Basic Terms, Circle of Willis, Corticospinal Tract
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Peri
around
ex: perimeter, periaqueductal gray
Para
beside
ex: paramedic, paraventricular nucleus
Hypo
below
ex: hypodermic, hypothalamus
Epi
on top of
ex: epiglottis, epithalamus, epidural
Ipsi
same
ex: ipsilateral
Contra
opposite
ex: contralateral
Coronal
Frontal plane
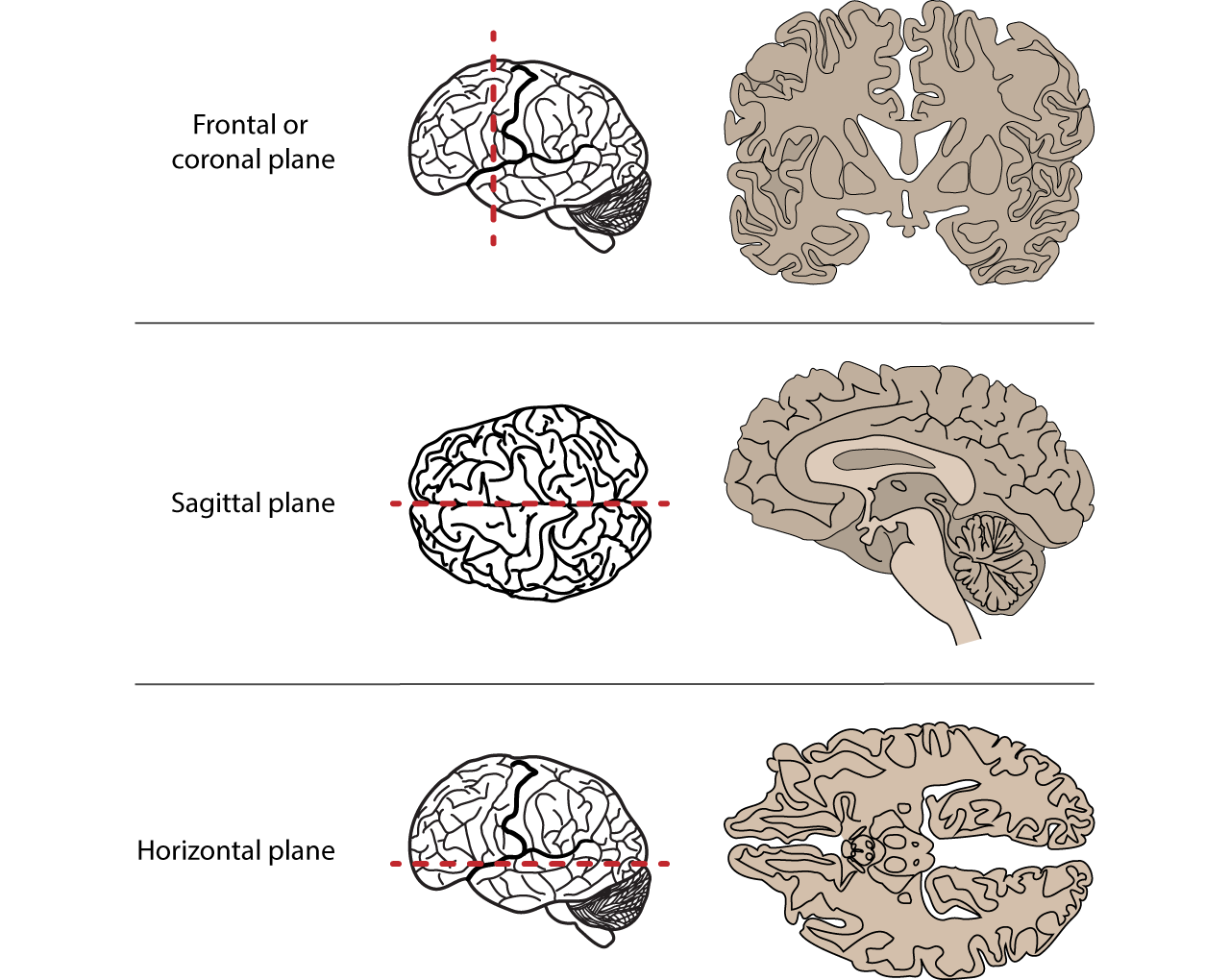
Axial
Transverse plane
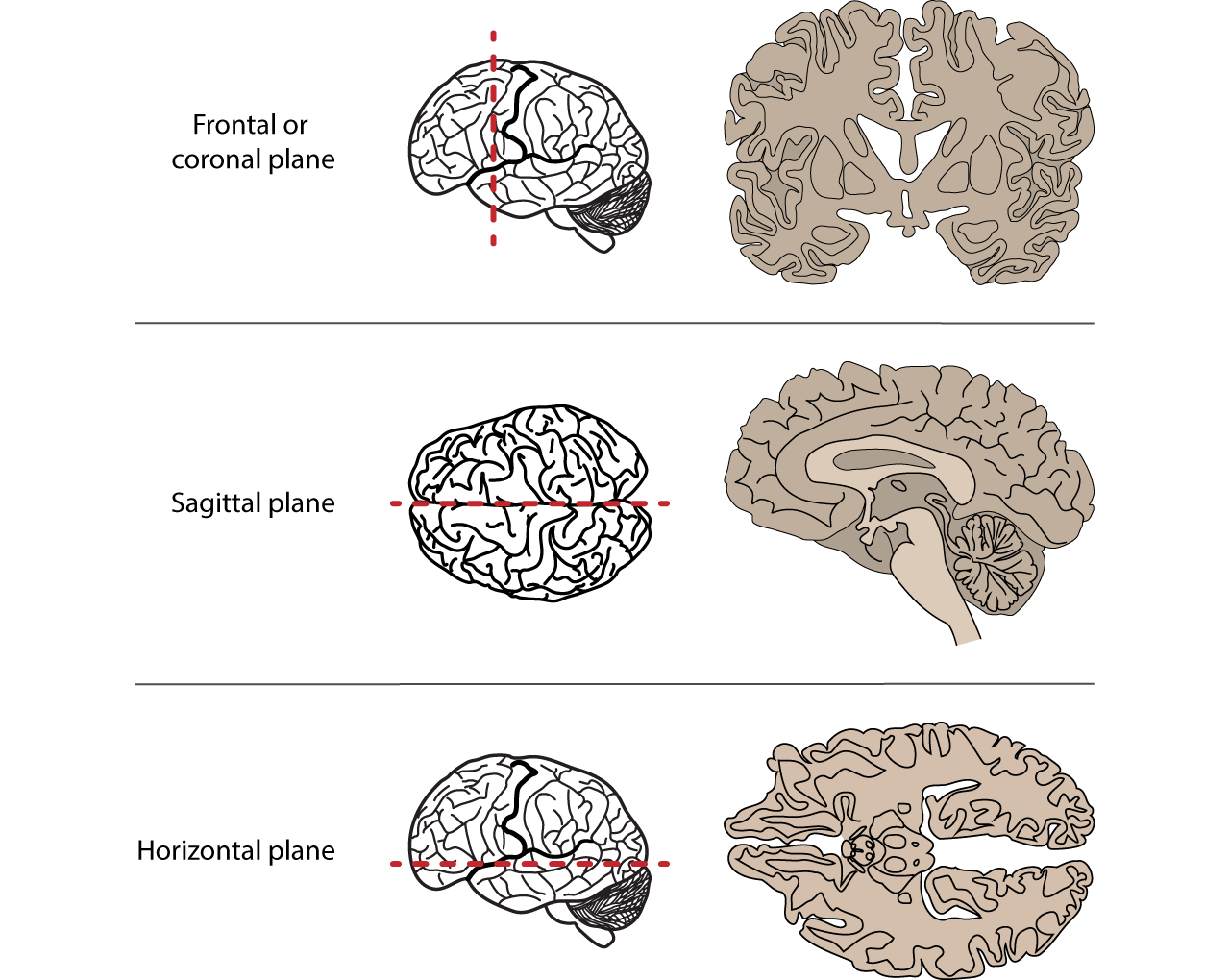
Sagittal plane
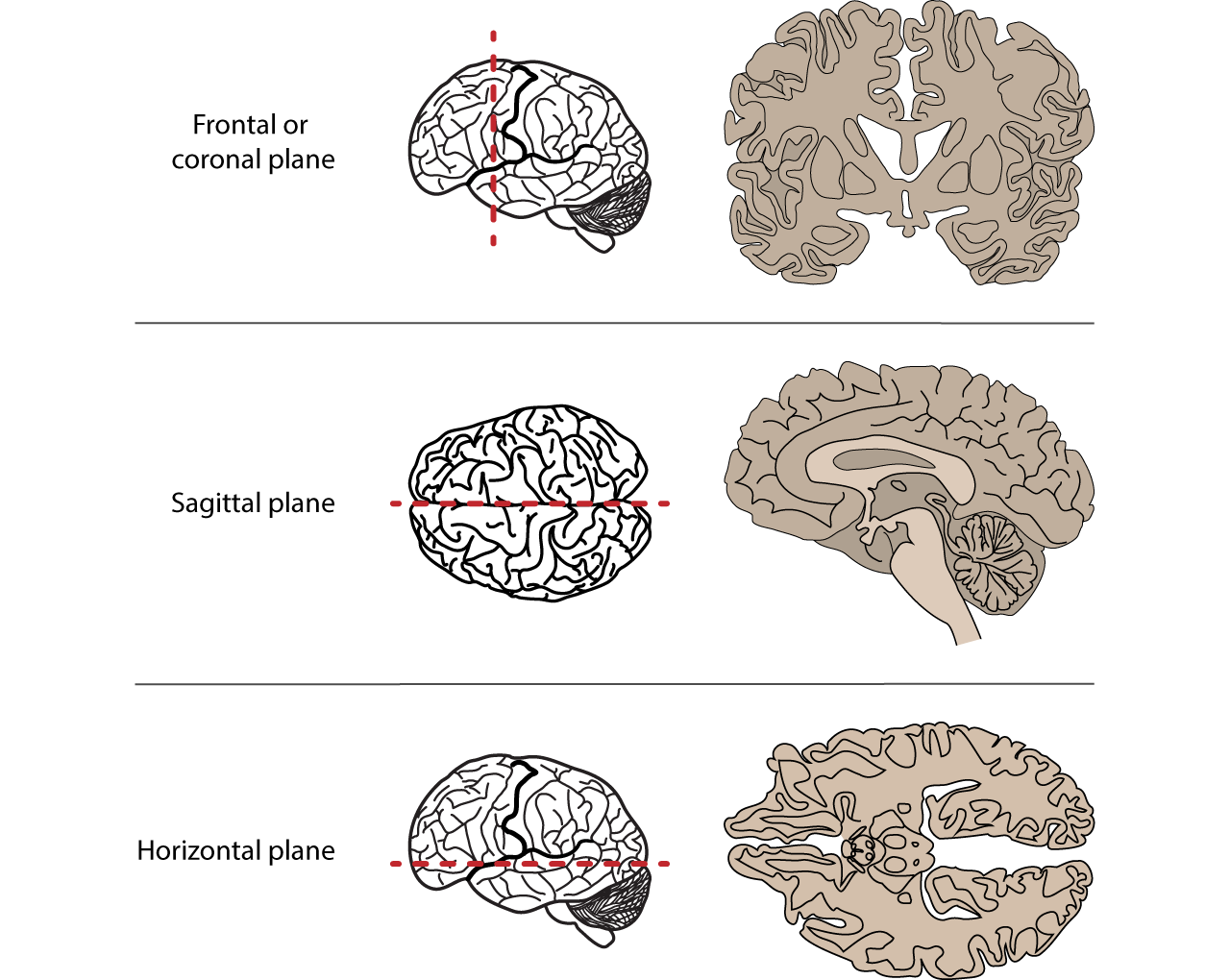
mid-sagittal
at the midline
para-sagittal
beside the midline
anterior, rostral
front of the brain/body
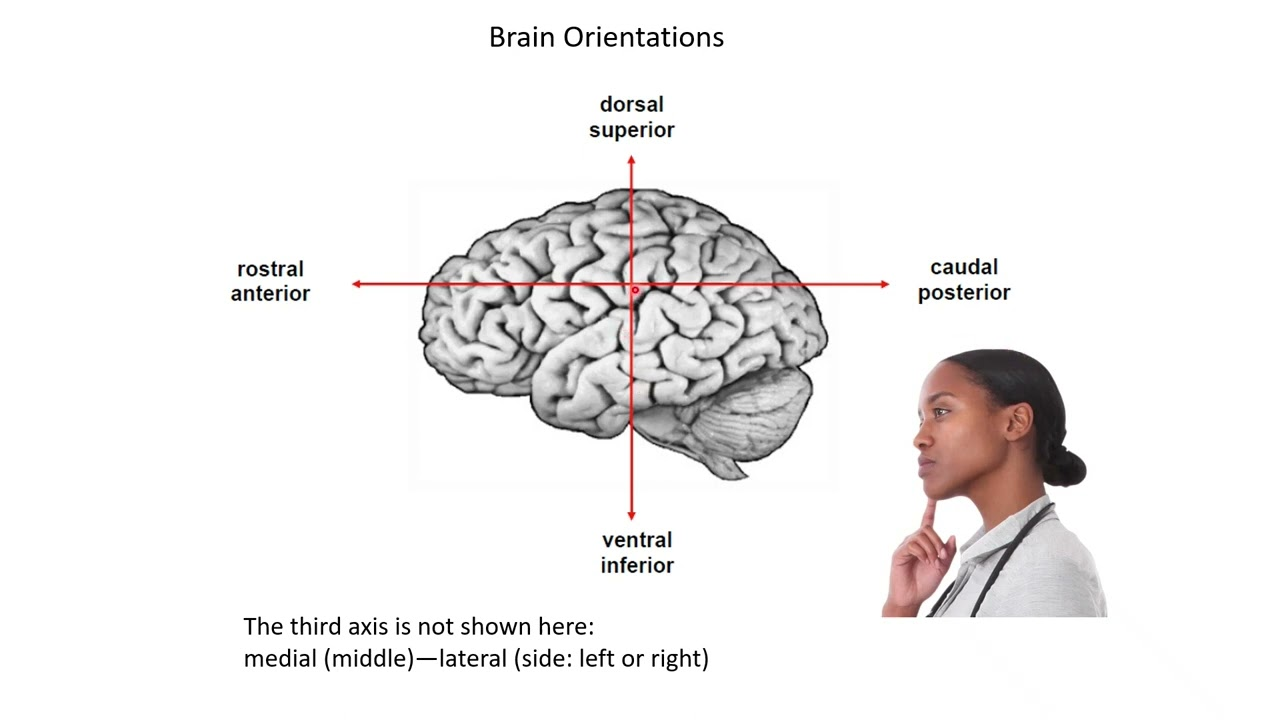
posterior, caudal
