BSCI 160 - Hardy-Weinberg Principle: a null model for population genetics
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
How can you tell if evolutionary forces are acting on a population?
If the Hardy-Weinberg Principle is not true
What is the Hardy-Weinberg Principle (1908)
a null model: what happens to allele and genotype frequencies when none of the evolutionary mechanisms are operating and mating is random
What does the Hardy-Weinberg Principle (HWP) allow us to do? (2 things)
identify when evolutionary agents are acting (and/or mating is non-random)
predict allele or genotypic frequencies IF assume no evolutionary agents are acting (and mating is random)
What are the five assumptions of the HWP?
no mutation
no migration (no gene flow)
no natural selection
no genetic drift
random mating
The HWP:
models __________ across whole __________
gametes go into ____ ____, paired at random
matings, population, gene pool
What is the gene pool?
all individuals alleles in a population for given locus (or loci) of interest
What is allele frequency?
proportion of total alleles composed of a particular allele
If 2 alleles are at a locus, A and a, how do we calculate
p = f(A) = ?
q = f(a) = ?
p = f(A) = (#A)/(#A+#a)
q = f(a) = (#a)/(#A+#a)
If genotype is AA, __ A added to the population
If genotype is aa, ___ a added to the population
If genotype is Aa, __ A and __ a added to the population
two, two, one, one
What is p + q?
1
Allele frequencies will ALWAYS sum to
1
What is genotype frequency?
proportion of total number of individuals composed of a particular genotype
f(AA) = ?
f(Aa) = ?
f(aa) = ?
f(AA) = (#AA)/(#total indivs)
f(Aa) = (#Aa)/(#total indivs)
f(aa) = (#aa)/(#total indivs)
Practice Problem:
N = 1000
#AA = 700, #Aa = 200, #aa = 100
What are the genotype and allele frequencies?
f(AA) = 0.7, f(Aa) = 0.2, f(aa) = 0.1
f(A) = 0.8, f(a) = 0.2
Genotype frequencies will ALWAYS sum to
1
What does it mean if p + q does not equal 1
you made a math error
What can you predict if you know allele frequencies?
the genotype frequencies
Given allele frequencies in parental generation:
Allele A1 = p = 0.7
Allele A2 = q = 0.3
Provide the possible genotypes.
A1A1, A1A2, A2A1, A2A2
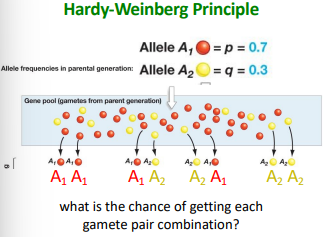
What is the chance of getting each gamete pair combination?
A1A1 = (0.7)(0.7) = 0.49
A1A2 = (0.7)(0.3) = 0.21
A2A1 = (0.3)(0.7) = 0.21
A2A2 = (0.3)(0.3) = 0.09
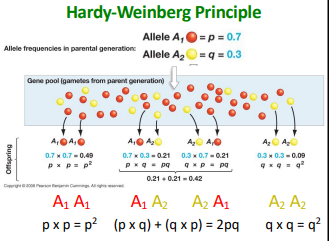
Predicted genotype frequences must equal ___
What is the formula?
one, p²+2pq+q²
The HWE can be extended to more than 2 alleles: true or false?
true
What does it mean if p2+2pq+q2 does not equal 1
math error
Hardy-Weinberg Principle Key Points (2)
the frequencies of genotypes A1A1, A1A2, A2A2 will be p², 2pq, and q² for generation after generation if the population is in “Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
allele frequencies do not change over time unless one of the HWE is violated
(note: non-random mating alone can change genotype frequencies but not allele frequencies)
Why is HWE useful?
helps determine if evolutionary agents are acting - must know actual genotype frequencies
agents are acting if the actual genotypic frequencies are not as expected
can compare observed to expected genotype frequencies
If f(AA) does not equal p² and/or f(Aa) does not equal 2pq and/or f(aa) does not equal q², then one or more evolutionary agents are acting (and/or non-random mating)
Given known allele frequencies, HWE tells us what genotype frequencies we should see if none of the assumptions are violated
helps determine what p and q are and what the genotype frequencies are assuming the population isin HW equilibrium
assuming HW equilibrium: population is not evolving and genotype frequencies are p2, 2pq, and q2
Can determine why there may be excess homozygotes given allele frequencies
Example Problem:
PKU, due to a recessive allele (a)
expressed in 1/10,000, so f(aa) = 1/10000
assuming HWE: what is f(a) = ?
q² = 1/10,000
q = 0.01
p = 1-q
p = 0.99
Can solve for genotypic frequencies with this information
Summary:
Hardy-Weinberg provides a ______________ _____ ______ to test for agents of ___________/____-_________ __________
HWE assumes that none of the ______ evolutionary agents are acting and mating is ________
HWE is useful in two distinct ways -
determine if evolutionary agents are acting (and/or mating is ___-_______), if you know __ and __ and observed __________ _____________
HWE predicts f(AA) = p², f(Aa) = 2pq, f(aa) = q²
calculate __ and __ (and ____________ ______________), if assume HWE
mathematical null model, evolution, non random mating, four, random, non random, p, q, genotype frequencies, p, q, genotypic frequencies