OB/GYN Final Exam Review
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
170 Terms
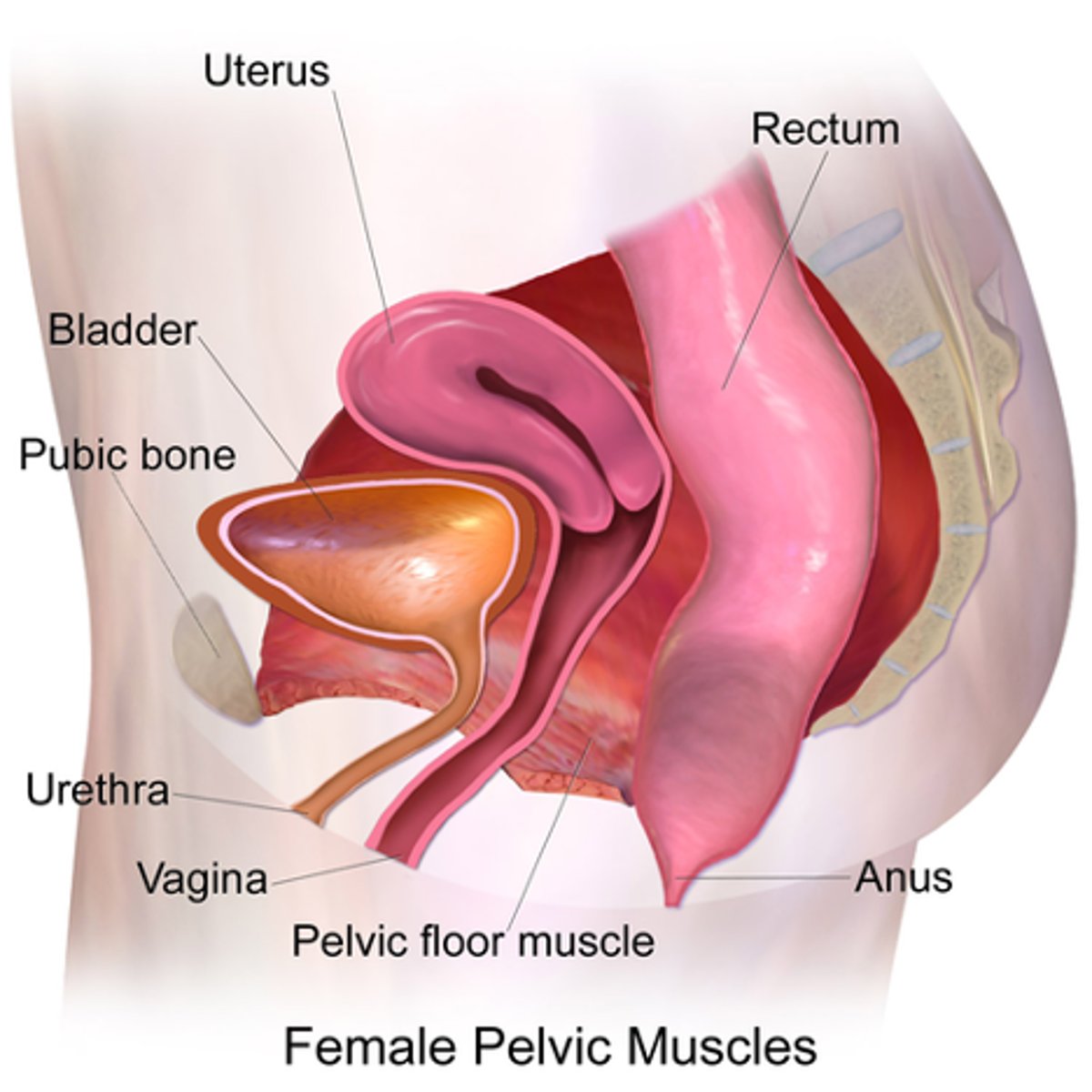
The female pelvis is in the ___ cavity
peritoneal
The pelvis extends from the ____ to the ____
iliac crests; pelvic diaphragm
What are the 3 layers of the uterine walls?
inner- endometrium
middle- myometrium
outer- serosa
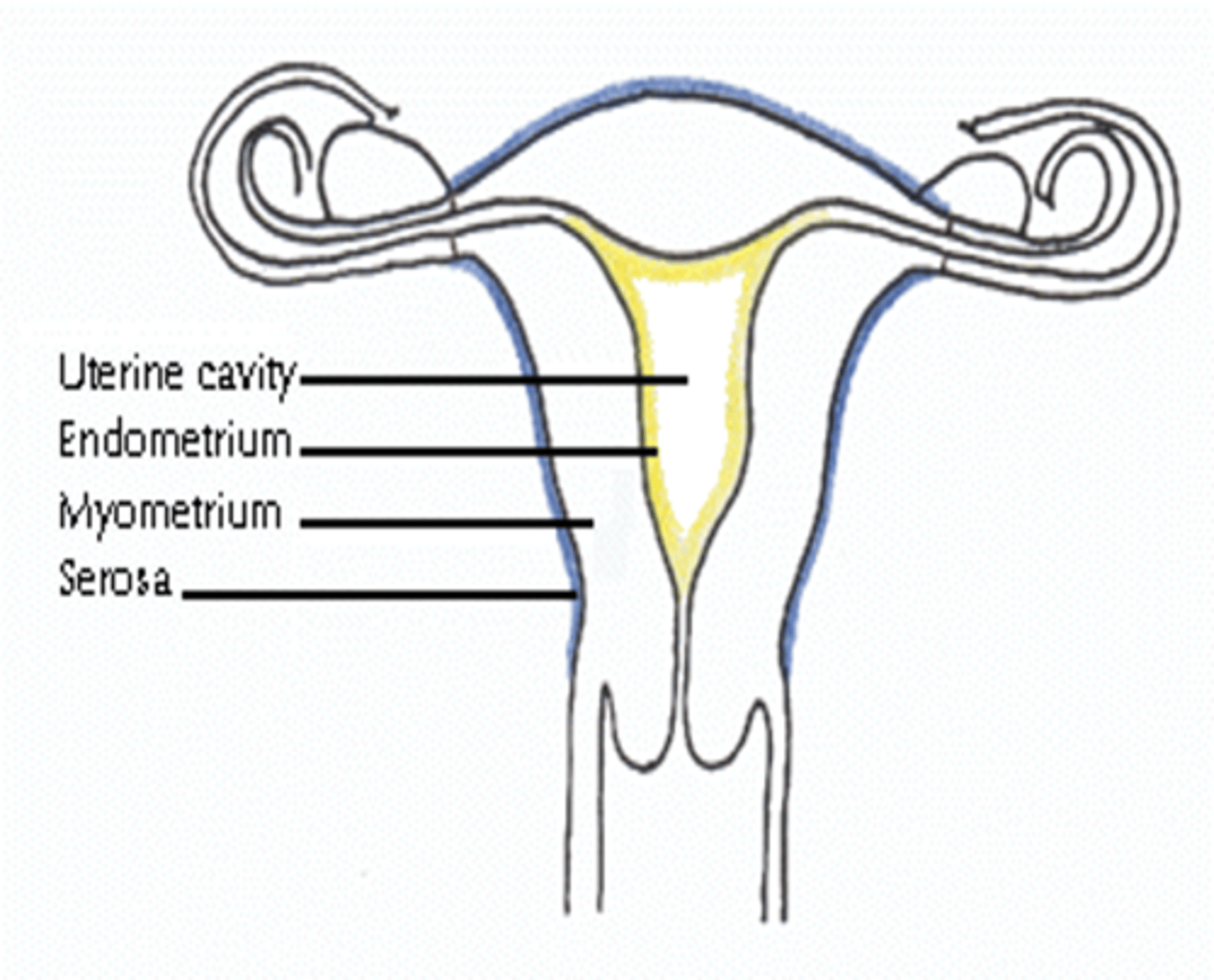
What is serosa also called?
