macro Final Exam Ch 15
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
The Federal Reserve was originally created to prevent _____ _____.
bank runs
Since WWII the Fed has carried out active _______ ______.
monetary policy
What is monetary policy?
The actions the Federal Reserve takes to manage the money supply and interest rates to pursue macroeconomic policy objectives
The Fed has four monetary policy goals:
Price stability
High employment
Money market stability
Economic growth
After WWII Congress passed the the Employment Act of 1946
to promote maximum employment, production, and purchasing power.
Price stability and high employment are often referred to as a
dual mandate
The Fed has three monetary policy tools at its disposal:
Open market operations
Discount policy
Reserve requirements
Open market operations, discount policy, and reserve requirements are three tools in which:
The Fed tries to keep both the unemployment and inflation rates low
Monetary policy targets:
The money supply
The interest rate
Higher interest rates result in:
A lower quantity of money demanded
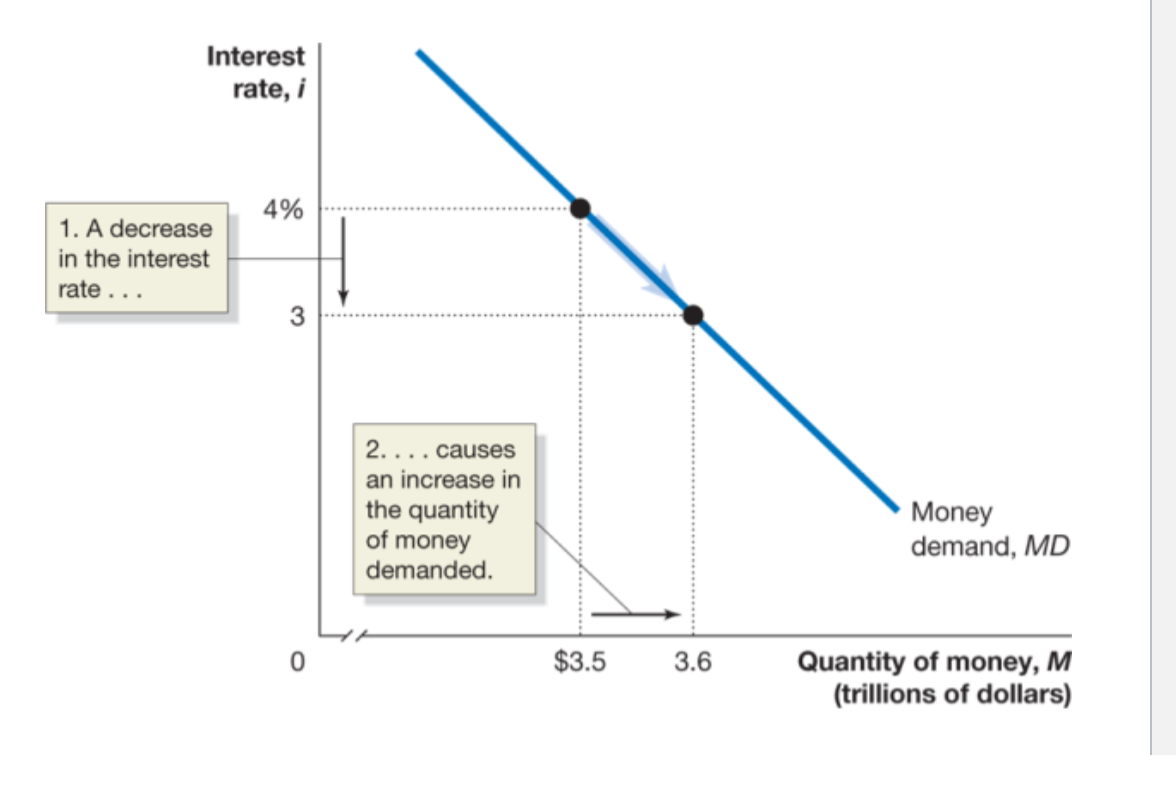
A decrease in the interest rate causes an increase in the quantity of money demanded
Why is it that higher interest rates result in a lower quantity of money demanded?
When the interest rate is high, alternatives to holding money begin to look attractive-like U.S. treasure bills
What causes the money demand curve to shift?
A change in the need to hold money, to engage in transactions.