back of the brain/body
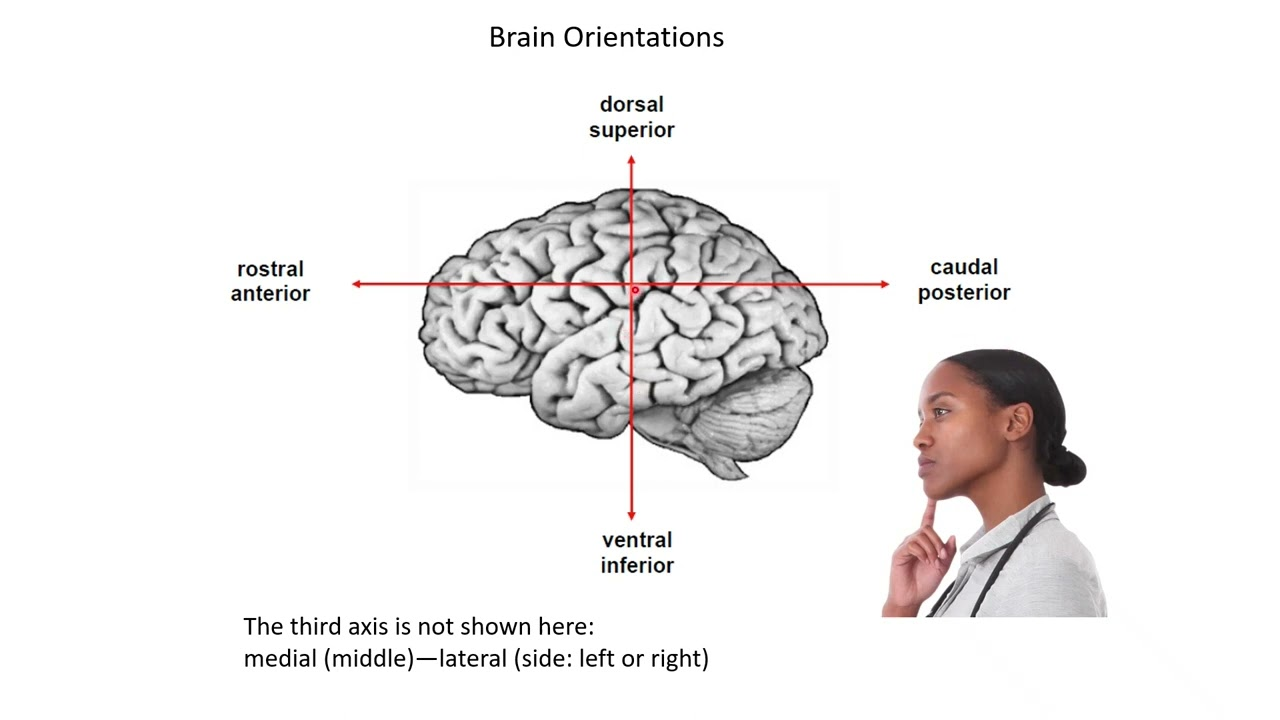
superior, dorsal
top part of the brain/body
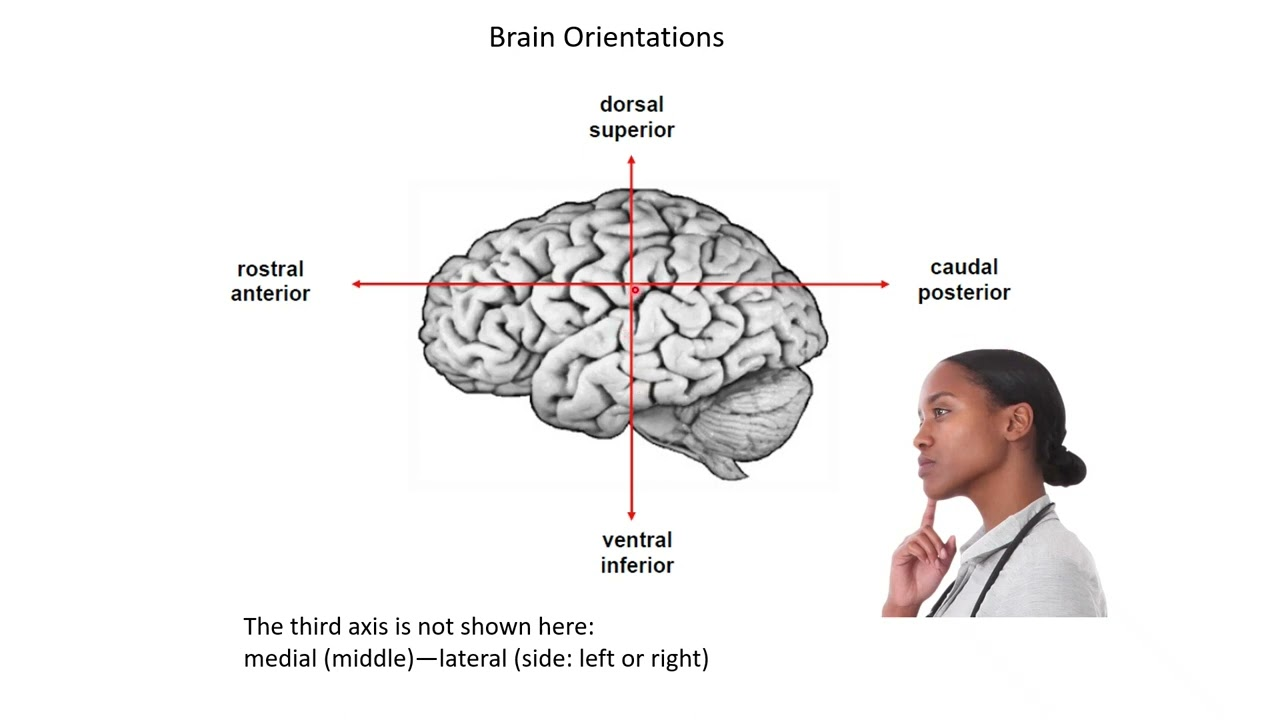
inferior, ventral
bottom part of the brain/body
medial view
Brain is cut down the middle (from the top of the head), showing the inside left/right
lateral view
Brain viewed from side
superior view
brain viewed from top
inferior view
brain viewed from below
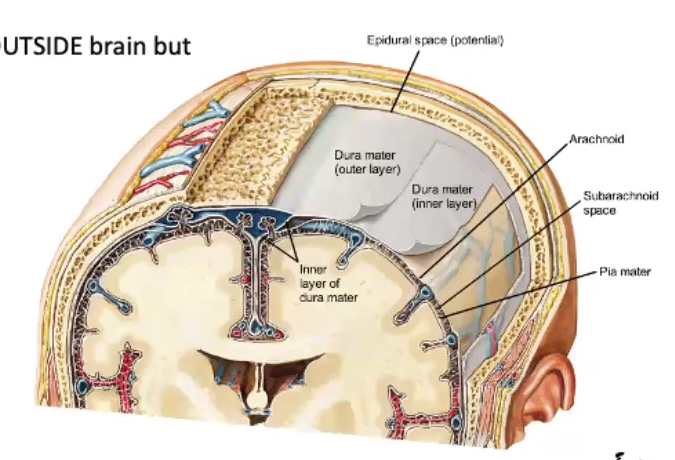
meninges
three layers of protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord
dura mater
outermost, toughest layer of the meninges
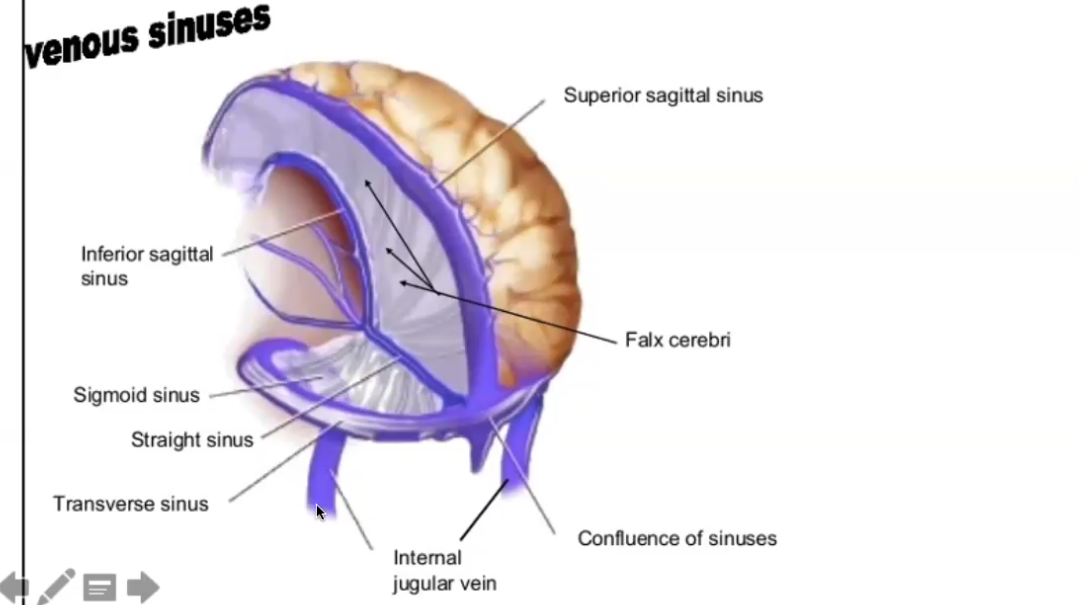
things used to remove deoxygenated blood from the brain.
