APHUG Unit 6
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/175
Last updated 6:58 AM on 3/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
176 Terms
1
New cards
city
relatively large, densely populated settlement w/ much larger population than rural towns & villages
2
New cards
urbanization
movement of people from rural areas to cities, major trend
3
New cards
urban
“relating to city”
4
New cards
food procurement
tending of fields/harvesting & prepping crops
5
New cards
agricultural surplus
farmers able to produce ore food than needed for themselves. creation of cities
6
New cards
socioeconomic stratification
structuring of society into distinct socioeconomic classes; control over good and people
7
New cards
first urban revolution
agricultural & socioeconomic innovations that led to the rise of cities
8
New cards
urban hearth areas
regions in which world’s first cities evolved (Mesopotamia, etc)
9
New cards
site
absolute location of place on earth, includes all physical features of location (terrain, harbors, rivers)
10
New cards
situation
relative location of place in reference to its surrounding features, places of human activities or its regional position w/ reference to other places
11
New cards
cities defined by…
(1) evolved spontaneously in different places (2) diffused ideas through trade, ocean voyages, conquest
12
New cards
aqueducts
eater transported into cities from remote regions using stone structures (Roman Empire)
13
New cards
urban growth…
(1) migration of ppl from rural cities (2) natural population increase
14
New cards
communism
all property is publicly owned & managed, cities poster class privilege (china)
15
New cards
capitalism
economic & political system in which country’s trade and industry are controlled by private owners for profit rather than owned by state
16
New cards
transportation
shaped and reshaped layout and size and their surroundings over time
17
New cards
streetcar suburbs
settlements outside of cities that had streetcar lines, fixed rail systems, allows workers to commute in and out of city
18
New cards
automobile
norm among middle classes, increased personal mobility
19
New cards
telegraph
faster delivery of info, revolutionized long-distance communication
20
New cards
telephone
diffusion wider and easier (no limits)
21
New cards
second urban revolution
industrial innovations in mining and manufacturing that led to increased urban growth, new kinds of industry, reshaped cities spatially and socially
22
New cards
downtown
emerged by economic activity, expanded and evolved into commerce and industry
23
New cards
leaders..
consensus or forced, responsible for organization of surplus, storage, and distribution, city’s infrastructure, water resources, garbage, sewage
24
New cards
redevelopment
set of activities and government policies intended to revitalize area that had fallen on hard times
25
New cards
metropolis
very large & densely populated city, particularly capital or major city of region (NYC)
26
New cards
metropolitan area
bigger than city, includes one or several urban areas with accompanying suburbs & rural areas economically and culturally connected with city (New York-New Jersey)
27
New cards
China’s “Supercities”
cities with more than 1 million inhabitants
28
New cards
urban area
self-governing place that contains at least 2500 ppl
29
New cards
urbanized area
more than 50,000 inhabitants
30
New cards
urban clusters
fewer than 50,000 inhabitants
31
New cards
metropolitan statistical areas
at least one urbanized area with at least 50,000 ppl at its core; central county + adjacent outlying counties that are socially and economically intergraded with central county measured by commuting volumes
32
New cards
micropolitan statistical areas
one or more urban clusters of 10,000-50,000 people at its core
33
New cards
towns
settlements smaller & less complex than cities, self-sufficient, have CBDs, residential and nonresidential land use
34
New cards
hamlets
CBD has nothing more than grocery store, post office, and gas station
35
New cards
suburbs
populated areas on outskirts of city, residential communities w/ own government, intentionally developed residential communities on periphery of city; most residents commute to job
36
New cards
urbanization rate
percentage of each nation’s population that lived in towns & cities
37
New cards
meta cities
extraordinary large settlements w/ regional population over 20 million (Tokyo)
38
New cards
mega cities
regional population over 10 million (Beijing)
39
New cards
“Regional”
includes city & surrounding metropolitan area
40
New cards
suburbanization
movement of people from urban core areas to surrounding outskirts of city
41
New cards
sprawl
tendency of cities to grow outward in unchecked manner
42
New cards
automobile cities
size & shape dictated by car ownership (Las Vegas)
43
New cards
decentrialize
shift some departments/operations to “branch offices” in suburban areas, closer to workforce
44
New cards
edge city
concentration of business, shopping, entertainment developed in suburbs, outside city’s traditional downtown
45
New cards
edge city must have…
(1) over 5 million sqft of office space (2) over 600,000 sqft of retail space (3) population increases every morning & decreases every afternoon (More jobs than homes) (4) states as end destination (5) history of not resembling city 3 yr prior
46
New cards
first wave of development
moving homes into suburbs away from work places
47
New cards
second wave og development
moving retail to where we lived “malling of America”
48
New cards
third wave of development
jobs to wear population lived, creating edge city
49
New cards
boomburbs
places with no more than 100,000 residents, large suburbs with own gov, loosely connected groups of large subdivisions, office parks, retail centers built around multiple highway intersections
50
New cards
boomburbs must have..
