OCR Gateway Chemistry: C2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Define Relative Atomic Mass
Its the average mass of an atom of an element compared to 1/12th of the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
Define Relative Formula Mass
Relative formula mass is the total mass of all the atoms in a chemical formula added together. It tells you how heavy a molecule is, measured in atomic mass units (amu) or grams per mole (g/mol).
What is the Mr in a reaction like?
In a reaction the Mr of the reactants = the Mr of the products as the atoms are just rearranged.
Define Empirical formula
The simplest whole number ratio of atoms in a compound.
How do you find empirical formula?
Find mass of each element.
Convert to moles:
Moles = Mass / atomic massDivide by smallest moles to get ratios.
Write the formula using those ratios.
What is the difference between pure and impure substances?
Pure Substances:
Made of only one type of particle.
Same properties (e.g., boiling/melting point).
Impure Substances:
Made of two or more types of particles.
Properties can change (e.g., different boiling/melting points).
What is filtration used for?
To separate a insoluble solute from a solvent e.g. sand from water.
What are the different parts of the filtration system?
includes an inlet for the liquid or gas, a filter to remove particles, a support layer, an outlet for the clean fluid, and a collection chamber for holding the filtered liquid.
Why is it better to use fluted filter paper in filtration?
Fluted filter paper increases the surface area.
What is simple distillation and how does it work?
A method to separate a liquid from a solution based on boiling points.
Heat the Solution
Place the mixture in a flask and heat it.
Evaporation
The liquid with the lower boiling point evaporates first.
Cooling
The vapor travels into a condenser, where it cools down.
Condensation
The vapor turns back into liquid.
Collection
The condensed liquid (distillate) drips into a separate container.
Separation Complete
The remaining liquid in the flask contains impurities.
What is fractional distillation and how does it work?
To separate two or more substances from a mixture in the liquid state.
It uses the different boiling points to do this. e.g. the different components of crude oil.
The substance with the lowest boiling point is condensed first. Each substance separated is called a fraction
What is crystallisation?
To separate a soluble solute from a solvent e.g. salt from salt water.
How does crystillisation work
Pour the solution into an evaporating dish and heat it with a Bunsen burner.
Stop heating when you see crystals starting to form.
Let it cool down.
Either leave it to let more water evaporate or filter out the crystals using filter paper and a funnel.
Dry the crystals in a warm oven.
What is chromatography?
To separate soluble solutes from each other, based on their different solubility in the solvent.
What are the phases of chromatography?
Stationary phase: the part that does not move (e.g. chromatogram paper)
Mobile phase: the part that does move (e.g. water or alcohol)
Rf value: distance the spot moved / distance the solvent moved.
Why should the start line in chromatography be drawn in pencil?
Pencil line drawn so that it doesn't run in the solvent
What are the stationary and mobile phases of thin layer chromatography?
Stationary phase: thin layer of silica or alumina powder spread over a plate of glass or plastic
Mobile phase: solvent
What are the chromatography types?
Paper Chromatography
Thin Layer Chromatography
Gas chromatography
What are the stationary and mobile phases of gas chromatography?
Stationary phase: silica or alumina powder packed
into a metal column
Mobile phase: unreactive carrier gas e.g. N 2
What do metals and non-metals form when reacted with oxygen?
Metals and non metals both react with oxygen to
form an oxide.
How can you tell if an oxide is a metal oxide or non-metal oxide?
If the oxide dissolves in water:
the metal oxide produces an alkaline solution
the non metals oxide produces an acidic solution
What are some properties of metals?
Good conductors of heat and electricity
Malleable: Can be beaten into thin sheets
Ductile: Can be stretched into thin wire
Possesses metallic luster
What are the properties of non-metals?
Poor conductors of heat and electricity
Brittle
Non-ductile
No metallic luster
Solids, liquids or gas at room temperature
Dull
What can the group on the periodic table tell you about an atom?
How many electrons in outer shell
What can the period on the periodic table tell you about an atom?
How many shells there are
How many electrons can each shell hold?
Shell 1: 2
Shell 2: 8
Shell 3: 8
What is an ion?
A charged atom
What is oxidation?
Loss of an electron
What is reduction?