dural venous sinuses
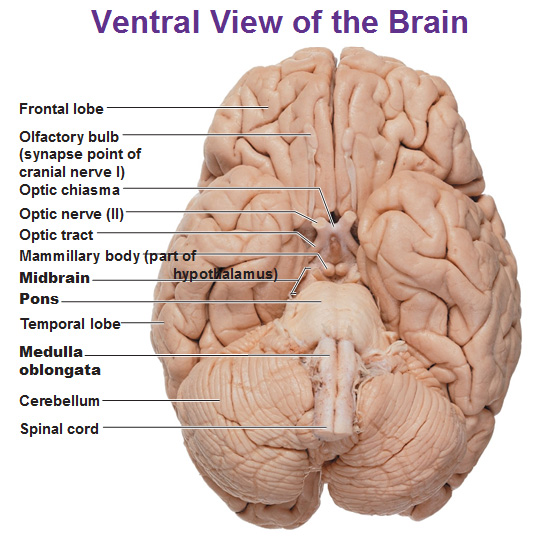
Olfactory bulbs
Process sensory information from the nose
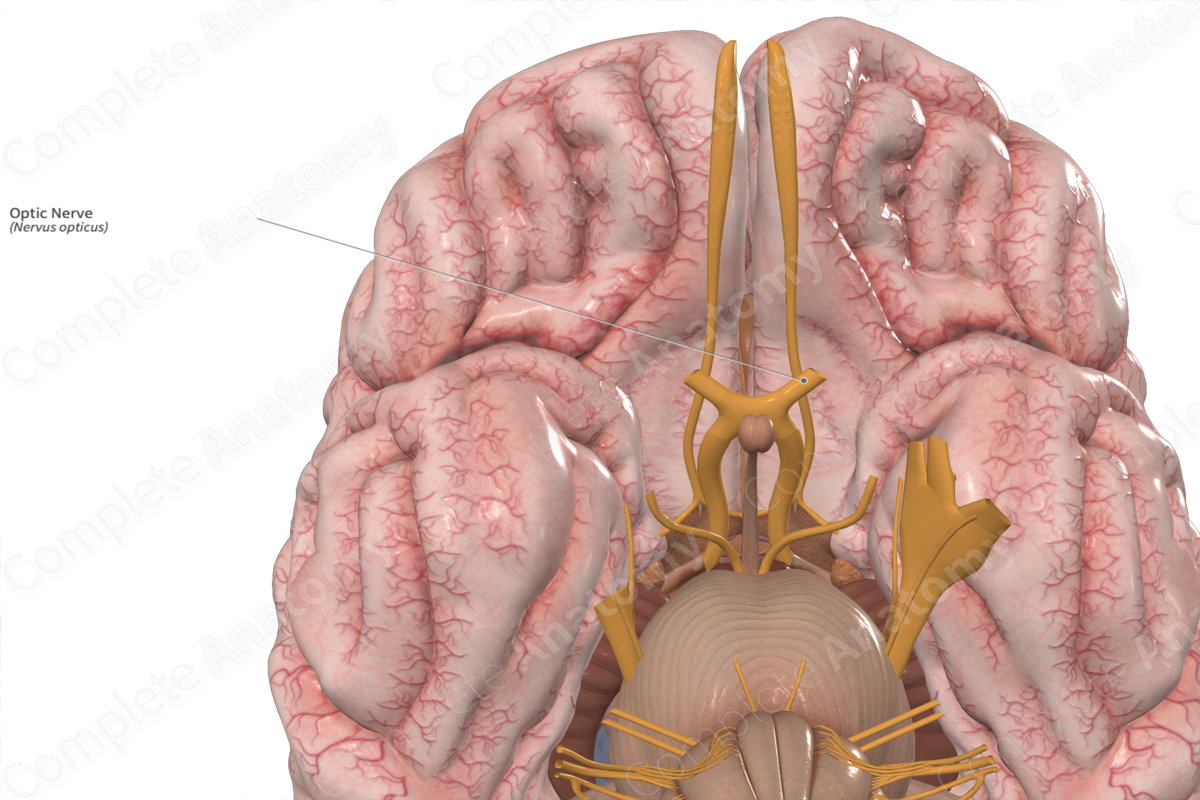
Optic nerve
nerves that transmit signals from the retina of each eye to the brain
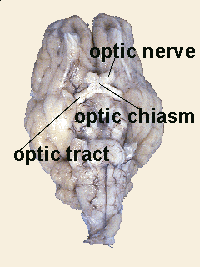
Optic chiasm
The X-shaped structure formed at the point below the brain where the two optic nerves cross over each other
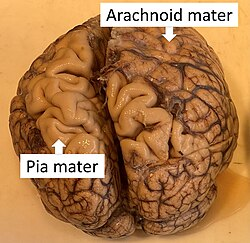
Arachnoid
middle layer of your meninges, thin, looks like spiderweb. usually has CSF under it.
Cerebrum
largest part of brain
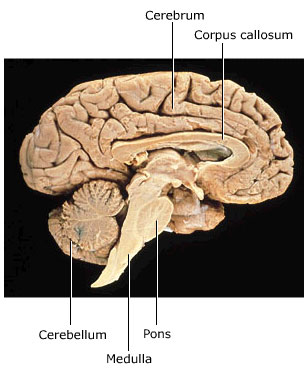
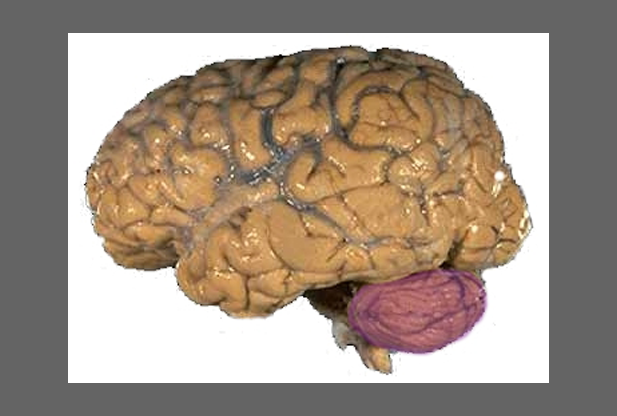
cerebellum
"little brain” between brainstem and cerebrum
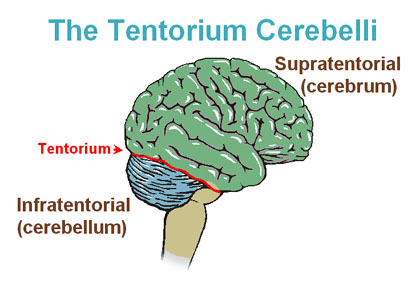
tentorium cerebelli
a fold of the dura mater, a tough membrane lining the skull, that separates the cerebellum and brainstem from the cerebrum
sinus pathway
smaller vessels go to superior sagittal sinus. straight sinus and transverse sinus work the same way. all flow together out of the jugular vein.f
pia mater
innermost meninge
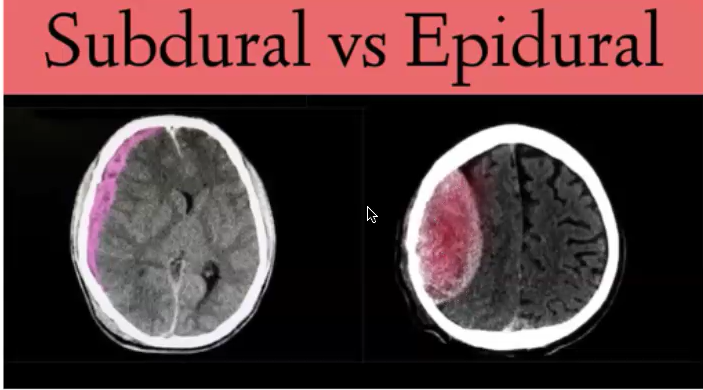
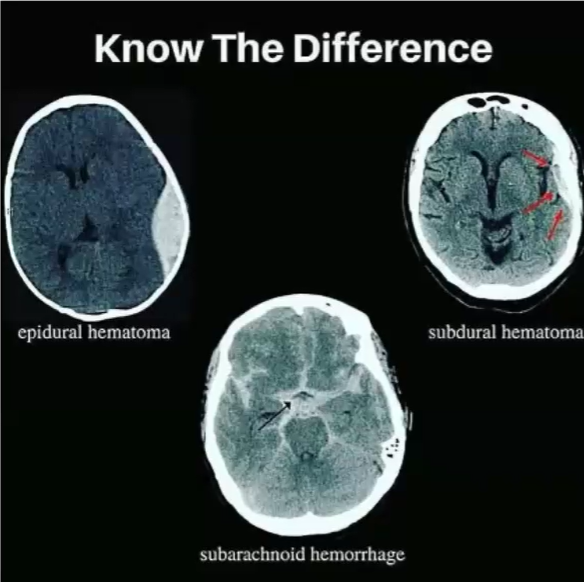
hematoma and its types
blood has leaked out and collected somewhere
subdural: below the dura (crescent)
epidural: above the dura (lens)
how to recognize CAT scan
Looks fuzzy
hemorrhage and its type
active bleeding in brain
subarachnoid means below the arachnoid layer. we can recognize it by the central pocket being lit up.
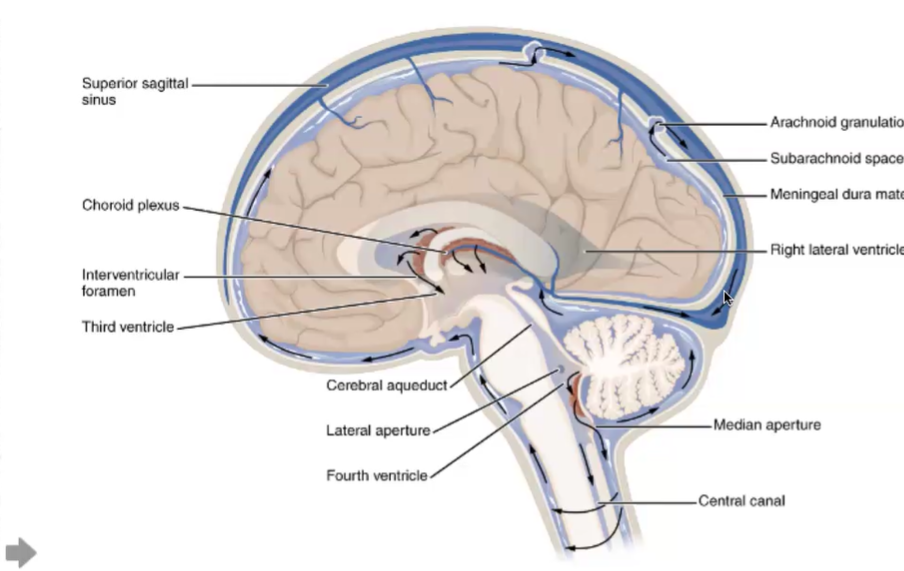
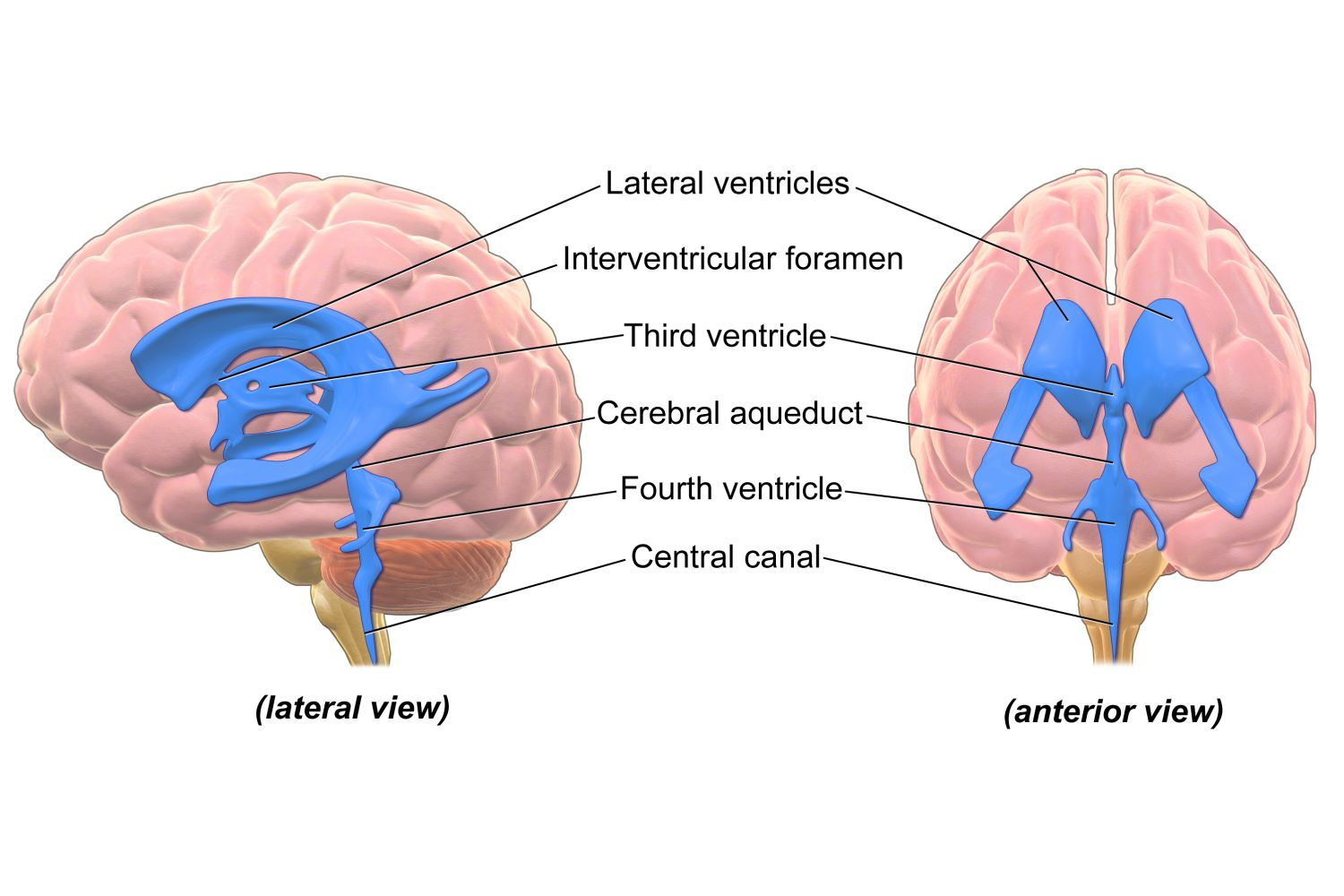
ventricle system
lateral ventricles have choroid plexues which creates CSF. Fluid drains into the 3rd ventricle, which is drained by the cerebral aqueduct, and into the 4th ventricle. CSF is released under arachnoid.
