CHEM 3300 / Topic 6b: Solid-State - Unit Cells
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What kind of directionality do metallic and ionic bonds exhibit? What is the reason for this?
No directionality, as structures fill space as efficiently as possible by having no regard for what direction they bond.
How is a lattice arranged?
What is a lattice point?
Name and differentiate the two types of solids.
Infinitely arranged with lattice points in three dimensions.
A point having the same structural elements associated with it, the same environment, post-translation.
Crystalline solid: Particles arranged in a regular, repeating pattern, having long-range order.
Amorphous solid: Particles not arranged in a regularly repeating pattern, having no long-range order.
Just to be entirely clear, just to nail it in your head, where do a crystal’s macroscopic shape and properties derive from?
Regularly repeating structural elements that make up the crystal.

What’s the difference between a crystalline solid and a crystalline lattice?
Crystalline solid is a type of solid, while a crystalline lattice is the arrangement of the particles in the crystalline solid.
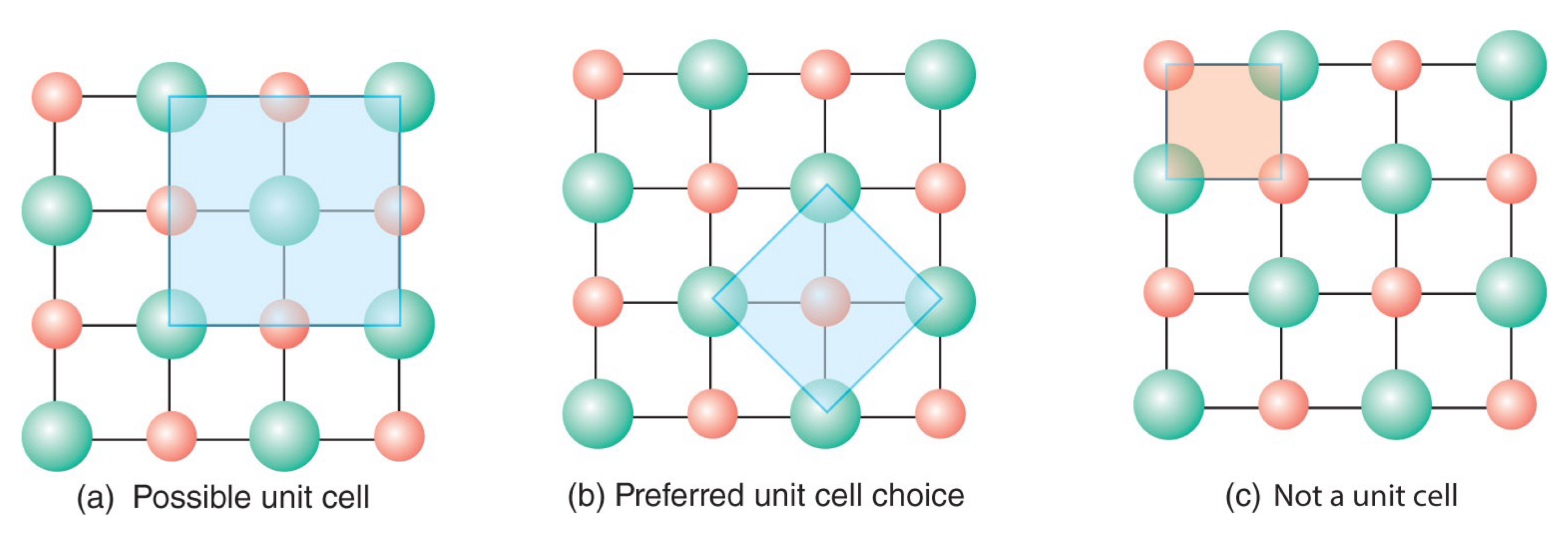
What is a unit cell?
The smallest parallel-sided region of structural elements that can be repeated over and over via translational symmetry to reproduce the same three-dimensional array.
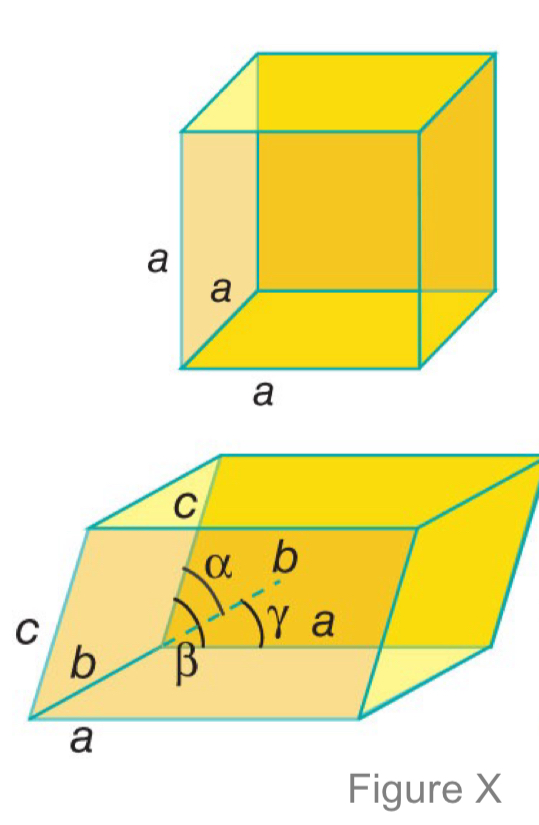
What are the unit cell parameters, a.k.a. the lattice parameters?
The three sides (a, b, and c) and three angles (α, β, and γ). These are properties describing a lattice.