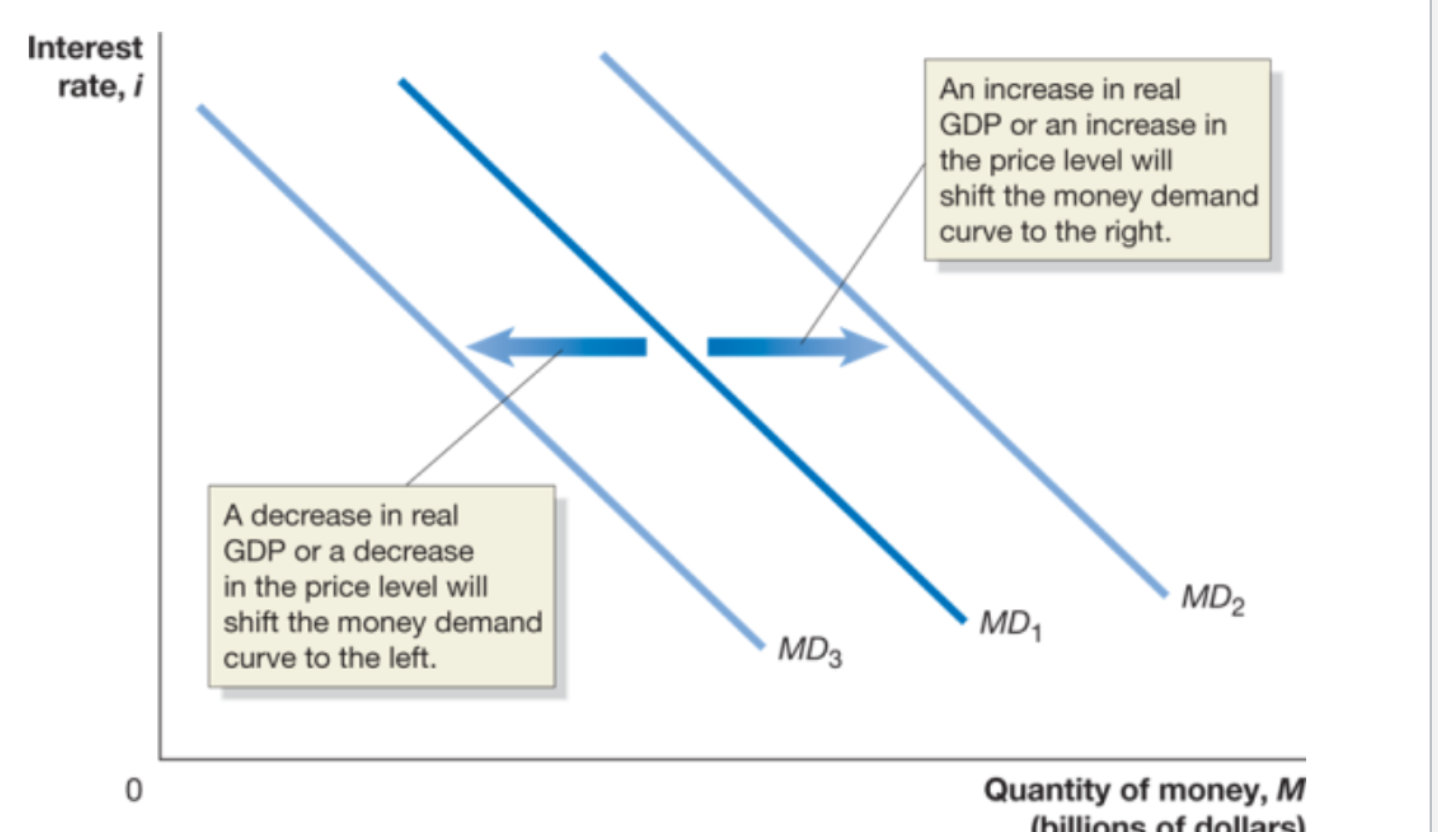
A decrease in real GDP or in price level will shift the money demand curve to the left
An increase in real GDP or an increase in the price level will shift the demand curve to the right
Decreases in real GDP or the price level decrease
money demand
To increase the money supply, the Fed:
buys treasury securities
To decrease the money supply, the Fed:
sells treasury securities
The money supply curve is what type of line?
