Chapter 4 Smartbook
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Identify the three parts of the cell theory.
Cells are the smallest units
All living organisms are composed of one or more cells
New cells come only from pre-existing cells by cell division
In terms of cell size, the majority of cells are:
too small to be seen with the unaided eye
A magnification tool that enables researchers to study the structure and function of cells is the .
microscope
Resolution is the ability of a microscope to do which of the following?
Accurately distinguish between two separate entites
The ratio between the size of an image of an object produced by a microscope and its actual size is called
Magnification
Which of these statements is not a part of the cell theory?
All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
All cells are replaced.
New cells come only from pre-existing cells by cell division.
Cells are the smallest units of life.
All cells are replaced.
Microscopes can be divided into two main categories based on the source of
Illumination
Most cells are visible to the naked eye.
false
Which of these is an optical instrument that allows researchers to view and study very small objects, such as cellular structures?
Microscope
Compared to a light microscope, the resolution of an electron microscope is about ______ times better.
100
The ability to observe two adjacent objects as distinct from one another, a measure of clarity, is called
resolution
What parameter of an optical instrument refers to its ability to make small objects appear larger?
magnification
What are the two main types of electron microscopy?
transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy
A light microscope utilizes _ for illumination, whereas an electron microscope uses a beam of _
light, electrons
In order to visualize the fine structure of viruses and cytoskeletal filaments at 10–25 nanometers in diameter, the type of microscopy that would be most effective is ______.
transmission electron microscopy
In terms of cell size, the majority of cells are:
too small to be seen with the unaided eye
To produce a detailed image of the three-dimensional surface of a sample, a biologist would use _ _ microscopy
scanning electron
What is the resolution of a very good light microscope?
about 0.2 μm
Resolution is the ability of a microscope to do _
Accurately distinguish between two separate entities
What do prokaryotes lack?
membrane-enclosed nucleus
Two general types of electron microscopy have been developed: electron microscopy and electron microscopy
transmission, scanning
Most bacteria are able to cause disease.
false
Which type of microscopy is used to provide high resolution of a cross-sectional view of a cell?
transmission electron microscopy
What is the phospholipid bilayer barrier between the cell and its external environment called?
plasma membrane
In scanning electron microscopy, the sample is coated with a thin layer of _ _, such as gold or palladium, and is then exposed to an electron beam that scans its surface
heavy metal
The area of the cell that is surrounded by the plasma membrane is called the ______.
cytoplasm
The wavelength of an electron is than visible light. Thus, the resolution of an electron microscope is than that of a light microscope
shorter, better
In bacteria, the genetic material is located in a region of the cytoplasm called the
nucleoid
Prokaryotes differ from eukaryotes because they lack a membrane-enclosed _, which houses the DNA
nucleus
Structures found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that are the sites of polypeptide synthesis are called
ribosomes
The prokaryotes that are abundant throughout the world in soil, water, and the human digestive tract are called _. While also common, the prokaryotes that are typically found in more extreme environments such as hot springs and deep-sea thermal vents are called _.
bacteria, archaea
A phospholipid bilayer that forms a barrier between a cell and its external environment is the plasma _
membrane
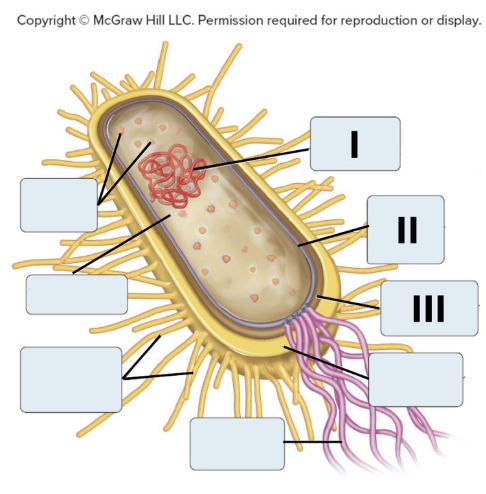
Label the parts of the bacterial cell: I = _, II = _, III = _
Nucleoid, Plasma Membrnae, Cell wall
In a bacterial cell, the region of the cell contained within the plasma membrane is called the
cytoplasm
Nearly all species of archaea and bacteria have rigid _ _ that supports and protects the plasma membrane and cytoplasm.
cell wall
Where is the DNA housed in a bacterial cell?