3rd ventricle looks like skinny line right on the midline when we do sagittal cut
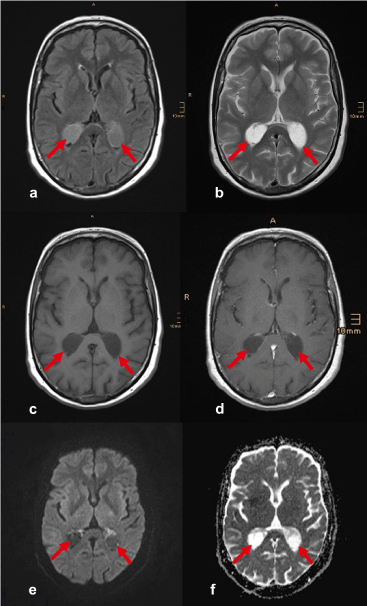
choroid plexus (draw MRI)
network of capillaries and specialized cells located within the ventricles of the brain. Its primary function is to produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
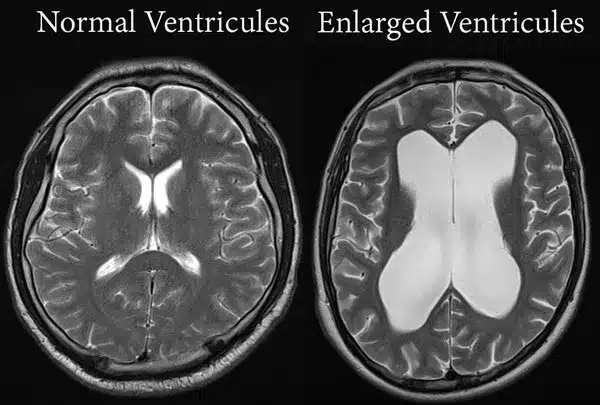
hydrocephalus, state effects and symptoms
buildup of CSF in the ventricles, compresses rest of brain and causes memory loss, etc.
spine vs. spinal cord
spinal cord is shorter than spine. in a spinal tap, the needle goes only where nerves are (sacral & lumbar region), and these move away from the needle.
telencephalon
part of embryonic brain in the prosencephalon (forebrain)
creates cerebral cortex & cerebral nuclei (amygdala, basal ganglia, basal forebrain)
associated ventricle: lateral
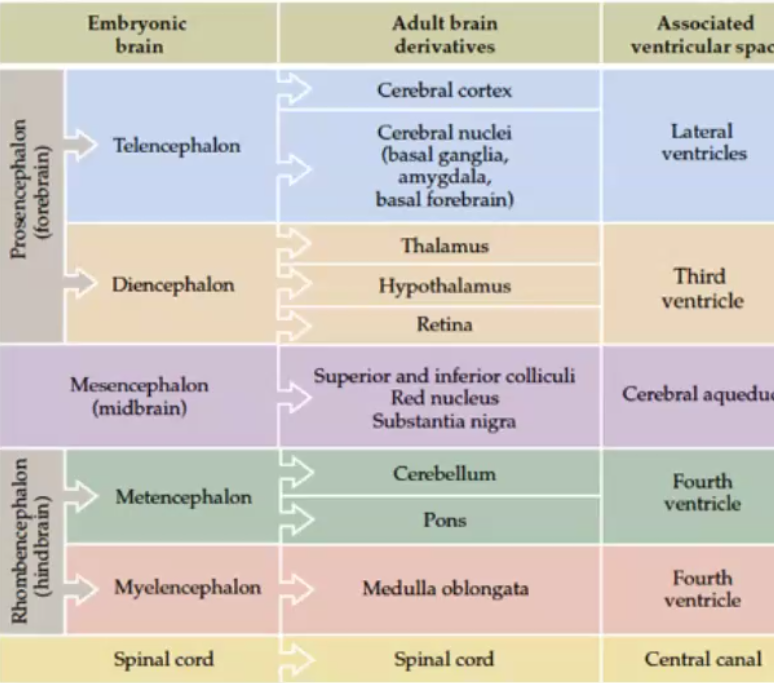
diencephalon
part of embryonic brain in the prosencephalon (forebrain)
creates thalamus, hypothalamus, & retina
associated ventricle: third
mesencephalon
midbrain