Gain of an electron
Why do atoms lose/gain electrons?
To get a full outer shell
Describe simple covalent bonding
A covalent bond is where two non metal atoms share a pair of electrons, so that they both have a full outer shell.
There is a force of attraction between the nucleus of each bonded atom and the shared electrons.
What is the melting and boiling point of covalently bonded atoms like?
Covalently bonded compounds usually have low melting and boiling points, but this can vary based on intermolecular forces.
What is the covalent bond like?
A covalent bond is strong.
How are covalent bonds shown?
Dot and cross diagrams
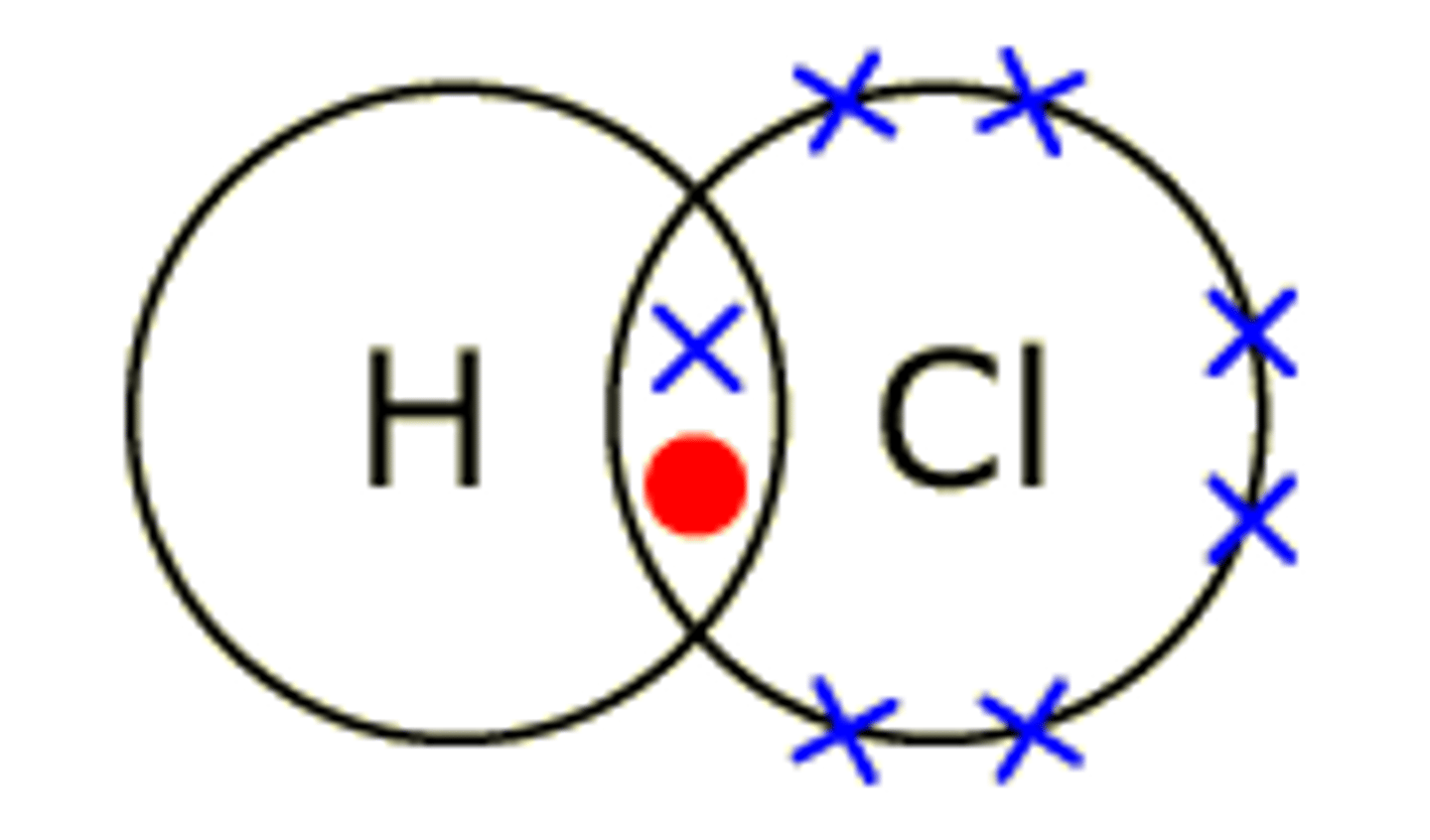
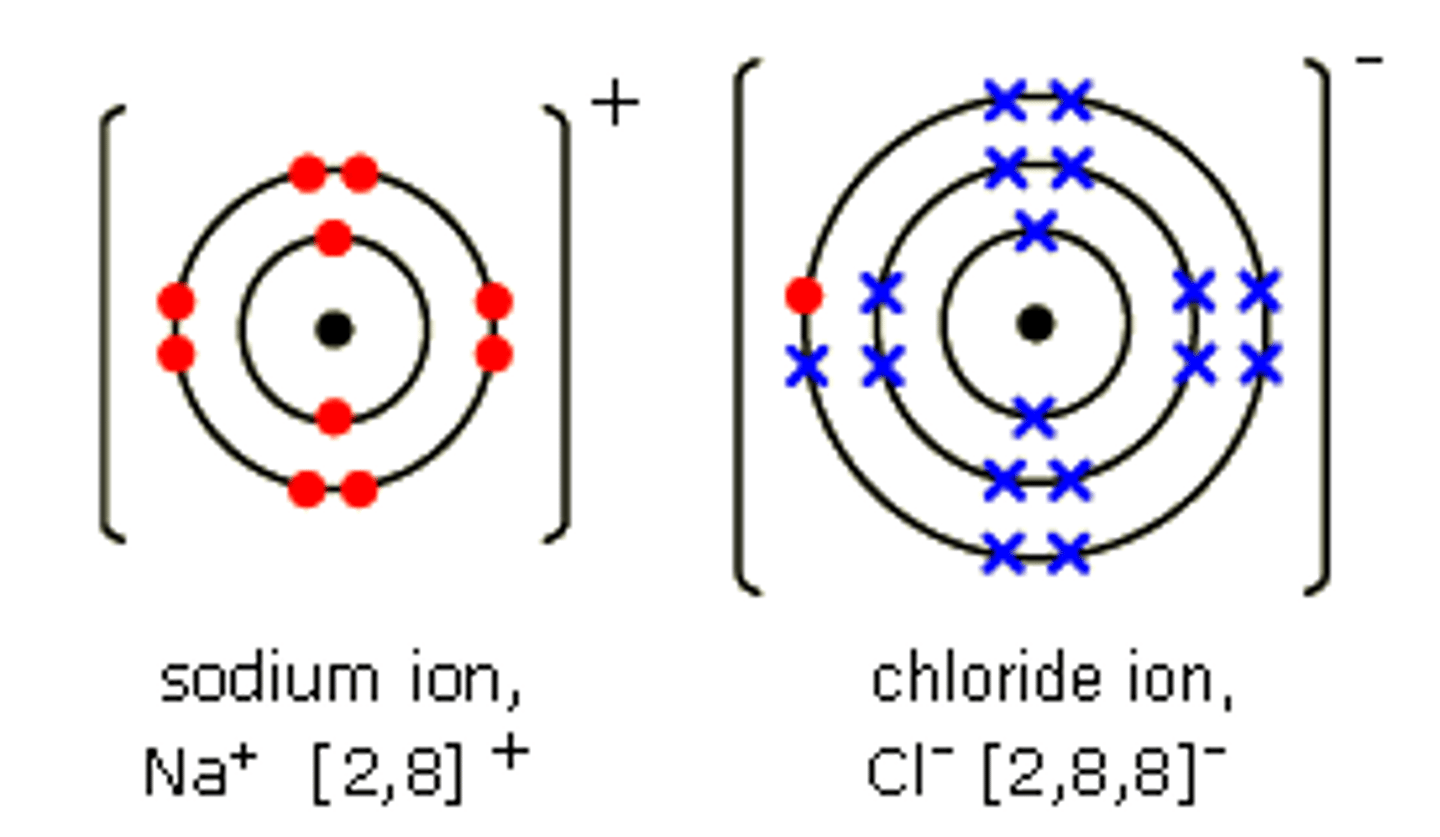
What is ionic bonding?