perimetrium
The endometrial cavity is continuous with the ___
vaginal canal
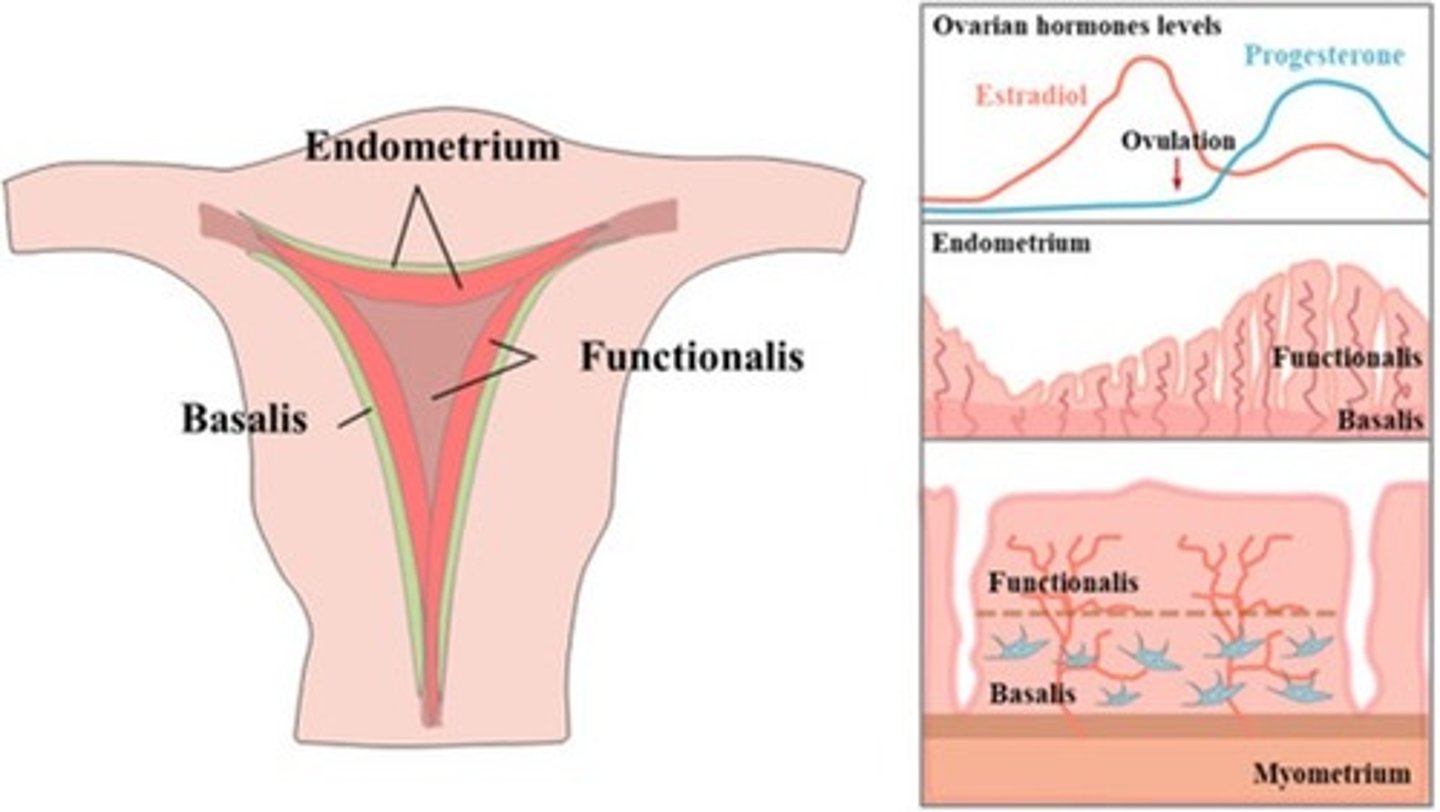
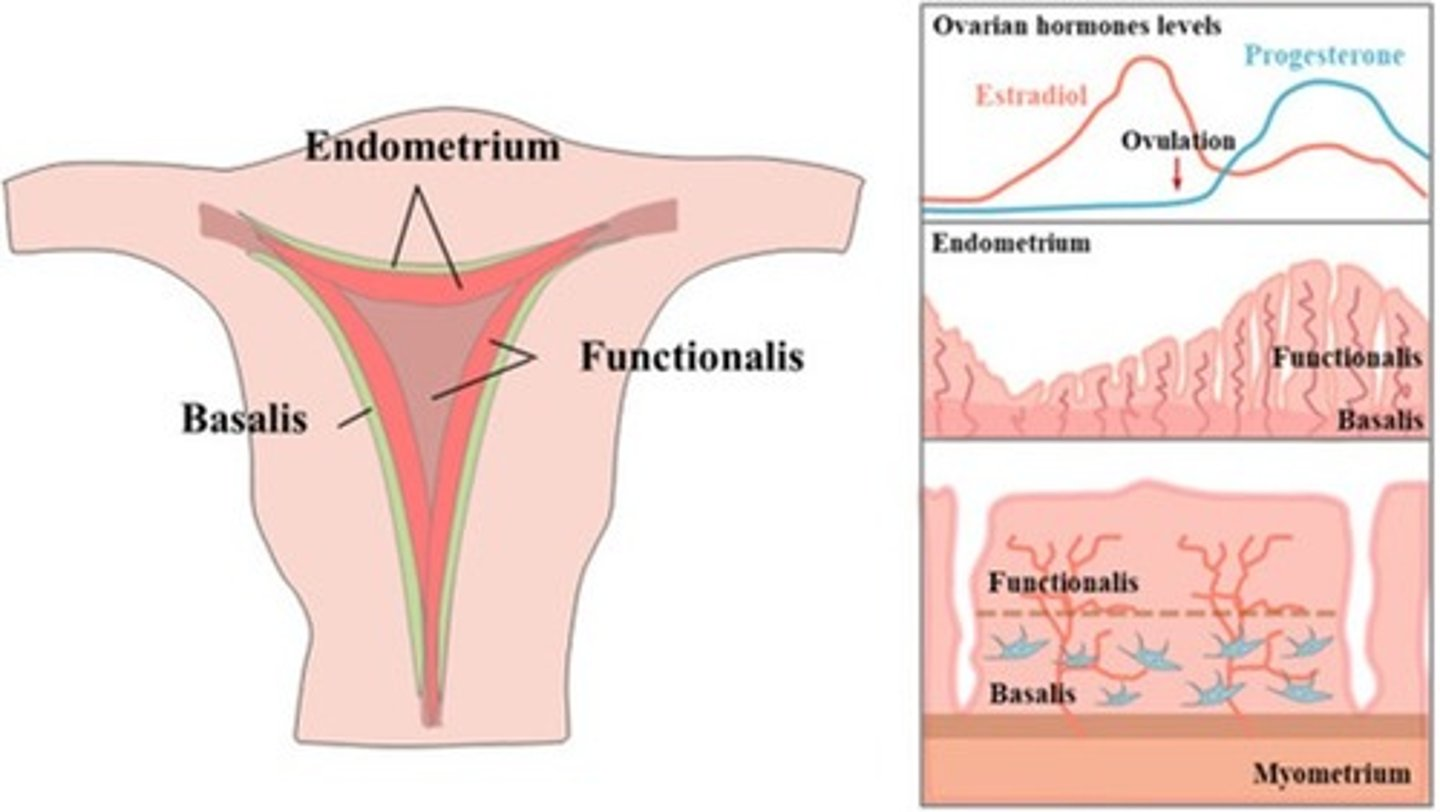
What are the 2 layers of the endometrium?