(1) large incorporated tract of land (2) fast, sustained development
51
New cards
infill development
building of new retail, business, or residential spaces on vacant, underused parcels in developed areas
52
New cards
exurb
suburbs often inhabited by well do families, near farmland, beaches, mountains; semirural districts located beyond
53
New cards
world cities
cities that become command & control centers of global economy, sites of major decisions abt world’s commercial networks & financial markets
54
New cards
nodes
places connected to other cities where international action & interaction occur (internationally & domestically)
55
New cards
global cosmopolitan class
population moves with ease from place to place, wealth, world cities are home (highest concentration in London)
56
New cards
Gated communities
highly second residential enclaves, located within the bounds of cities, privately governed
57
New cards
transportation serveices
world cities hub of services, built on major waterways, major international airports, railroad & highway networks, high-speed rail system
58
New cards
international organizations
located in world cities (World Health Organization (WHO), United Nations Educational, Scientific, Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
59
New cards
urban systems
a set of interdependent cities or urban places connected by networks; territories within nation, state, or province
60
New cards
urban hierarchy
ranking of cities, largest & powerful at top of hierarchy
61
New cards
rank-size rule
states population of a settlement is inversely proportional to its rank in urban hierarchy (1/2 to 1/3 to 1/4 etc.)
62
New cards
primate city