An ionic bond is a strong electrostatic attraction between
oppositely charged ions.
What happens in ionic bonding?
When a metal reacts with a non metal , electrons are
transferred from the metal atom to the non metal atom so
both achieve more stable electronic structures, with full outer
shells.
What are features of ionic bonding?
Electrons are transferred between atoms.
Forms positive (cations) and negative (anions) ions.
Creates strong attractions between the ions.
Arranges ions in a crystal structure.
Results in high melting and boiling points.
Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted.
How are ionic bonds shown?
Dot and cross diagrams
What is giant covalent bonding?
Many non-metal atoms joined by covalent bonds and
arranged in a repeating regular pattern called a giant
covalent lattice.
What are features of a giant covalent lattice?
They have high melting points and boiling points as there are many strong covalent bonds to break.
The formula for these structures is given as the empirical
formula even though many many atoms make up the lattice.
What are polymers?
Long chains made from many smaller molecules called
monomers joined together.
How are the atoms in a polymer joined together?
In between the polymer chains there can be strong covalent bonds called crosslinks, or weak intermolecular forces.
What are the features of a thermosetting polymer?
Thermosetting polymer:
Strong covalent bonds between the polymer chains that are called crosslinks.
High melting point
Char/burn on heating so cannot be remoulded
What are the features of a thermosoftening polymer?
Thermosoftening polymer
Weak intermolecular forces in between the chains.
Low melting points so
Will melt on heating and can be reshaped.
What is metallic bonding?
The metallic bond is the strong electrostatic force of
attraction between the sea of delocalised electrons and the closely packed, positively charged metal ions.
What is the arrangement of metallic bonding?
Their atoms are packed together in a regular way, forming a giant metallic lattice.
The outer electron(s) are delocalised and can move throughout the structure.
What are the features of metallic bonding?
They have a high melting point.
The more delocalised electrons there are per positive ion, the
higher the melting point.
Who arranged the periodic table 1st and what did he do?
Mendeleev arranged elements in order of increasing atomic weight and grouped elements with similar chemical properties together.
Crucially, he left spaces for elements that had not yet been discovered and predicted their properties.
Who arranged the periodic table 2nd and what did he do?
Mosely
Extended the work and discovered that the atomic number was the number of protons.
Define allotrope
Allotropes are different forms of an element which are in the same state but the atoms are arranged differently.
This means they have different properties.
What are carbon's allotropes?
Diamond, graphite, graphene, fullerenes
What is the carbon allotrope like in Diamonds?
In DIAMOND each carbon covalently bonds to 4 other carbons in a giant covalent lattice.
Covalent bonds are very strong so diamond has a high melting point and is very hard.
What is the carbon allotrope like in graphite?
In GRAPHITE each carbon atom only covalently bonds to 3 other carbons.
One electron per atom is delocalised and is free to move through the structure so graphite conducts electricity Graphite has a layered structure.
There are many strong covalent bonds within the layer so graphite has a high melting point.
There are weak intermolecular forces between the layers so
they can slide over each other making graphite a good lubricant.
What is the carbon allotrope like in graphene?
Graphene is a carbon allotrope that consists of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional honeycomb lattice.
What are fullurenes?
Fullerenes are a type of carbon molecule shaped like hollow spheres or tubes.
Properties: They have unique properties, such as high strength, electrical conductivity, and the ability to trap other molecules inside.
What happens to bonds when a substance changes state?
When a substance changes state, bonds between its particles break or form, allowing the particles to move more freely or come closer together.
What is a nano particle?
A particle that is between 1 and 100nm across and consists of only a few hundred atoms. 1nm is 1 X 10 ^-9 m.
What are the properties of nanoparticles?
Small Size: Typically between 1 to 100 nanometers in size.
Large Surface Area: Have a high surface area-to-volume ratio, which enhances their reactivity and interaction with other substances.
Reactivity: More chemically reactive than larger particles due to their high surface area.
Strength: Many nanoparticles are stronger and lighter than bulk materials.
What are the risks of nanoparticles?
include potential toxicity to health, cell damage, environmental impact and catalyse reaction that could be harmful