creates superior and inferior colliculi, red nucleus, and substantia nigra
associated ventricle: cerebral aquaduct
metencephalon
part of embryonic brain in the rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
creates cerebellum and pons
associated ventricle: fourth
myelencephalon
part of embryonic brain in the rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
creates medulla oblongata
associated ventricle: fourth
spinal cord ventricle
central canal
lobes of the brain
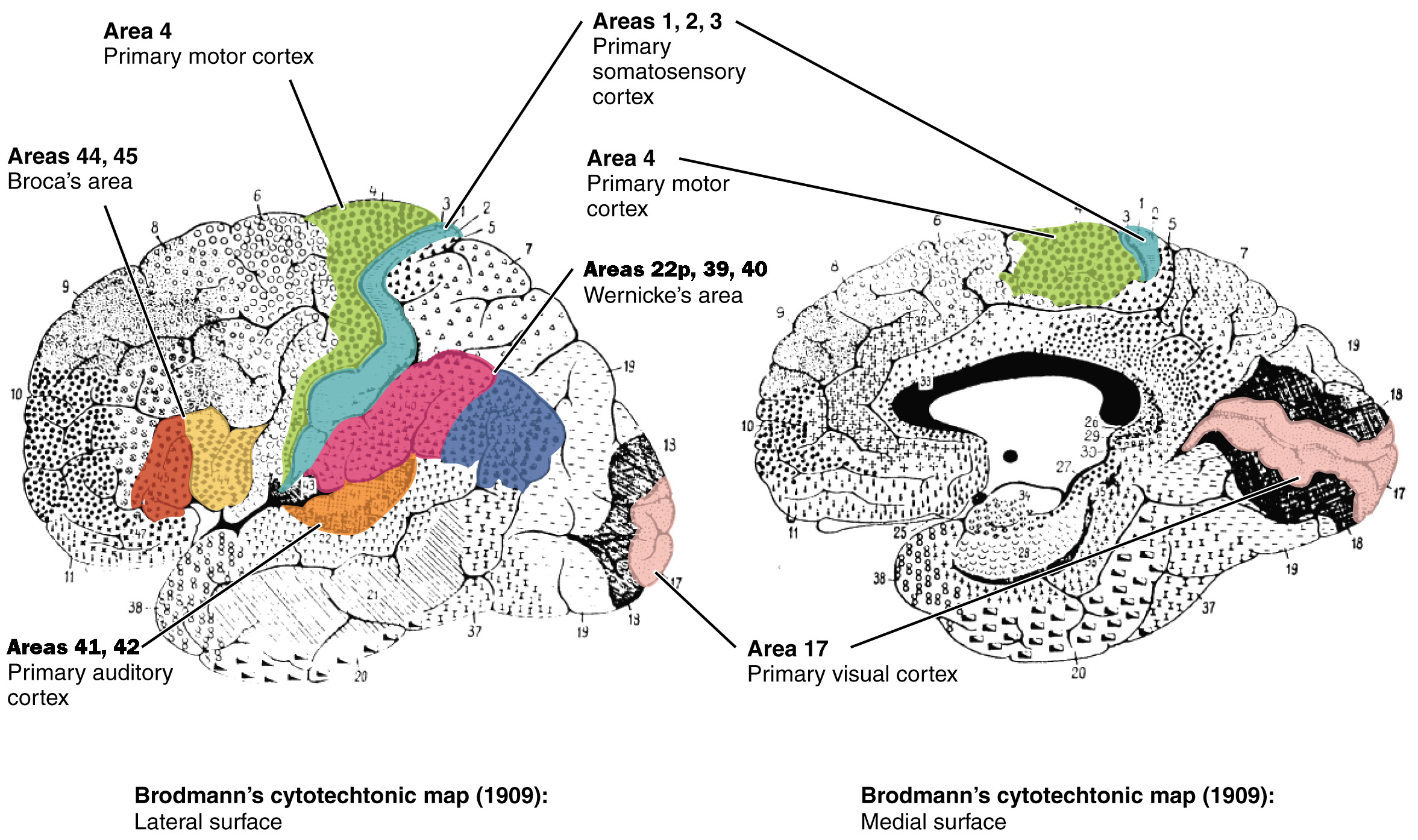
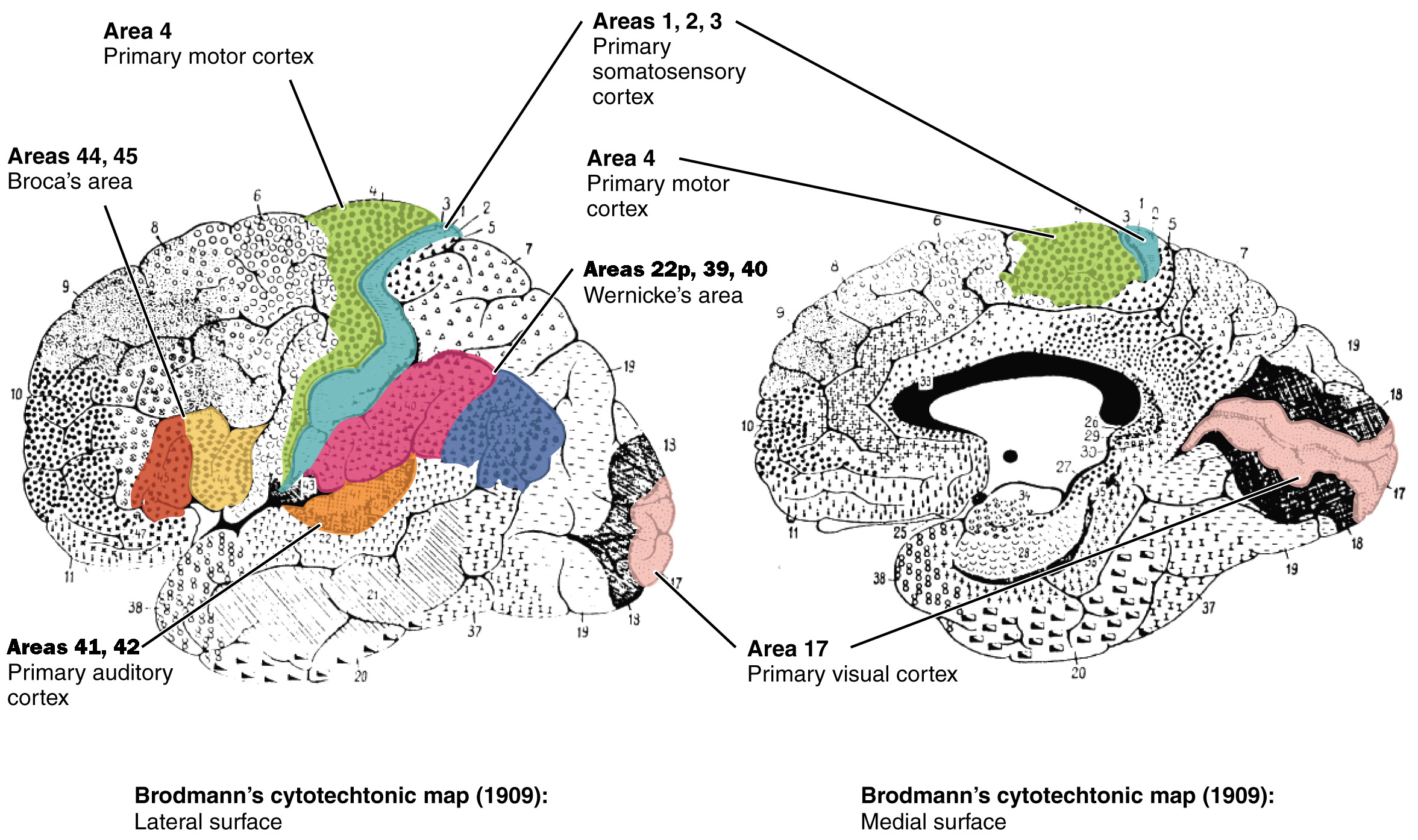
Brodmann’s areas
way to divide the brain (ex:BA4)
central sulcus
prominent groove on the surface of the brain that separates the frontal and parietal lobes
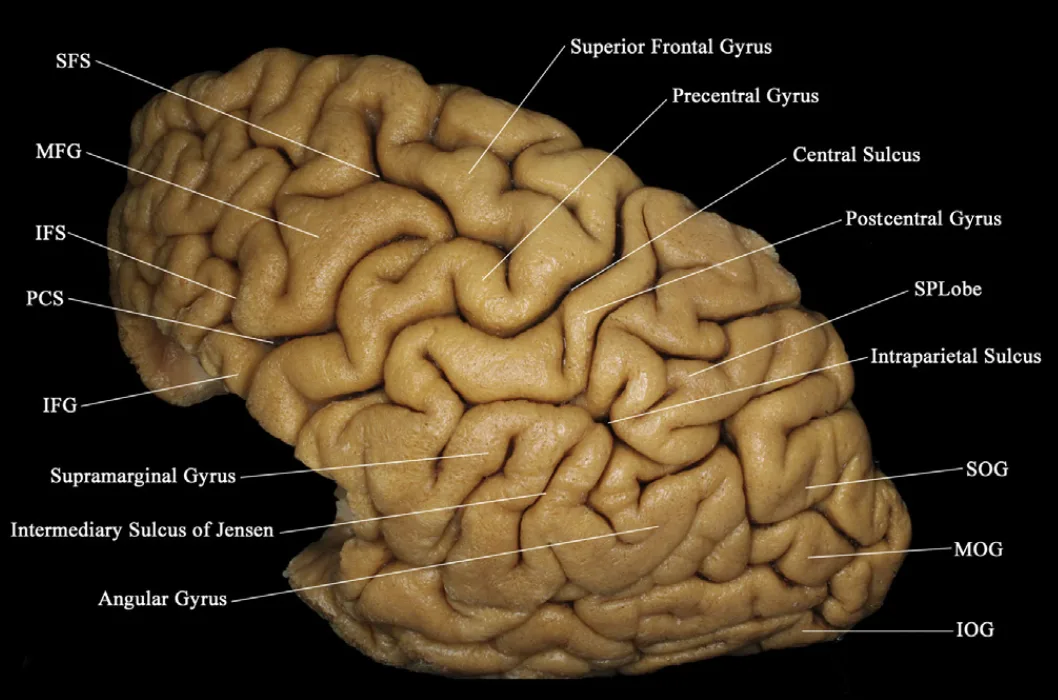
primary motor cortex (BA)
state alternate name
also precentral gryrus (anterior to central sulcus)
BA4
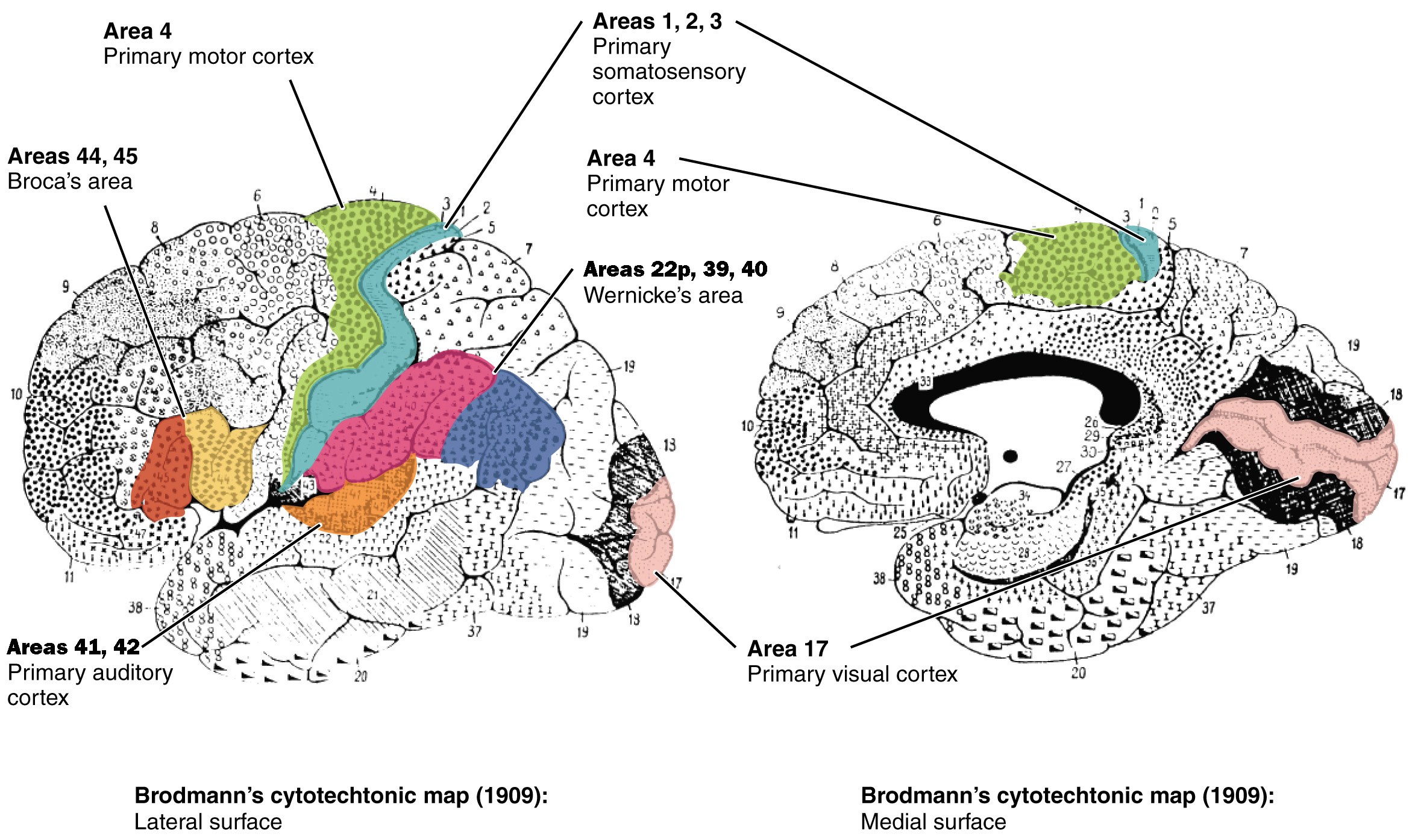
primary somatosensory cortex (BA)
aka…
postcentral gyrus
BA1, BA2, BA3
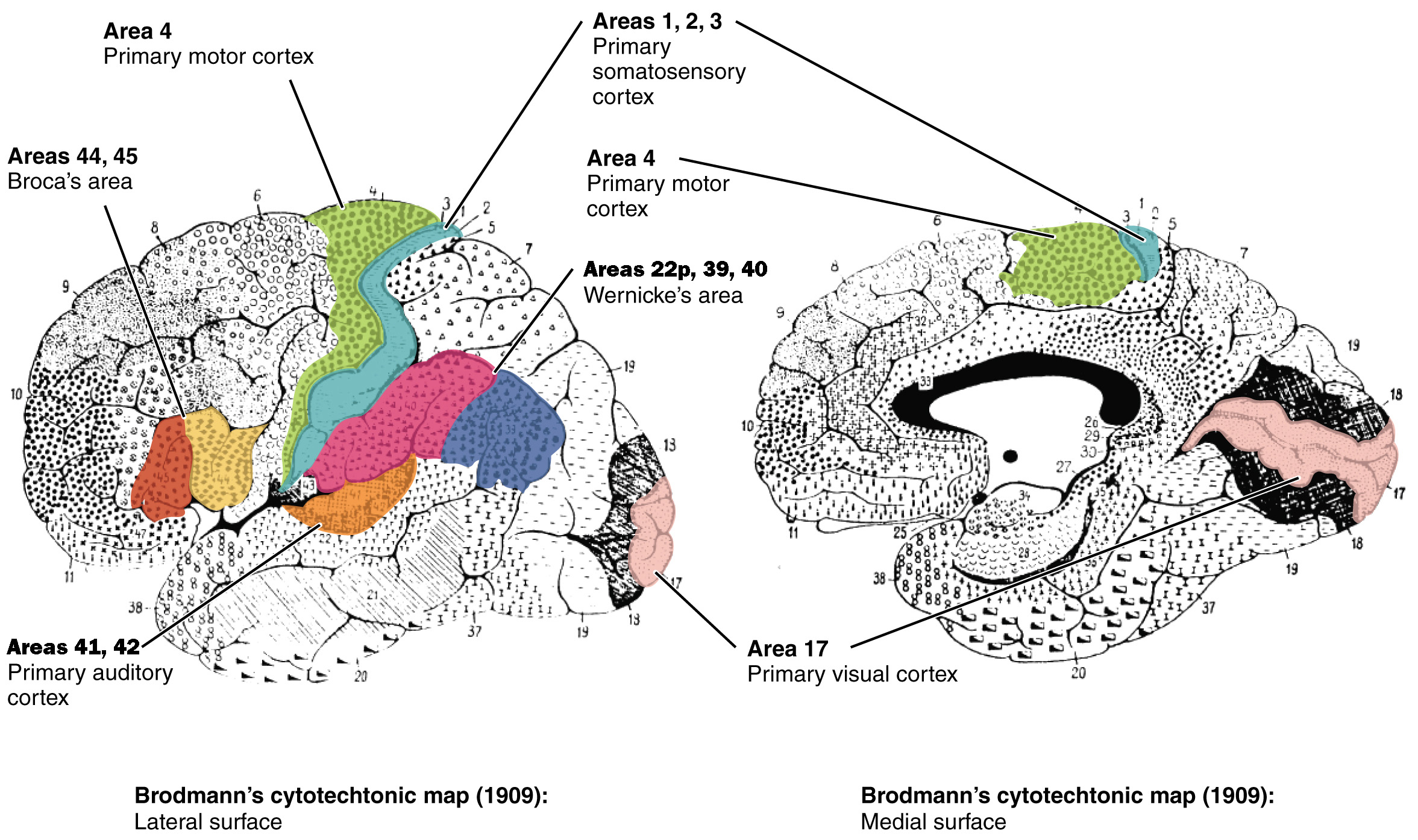
primary visual cortex (BA)
BA17
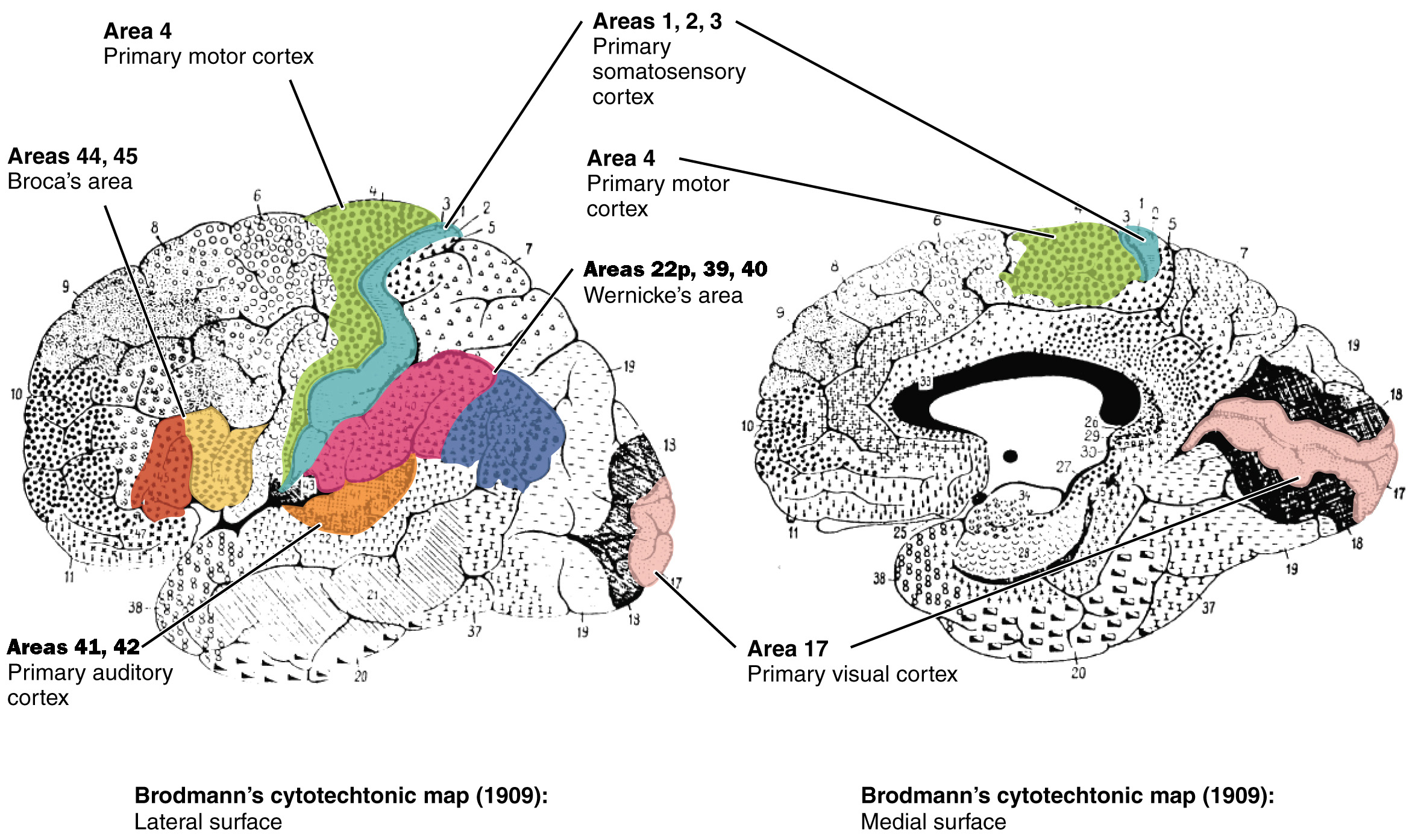
