redox
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what is oxidation number
the amount of electrons an atom loses/gains while bonding
what are the rules for oxidation
-pure elements (H₂,O₂)always have an oxidation number of 0
-place the oxidation number before the element
-all the oxidation numbers in a molecule will equal 0
-molecules don’t have an oxidation number unless its a charged molecule
what is oxidation and reduction (oxygen)
oxidation - gain of oxygen
reduction - loss of oxygen
what is oxidation and reduction (electrons)
oxidation - loss of electrons
reduction - gain of electrons
what is oxidation and reduction (oxidation number)
oxidation - increase in oxidation number
reduction - decrease in oxidation number c
common trends for oxidation number
metals - always positive
transition metals can change oxidation number
group 4 elements change a lot
non metals - mostly negative
oxygen - mostly -2
hydrogen - mostly +1
fluorine - always -1
some exceptions in oxidation number
oxygen becomes positive when with fluorine (FlO)
oxygen becomes -1 when in a peroxide (C-O-O-C)
in metal hydrides hydrogen becomes -1
what are spectator ions
ions that remain unchanged in the reaction
Roman numerals
sometimes to show what oxidation number an element has Roman numerals are placed at the end of the name to show the oxidation number
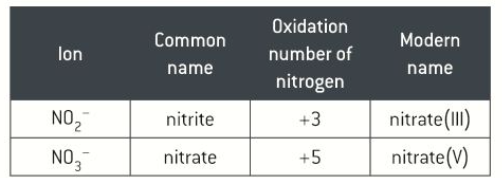
what is a redox reaction
a reaction where a species gets oxidised and another species gets reduced
what is a disproportionation reaction
a reaction where an element undergoes both oxidation and reduction
example of a disproportionation reaction
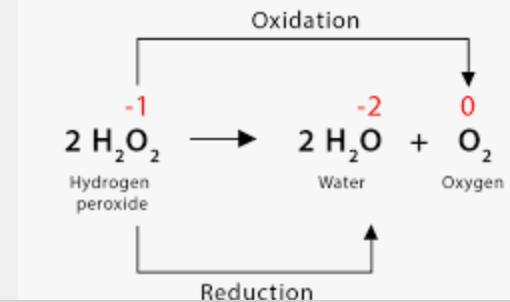
how does redox relate to electronegativity
most of the elements that have a negative oxidation number have a high electronegativity (Fl)
so they are more likely to attract the negative electrons so that’s why they have a negative oxidation number as they gain electrons