1. functionalis
2. basalis
The functionalis layer is a ___ layer that ___
superficial; sheds during menstrual cycle
The basalis layer is a ___ layer that is ___
deep; permanent
What is the widest and most superior part of the uterus?
fundus
What is the largest part of the uterus?
corpus / body
What is the uterine isthmus also called?
lower uterine segment
The cervix is ___ long
2 to 4 cm
Infantile / prepubertal uterus:
- length:
- width:
- thickness:
2.5 cm long
2 cm wide
1 cm thick
Postpubertal, nulliparous uterus:
- length:
- width:
- thickness:
7 to 8 cm long
3 to 5 cm wide
3 to 5 cm thick
Multiparous uterus:
- length:
- width:
8.5 cm long
5 cm wide
In a postmenopausal uterus, size significantly ___ and the uterus assumes a ___ shape again
decreases; prepubertal
Verted = ___
Flexed = ___
tilt
bend
What is the most common uterine position?
anteverted
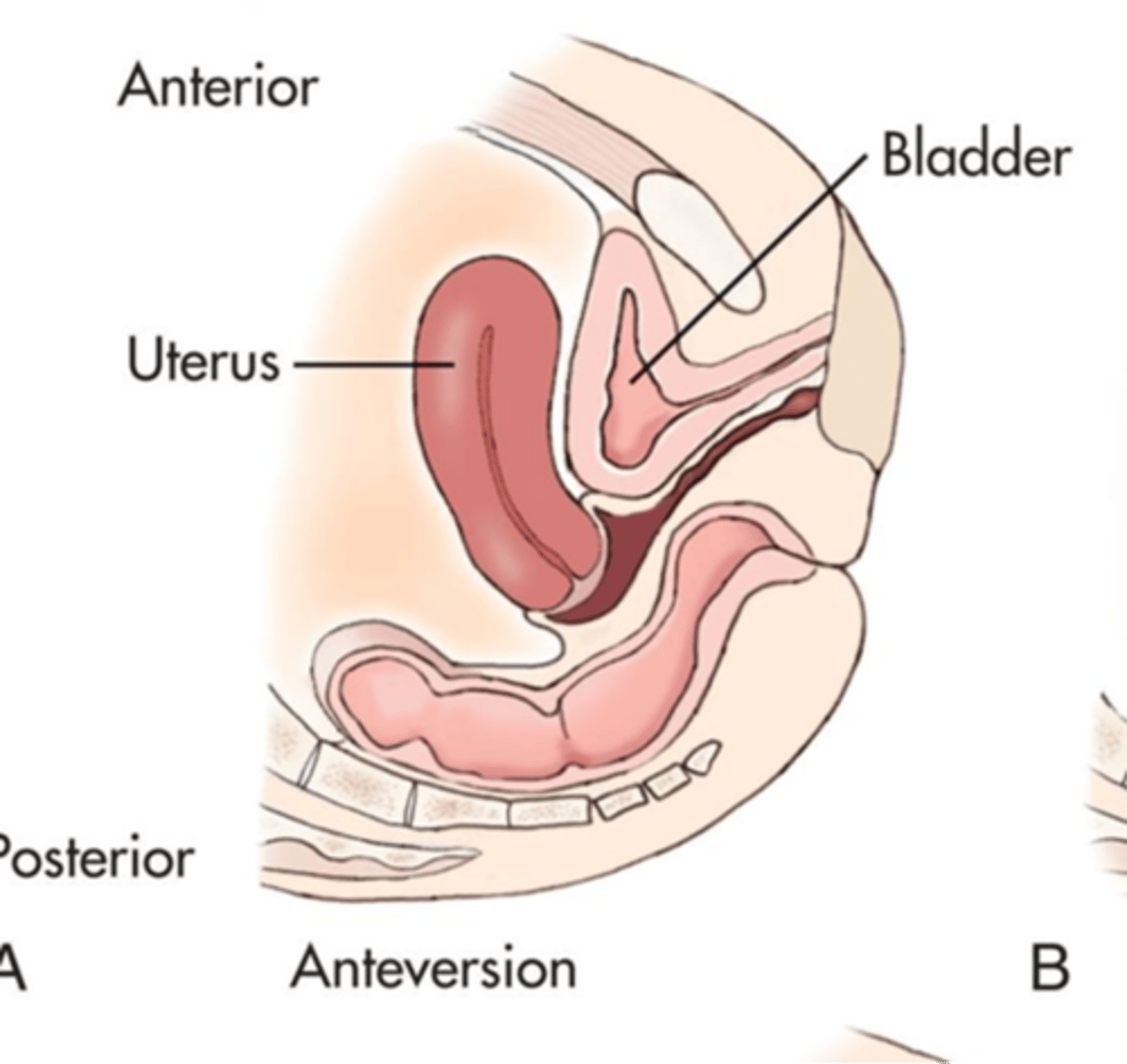
What is an anteverted uterus?
fundus and body tilt forward, cervix and vagina form 90 degree angle
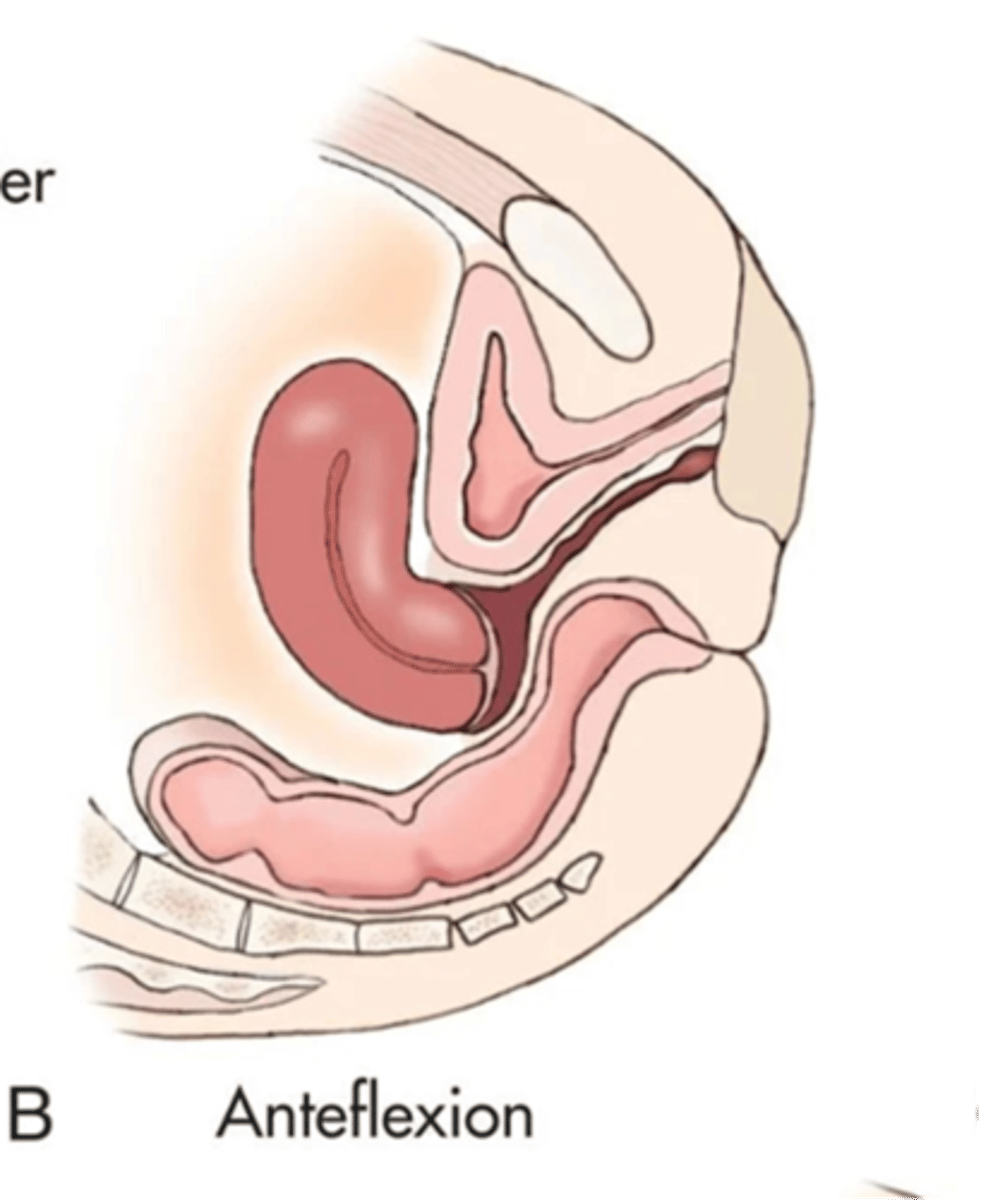
What is an anteflexed uterus?
