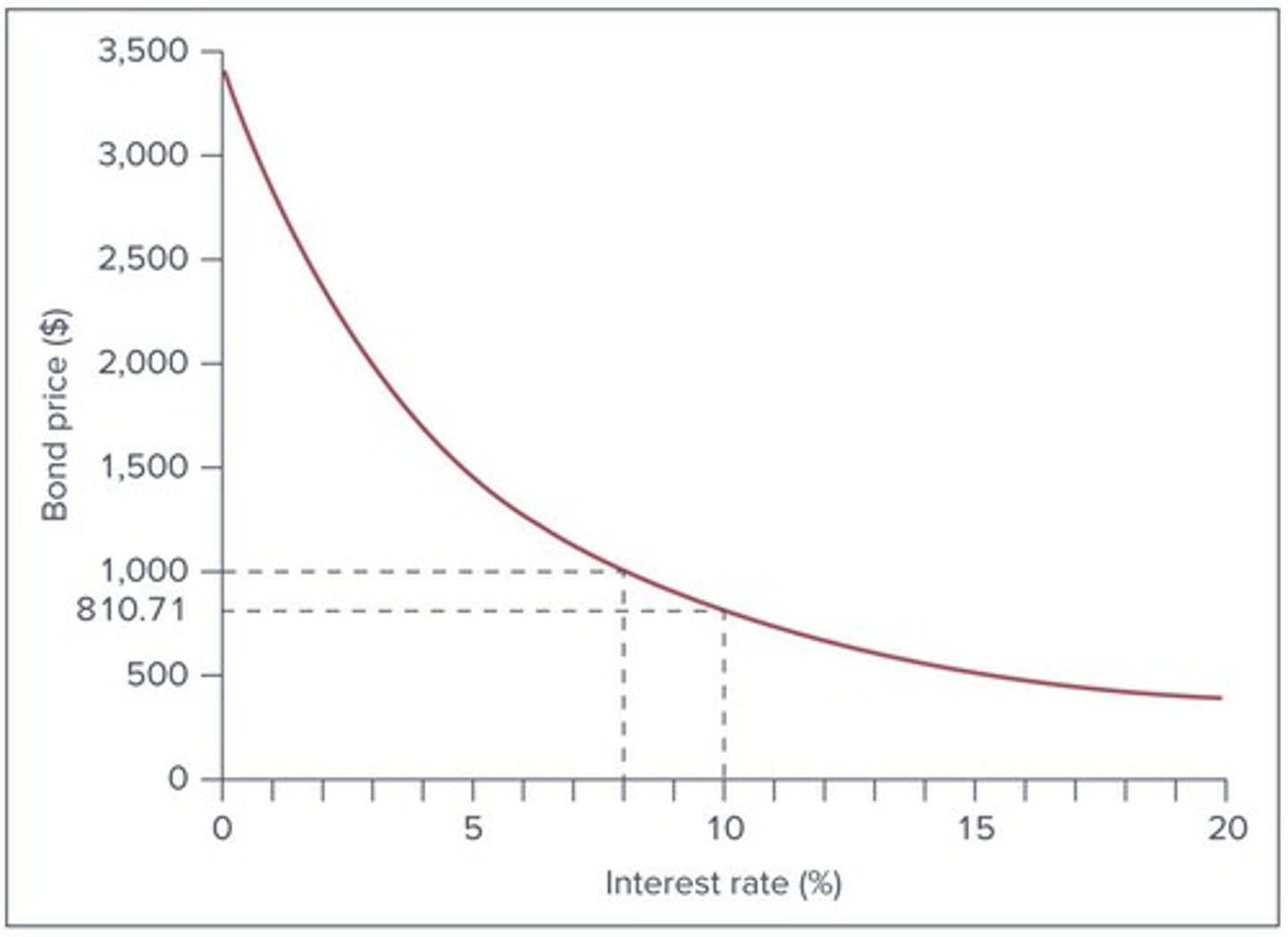
Bond value
Present value of coupons + Present value of par value
Annuity Factor
1/r * (1 - (1/(1 + r)^T))
Present Value Factor
1/(1 + r)^T
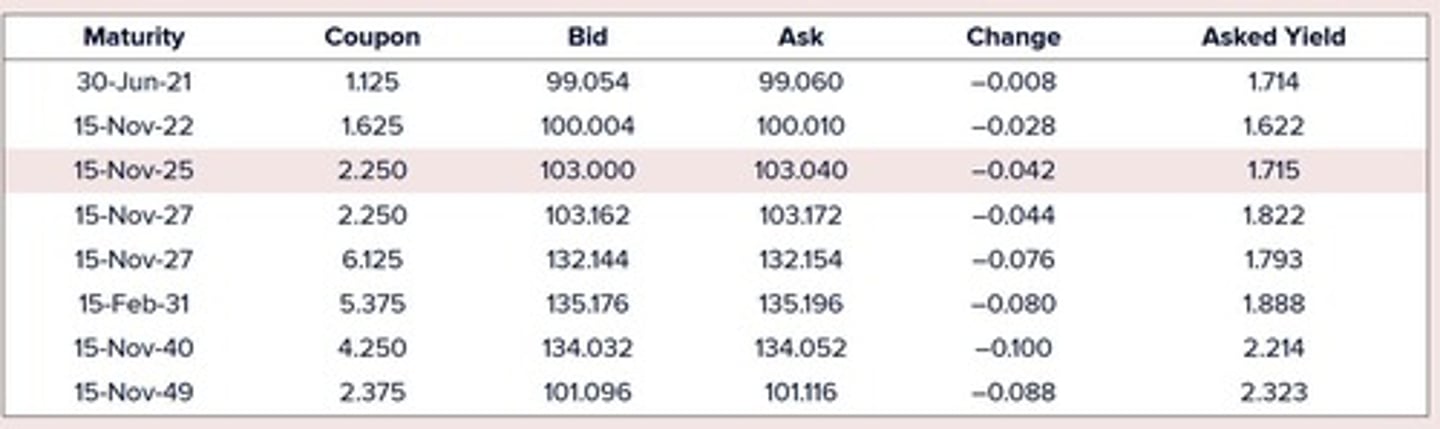
Example of Bond Pricing
Consider 30-yr bond with a 8% semi-annual coupon and par value of $1000
Yield to Maturity
Annualized discount rate (i.e. r × N) that makes the PV of payments equal the price for a bond paying N times a year.
Average rate of return
Average rate of return earned by an investor purchasing a bond at a given price
Bond price formula
Bond price = Coupon × Annuity factor(r, T) + Par value × PV factor(r, T)
Current yield
Current yield = Annual Coupon, differs from the coupon rate because it uses bond price instead of par value and differs from the yield to maturity because it doesn't account for changes in bond prices.
Premium bonds
Bonds that sell above par value.
Discount bonds
Bonds that sell below par value.
Yield to Maturity (YTM)
The total return anticipated on a bond if the bond is held until it matures.
Example of Yield to Maturity
Suppose you have a 8% semi-annual coupon on a 30-yr bond with a face value of $1000 and bond price of $1276.76.
Bond equivalent yield
Bond equivalent yield is calculated as r × n, where n is the number of periods within a year.
Effective annual yield
Effective annual yield is the return after accounting for compound interest, calculated as (1 + r)n.
Yield to Call
Yield to call is how much investors should demand if the firm calls its bond after call protection is over.
Callable bond
A bond that can be redeemed by the issuer prior to its maturity.
Reinvestment rate (RR)
Rate at which a coupon payment can be reinvested.
Realized compound return (RCR)
Compound rate of return on a bond with all coupons reinvested until maturity.
Total Value calculation
Total Value = Coupon1(1 + RR1) + Coupon2 + Par Value.
Realized Compound Return formula
V0(1 + r)T = VT.
Horizon analysis
Analysis of bond returns over a multiyear horizon using forecasts of YTM and RR.
