Midterm 3 (20-27) - BIS 2A
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/427
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:09 AM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
428 Terms
1
New cards
DNA =
deoxyribose + phosphates + four bases
2
New cards
purines
adenine and guanine
3
New cards
pyrimidines
cytosine, uracil, thymine
4
New cards
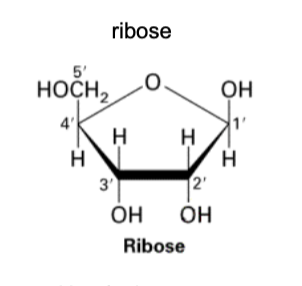
Ribose has:
four OH groups.
5
New cards
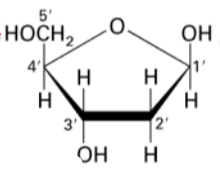
Deoxyribose has:
three OH groups.
6
New cards
In DNA, deoxyribose connects:
5' to 3'.
7
New cards
nucleoside
ribose and base, no phosphate
8
New cards
nucleotide
ribose, nitrogenous base, phosphates
9
New cards
Bases connect to the ___ OH group.
1'
10
New cards
lesson from 100 years of DNA chemistry (-1950)
components and covalent connectivity of DNA
11
New cards
Chargaff's rule
percentage of G always equaled C and percentage of A always equaled T
12
New cards
Why is the constant ration of A to T (and G to C) in plant, animal, prokaryotic, and fungal genomes really significant?
a) It means the fraction of bases that are purines always balances the fraction
that are pyrimidines
b) It is what defines the difference between DNA and RNA
c) It suggests that A is somehow “paired” with T and G is paired with C
d) It suggests that purines pair with purines and pyrimidines pair with pyrimidines
a) It means the fraction of bases that are purines always balances the fraction
that are pyrimidines
b) It is what defines the difference between DNA and RNA
c) It suggests that A is somehow “paired” with T and G is paired with C
d) It suggests that purines pair with purines and pyrimidines pair with pyrimidines
c)
13
New cards
Watson-Crick model told us about:
replication, coding, repair, and recombination in DNA.
14
New cards
Watson-Crick model
DNA is a helix w/ width of purine plus a pyrimidine and a sugar phosphate backbone on the outside
15
New cards
features of Watson-Crick model
- two strands, anti-parallel
- H bonding between strands, A-T and G-C always base paired
- base pairs stacked = plates parallel
- H bonding between strands, A-T and G-C always base paired
- base pairs stacked = plates parallel
16
New cards
A-T and G-C make the ___________, with ___________________.
same shape, same length and width
17
New cards
DNA redundancy
each strand has equivalent information, this is essential to function as genetic material
18
New cards
Why is information on each DNA strand redundant?
Base pairing rules what is inserted - two identical copies are made, sequence can be copied again and again
19
New cards
If one strand is 5' TGCCCTAT 3', the complementary strand is:
a) 5’ TATCCCGT 3’
b) 5’ ATAGGGCA 3’
c) 5’ ACGGGATA 3’
d) 5’ TGCCCTAT 3’
a) 5’ TATCCCGT 3’
b) 5’ ATAGGGCA 3’
c) 5’ ACGGGATA 3’
d) 5’ TGCCCTAT 3’
b)
20
New cards
DNA and RNA read, written, and synthesized:
5' to 3'.
21
New cards
DNA could be single stranded and only transiently double-stranded during replication, but:
this has a high mutation rate (viruses).
22
New cards
How does DNA 'pay' to elongate its 3' end?
By releasing free phosphates: dNTP > dNMP + PPi
23
New cards
dNTPs can only be added to:
a preexisting 3' OH.
24
New cards
DNA synthesis always needs a:
primer.
25
New cards
Lagging strand synthesis requires:
constant addition of RNA-based primers.
26
New cards
Leading strands run:
long and continuously.
27
New cards
Lagging strands are:
short patches that are made and then joined later.
28
New cards
Okazaki fragments
the short sequences of DNA nucleotides made to be joined later (lagging strand)
29
New cards
DNA polymerase I
removes RNA primers and replaces them with DNA nucelotides
30
New cards
DNA polymerase III
synthesizes daughter strands
31
New cards
helicase
separates parent DNA strands
32
New cards
ligase
contacts Okazaki fragments
33
New cards
primase
generates RNA primers
34
New cards
telomerase
lengthens telomeres by adding many copies of a short repetitive sequence to the ends of chromosomes
35
New cards
topoisomerase
reduces super-coiling of DNA by cutting the backbone, allowing helices to operate
36
New cards
Synthesis of the leading strand is simple, because:
only adding complementary bases is needed.