fundus and body bend forward, cervix and vagina form 90 degree angle
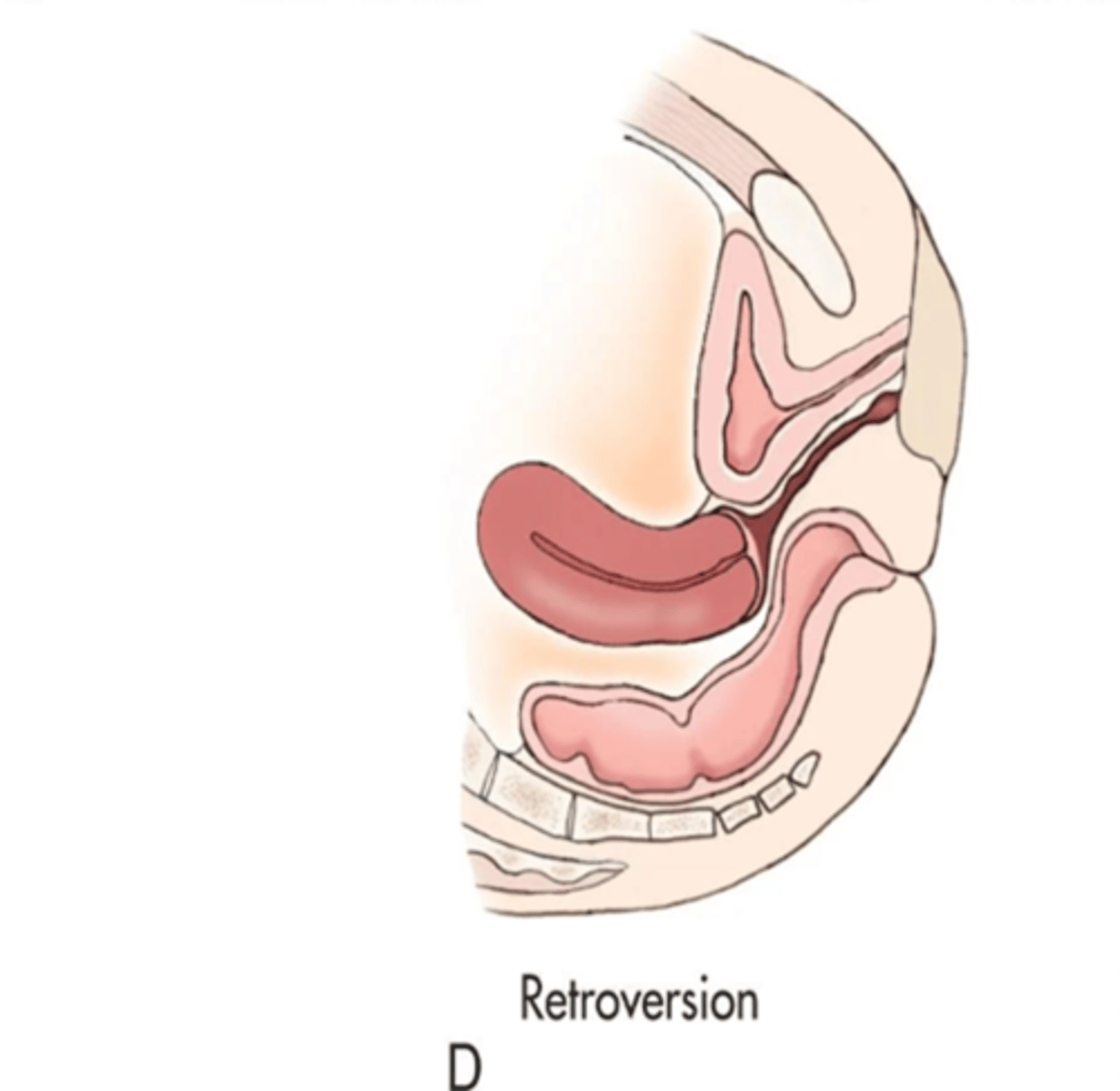
What is a retroverted uterus?