largest city more than twice as many people in second-largest, largest than any other city, dominates economic, political culture life
63
New cards
central place theory
model attempt to understand why cities are located where they are, based on five assumptions (Walter Christaller)
64
New cards
central places
settlements that make certain types of products & services available to customers
65
New cards
threshold
number of people required to support a business
66
New cards
range
distance people will travel to acquire a good or service
67
New cards
First order places
large regional cities
68
New cards
Second order places
Regular cities
69
New cards
Third order places
towns
70
New cards
fourth order places
hamlets and villages
71
New cards
gravity model
mathematical model that attempts to predict how places will interact; the closer 2 places are, the more they influence each other (distance increases, interaction decreases) P1+P2/D^2
72
New cards
models
generalizations that help us organize information & identify the patterns of observed arrangements
73
New cards
concentric zone model
model of city’s internal organization that shows rings of factory production & different residential zones radiating outward from CBD (zones: CBD, zone of transportation, zone of independent worker’s homes, middle-class residents, commuter’s zone)
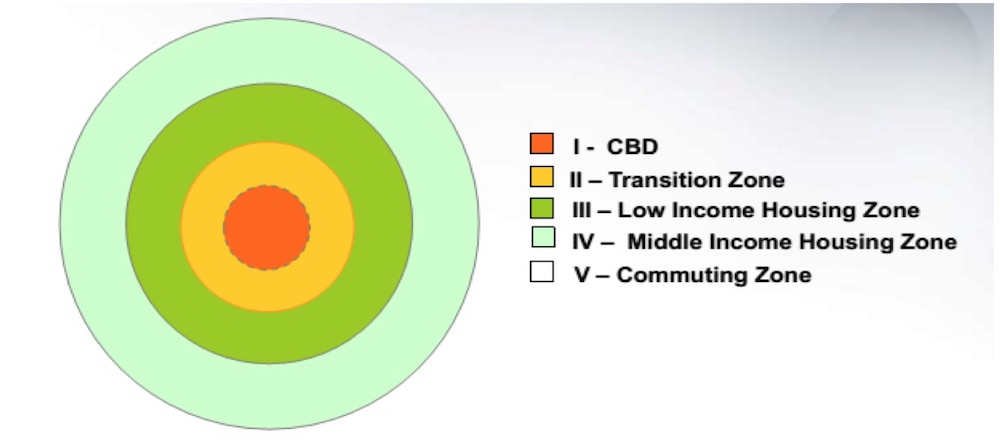
74
New cards
hoyt sector model
focuses on transportation & communications as drivers of city layout; people will live in different sectors based on income levels
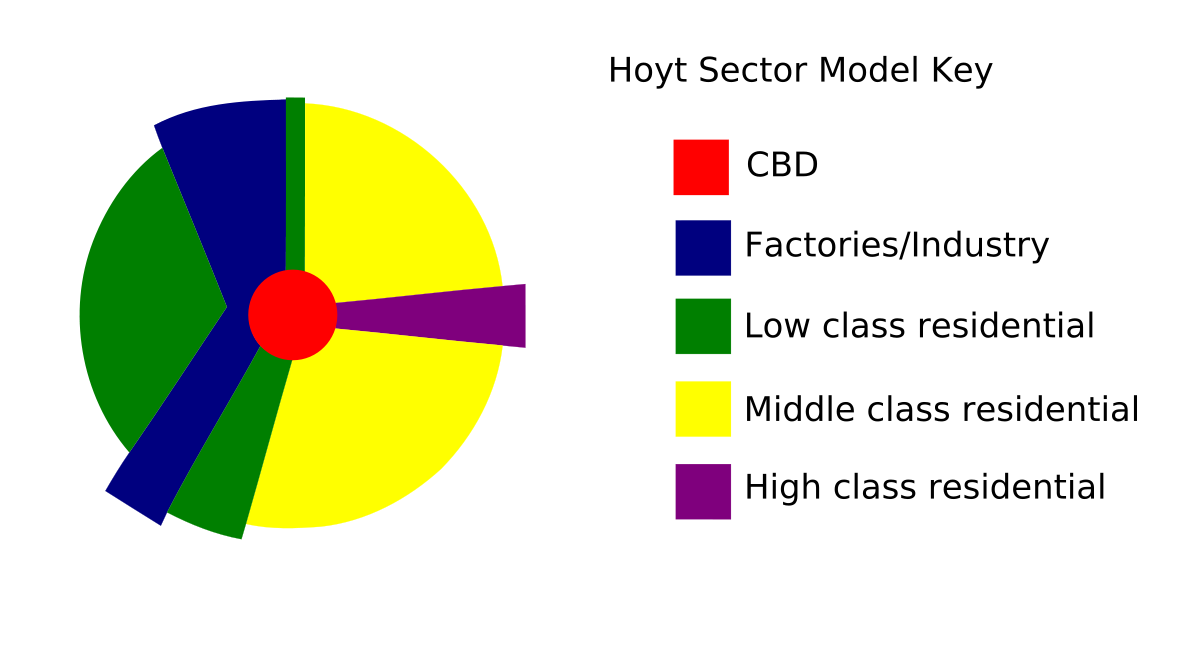
75
New cards
multiple-nuclei model
does not have one central area, but instead has several nodes that act as regional centers for economic or residential activity within one larger city