37
New cards
Synthesis of the lagging strand is complicated because:
RNA primers constantly need to be added to follow the add to 3' rule.
38
New cards
For the leading strand, a ___ is needed at the origin of replication.
primer
39
New cards
All replication proteins are:
bounded together.
40
New cards
clamp loader
loads on clamps - helps keep replicative polymerase on its template
41
New cards
When helicase unwinds DNA, there are two __________ generated.
replication forks
42
New cards
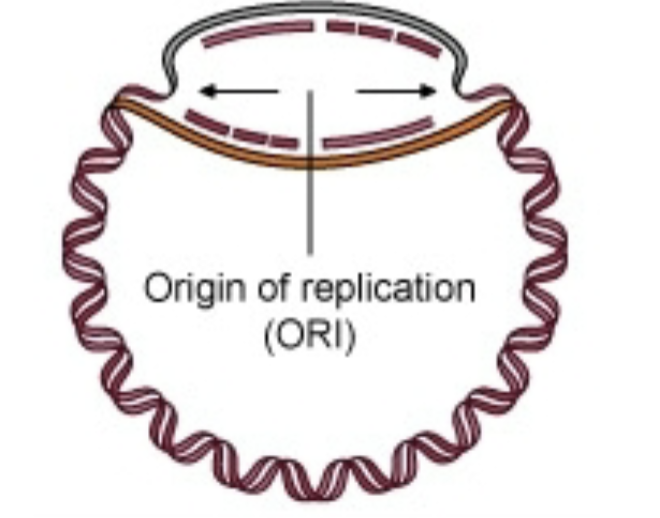
How many DNA polymerases would be in this picture, and where?
43
New cards
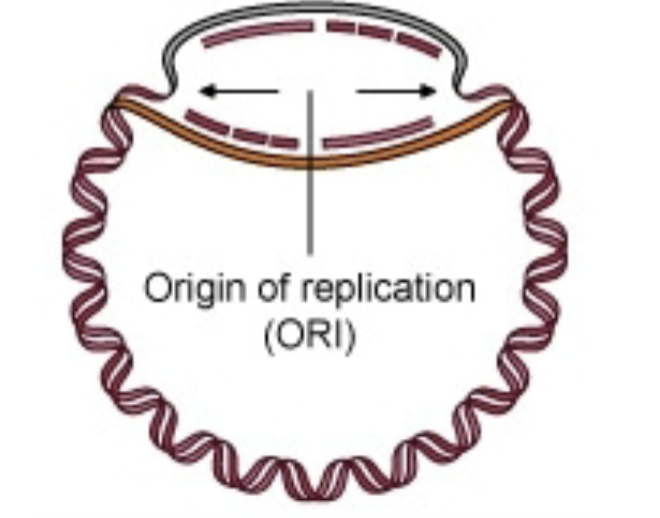
How many primers would be in this picture and how many primases?
44
New cards
When does DNA polymerase III drop off the template?
When it meets the 5' end of the primer
45
New cards
Where does DNA polymerase I start replicating?
3' OH ends
46
New cards
DNA polymerase I is:
a polymerase and a exonuclease
47
New cards
DNA polymerase I replaces RNA with:
DNA.
48
New cards
What is an issue at the end of lagging strand synthesis on linear chromosomes?
Each time, the chromosome will get smaller as it replicates, losing DNA.
49
New cards
Do somatic cells have telomerase?
No, only embryonic and gremlin cells do
50
New cards
Telomerase is a ______________.
reverse transcriptase - its a DNA polymerase that reads an RNA template.
51
New cards
What replication-related problem is solved by telomerase?
a) The inability of the cell to initiate DNA synthesis without building on a pre-existing “primer”.
b) The inability of the cell to terminate replication of a circular template.
c) The requirement for a “promoter” to initiate DNA synthesis
a) The inability of the cell to initiate DNA synthesis without building on a pre-existing “primer”.
b) The inability of the cell to terminate replication of a circular template.
c) The requirement for a “promoter” to initiate DNA synthesis
52
New cards
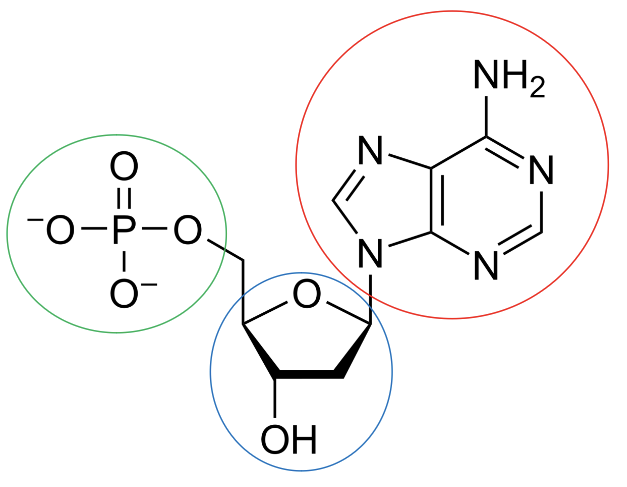
What is circled in green?