fundus and body tilts backward, fundus and vagina are aligned
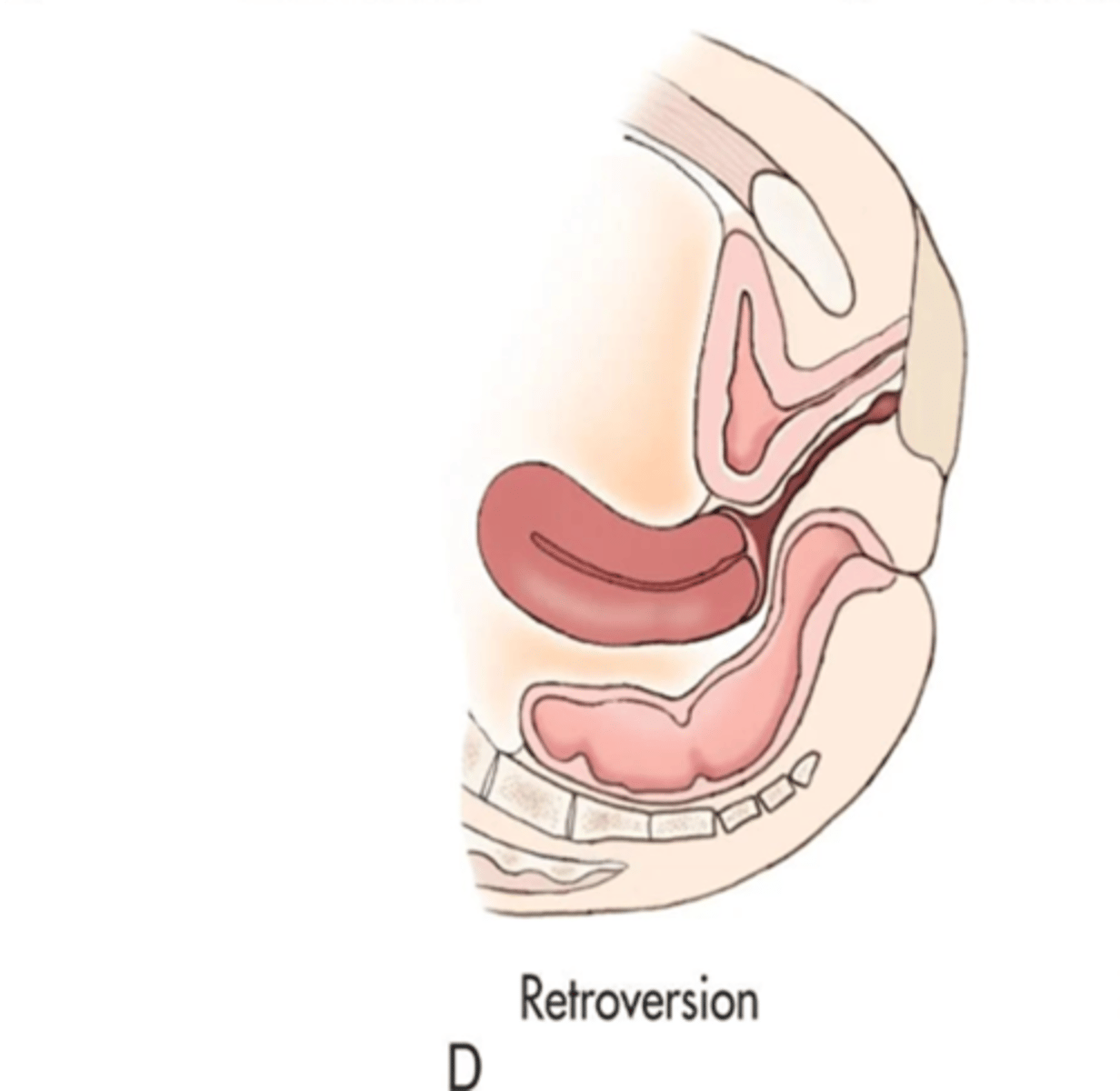
A retroverted uterus is common with ___
multiparity
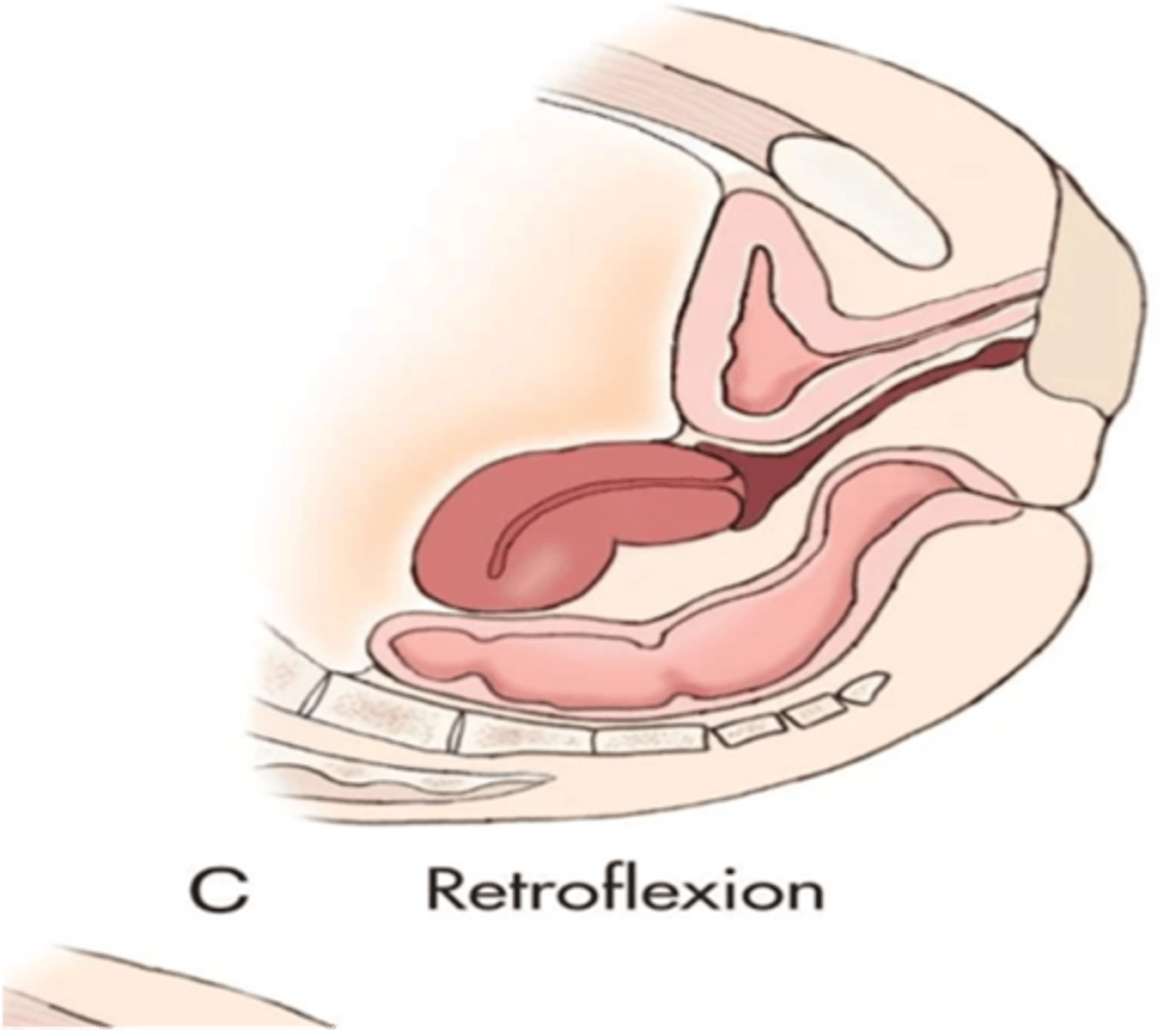
What is a retroflexed uterus?
body and fundus bend backward; fundus is adjacent to cervix and points down
What uterine condition is seen when only one malarian is formed?
unicornuate uterus
What are fallopian tubes also called?