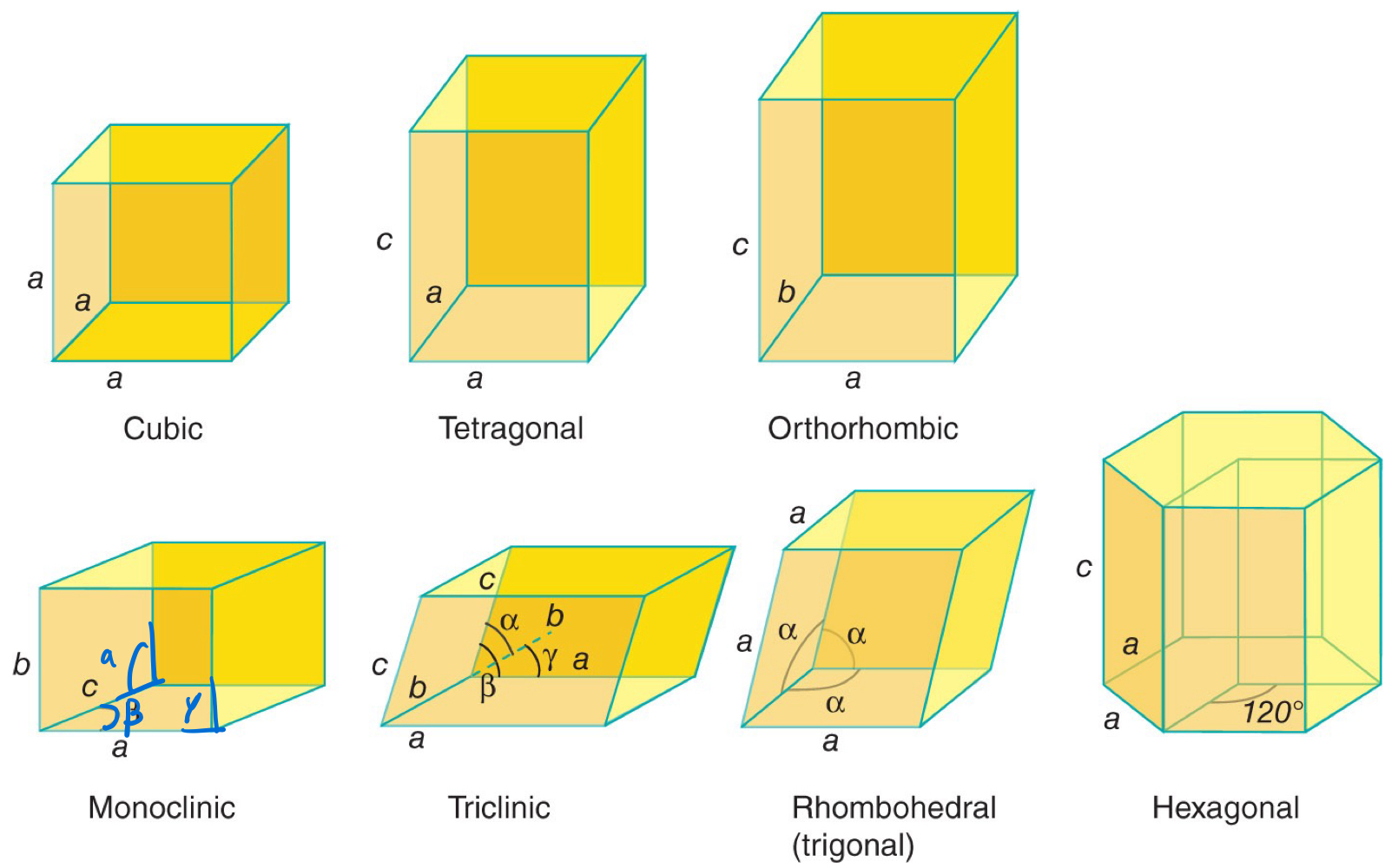
Each _____ _______ adopted by compounds belong to one of seven _____ _______.
Each ordered structure adopted by compounds belong to one of seven crystal systems.
Where are the lattice points of a primitive unit cell located - edges, corners, or faces?
How many atoms are there per primitive unit cell then?
Cubic unit cell with lattice points only at the corners, containing then in total one atom per entire cell.
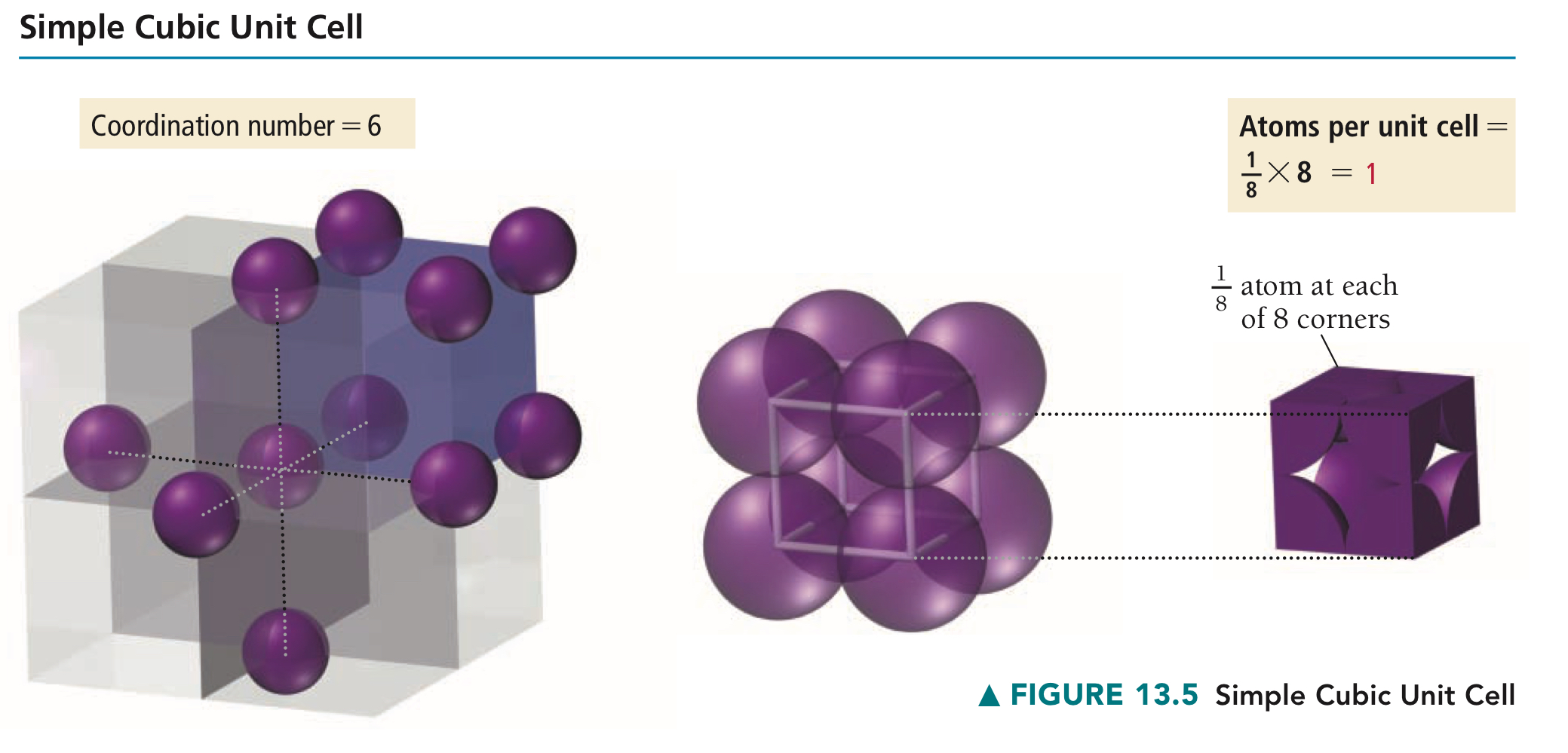
Why does one primitive unit cell have one atom in total?
In each of the corners, the atoms, or the lattice points, are 1/8. 8 corners × 1/8 lattice point = 1 atom per unit cell.
What translational symmetry does a P unit cell have?
In a primitive unit cell, of a hole in the centre, what is its coordination number?