The phosphate group
53
New cards
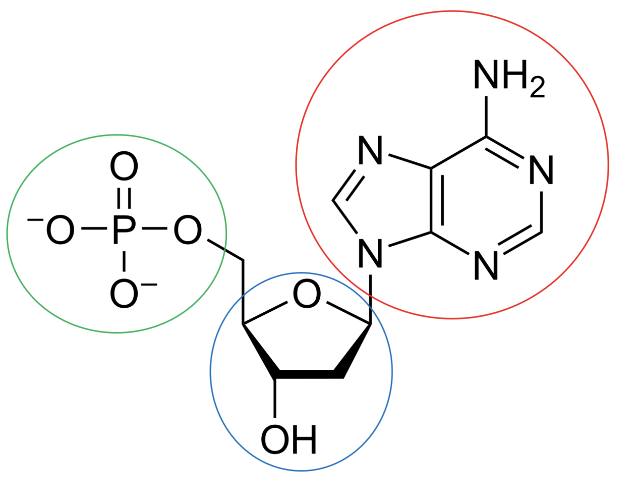
What is circled in blue?
The sugar
54
New cards
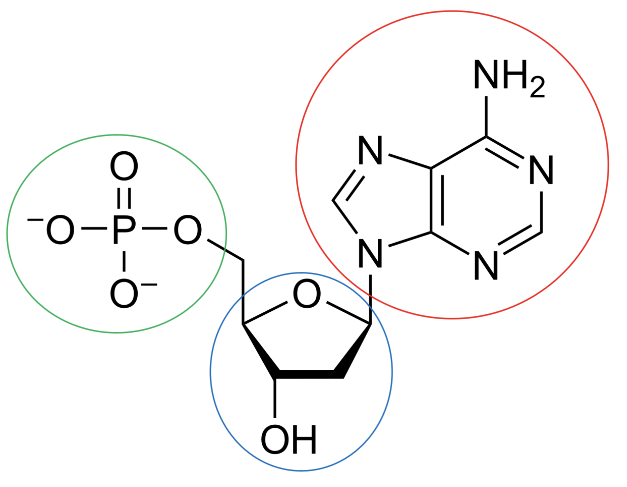
What is circled in red?
The nitrogenous base
55
New cards
What kind of bio molecule is DNA?
Nucleic acid
56
New cards
What are DNA monomers called?
Nucleotides
57
New cards
Carbon atoms in a sugar are labeled using:
1', 2', 3', 4', 5'
58
New cards
Which carbon atom in the sugar is attached to the nitrogenous base?
The 1' carbon
59
New cards
Which carbon atom in the sugar is attached to the phosphate group?
The 5' carbon
60
New cards
glycosidic bond
the bond between the 1' carbon and the nitrogenous base in a nucleotide
61
New cards
Is the glycosidic bond polar or non-polar?
Polar (C-N electronegativity)
62
New cards
What is the purpose of DNA?
Storing genetic information
63
New cards
What part of the DNA stores genetic information?
The nitrogenous base
64
New cards
What four nitrogenous bases are in DNA?
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine
65
New cards
What four nitrogenous bases are in RNA?
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil
66
New cards
What is the difference between purines and pyrimidines?
Purines have two rings while pyrimidines have one ring
67
New cards
What is the difference between the 5' and 3' end of a pentose sugar?
The 3' end has a hydroxyl group attached and the 5' end has a phosphate group attached
68
New cards
How many hydrogen bonds occur between adenine and thymine?
Two
69
New cards
How many hydrogen bonds occur between guanine and cytosine?
Three
70
New cards
DNA is ____________.
double-stranded
71
New cards
DNA runs __________.
anti-parallel
72
New cards
What is the name of the bond that connects two nucleotides?
Phosphodiester bond
73
New cards
What atoms are involved in the phosphodiester bond?
Oxygen and phosphorous
74
New cards
Is the phosphodiester bond polar or non-polar?
Polar (O-P electronegativity)
75
New cards
Two nucleic acid motors are joined by:
coupling an exergonic reaction with an endergonic reaction.
