Neurons/Parts Of A Neuron
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
Dendrite
the bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
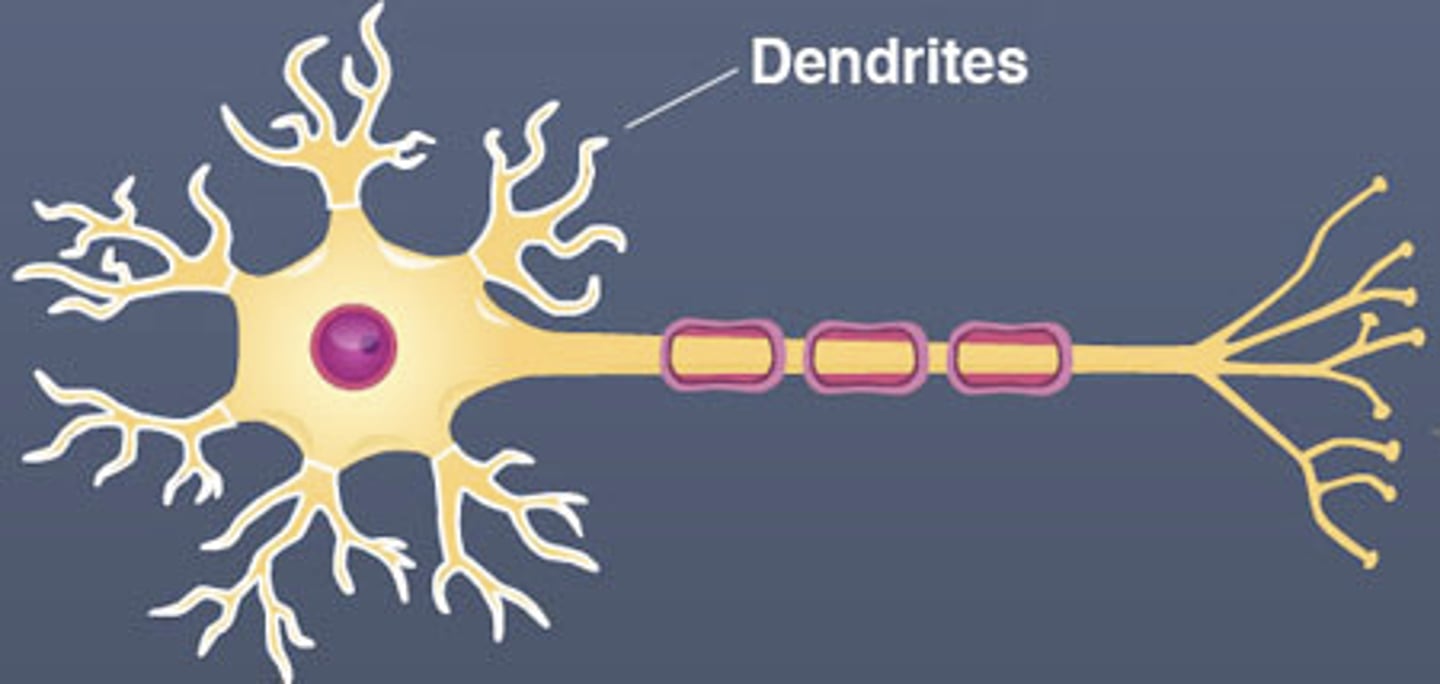
Axon
the extension of a neuron ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons
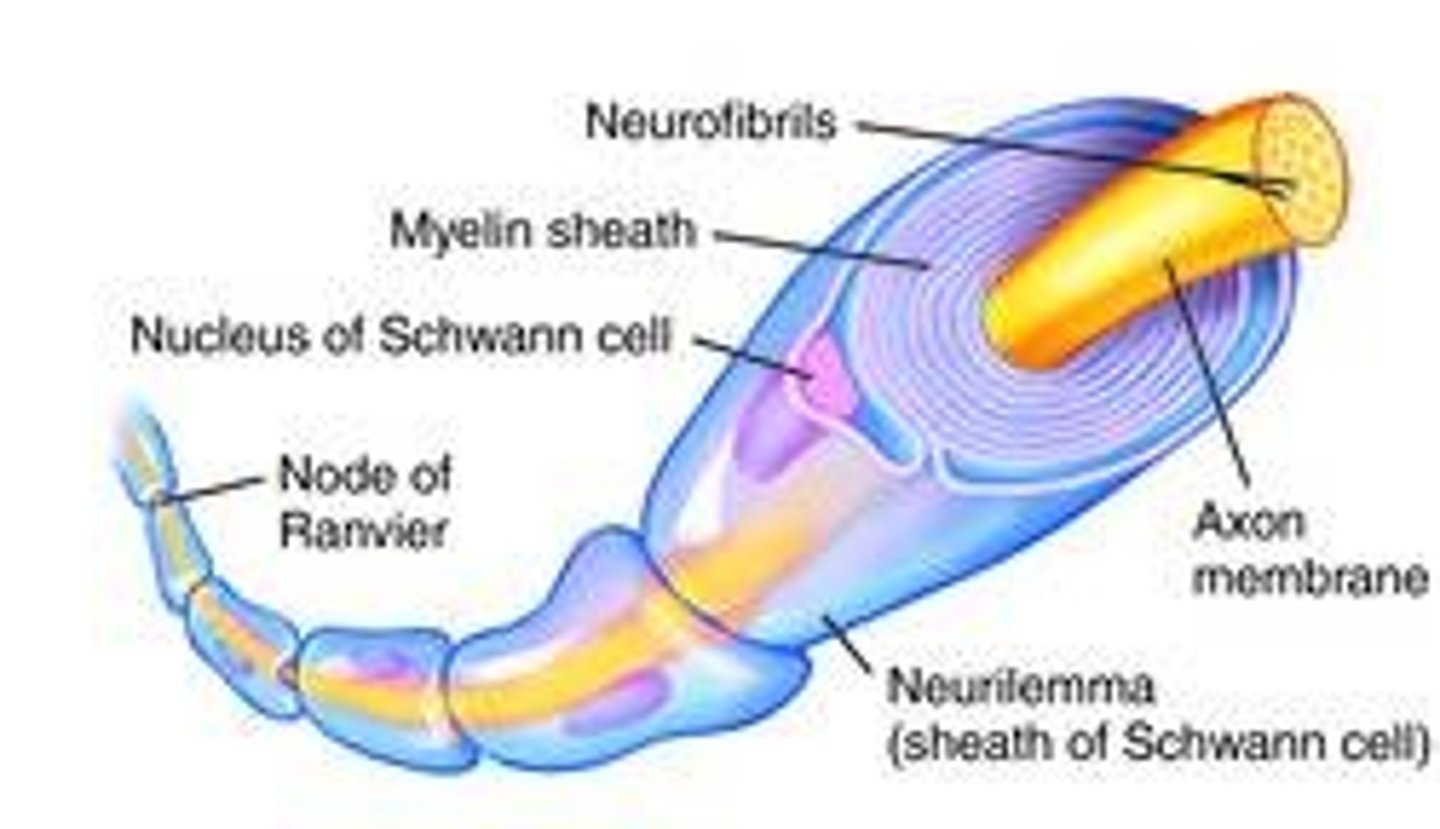
Myelin Sheath
a layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses
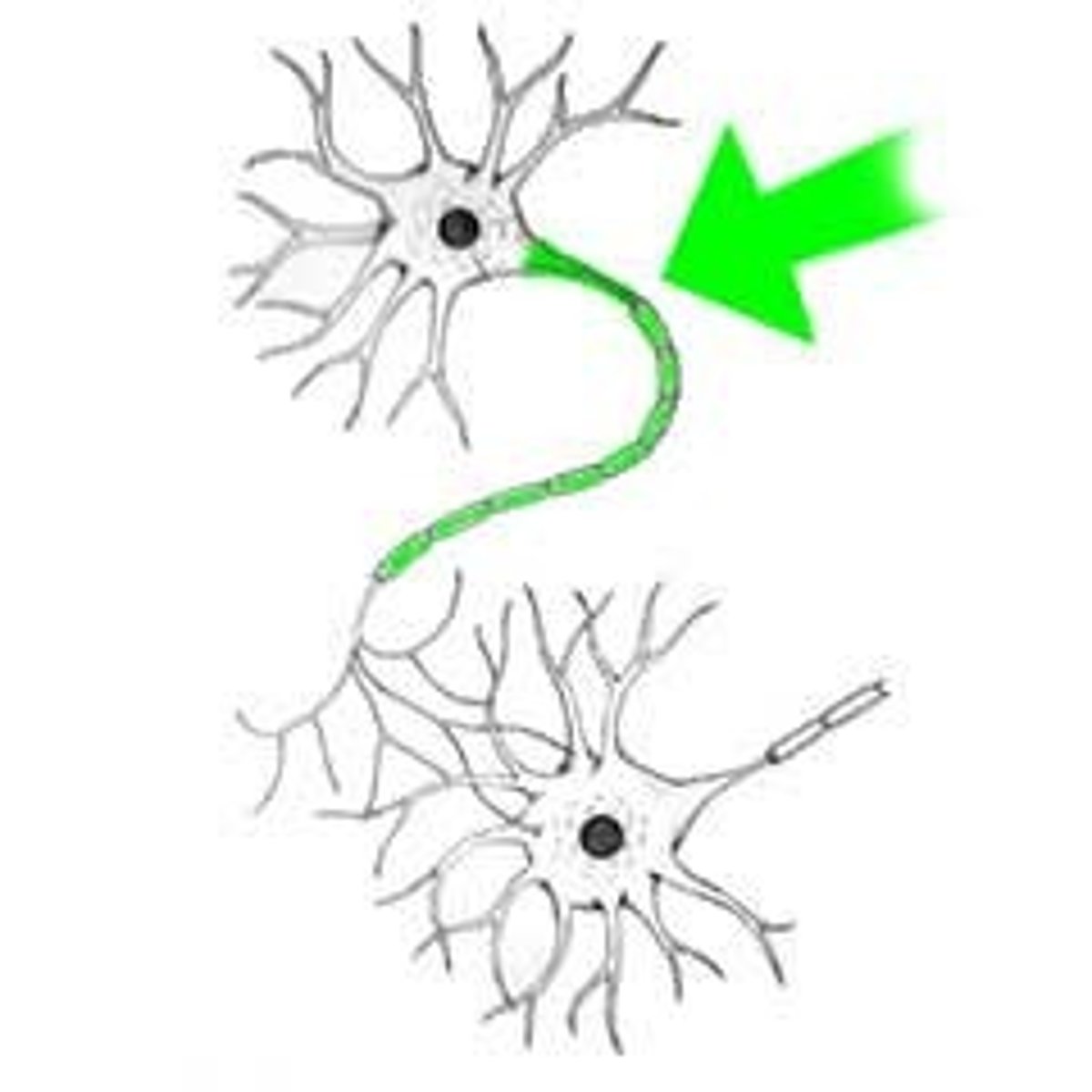
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that reverse the synaptic gaps between the neurons. when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse
Types Of Neurotransmitters
1. Acetylcholine
2. Dopamine
3. Serotonin
4. Norepinephrine
5. GABA
6. Glutamate
Soma
the cell body responsible for maintaining the life of the cell
sensory neurons
neurons that receive information from the external world and convey this information to the brain via the spinal cord
motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
Interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory neurons and motor neurons
Nodes
gaps in the myelin sheath that expose parts of the axon. Allows impulses to travel faster down the axon