A vertical line
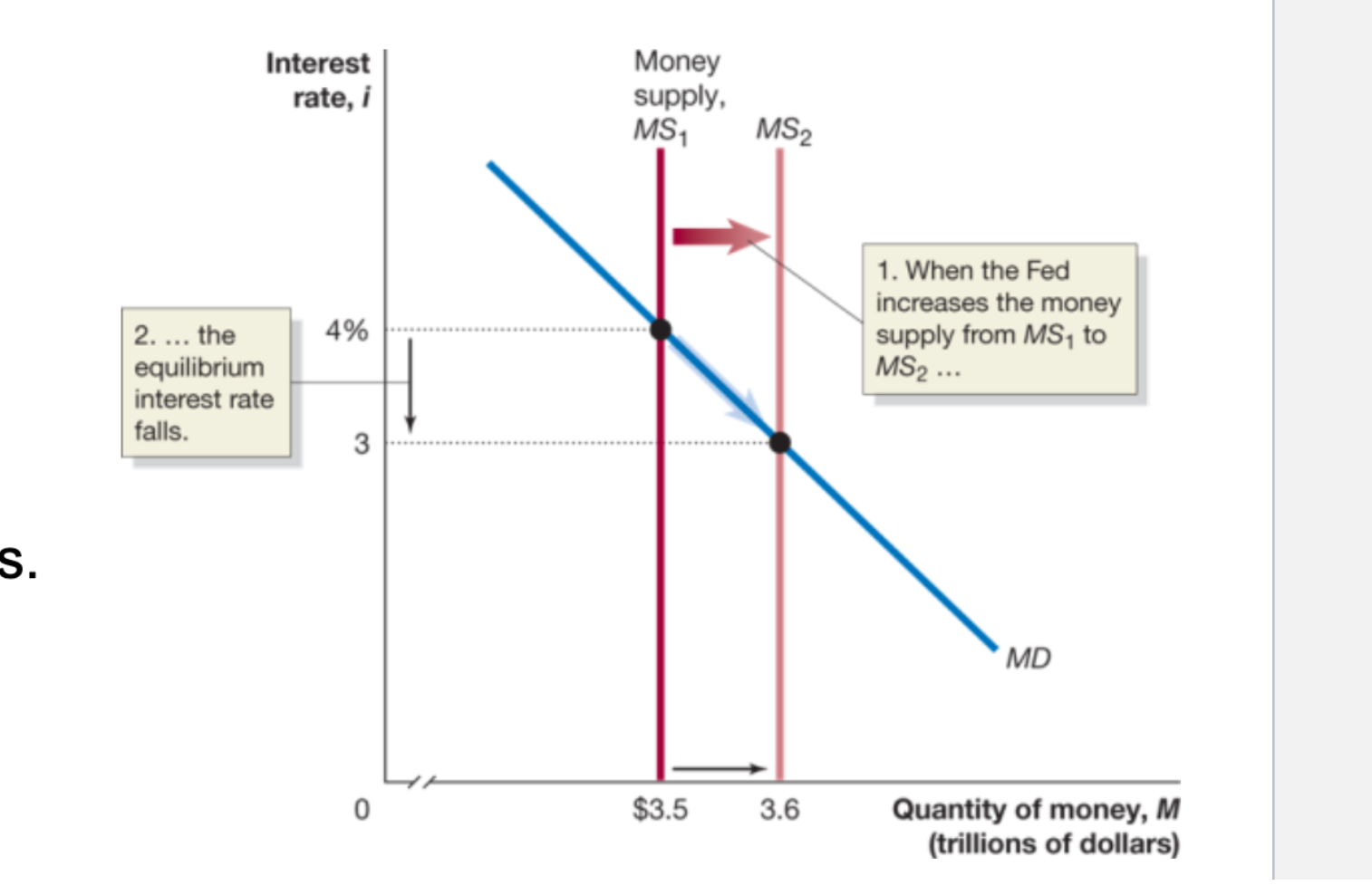
When the Fed increases the money supply from MS1 to MS2:
The equilibrium interest rate falls
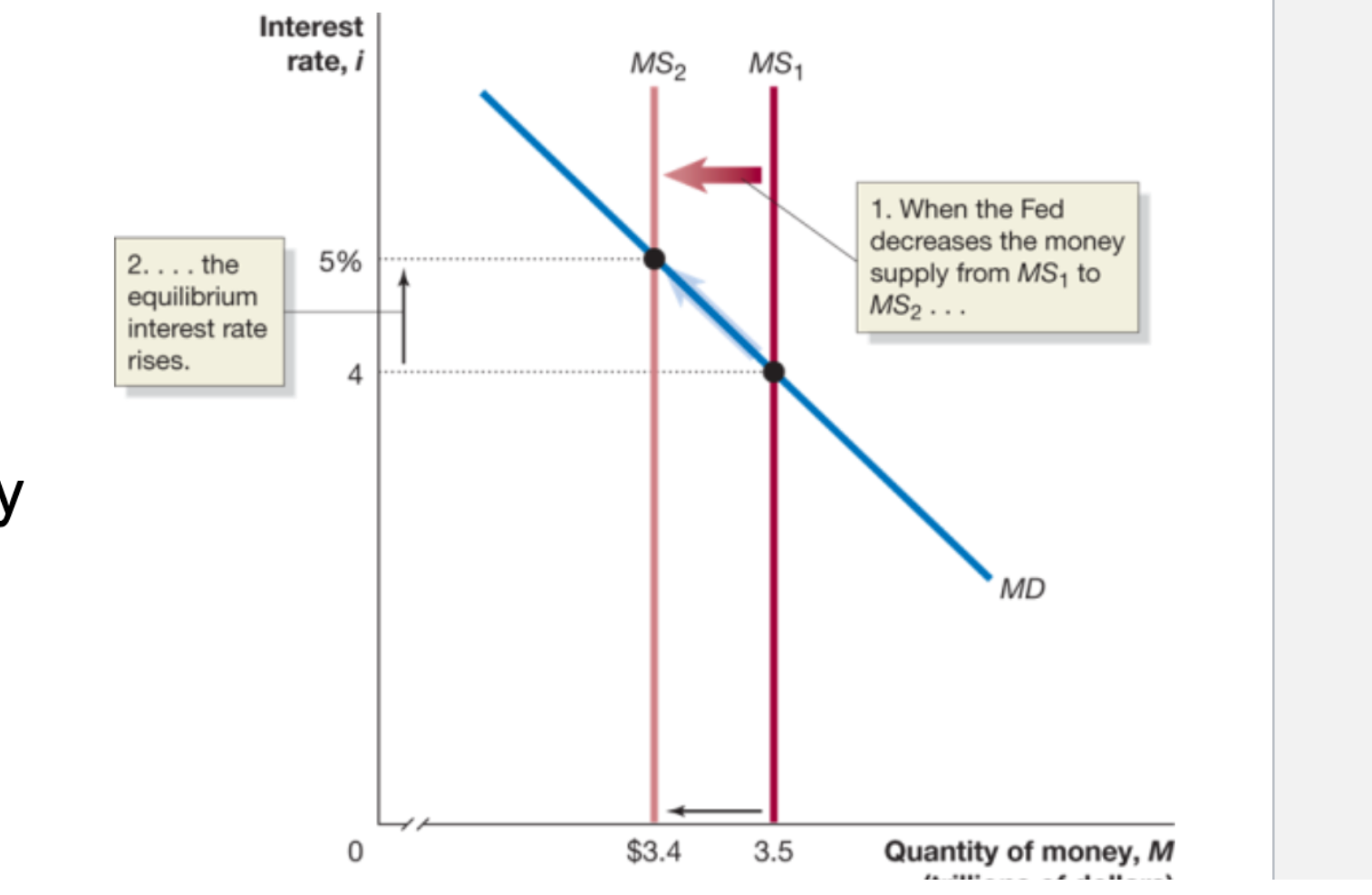
When the Fed decreases the money supply from M2 to M1:
The equilibrium interest rate rises
The money market model:
Concerned with short-term ate of interest
Most relevant for the Fed
1968 through late 1982 is called what?
The Great Inflation is what its called!
Most of the 1950s and 1960s the inflation rate
was 4 percent or less
When _______ became chair of the Federal Reserve’s Board of Governors in August 1979, he emphasized fighting inflation.
Paul Volcker
In addition to price stability, ______ (or a low rate of unemployment) is an important monetary policy goal.
high employment
What did congress do in 1946?
They passed the Employment Act of 1946
The main way that the Fed can influence aggregate demand is through its ability to affect _______.
interest rates.
The interest rates that have the most effect on aggregate demand are _________, corporate bonds, and U.S. Treasury bonds.
the real interest rates on mortgage loans
The interest rates that have the most effect on aggregate demand are the real interest rates on mortgage loans, __________, and U.S. Treasury bonds.
corporate bonds
The interest rates that have the most effect on aggregate demand are the real interest rates on mortgage loans, corporate bonds, and U.S. ______.
Treasury bonds
What are the most important interest rates on aggregate demand in this chapter?
There are three!