Nucleoid Region
What structure functions in polypeptide synthesis?
Ribosome
Appendages used by prokaryotic cells to move are called
flagella
Most bacteria are able to cause disease.
False
Aside from bacteria and archaea, all other species are
eukaryotes
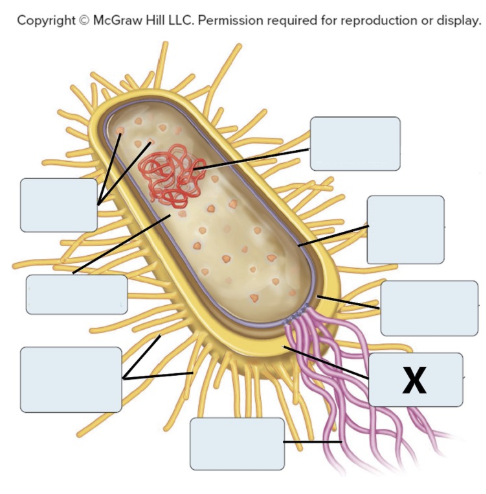
X = _
glycocalyx
Describe the cell walls of most bacteria and archaea
rigid
Where is most of the DNA located in a eukaryotic cell?
Nucleus
In bacteria, the genetic material is located in a region of the cytoplasm called the _
nucleoid
Describe an organelle
A membrane-bound component with its own unique structure and function
What is used by prokaryotes to move?
Flagella
Which of the following organisms are eukaryotes?
Archaea
Plants
Fungi
Animals
Bacteria
Plants, fungi, animals
What cells have membrane-bound organelles to compartmentalize functions?
Eukaryotic cells only
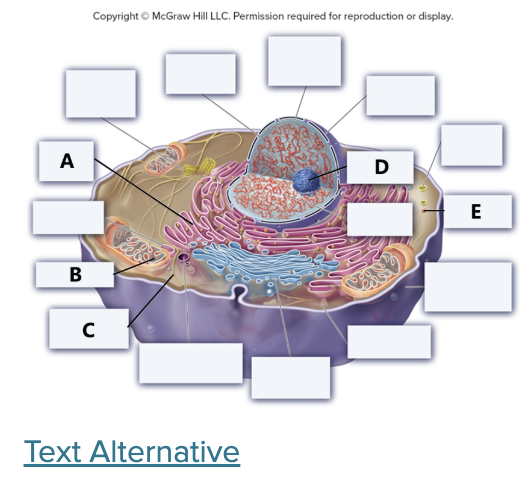
A = Rough ER, B = Mitochondrian, C= Cytoskeleton, D = Nucelolus, E = Ribosome
In eukaryotic cells, most of the DNA is housed in an internal compartment, or organelle, called the _
nucleus
Plant cells and animal cells have similar organelles. However, plants cells have unique structures including chloroplasts, a central _ and a cell _
vacuole, wall