primary auditory cortex (BA)
BA41, BA42
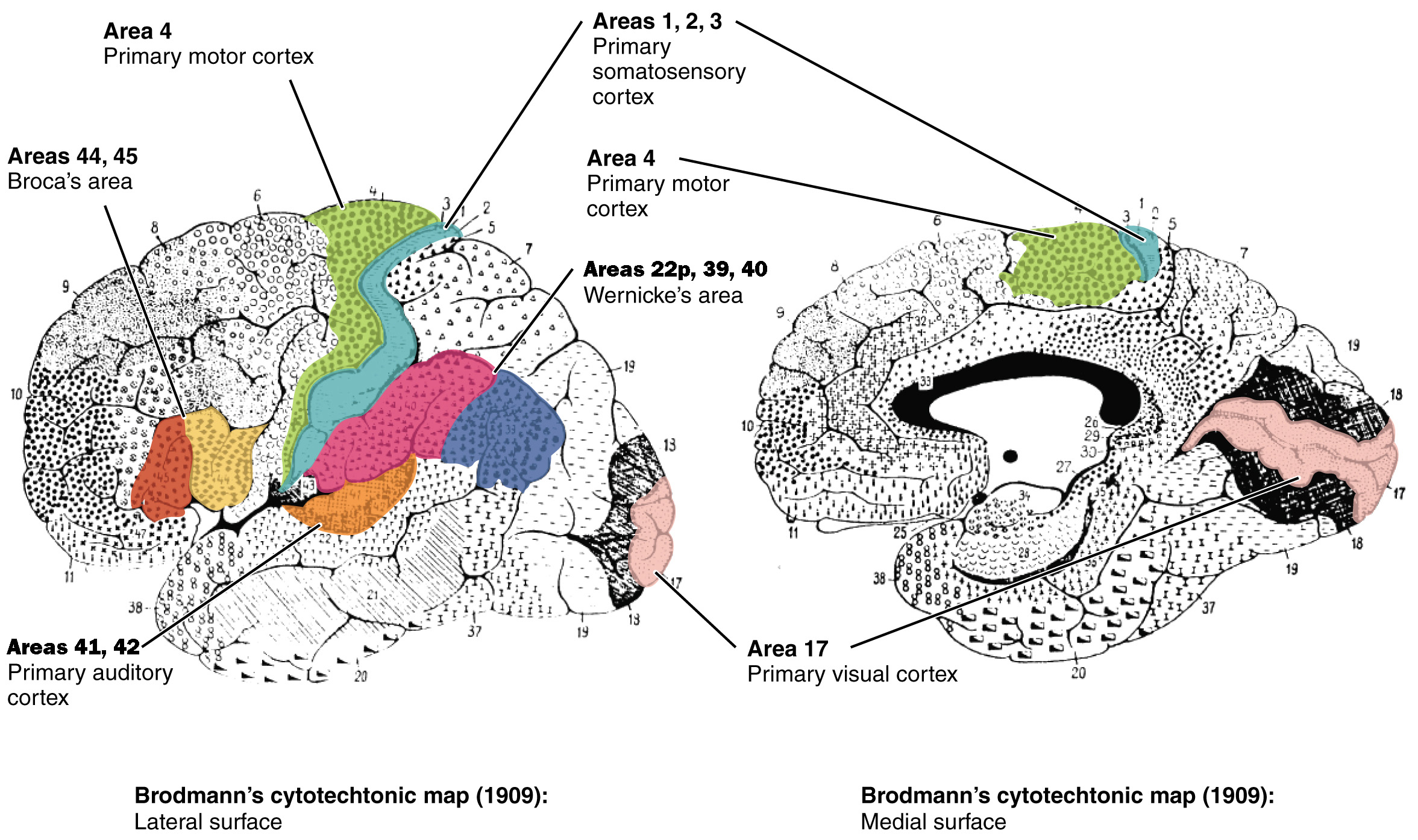
lateral fissure/lateral sulcus
deep groove in cerebral cortex, separates frontal and temporal lobes, above BA41 & BA42
BA44, BA45
Broca’s area (BA)
Broca’s aphasia
Have trouble physically speaking/getting words out, can understand speech
Wernicke’s aphasia
Speak fluently but words don’t make sense, can’t understand speech
Wernicke’s area (BA)
BA22p, BA39, BA40
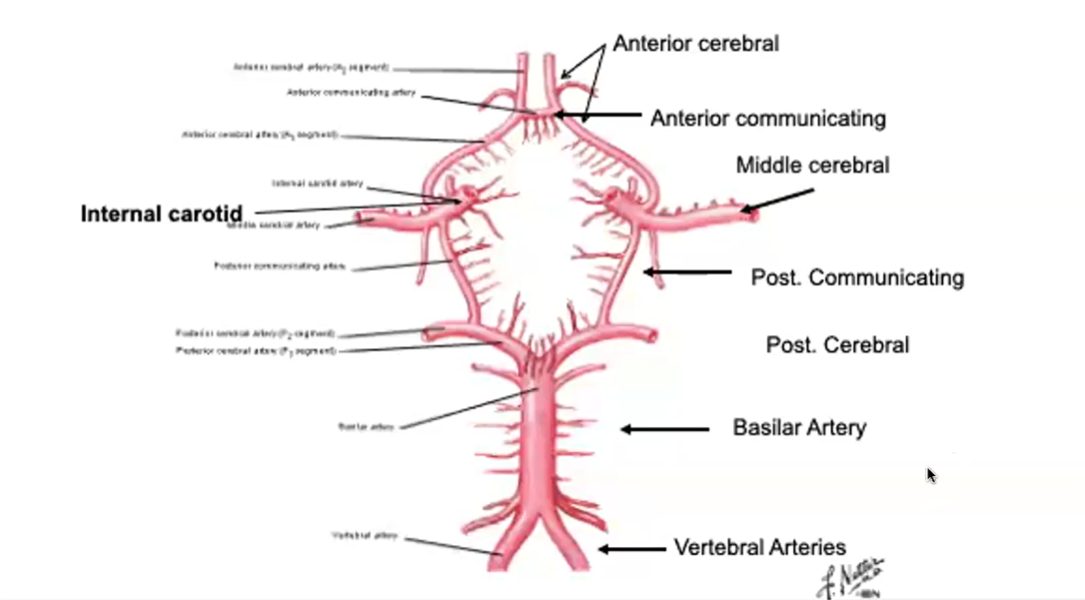
Internal Carotid Artery
Humans have one on each side of the neck. Deliver oxygen-rich blood to the brain. Split into two big artery pairs on each side: middle cerebral artery & anterior cerebral artery
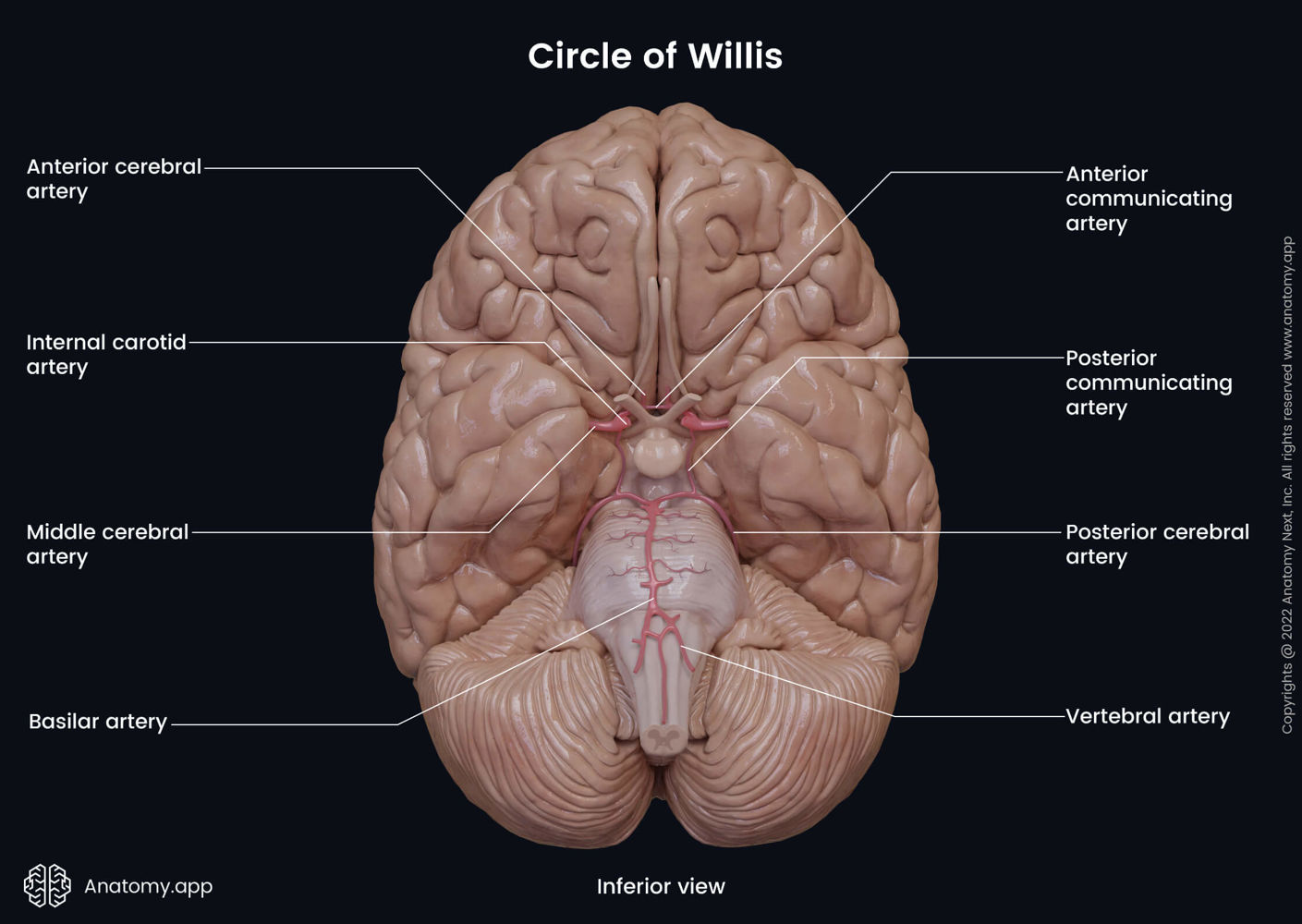
Middle Cerebral Artery supplies…
Travels to lateral side of the brain, where it supplies oxygen (surface). Goes through lateral fissure.
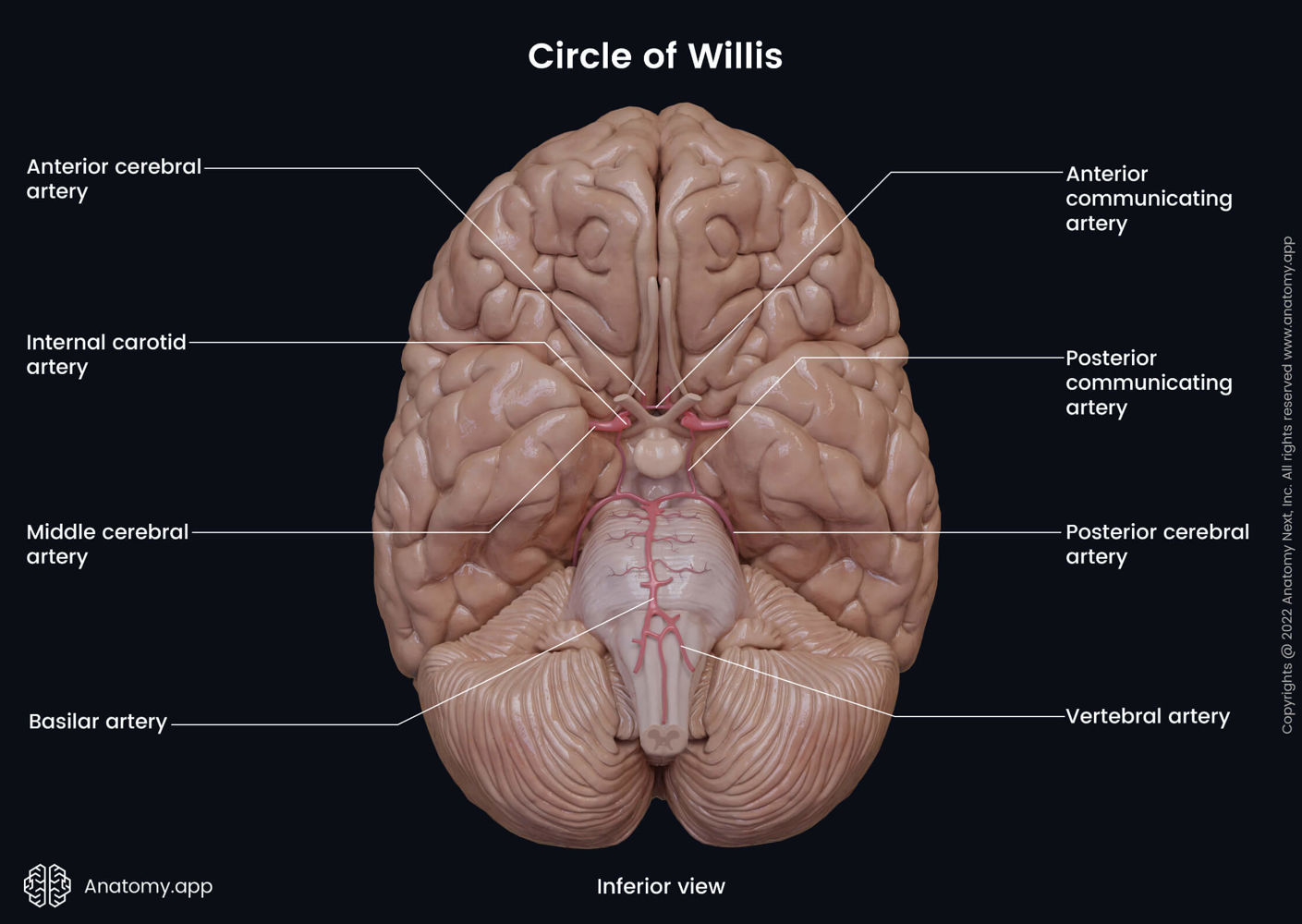
Anterior Cerebral Artery supplies…
Travels to anterior part of the brain, where it supplies oxygen. Goes through longitudinal fissure. Supplies oxygen to medial surface of cortex.
