IB Bio SL Flashcards, Membranes and Neurons
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Outline the function of cholesterol in cell membranes
Reduces fluidity of membrane
Reduces permeability of membrane to some molecules
List functions of proteins found in cell membrane
Facilitated diffusion by channel proteins
Active transport by protein pumps
Cell recognition by glycoproteins
Receptors for hormones
Cell adhesion
Outline simple diffusion
Passive movement of molecules along a concentration gradient
Passive transport
Outline facilitated diffusion
Passive transport
Passive movement of molecules along a concentration gradient through a protein channel
Outline osmosis
Passage of water through a membrane from lower solute concentration to a higher solute concentration
Usually uses a protein channel
Passive transport
Outline passive transport
Does not require ATP
Molecules move from high concentrations to low concentrations (concentration gradient)
Outline the process of the Sodium-Potassium pump
Active transport
Pump binds to the three intracellular Na ions
ATP molecule attaches to the protein
ATP phosphorylated, loses one phosphate molecule, resulting in ADP
Phosphorylation causes the pump to change its shape, causing Na ions to exit cell
Two extracellular K ions bind to pump
Phosphate group released from pump
Causes protein to retain its original shape, releasing K+ into the cell
Outline endocytosis
Allows large molecules to enter cell that cannot fit through membrane proteins
Portion of the plasma protein is pinched off to enclose macromolecules, creating a vesicle around it
Temporarily changes shape of membrane
Ends of the cell membrane resume the correct shape, vesicle is taken into the cell
Active transport
Outline exocytosis
Active transport
Protein produced by the ribosome of the ER
Protein exits ER and enters the Golgi apparatus on the cis side
Protein is modified and packaged in a vesicle, then exits the trans side of the Golgi
Vesicle with protein fuses with the cell membrane and the contents are secreted from the cell
Outline hypertonicity in osmosis
When the solution has a high concentration of solutes relative to the cell
Water flows out of the cell to reach equilibrium of solutes
May cause the cell to shrivel up
Outline hypotonicity in osmosis
When the solution has a low concentration of solutes relative to the cell
Water flows into the cell to reach equilibrium of solutes
May cause the cell to inflate and burst
Outline isotonicity in osmosis
When the solution has an equal concentration of solute relative to the cell
No water flow
Tissues or organs to be used in medical procedures must be bathed in a solution with the same osmolarity as the cytoplasm to prevent osmosis to create an isotonic situation once transferred into the body
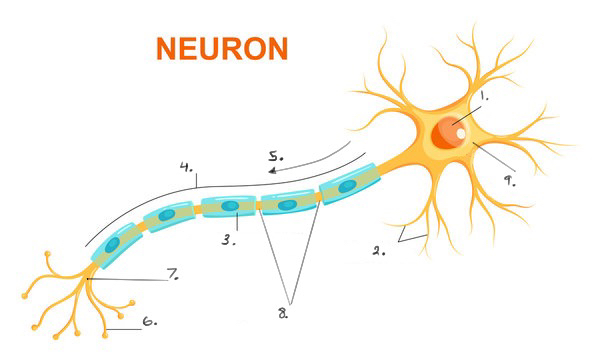
Label parts of a neuron
Nucleus
Dendrites
Myelin sheath, made of lipid Schwan cells
axon
action potential
axon terminal button
synaptic terminals
nodes of Ranvier
cell body
Explain the action of neonicotinoid pesticides in insects
Has similar structure to a neurotransmitter such as acetylcholine
Binds to postsynaptic receptors that normally accept acetylcholine in postsynaptic membrane
When pesticide binds to receptor proteins, action potential isn’t propagated nor is itbroken down by acetylcholinesterase
Receptor is blocked and overstimulated, leading to paralysis and furthermore death
Outline neurones
Designed to transport electrical impulses
Can be long or short
Electrical impulses are received in the dendrites, then transmitted through the axon and ends at the synaptic terminal buttons
Synaptic terminal buttons release the neurotransmitter to continue the electrical impulse to the next neuron
A group of neurons is called a nerve
Outline the function the myelin sheath
Increases the rate at which an action potential passes down an axon
Schwann cells, lipids and squishy
Surrounds axons
Active potential goes around them
Acts as an insulator and prevents charge leakage through the membrane
Wrapped around axon multiple times
Outline resting potential
State where the neuron is not sending an imuplse
Polarized
Na+ out, K+ in, through sodium-potassium pump
Transports 3 Na+ out for every 2 K+ in
Cytoplasm has permanent negativity, results in net positive charge outside the axon membrane
-70mV
Describe how an action potential is propagated down the axon
Nerve impulses are action potentials propagated along axons of neurons
Resting potential is -70mV, Sodium-potassium pumps maintain resting potential, more Na+ outside, more K+ inside
Action potential stimulates wave of depolarization along the axon
When neuron is stimulated, if the threshold potential is reached, Na+ channels open, Na+ diffuses in, depolarizing as inside becomes more positively charged
Depolarized area then initiates the next area of the axon to open Na+ channels, causing action potential to move down axon, self-propagating part, self-propagates to the axon end
K+ moves out of the cell, repolarizing and goes back to resting potential
No such thing as a strong or weak impulse, only minimum impulse required to stimulate
Outline Saltatory Conduction
Phenomenon where an action potential of myelinated axons skips from one node of Ranvier to the next
Action potential doesn’t have to undergo ion movements in area under the myelin sheath
This jumping from one node to the next causes the impulse to travel faster because it allows areas of the membrane to be skipped
More efficient
Requires less ATP
Only places where resting potentials need to be re-established is at the nodes of Ranvier
What is an example of a neurotransmitter?
Acetylcholine
Outline synaptic transmission
Action potential (AP) has travelled to the axon terminal buttons filled with vesicles full of neurotransmitters (NT)
AP activates voltage-gated Ca+ channels to take in Ca+, making the vesicles fuse with the cell membrane
NT released into the synapse cleft
Dendrites in postsynaptic neuron (second neuron) receive neurotransmitter through a receptor protein
Binding causes an ion channel to open and Na+ diffuses in
Initiates action potential, moves down the postsynaptic neuron
Neurotransmitter is broken down by an enzyme and released from the receptor protein, diffusing back to be reassembled in the receptor protein buttons (reuptake)
Ion channel closes to Na+
Define synapse
Area where two or more neurons adjoin and one neuron communicates with another through chemicals
Define amphipathic
Having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts, can be seen in the membrane bilayer
Outline the significance of the surface area to volume ratio in the limitation of cell size
Surface area of the cell affects the rate of material exchange
When the cell increases in size, so does its chemical activity
When the cell grows, more substances need to be taken in and waste products excreted
When the cell gets bigger, its surface area to volume ratio gets smaller
Substances will not be able to enter the cell fast enough