Properties of YTM, RR, & RCR
When RR equals the YTM, then the RCR equals the YTM; when RR is higher than the YTM, then the RCR is higher than the YTM; when RR is lower than the YTM, then the RCR is lower than the YTM.
Interest rates effect on callable bonds
Interest rates fall → Future payments expensive; Interest rates rise → Future payments cheaper.
RCR with RR equal to YTM
If RR equals YTM, then RCR equals YTM.
RCR with RR less than YTM
When RR is lower than the YTM, then the RCR is lower than the YTM.
RCR with RR greater than YTM
When RR is higher than the YTM, then the RCR is higher than the YTM.
Reinvestment rate risk
Uncertainty surrounding the cumulative future value of reinvested bond coupon payments.
Bond prices
Must adjust to compensate or cost investors.
Coupon rate
Determines whether a bond sells above or below par based on its comparison to the market rate.
Selling above par
Occurs when the coupon offers more than the market rate.
Selling below par
Occurs when the coupon offers less than the market rate.
Price at maturity
Must equal par value.
After-tax risk-adjusted basis
Rates must be comparable on this basis.
Holding-period return (HPR)
Calculated as Total Annual Coupons + Final Bond Price - Initial Bond Price.
Yield to Maturity (YTM)
Based on bond's coupon, current price, and par value at maturity.
Difference between YTM and HPR
YTM is based on bond's coupon, current price, and par value at maturity; HPR is based on bond's coupon, current price, and price at the end of a holding period.
Market rates fall
Holding-period return will reflect a rise in price.
Market rates rise
Holding-period return will reflect a fall in price.
Longer horizons
At longer horizons, the YTM will reflect reinvestment of coupons.
Example of HPR
Consider a 3-yr bond with a 7% annual coupon and face value $1000.
Capital Gains
The increase in the bond's price over time.
Bond Characteristics
Attributes that define a bond's behavior and pricing.
Bond Pricing
The process of determining the fair value of a bond.
Price
Price = 70 × Annuity Factor(8%, 3) + 1000 × PV Factor(8%, 3)
Holding Period Return (HPR)
HPR = (982.17 − 974.23 + 70) / 974.23 = 8%
Original Issue Discount Bonds
Bonds issued with low coupon rates, sell below par value