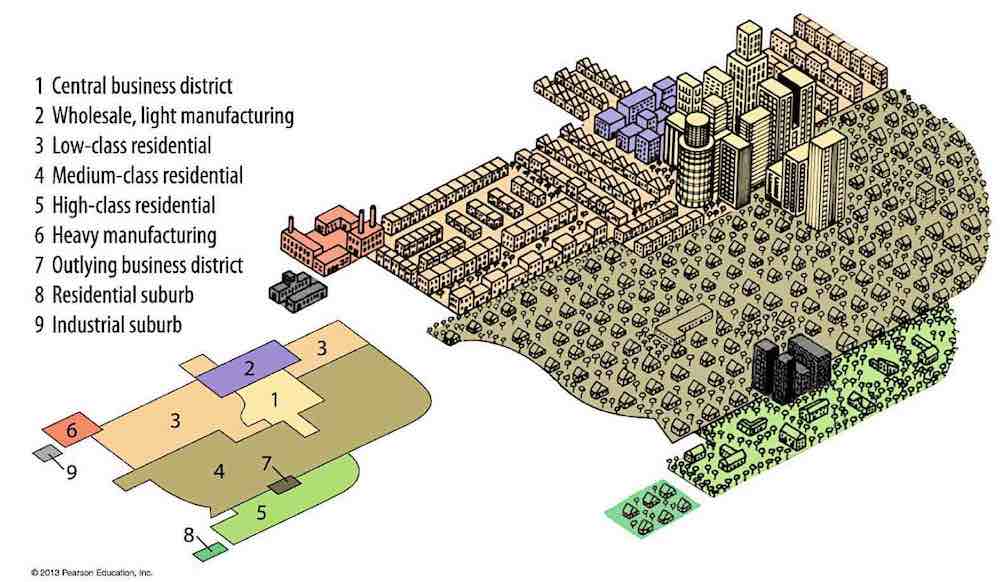
76
New cards
galactic city model/peripheral model
a city with growth independent of the CBD that is traditionally connected to the central city by means of an arterial highway or interstate.
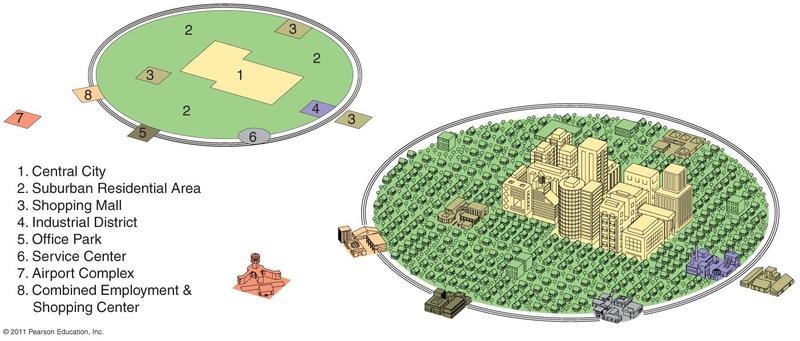
77
New cards
bid-rent theory
land/real estate/rental costs are higher in and around a city's central business district due to demand

78
New cards
Latin American City Model
griffin-ford model, cities have a central business district, one dominant elite residential sector, and a commercial spine
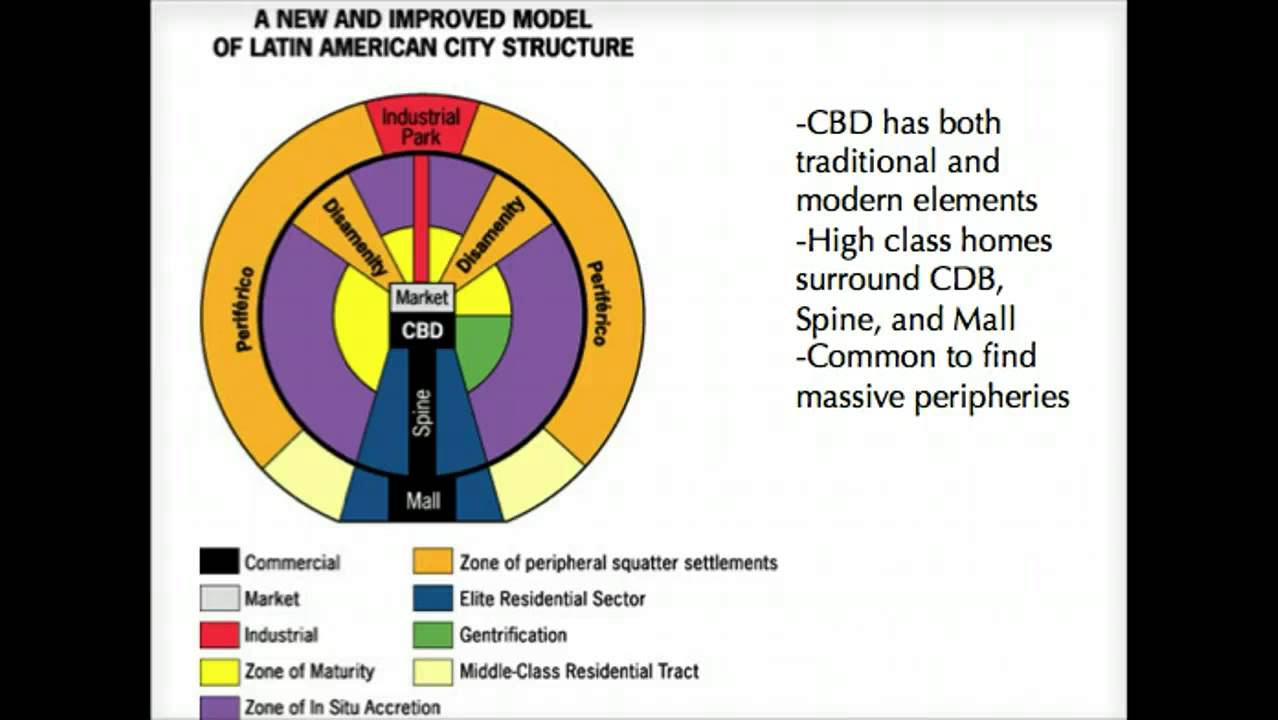
79
New cards
traditional market sector
sells everyday goods (1/2 of Latin American City Model CBD)
80
New cards
modern CBD sector
primary businesses, entertainment venues, employment (1/2 of Latin American City Model CBD)
81
New cards
commercial spine
extension of the CBD & flanked by elite residential sector, ends at mall, opposite end of market, spine-like sector for industry, ends in industrial park
82
New cards
zone of maturity
rings CBD/market center, occupied by mid-class & contains best housing
83
New cards
zone of situ accretion
transitional area between poorest parts & zone of maturity, modest housing for those in lower middle class
84
New cards
disamenity sector
the zone that offers few services & home to very poor; barrios/favelas, little to no law enforcement, lack of amenities (water, electricity, fresh food)
85
New cards
Southeast Asian city model
models for other emerging market economies, medium-sized port cities in SA, focal point: old colonial port zone w/ surrounding commercial districts