Translational symmetry with the unit cells next to it.
8.
Where are the lattice points of a body-centred (I) unit cell located - edges, corners, or faces?
How many atoms are there per body-centred unit cell then?
Cubic unit cell with lattice points at the corners and at the centre, then containing a total of 2 lattice points per I unit cell.
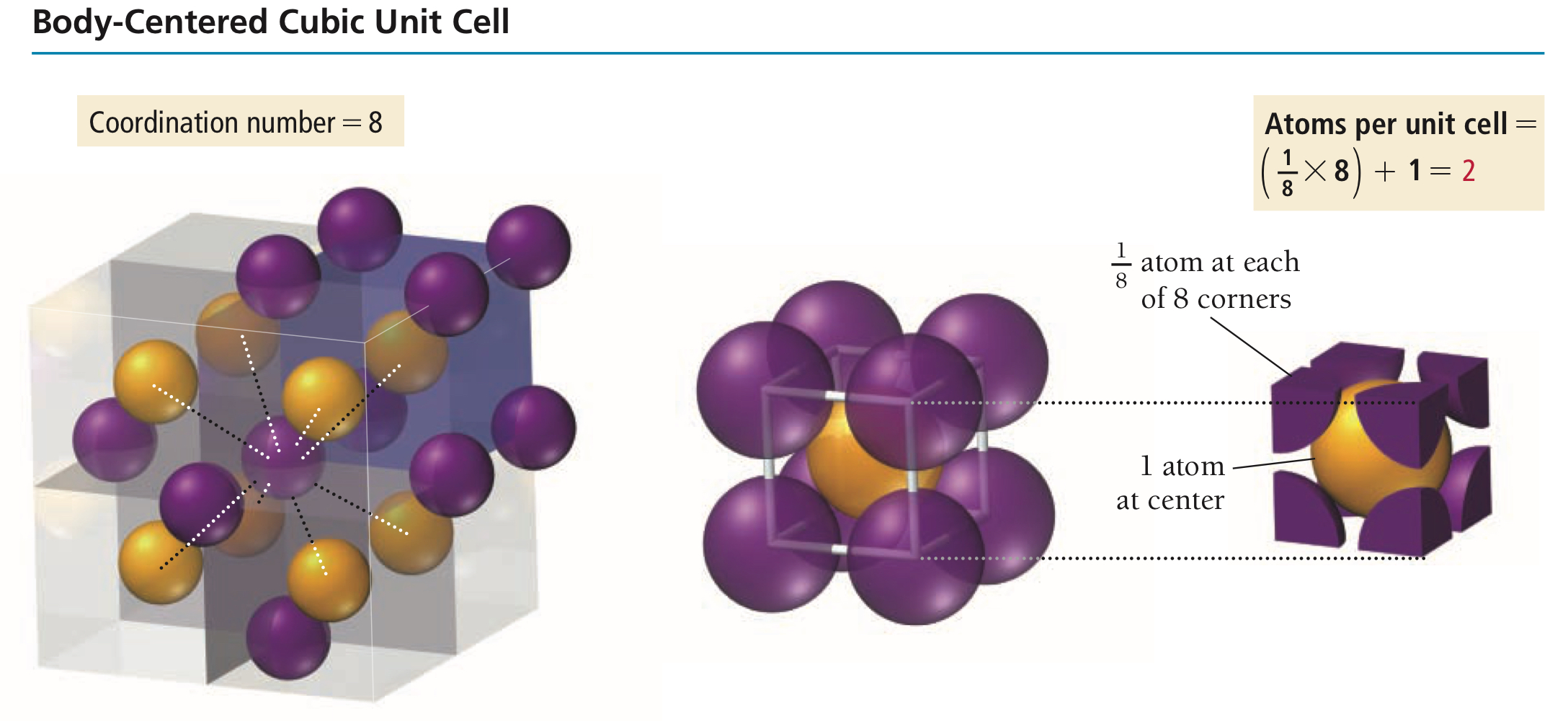
Why does a body-centred unit cell have two lattice points in total?
Take 1/8 from each of the 8 corners, take 1 entire sphere at the centre, and you have a sum of 2.
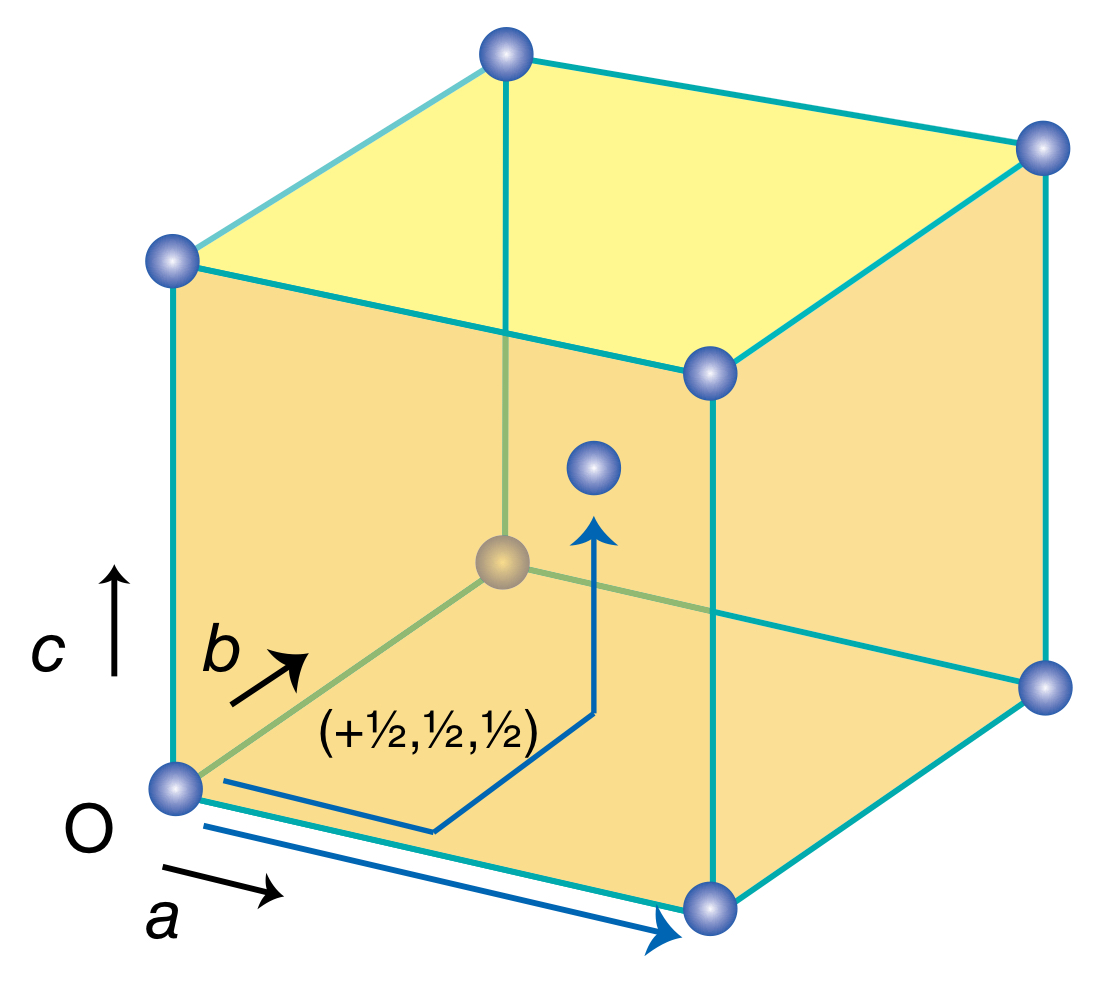
What translational symmetry does an I unit cell have?