uterine tubes
oviducts
The fallopian tubes are ____, muscular tubes
coiled
The fallopian tubes emerge from the ____ margins of the uterine cornua
superolateral
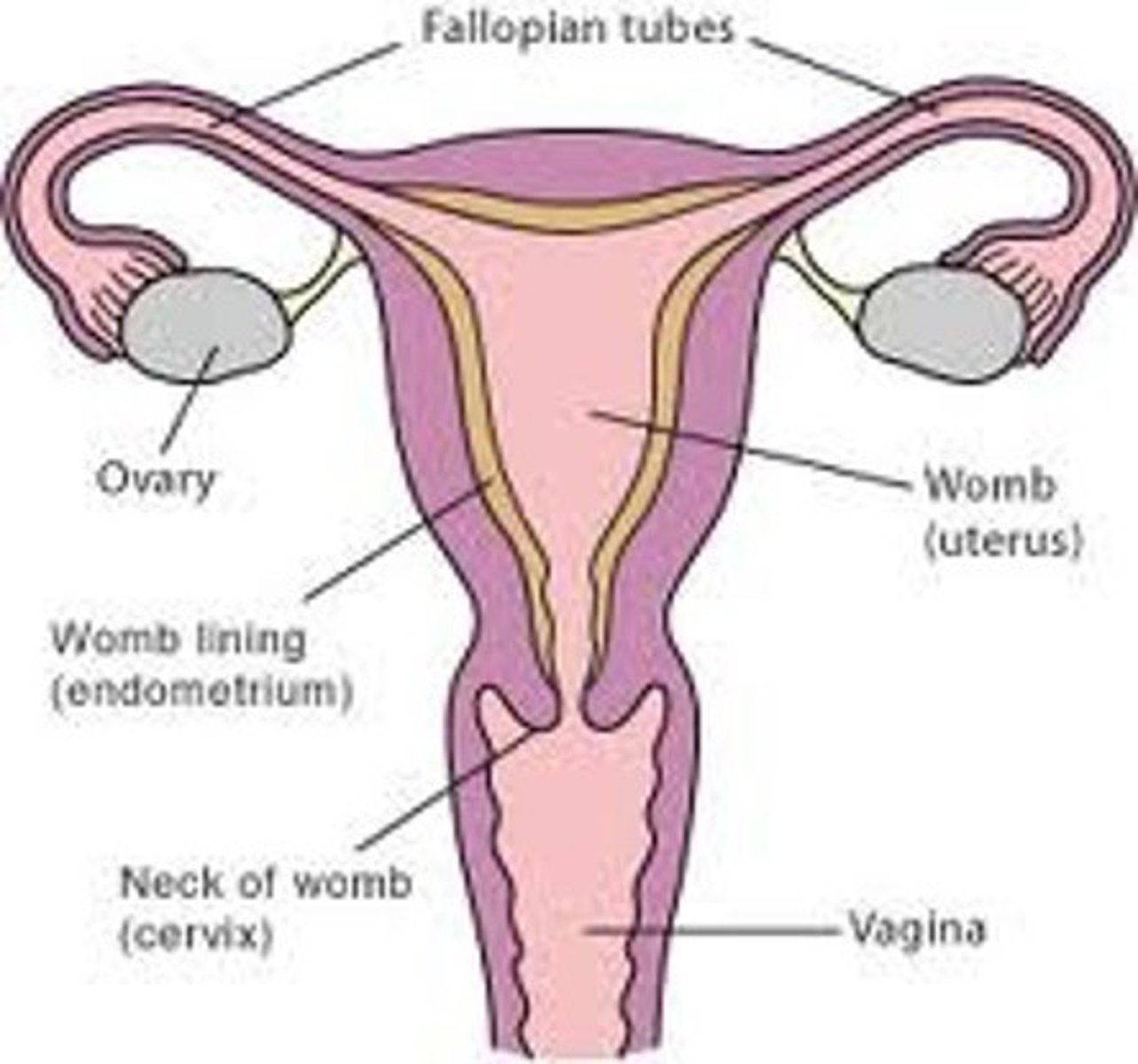
The fallopian tubes direct mature ___ to the ___ through ___
ovum; uterus; peristalsis
The fallopian tubes are ___ long with a diameter of ___
10 to 12 cm
1 to 4 mm
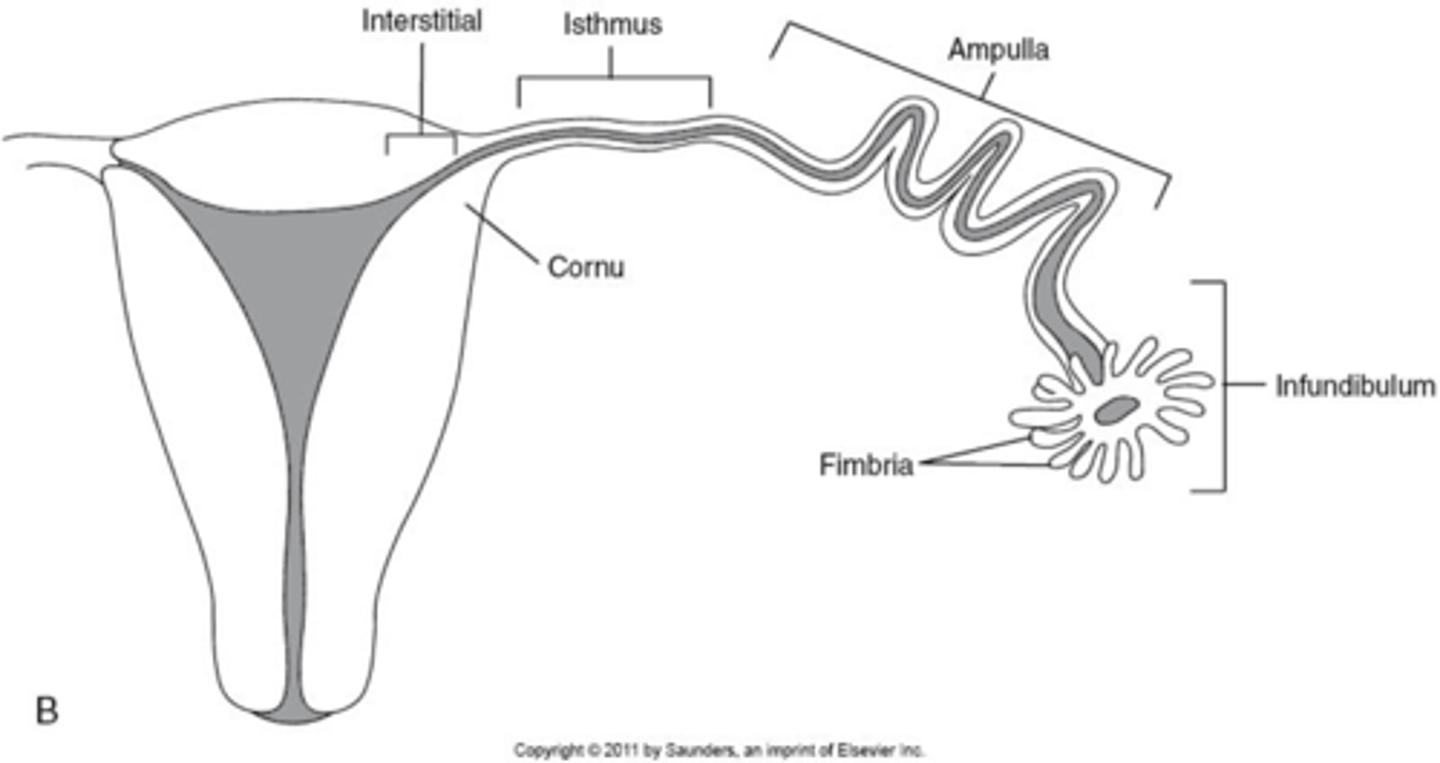
What are the 4 segments of the fallopian tubes?
1. interstitial
2. isthmus
3. ampulla
4. infundibulum

What part of the fallopian tube is the widest segment where fertilization occurs?