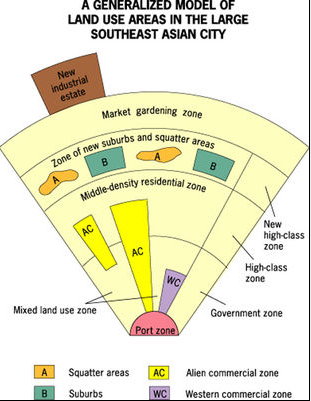
86
New cards
alien commercial zones
populated primarily by Chinese merchants, residences attached to business
87
New cards
mixed land-use zones
surrounds commercial zones, various economic activities & some housing
88
New cards
market gardening zone
light agriculture takes place & small industrial park accommodates growing economic sector
89
New cards
Sub-Saharan African city model
imprint of European colonial powers, 3 CBDs with distinct functions & building styles
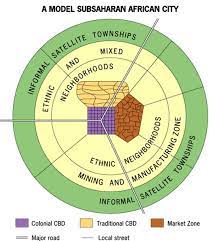
90
New cards
colonial CBD
place for informal markets & transitional business center, commerce conducted curbside nonpermanent stalls or permanent storefronts
91
New cards
traditional business center
zone of traditional one story buildings
92
New cards
market zone
open-air, informal, essential to city’s residents
93
New cards
shantytowns
outer ring, grows rapidly due to unchecked in-migration from rural areas
94
New cards
city models
help understand city structure, land-use patterns, and population density (although no model fits perfectly)
95
New cards
land use driven by…
utility (usefulness), accessibility (transportation, technologies), transportation (automobile)
96
New cards
population density
total population divided by total land area
97
New cards
perceived density
general impression of estimated number of people present in given area, qualitative data (what ppl see/think)
98
New cards
high population density
ex. high rise apartment building
99
New cards
low population density
single fam homes on large land
100
New cards
population density gradient
distance from CBD increases, population density continuously decreases