What is the coordination number of each lattice point in an I unit cell?
It has translational symmetry with the unit cell next to it and from O to +1/2, +1/2, +1/2.
8.
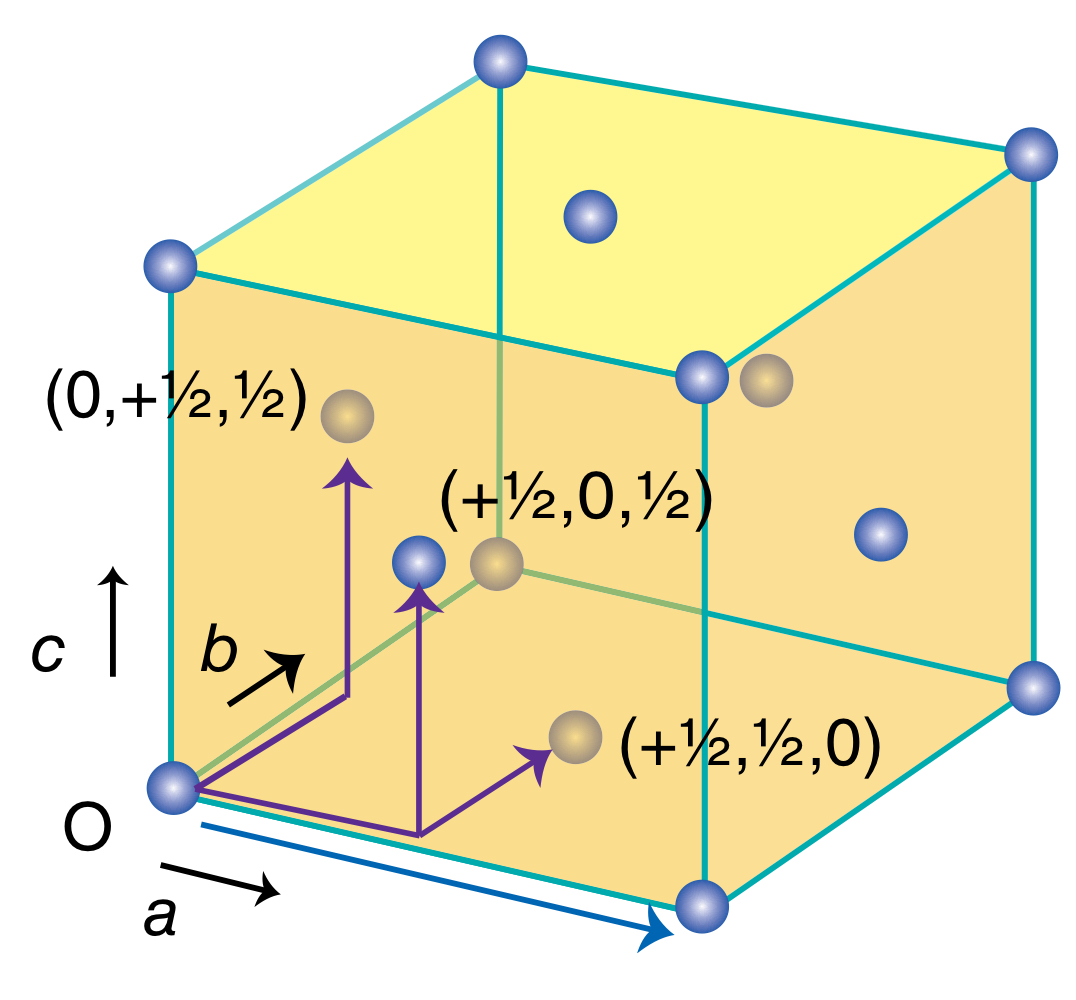
Where are the lattice points of a face-centred (F) unit cell located - edges, corners, or faces?
How many atoms are there per face-centred unit cell then?
Cubic unit cell with lattice points at the corners and one at the centre of each face.
4.
How many lattice points does a face-centred unit cell have? Explain.
4 lattice points. Take 1/8 of each of the 8 corners, and take 1/2 of each of the 6 faces, you get a sum of 4.
What translational symmetry does a face-centred cubic unit cell have?
Translational symmetry with a unit cell next to it.
Translational symmetry from O to (+1/2, +1/2, 0).
Translational symmetry from O to (+1/2, 0, and +1/2).
Translational symmetry from O to (0, +1/2, +1/2).
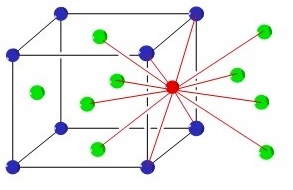
In a face-centred unit cell, how many neighbours does one lattice point have? Rather, what is its coordination number?
12.
Out of all the three unit cell types, which is the cubic unit cell with the most efficiency in packing, and why?
FCC, because it has the most efficient use of space, using 74% of space and coordinating with 12 atoms.
What are the two types of close-packed systems?
Hexagonal-close packing and cubic close-packing.
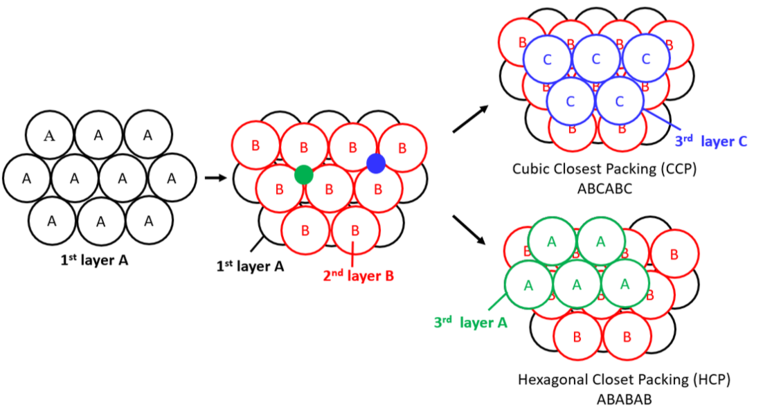
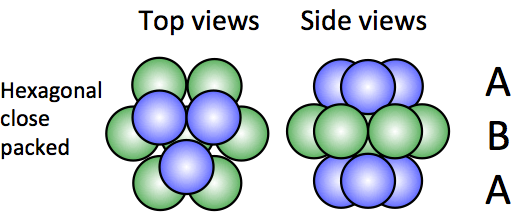
What is hexagonal close-packing, and what is its unit cell?