Zero-Coupon Bonds
Bonds that carry no coupons, such as T-bills
Treasury STRIPS
Each semiannual coupon is treated as a zero-coupon bond
Price of 30-year zero-coupon bond
Price = 1000 / (1+r)^T
Taxable Interest Income
IRS calculates taxable interest income from the price appreciation even if original-issue discount bond does not sell
Imputed Interest Income
IRS will impute interest income as 63.04 - 57.31 = 5.73
Capital Gains
Calculated as 64.72 - 63.04 = 1.68
Bond Ratings
Rating agencies assess credit risk of firms; bonds rated BBB or Baa and above are considered investment grade
Coverage Ratios
Ratio of company earnings to fixed costs (e.g. times-interest-earned ratio, fixed-charge coverage ratio)
Leverage Ratios
Measures how debt laden a firm is (e.g. debt-to-equity)
Liquidity Ratios
Measures the firm's ability to raise cash (e.g. current ratio, quick ratio)
Profitability Ratios
Measures overall performance (e.g. return on assets, return on equity)
Bond Indenture
Contract between the issuer and bondholder specifying restrictions protecting the bondholder
Sinking Fund
Issuer must periodically repurchase some bonds prior to maturity
Subordination Clause
Restricts additional borrowing, may allow subordinated/junior debt
Yield-to-Maturity
Represents maximum possible yield; expected yield to maturity must take into account default
Default Premium
Premium to compensate for default risk; difference between promised yield and riskless government bond
Credit Default Swaps
Insures against the default risk of a bond
Term Structure of Interest Rates
The relationship between yields to maturity and terms to maturity across bonds
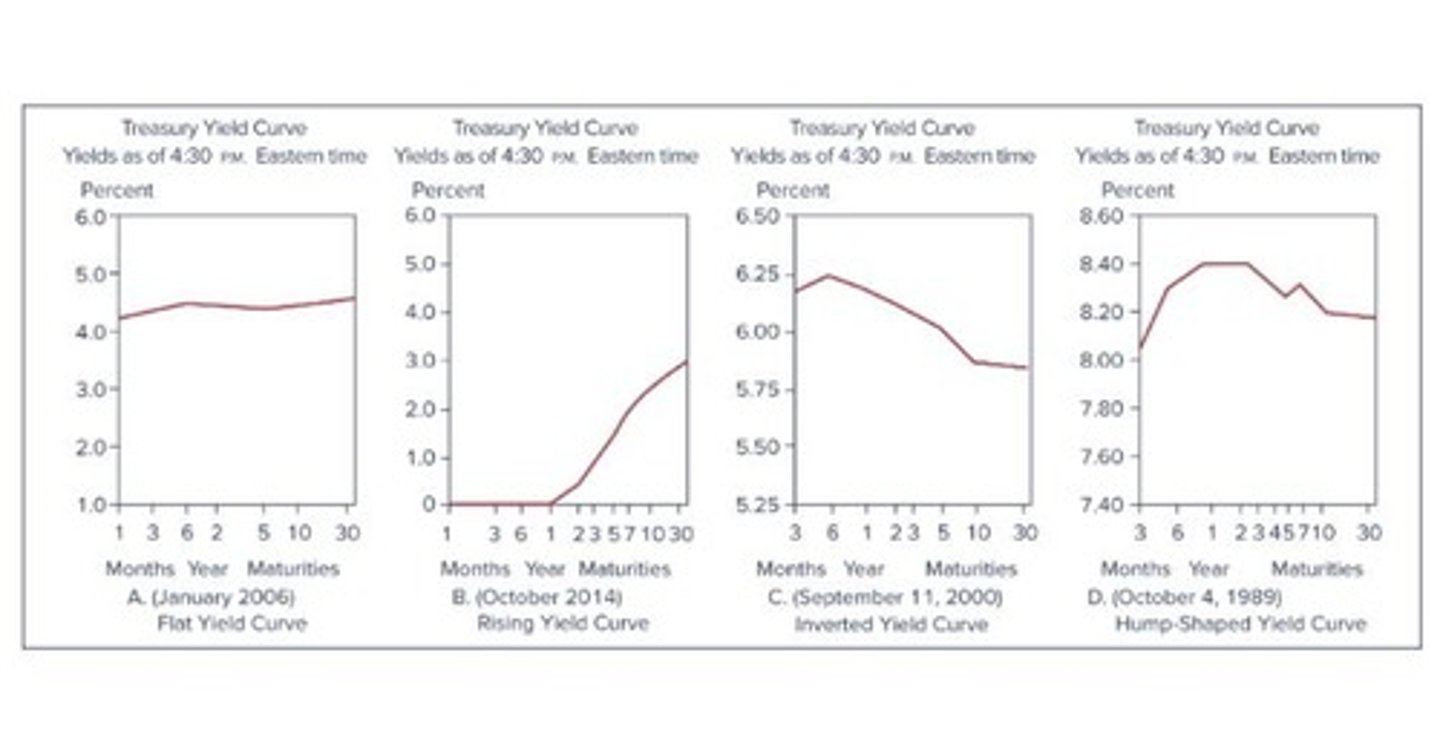
Expectations Theory
Slope of the yield curve is due to expectations of changes in short-term rates
Forward Rate
Inferred future interest rate based on current yield curve
Example of Forward Rates
Using YTM values to calculate implied forward rates for future periods
ynew1
0
ynew2
0
Price of a two-year zero-coupon bond
811.62 when YTM is 11%
Price with ynew1
892.78 when discounted by (1 + 0.1201)
HPR
0.10 calculated as (892.78 - 811.62) / 811.62
Liquidity Preference Theory
Investors demand a risk premium on long-term bonds.