- very unlikely to have stroke (blood clot/blockage) in this artery
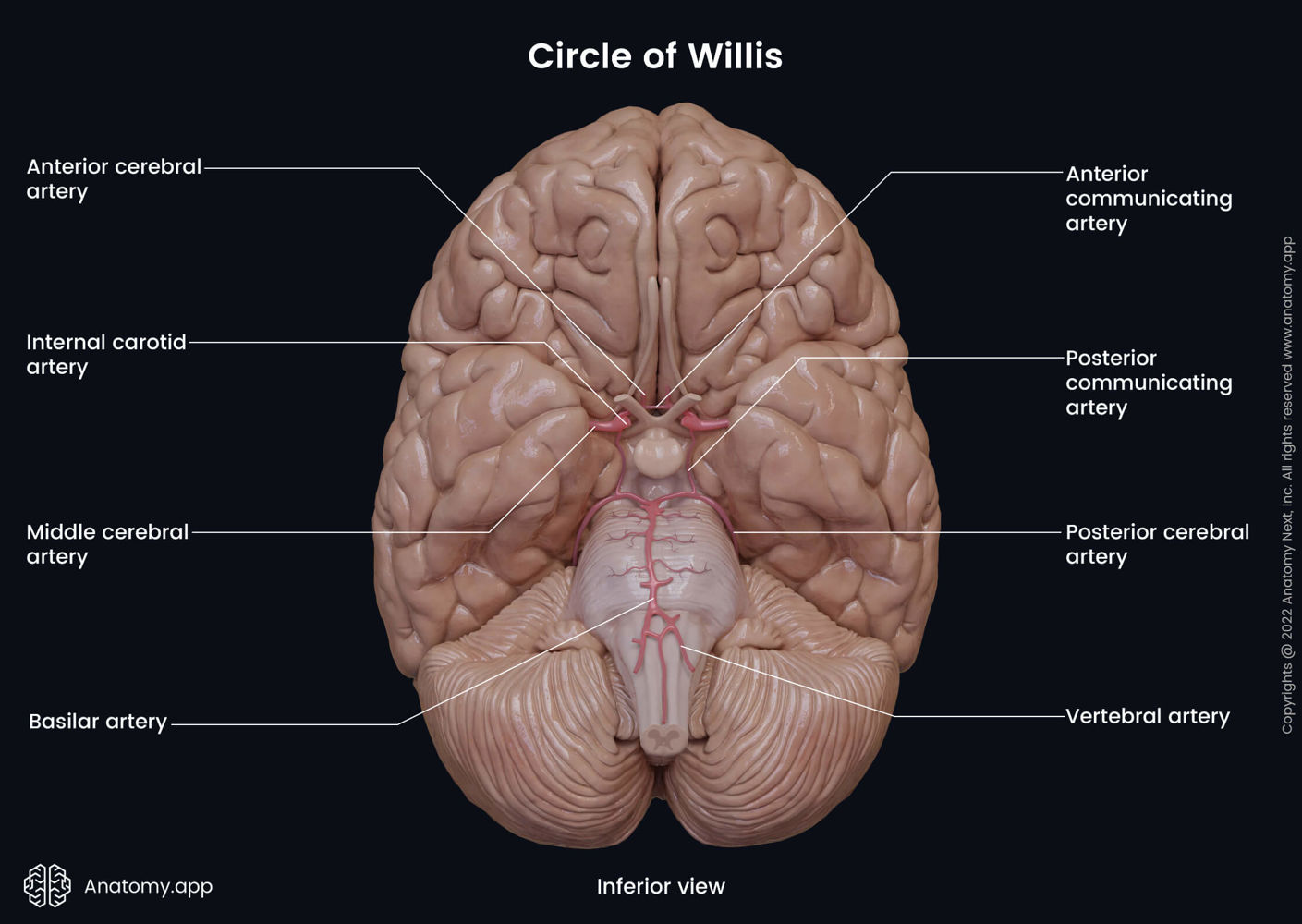
Anterior Communicating Artery
Connects the anterior cerebral arteries on both sides of the brain. Aka the arterial bridge.
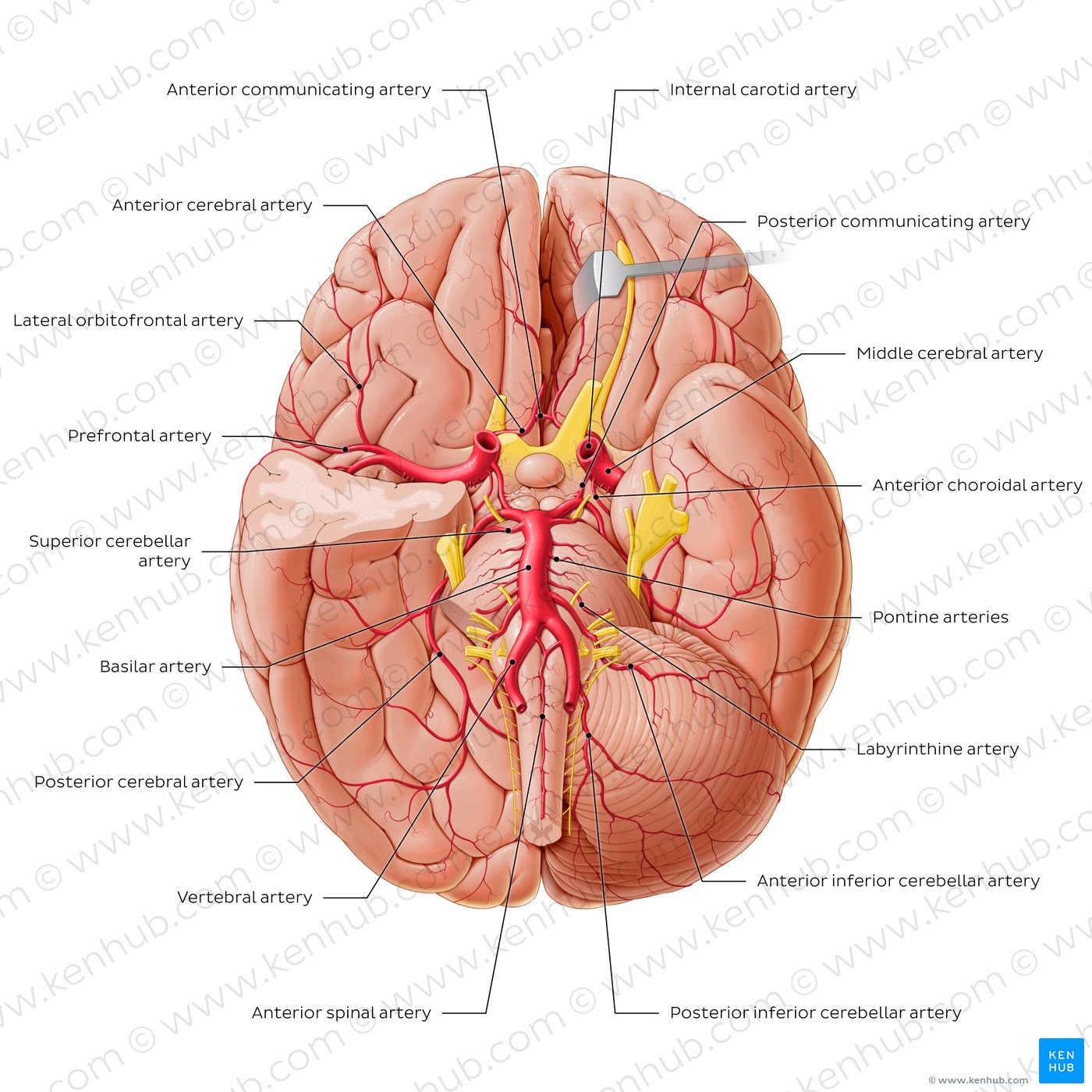
Vertebral Arteries
Another method of delivering oxygen-rich blood to the brain. Start as two and then fuse on the mid-line, creating the basilar artery.
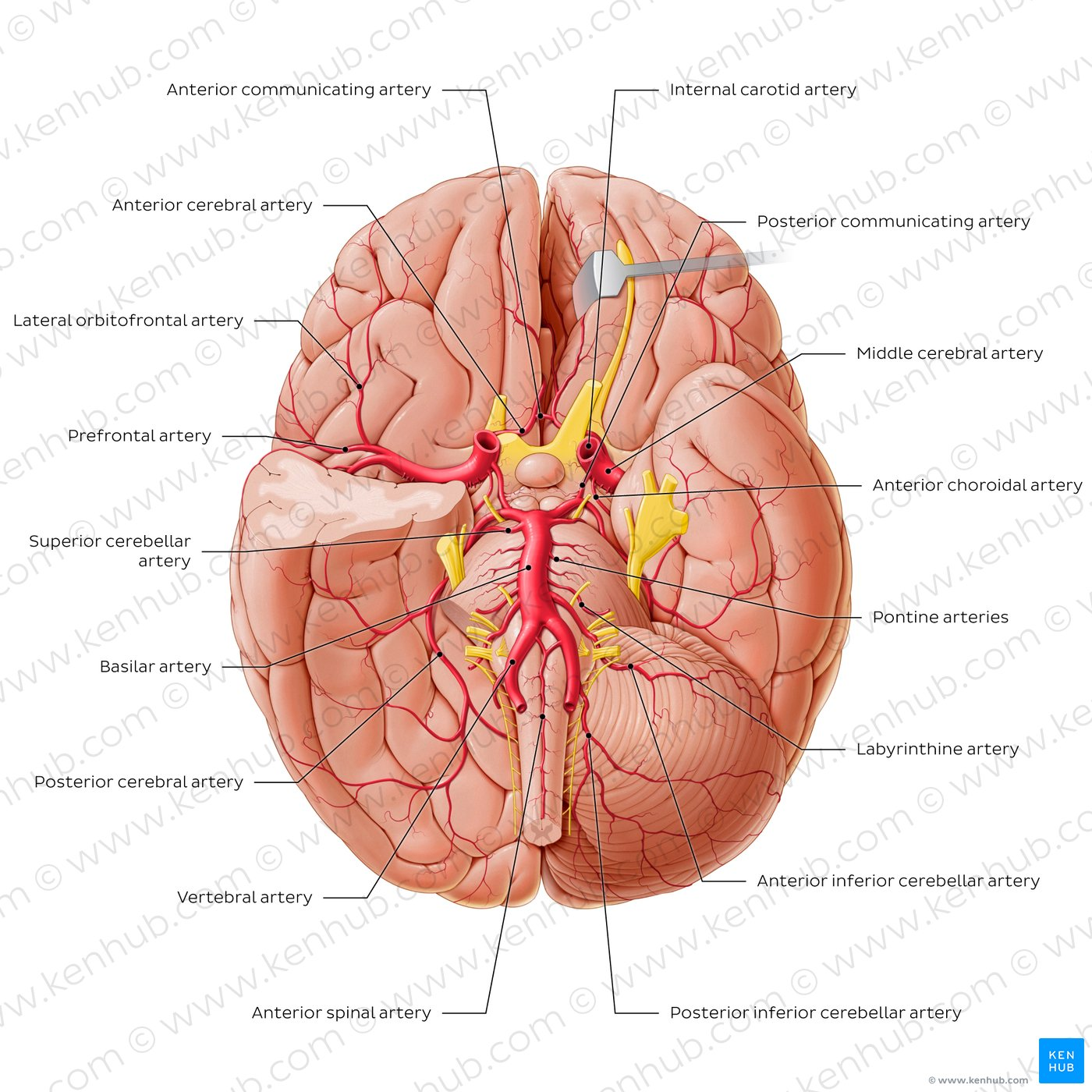
Basilar Artery
Splits into posterior cerebral arteries on both sides of the brain.