Close packing wherein you get a layering of A, B, A, B, and so on. Its unit cell is hexagonal.
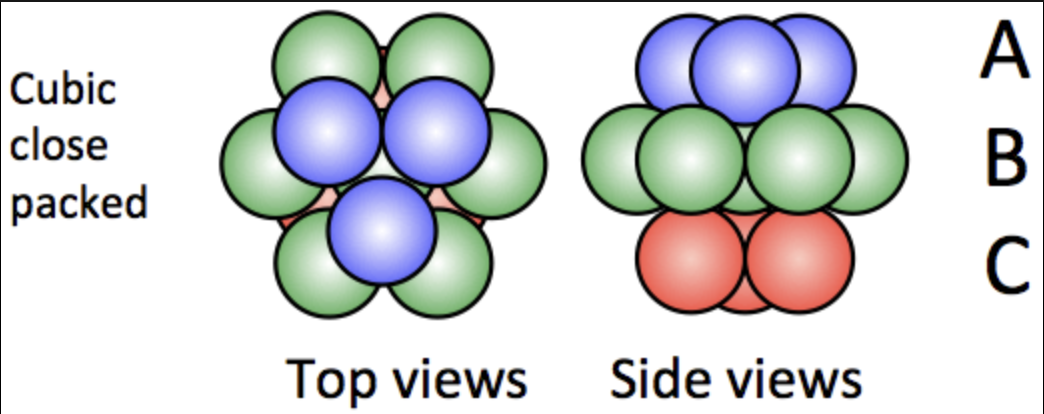
What is cubic close-packing, and what is its unit cell?
Close-packing wherein you get a layering of A, B, C, A, B, C, and so on. Its unit cell is cubic.
Close-packed structures would fill 74% of the space, but 26% is left empty. What do these vacancies represent?
Holes that are filled with a second type of atom, aside from the other type of atom that make up the host lattice.
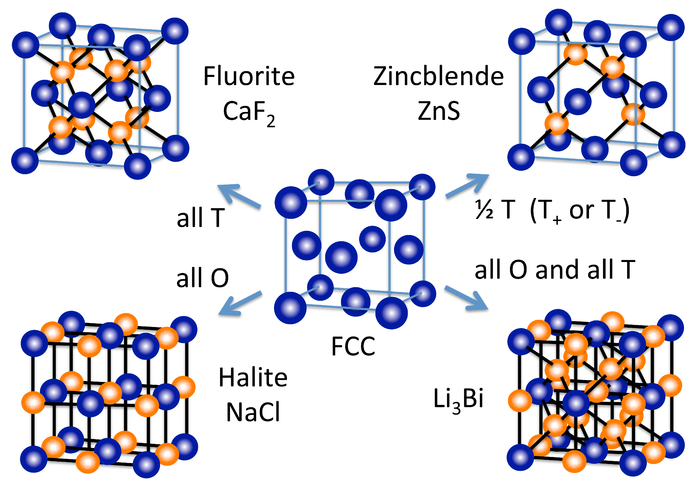
Therefore, what are the two types of holes in close-packed structures?
Octahedral and tetrahedral.
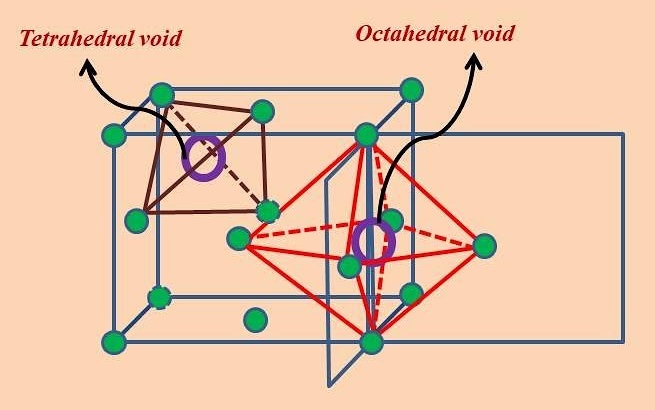
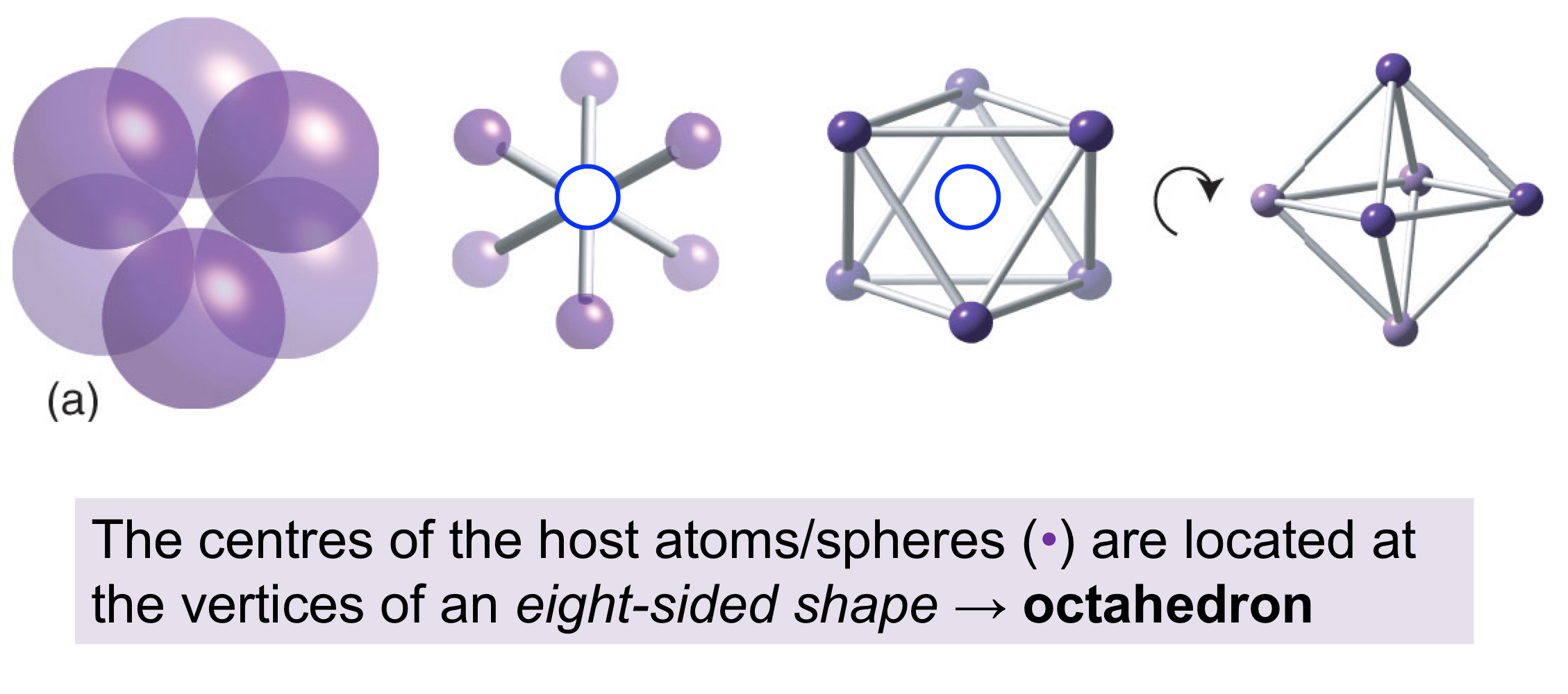