Real interest rates on mortgage loans
Corporate bonds
Treasury bonds
During times when banks need additional reserves, they borrow in the _________ market from other banks or from certain other nonbank financial firms.
federal funds
What is the federal funds rate?
The interest rate banks charge each other in the federal funds market
When the Fed wants to implement an expansionary monetary policy in order to increase the growth of aggregate demand, real GDP, and employment, it ______ its target for the federal funds rate.
lowers
When the Fed wants to implement a contractionary monetary policy in order to decrease the growth of aggregate demand to reduce the inflation rate, it ______ its target for the federal funds rate.
raises
What does the Fed actually not do?
The Fed does NOT set tge federal funds rate
So, as the federal funds rate increases, the .
quantity of reserves demanded declines.
The discount rate puts a _____ on the federal funds rate.
ceiling
To expand aggregate demand when facing a zero lower bound, the Fed has relied on _________ and forward guidance.
quantitative easing
To expand aggregate demand when facing a zero lower bound, the Fed has relied on quantitative easing and _________.
forward guidance.
Quantitative easing
increasing aggregate demand by buying long-term securities, such as 10-year treasury notes.
Clearly, policymakers at the Fed believe that quantitative easing is an effective policy when facing a _______ for the federal funds rate because, having first used it in 2008, they returned to using the program in 2020.
zero lower bound
_______ refers to statements by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) about how it will conduct monetary policy in the future.
Forward guidance
The Fed’s two most important monetary policy tools are interest rates on reserve balances (IORB) and _____.
The interest rate on overnight reverse repurchase agreements
The Two Tools the Fed Uses When Faced with a Zero Lower Bound
Quantitative reasoning
Forward guidance
The Fed’s Three Traditional Tools
Open market operations (buying and selling treasury securities)
Discount rate
Reserve requirements
The Fed's two most important monetary policy tools are
the interest rate it pays banks on their reserve balances and the interest rate on overnight reverse repurchase agreements
Interactions among households and firms determine real GDP and the price level
NOT the Fed
The Fed attempts to achieve its goals through
Policy Tools
Policy Instrument (federal funds rate)
Intermediate target
The Fed needs to carry out a contractionary monetary policy by
increasing interest rates.
The Fed implements an expansionary monetary policy of
decreasing interest rates
Why would the Fed intentionally use contractionary monetary policy to reduce real GDP?
The Fed intends to reduce inflation, which occurs if real GDP is greater than potential GDP.
The late _______________ famously described the monetary policy lags as “long and variable,” meaning that it can take months or years for changes in monetary policy to affect real GDP and inflation and that the lags vary based on economic circumstances.
Nobel Laureate Milton Friedman
If the Fed is too slow to react to a recession and applies an expansionary monetary policy only after the economy begins to recover, then
inflation will be higher than if the Fed had not acted.
Investment banks can be subject to liquidity problems because
they often borrow short term, sometimes as short as overnight, and invest the funds in longer-term investments
Which of the following best explains how the Federal Reserve acts to help prevent banking panics?
The Fed acts as a lender of last resort, making loans to banks so that they can pay off depositors
An increase in interest rates affects aggregate demand by
shifting the aggregate demand curve to the left, reducing real GDP and lowering the price level.
As the interest rate increases,
consumption, investment, and net exports decrease; aggregate demand decreases.
Why is the Fed unable to entirely eliminate recessions?
Monetary policy has long and variable lags and thus cannot fine-tune the economy in a way that would completely eliminate recessions.
Yes, it is surprising that the Bank of Japan was following a doveish monetary policy, since with high inflation, one would expect
the Bank of Japan to be hawkish and significantly raise interest rates
A "doveish" monetary policy is a
A "doveish" monetary policy is a policy that reduces interest rates or increases rates slowly.
Increasing the federal funds interest rate
is contractionary policy
If the economy moves into recession, monetarists argue that the Fed should
keep the money supply growing at a constant rate
Monetarism, or targetting the money supply is:
no longer used in macroeconomic theory
Nominal interest rate
The stated interest rate on a loan
Real interest rate
The nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate
With a negative interest rate
a borrower pays lender back with less than the amount borrowed
What is the Taylor Rule?
What is the Taylor Rule?
A formula developed by John Taylor that links the Federal Reserve's target for the federal funds rate to key economic variables.
What does the Taylor Rule start with?
It starts with an estimate of the equilibrium real federal funds rate—adjusted for inflation—where real GDP equals potential GDP in the long run.
What value does Taylor assign to the equilibrium real federal funds rate?