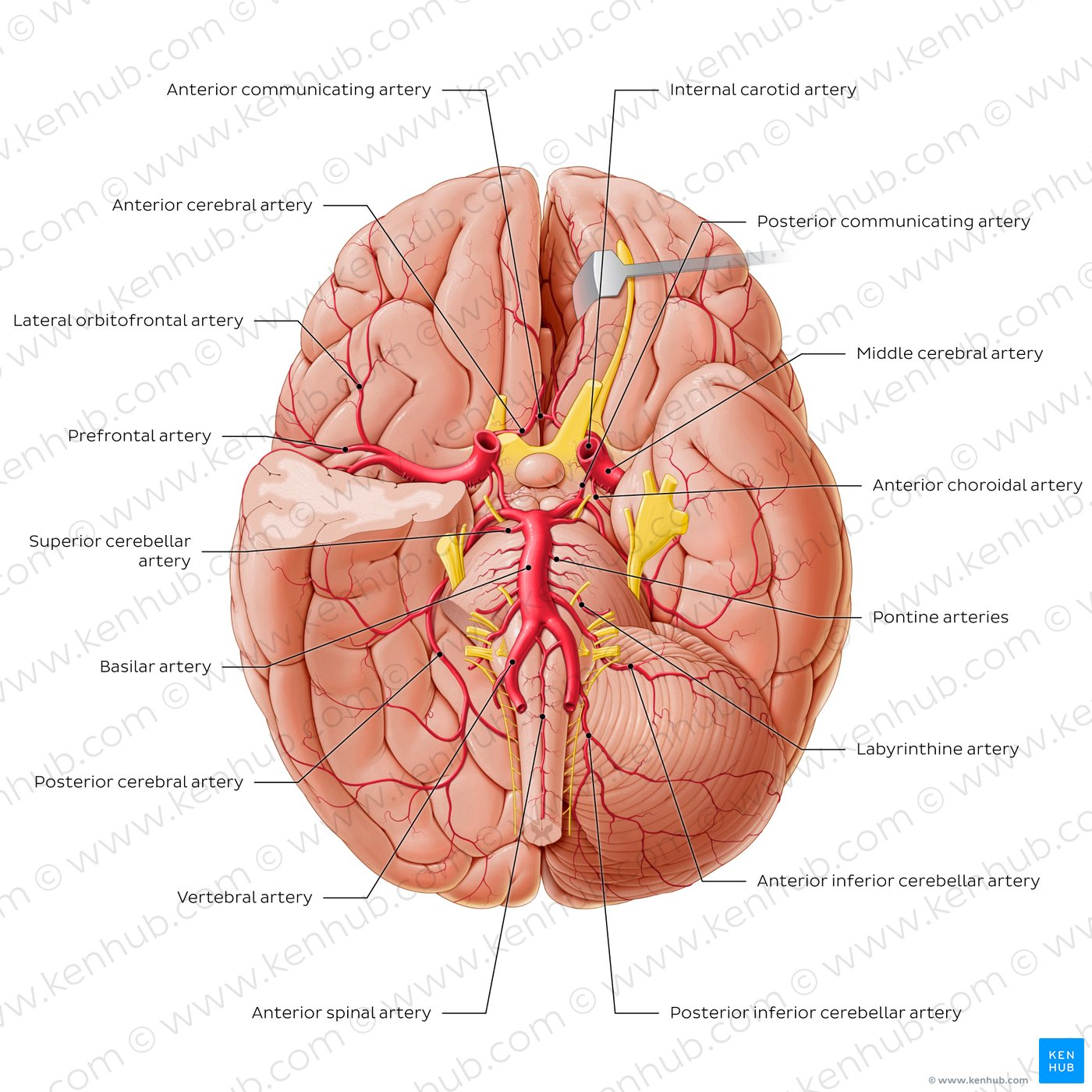
Posterior Cerebral Arteries supply…
occipital lobe, and inferior and medial part of temporal lobe (amygdala & hippocampus)
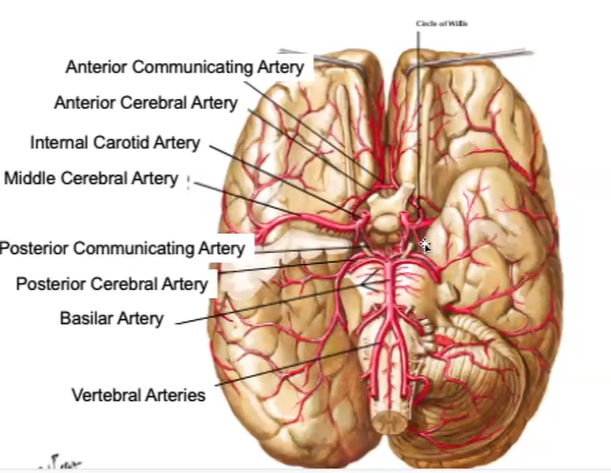
Posterior Communicating Artery
Connects internal carotid to posterior cerebral artery
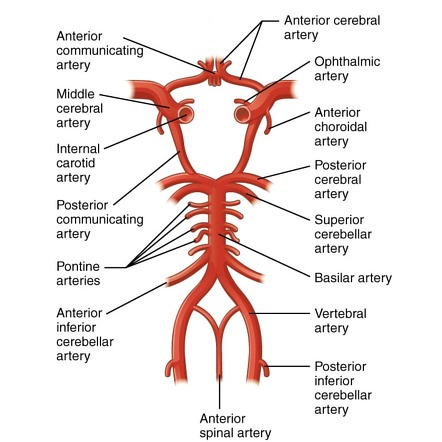
Circle of Willis
Aneurysm
bulging of the artery
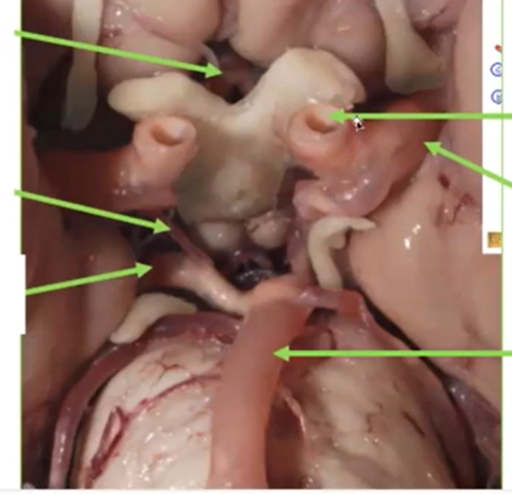
Aneurysms typically happen
at junctions in the circle of Willis. These are weak spots
Three cerebral arteries
Middle cerebral artery: cortex (frontal, parietal, temporal)
Posterior cerebral artery: occipital lobe, inferior temporal lobe (amygdala, hippocampus)
Anterior cerebral artery: prefrontal lobe, medial surface till occipital lobe
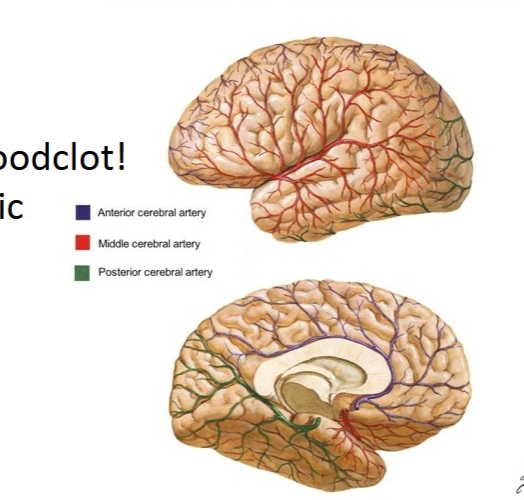
If Middle Cerebral Artery is blocked on left hemisphere…
Affected left hemisphere =
Broca’s area (left hemisphere)
Wernicke’s area (left hemisphere)
Temporal lobe
Motor cortex (on right side of body)
Somatosensory cortex (on right side of body)
If one Internal Carotid is blocked…
Person will have no symptoms because blood can just flow in through the other internal carotid and to the other sides with the anterior communicating artery
blood from basilar artery can go to side where carotid is blocked and supply that side and middle cerebral
Optic nerves vs. Internal corotid
Internal carotid is tube
Optic nerve is white tissue
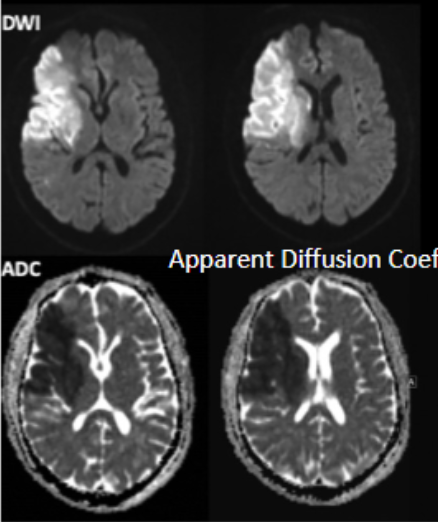
Ischemic
Stroke where blood clot plugs up an artery
brighter/darker section of brain on MRI/CT
Hemorrhagic
Stroke where there is bleeding in the brain
Shows up as big bright spot on MRI/CT
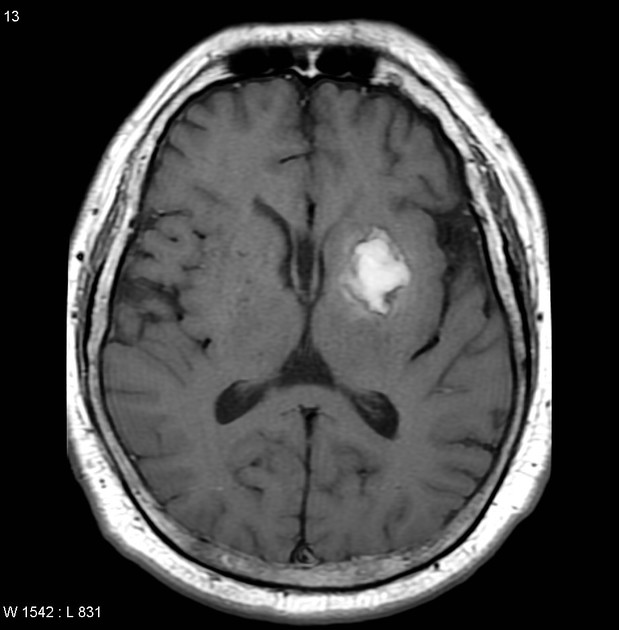
Aneurism
a bulge in the wall of a blood vessel, usually an artery, caused by a weakened area in the vessel wall
if it bursts = death
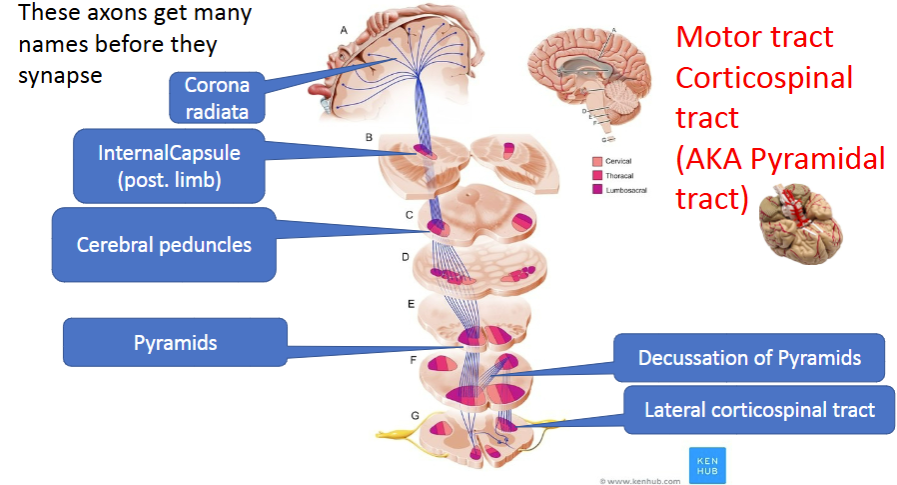
corticospinal tract function and OTHER NAMES
Cell bodies are in motor cortex in prefrontal gryus
Axons/synapse are in spine
aka pyramidal tract
aka motor tract
aka descending tract
CONTROLS MOTOR MOVEMENT
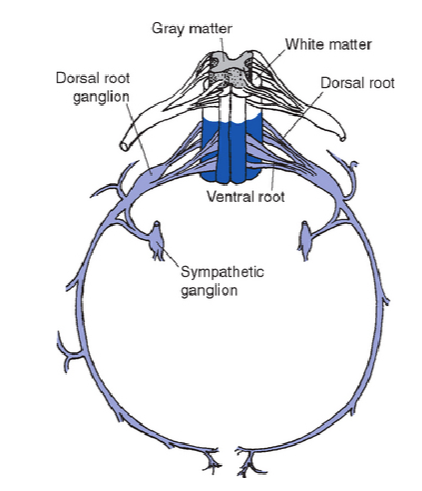
spinal roots
dorsal: “top,” cell bodies are in dorsal horn in spine, axons synapse somatosensory info to spine, AP starts at axons
ventral: “bottom,” cell bodies are in ventral horn in spine, axons leave spinal cord to synapse on muscles, AP starts at axon hillock
roots are the roads (axons) and they deliver signals to the horns
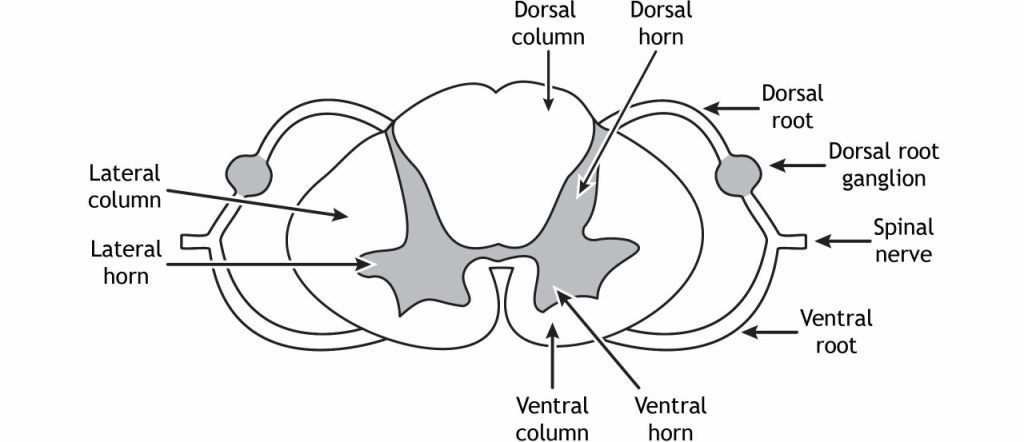
Spinal cord segments each have their own..
dorsal and ventral root
Names of axons in corticospinal tract
cerebral peduncles →
pons →
pyramids (in medulla)
Pons & Medulla