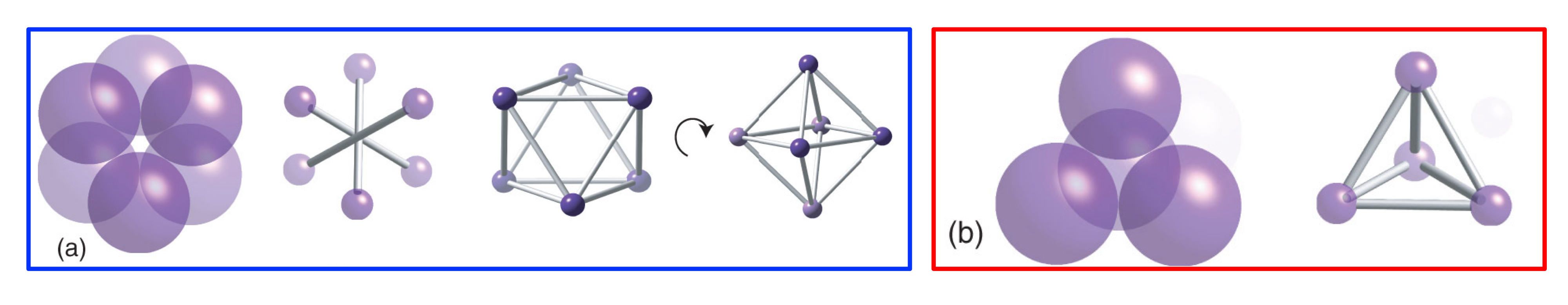
How is an octahedral hole formed?
An arrangement of close-packed spheres with spheres positioned on the top in “non-centre holes,” leaving a hole in the centre, with octahedral geometry and a coordination number of six.
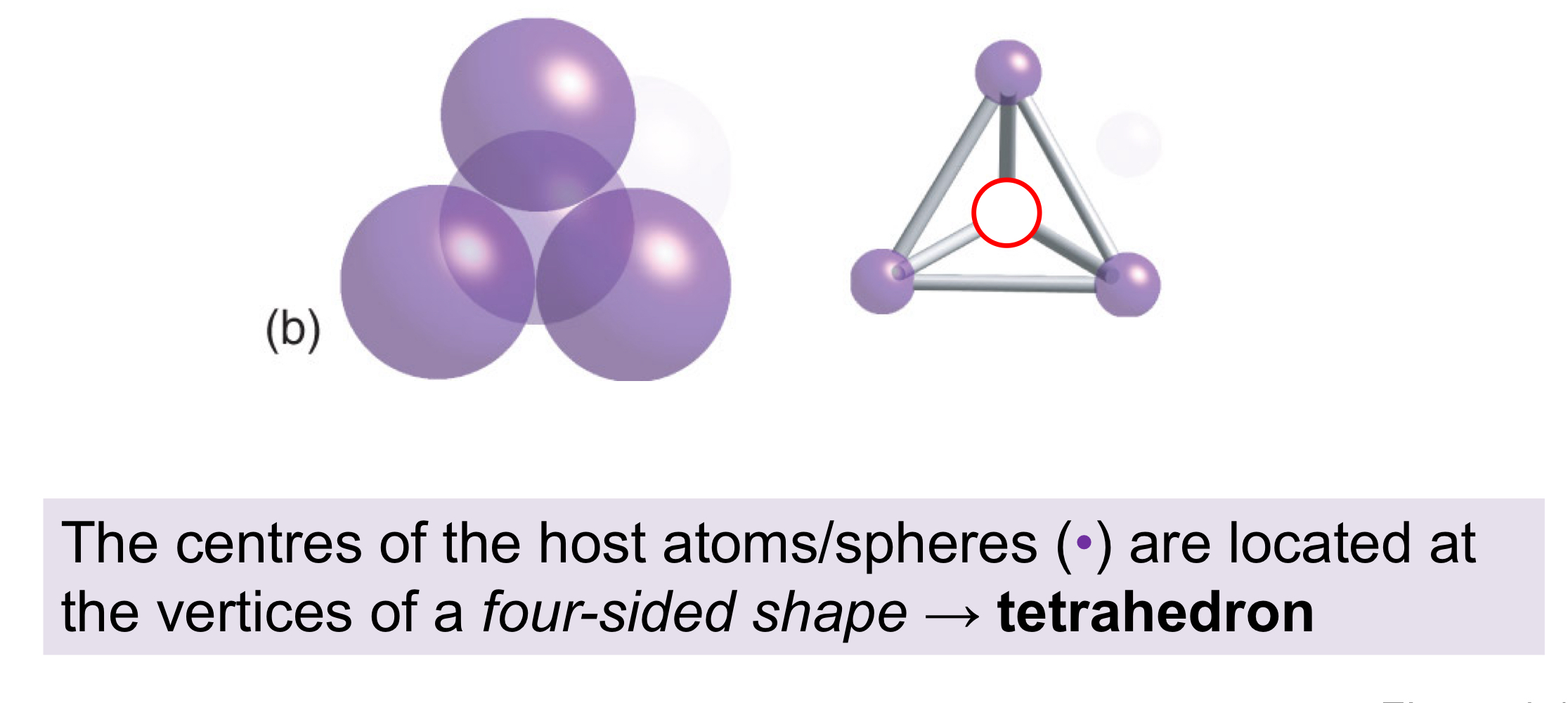
How is an tetrahedral hole formed?
An arrangement of close-packed spheres with a sphere positioned on the top in the "centre” hole, leaving a hole in the centre, with tetrahedral geometry and a coordination number of four.
In a close-packed structure, how many octahedral holes are there, and what is the radius of each octahedral hole?
For every (n) host sphere, there will be (n) octahedral holes, each with a rOh hole of 0.414 x rhost sphere.