ampulla
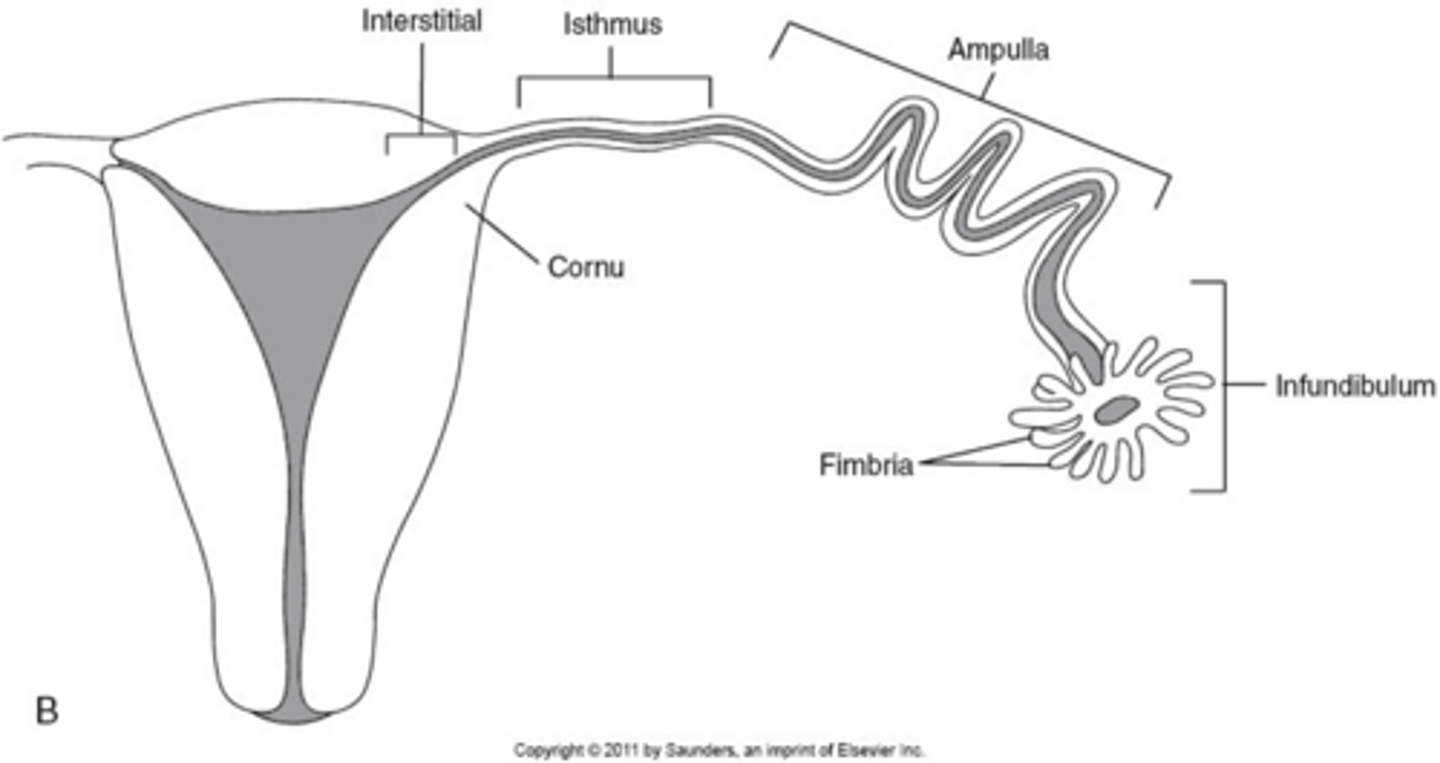
What part of the fallopian tube is the most dangerous to have an ectopic pregnancy?
interstitial bc most vascular
Ovaries are located in the ___ within the ___
adnexa; true pelvis
Ovaries are ___ to the internal iliac arteries and ___ to ureters
medial; anterior
Ovary size varies depending on patient:
age
menstrual cycle phase / status
Ovaries are ___ at birth with little change until age ___
large; 5-6
Prepubertal ovaries have a volume of ___
3 mL
Postpubertal ovaries are ___ long, ___ wide, and ___ thick
3 x 2 x 2
Postpubertal ovaries have a volume of ___
9.8 mL