The general term used to describe a membrane-bound structure within a cell that has its own unique structure and function is _
organelle
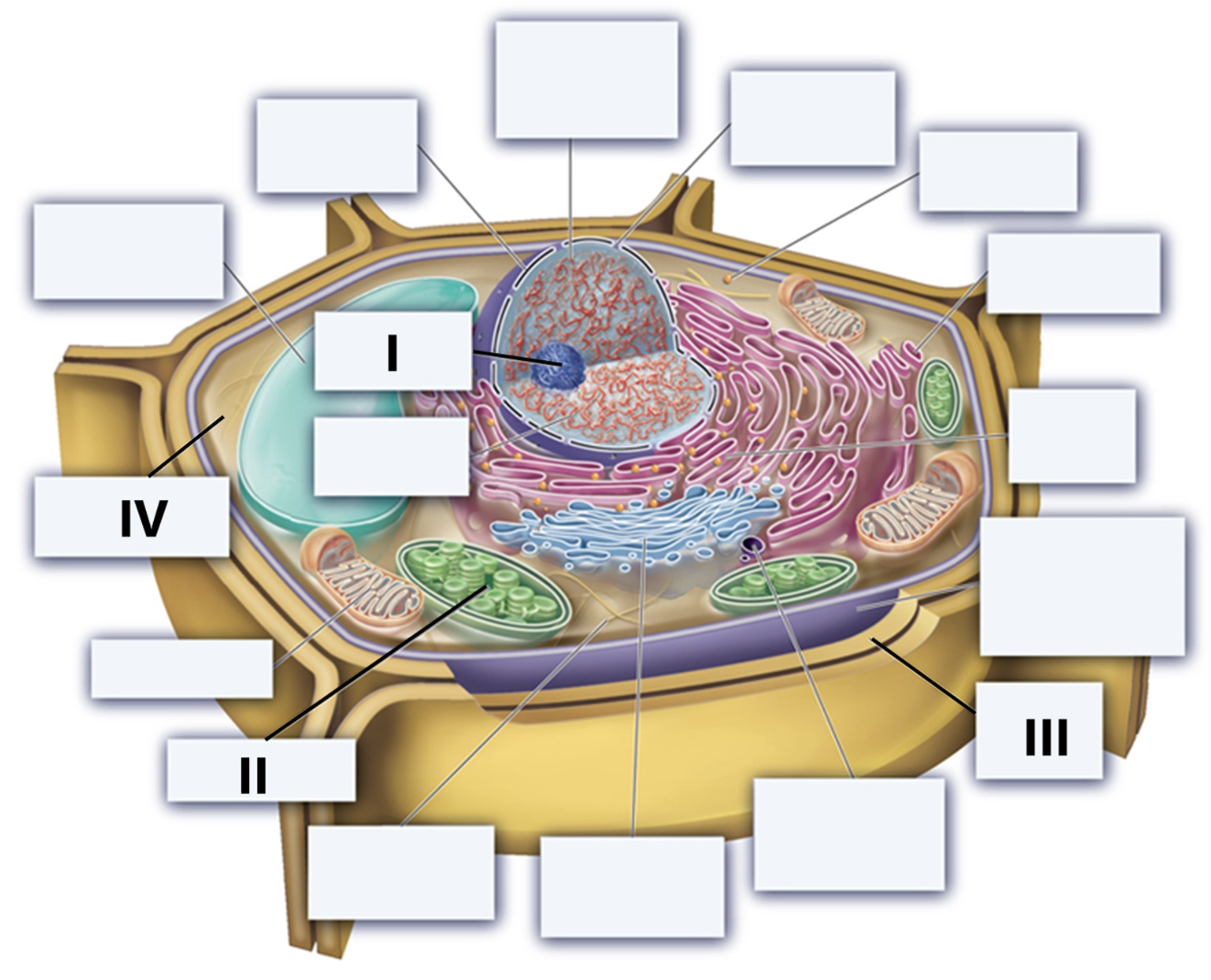
I = Nucleolus, II = Chloroplast, III = Cell Wall, IV = cytosol
Appendages used by prokaryotic cells to move are called __.
flagella
Which of the following is the best reason for cells being small?
Multiple choice question.
The cell membrane can only stretch so much and so cannot accommodate the larger size.
Larger cells would create too much heat and enzymes will denature.
Larger cells would not be able to get necessary gases and nutrients quickly enough.
Larger cells would require more nutrients and there is usually a limited supply.
Larger cells would not be able to get necessary gases and nutrients quickly enough.
Eukaryotic cells have many membrane-bound compartments called _, whereas prokaryotic cells do not exhibit compartmentalization.
organelles
A low surface area-to-volume ratio enables cells to take up nutrients and eliminate wastes efficiently.
False
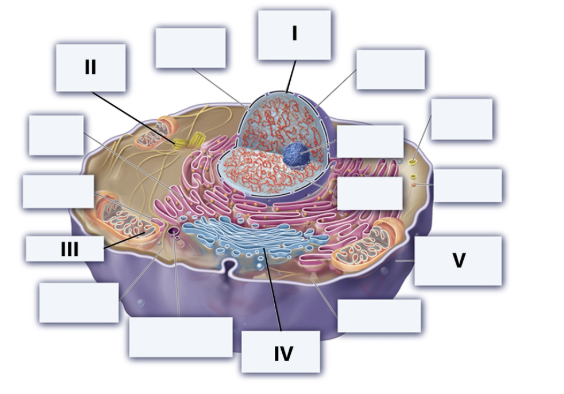
I = Nucleus, II = Centrosome, III = Mitochondrion, IV = Golgi apparatus, V = Plasma membrane
Plant and animal cells have identical internal organelles and structures.