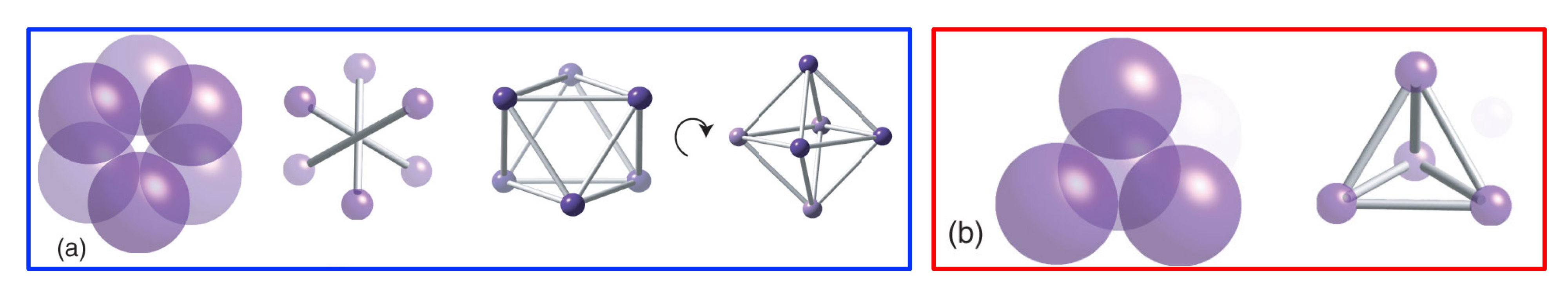
In a close-packed structure, how many tetrahedral holes are there, and what is the radius of each octahedral hole?
For every (n) host sphere, there will be (2 x n) tetrahedral holes, each with a rTd hole of 0.225 x rhost sphere.
Where two types of spheres with different radii pack together in a crystalline solid, e.g. cations and anions, what forms the close-packed array, and what occupies the holes?
The larger spheres, usually the anions, form the close-packed array, while the smaller spheres, usually the cations, occupy the holes.
Alloy
Combination of metallic elements, producing metallic solid.
Substitutional alloy
A solid solution in which one metal atom replaces another in its crystal lattice.
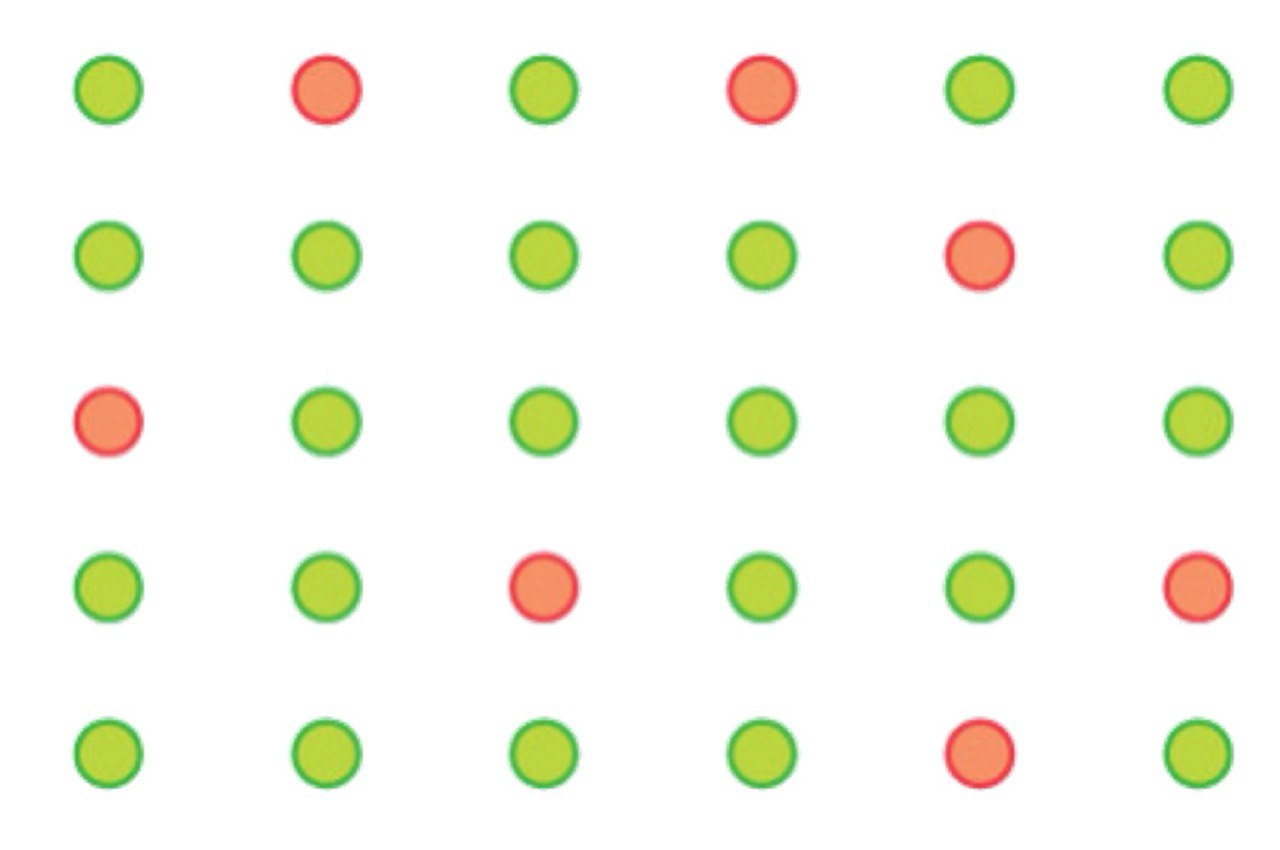

What are the three criteria of substitutional alloys?
Atomic radii of elements are within 15% of each other.
The pure metals of each substance usually adopt the same crystal structure.
The components of solid solution should have similar electronegativity, otherwise electron transfer will occur.
Interstitial alloy
A solid solution in which metal atoms are placed in the holes or interstices of a crystal lattice.