76
New cards
exergonic reaction in joining nucleic acid monomers
hydrolysis of the phosphoanhydride bond between phosphate groups
77
New cards
endergonic reaction in joining nucleic acid monomers
3' -OH group and phosphate attached to 5' (= phosphodiester bond)
78
New cards
Do nucleic acids have a charge?
DNA and RNA are negatively charged (because of the phosphate groups)
79
New cards
Where does DNA replication begin?
At the origin of replication (ORI)
80
New cards
What enzyme binds to the ORI?
Helicase
81
New cards
Why might eukaryotic organisms have more than one origin of replication?
So that DNA replication can occur in a shorter amount of time (DNA is large)Wh
82
New cards
What interaction holds DNA strands together?
Hydrogen bonds
83
New cards
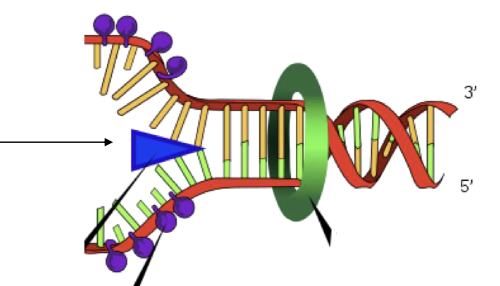
What does the blue triangle represent?
Helicase
84
New cards
When helicase is unwinding DNA, what potential issue could arise?
The DNA can become over-twisted in front and under-twisted behind
85
New cards
What enzyme can resolve supercoiling in DNA?
Topoisomerase
86
New cards
What direction does DNA polymerase III move along the template strand?
3' to 5'
87
New cards
What direction does DNA polymerase III synthesize the daughter strand?
5' to 3'
88
New cards
What enzyme informs DNA pol III where to begin daughter strand synthesis?
Primase
89
New cards
How does the cell obtain the same strands of DNA every time DNA is replicated?
A-T and G-C, base-stacking and base-pairing, ways to find errorsQ
90
New cards
Which would be the consequence of DNA replication without ligase?
A) It would result in lots of ‘nicks’ or breaks in the DNA sugar-phosphate backbone.
B) Only the leading strand would be replicated, as the cell would be unable to replicate the lagging strand.
C) Replication would stall once all the nucleotides had been used up in the cell.
D) Replication would be unable to start.
E) The cell would need to repair multiple incorrectly paired bases between the template and newly synthesized strands of the DNA.
A) It would result in lots of ‘nicks’ or breaks in the DNA sugar-phosphate backbone.
B) Only the leading strand would be replicated, as the cell would be unable to replicate the lagging strand.
C) Replication would stall once all the nucleotides had been used up in the cell.
D) Replication would be unable to start.
E) The cell would need to repair multiple incorrectly paired bases between the template and newly synthesized strands of the DNA.
A)
91
New cards
The phosphodiester bond between the 5' -PO4 and 3' -OH is not formed in the Okazaki fragment. Which enzyme is inhibited or malfunctioning?
A) DNA polymerase III
B) Primase
C) Helicase
D) DNA Polymerase I
E) Ligase
A) DNA polymerase III
B) Primase
C) Helicase
D) DNA Polymerase I
E) Ligase
E)
92
New cards
A piece of double-stranded DNA has 30% A. What will be the % G?
A) 30%
B) 40%
C) 20%
D) 70%
E) Indeterminate from the given information.
A) 30%
B) 40%
C) 20%
D) 70%
E) Indeterminate from the given information.
C)
93
New cards
The nitrogenous base is linked to the ribose or deoxyribose sugar via a __________ at the _ carbon.
A) Glycosidic bond, 5’
B) Peptide bond, 2’
C) Hydrogen bond, 4’
D) Phosphoanhydride bond, 3’
E) Phosphodiester bond, 1’
F) None of the above
A) Glycosidic bond, 5’
B) Peptide bond, 2’
C) Hydrogen bond, 4’
D) Phosphoanhydride bond, 3’
E) Phosphodiester bond, 1’
F) None of the above
F)
94
New cards
How so mutations occur? (1)
Through replication errors
95
New cards
Replication errors can be:
mistakes or replication of a damaged template.
96
New cards
How do mutations occur? (2)
Through erroneous repair of DNA damage
97
New cards
Cancer is caused by:
somatic mutations.
98
New cards
risk factors for cancer
genotoxin exposure, age
99
New cards
Replicative DNA polymerase produces a mutation:
1/10^6 times
100
New cards
DNA polymerase proofreading
enzyme's groove must fit the base pair or it will start over