2 percent.
What are the four components used in the Taylor Rule to set the target federal funds rate?
The current inflation rate
The equilibrium real federal funds rate
The inflation gap (current inflation – target inflation)
The output gap (percentage difference between real GDP and potential GDP)
What is the inflation gap in the Taylor Rule?
The difference between the current inflation rate and the Fed’s target inflation rate.
What is inflation targeting?
A monetary policy strategy where a central bank publicly sets a specific inflation rate target and is judged based on its success in achieving that target.
A monetary policy strategy where a central bank publicly sets a specific inflation rate target and is judged based on its success in achieving that target.
inflation targeting
Why is inflation targeting useful?
It provides a clear framework for monetary policy and increases transparency and accountability.
Does inflation targeting mean the Fed can't respond to recessions?
No, inflation targeting is flexible—it allows the Fed to respond to recessions and other problems, especially during severe downturns.
What does inflation targeting mainly focus on outside of recessions?
It focuses on inflation levels and inflation forecasts to guide monetary policy decisions.
Why do most economists support inflation targeting in the long run?
Because monetary policy affects inflation more than it affects real GDP growth over the long term.
How does inflation targeting influence expectations?
It anchors inflationary expectations by signaling that inflation will return to the 2% target even if it temporarily rises or falls.
How does inflation targeting promote accountability?
It gives the public and government a clear standard to measure the Fed’s performance against.
When the central bank commits to conducting policy in a manner that achieves the goal of holding inflation to a publicly announced level, it is using
They. use inflation targeting
As we have seen, the Fed’s traditional response to a recession is to
ower the target for the federal funds rate.
By December 2008, the Fed had effectively lowered the target for the federal funds rate to zero, but the zero interest rate alone did not result in a sufficient increase in aggregate demand to end the recession.
As we’ve seen, economists refer to this situation as the zero lower bound problem.
There are two main explanations for bubbles:
An investor may be caught up in the enthusiasm of the moment and, by failing to gather sufficient information, may overestimate the true value of the stocks.
An investor may expect to profit from buying stocks at inflated prices if the investor can sell them at even higher prices before the bubble bursts.
Bubble explanations simplified
Unrealistic enthusiasm
Expected profit before bubble bursts
If prices of single-family homes rise significantly relative to rents for single-family homes,
it is likely that the housing market is experiencing a bubble.
How did the mortgage market work before the 1970s?
Banks and savings & loans kept mortgages on their books until borrowers fully paid them off.
Why were Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac important to the housing market?
They enabled banks to make more loans and helped expand access to home ownership by reducing risk in mortgage investments.
What role do Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac play in the mortgage market?
They buy mortgages from banks and help create a liquid secondary market, reducing risk for investors.
How did Congress address investor fears of mortgage default?
By using government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs) like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to stand between investors and lenders.
What was the main barrier to creating a secondary mortgage market?
Investors were hesitant to buy mortgages due to the risk of borrower default.
How does a secondary mortgage market help banks make more loans?
Banks can sell existing mortgages to investors and use the money received to issue new mortgages.
ACTION
The Treasury moved to have the federal government take control of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. Although the federal government sponsored Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, they were actually private businesses. The firms were placed under the supervision of the Federal Housing Finance Agency.
GOAL
Avoid further devastating a weak housing market. The Treasury believed that the bankruptcy of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac would have caused a collapse in confidence in mortgage-backed securities.
ACTION:
The Fed and the Treasury helped JPMorgan Chase acquire the investment bank Bear Stearns, which was close to failing.
GOAL:
Avoid a financial panic that the Fed and the Treasury believed would result from the failure of Bear Stearns. Its failure might have caused many investors and financial firms to stop making loans to other investment banks.
ACTION
March 2008
The Fed announced that it would loan up to $200 billion of Treasury securities in exchange for mortgage-backed securities.
GOAL
Make it possible for primary dealers that owned mortgage-backed securities that were difficult or impossible to sell to have access to Treasury securities that they could use as collateral for short-term loans.
oof
oof
Which of the following is a monetary policy response to the economic recession of 2007–2009 and the accompanying financial crisis
The Fed provided loans directly to corporations by purchasing commercial paper.
The Fed purchased large amounts of mortgage-backed securities.
The Fed expanded the eligibility for discount loans to firms other than commercial banks.
The Main Street New Loan facility
exposed the Fed to the criticism that it had done more to help large firms and banks than to help small and medium-sized businesses that were struggling to survive the pandemic