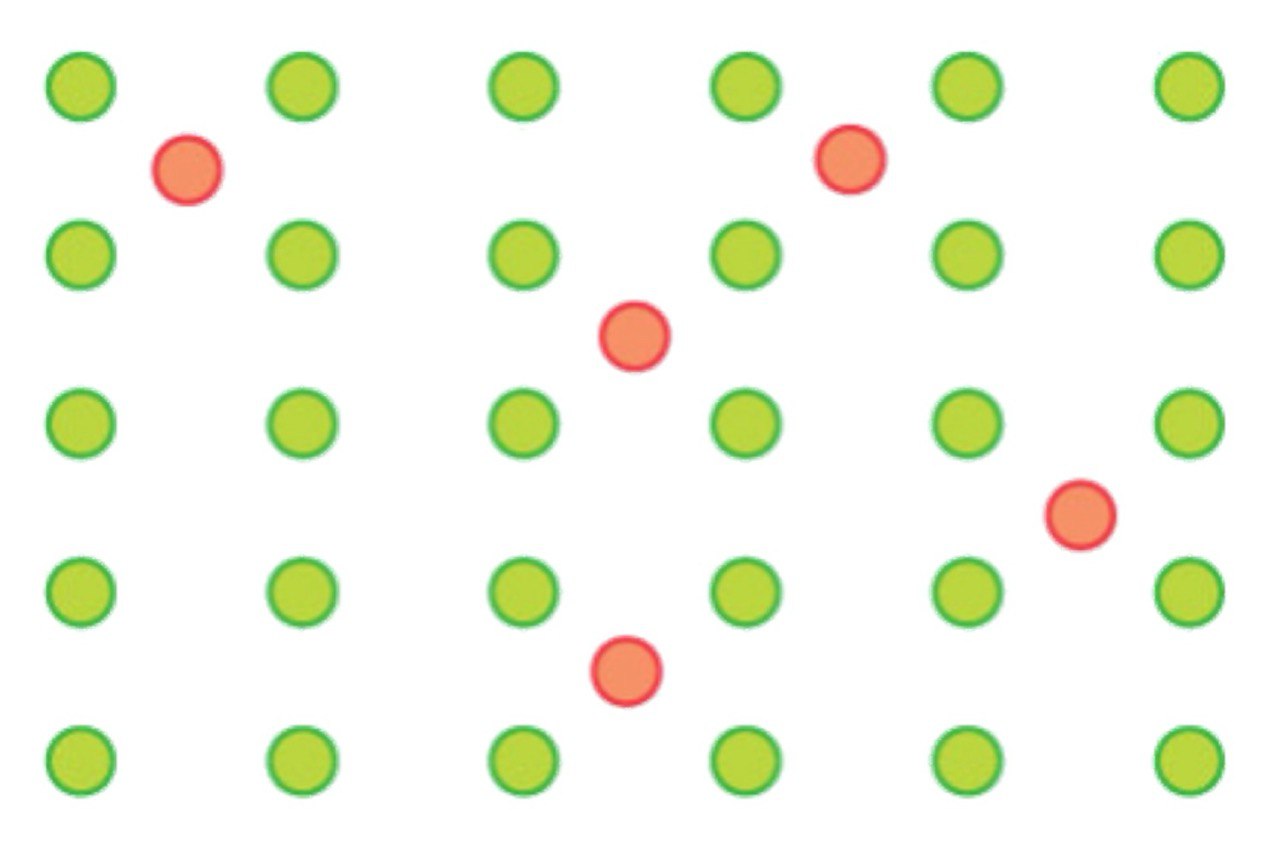
What are the two criteria of interstitial alloys?
Small atoms can enter holes without destroying the host structure.
No electron transfer.
Intermetallic alloys
A solid solution with the presence of a regular arrangement of interstitial atoms, leading to entirely new structures unrelated to parent structures.
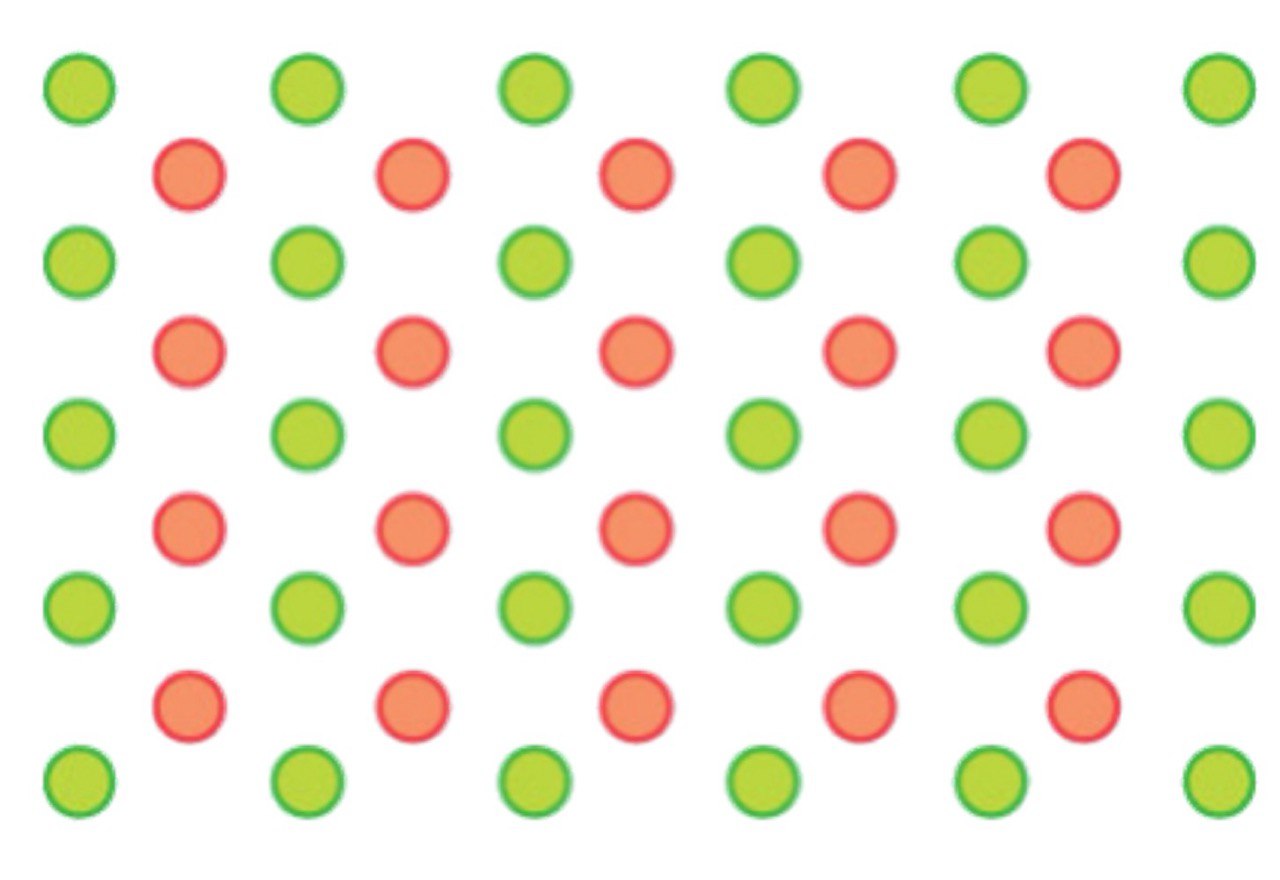
Compounds usually adopt _____ ______ that can be understood in terms of ____ _____ _____ of larger ions with smaller ions filling the _____.
Compounds usually adopt crystal structures that can be understood in terms of close-packed lattices of larger ions with smaller ions filling the holes.
rionic ______ with increasing coordination number.
rionic increases with increasing coordination number.
What does the radius ratio (γ) describe?
Range of ratios of ion sizes a given coordination number can support before the surrounding ions get too close and repel each other.
Per atom in a close packed lattice, how many octahedral holes are there? How many tetrahedral holes are there?
1 atom gives 1 octahedral hole and 2 tetrahedral holes.