False
As the radius of a cell gets larger, the SA/V ratio _.
gets smaller
What term describes the region of a eukaryotic cell that is outside the membrane-bound organelles but inside the plasma membrane?
Cytosol
The size of a metabolizing cell is limited by:
its surface area-to-volume ratio.
In order to take up nutrients and export wastes efficiently, a cell's surface area-to-volume ratio should be ______.
high
The region that is enclosed by the plasma membrane but outside the organelles is called the _. It is the location of chemical reactions by which cells produce the materials and utilize the energy necessary to sustain life.
cytosol
What type of cell would have the hardest time exporting waste?
large and round
The region of a eukaryotic cell that is outside the membrane-bound organelles but inside the plasma membrane is the
cytosol
Three different types of protein filaments that make up the cytoskeleton.
Microtubules, intermediate filaments, actin filaments
Microtubules are cytoskeletal structures composed of which protein?
Tubulin
Most cells are small because the ability to exchange nutrients and wastes is limited by the surface _ to _ratio.
area, volume
Within the centrosome, there is a pair of structures arranged perpendicular to each other called the
centrioles
The functions of microtubules include ______
moving chromosomes during mitosis and maintaining cell shape and organization
A structure that has a staggered alignment of different proteins such as keratin and lamin and may be found in such places as skin and kidney cells is called a(n) _ filament.
intermediate
As the radius of a cell gets larger, the SA/V ratio Blank______.
gets smaller
Long, hollow, cylindrical structures about 25 nm in diameter and composed of the protein tubulin are called
microtubules
Nondividing animal cells contain a single structure near their nucleus called the _
centrosome
What are the thinnest cytoskeletal filaments (7nm)
Actin filaments
What cytoskeletal filaments are responsible for moving chromosomes during mitosis and for organizing the cell's organelles?
microtubules
The class of proteins that use ATP as a source of energy to promote various types of movements is called
motor
Describe intermediate filaments
Twisted filament that can be composed of keratin or lamin
Cilia and flagella are two types of cell appendages that use which of these to facilitate movement?
Microtubules and motor proteins
Which of the following is NOT part of the endomembrane system?
Endoplasmic reticulum
Mitochondrion
Lysosome
Golgi apparatus
Nuclear envelope
Mitochondrion
Microfilaments is another name for
actin filaments
The nucleus is enclosed by a double membrane structure called the _
Nuclear envelope
The protection and organization of the genetic material of the cell are the primary functions of the _
nucleus
Where does the assembly of ribosome subunits occur?
nucleolus
How many subunits make up a ribosome?
Two: one large and one small
What is the double membrane structure that surrounds the nucleus called?
Nuclear envelope
The membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum form which of the following?
Cisternae, fluid-filled tubules
What are major functions of the nucleus?
Gene regulation and protecting the genome
The ER membrane encloses a single compartment called the ER
lumen
What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Sorting proteins destined for other locations
The smooth ER is _ with the rough ER
continuous
Glycosylation
Process of covalently attaching a carbohydrate to a protein or a lipid
What organelle synthesizes lipids, stores calcium ions, and detoxifies harmful organic molecules?
Smooth ER
What organelle in liver cells produces enzymes that detoxify harmful organic molecules?
Smooth ER
In animals, carbohydrates are stored in _ granules adjacent to the smooth ER membrane in liver cells. These release energy upon demand.
glycogen
Enzymes in the smooth ER are involved in the synthesis and modification of ______.
lipids
What are the functions of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
storage of calcium ions, detoxification of harmful organic molecules, synthesis and modification of lipids
Describe the structure of the golgi apparatus
A stack of flattened membranes, each enclosing a single compartment
Overlapping functions of the golgi apparatus
Protein processing, secretion, sorting