Postpubertal ovaries volume ___ during ovulatory phase and ___ during luteal phase
increase; decrease
Postmenopausal ovaries have a volume of ___
5.8 mL
How do you find the volume of ovaries?
length x width x height x 0.5
Psoas muscles extend from the ___ aspects of the lumbar vertebrae across the ___ abdominal wall to the ___
lateral; posterior; iliac crest
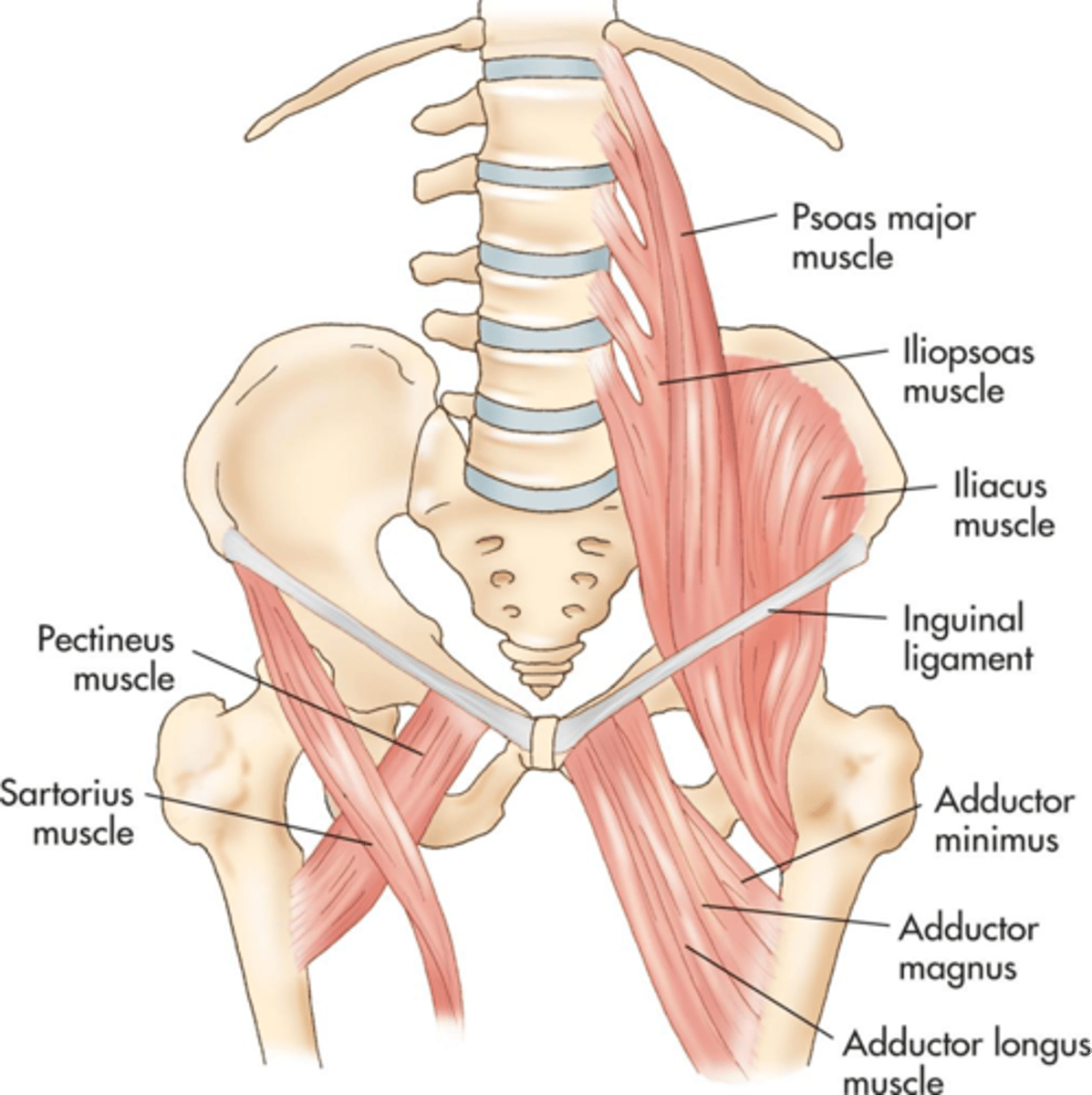
Illiopsoas muscles travel ___ from the psoas to insert into the ___ of the femur
anteroinferior; lesser trochanter
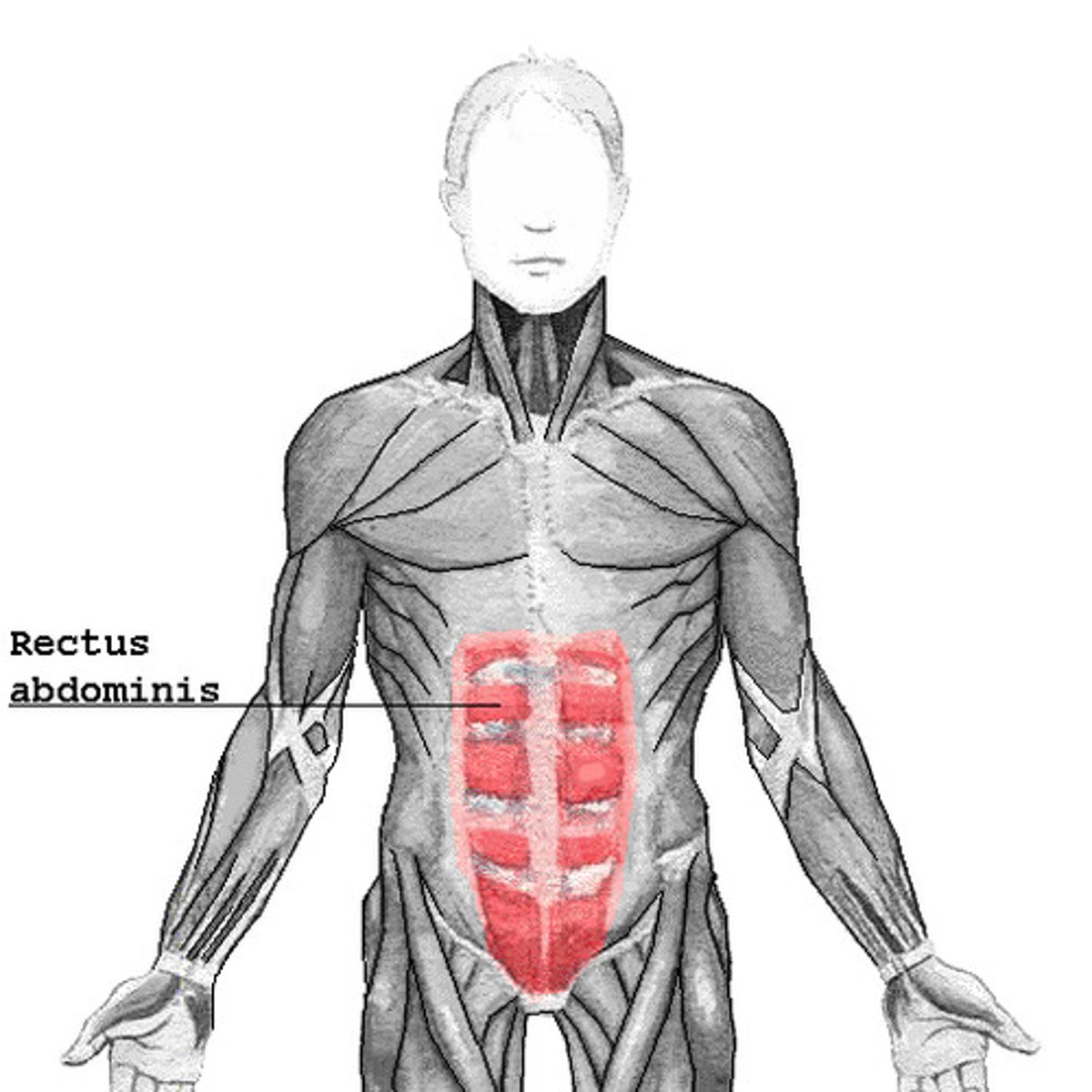
Rectus abdominis muscle extends from the ___ and ___ down to the ___
6th rib; xiphoid; pubis symphysis
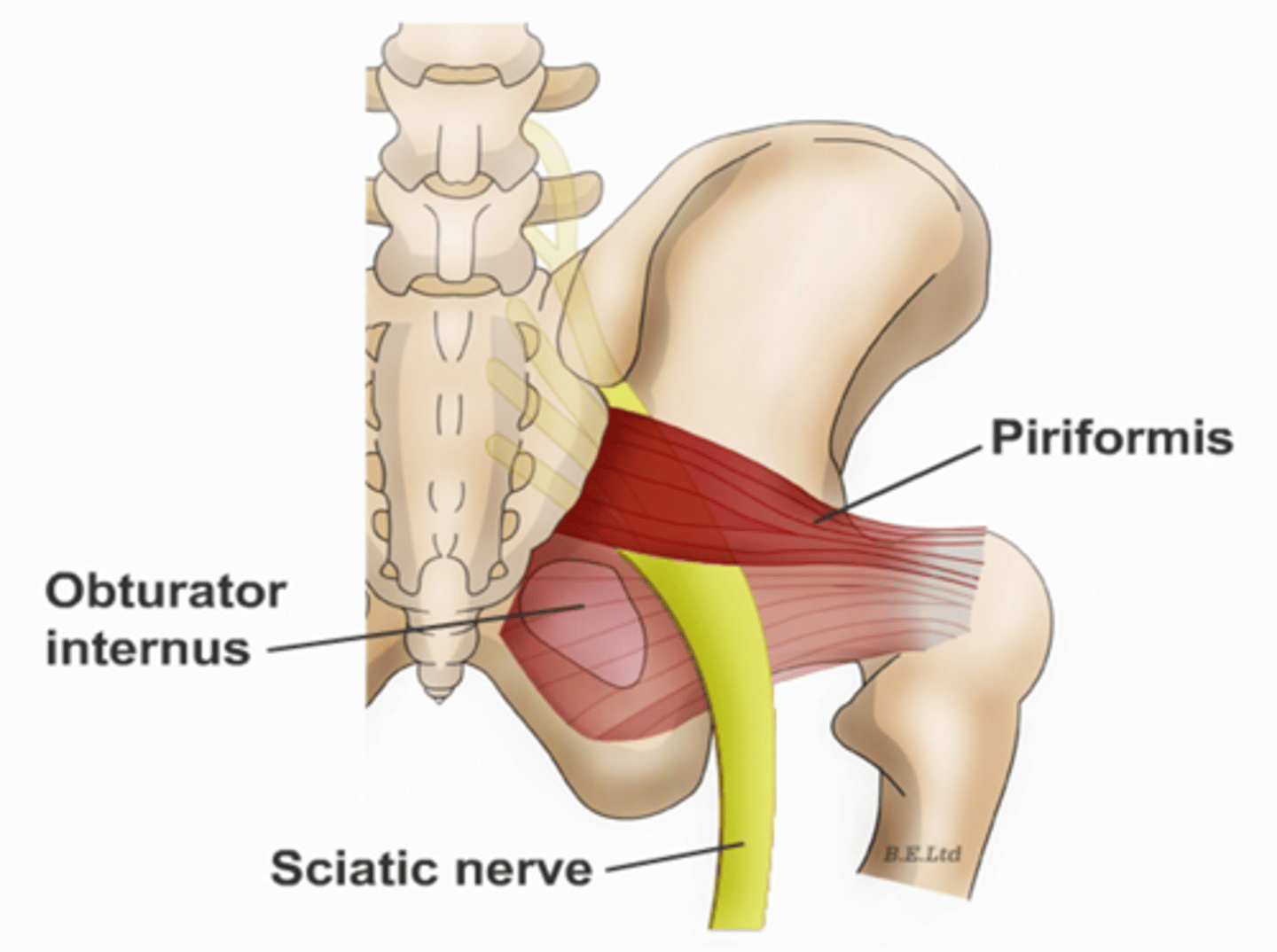
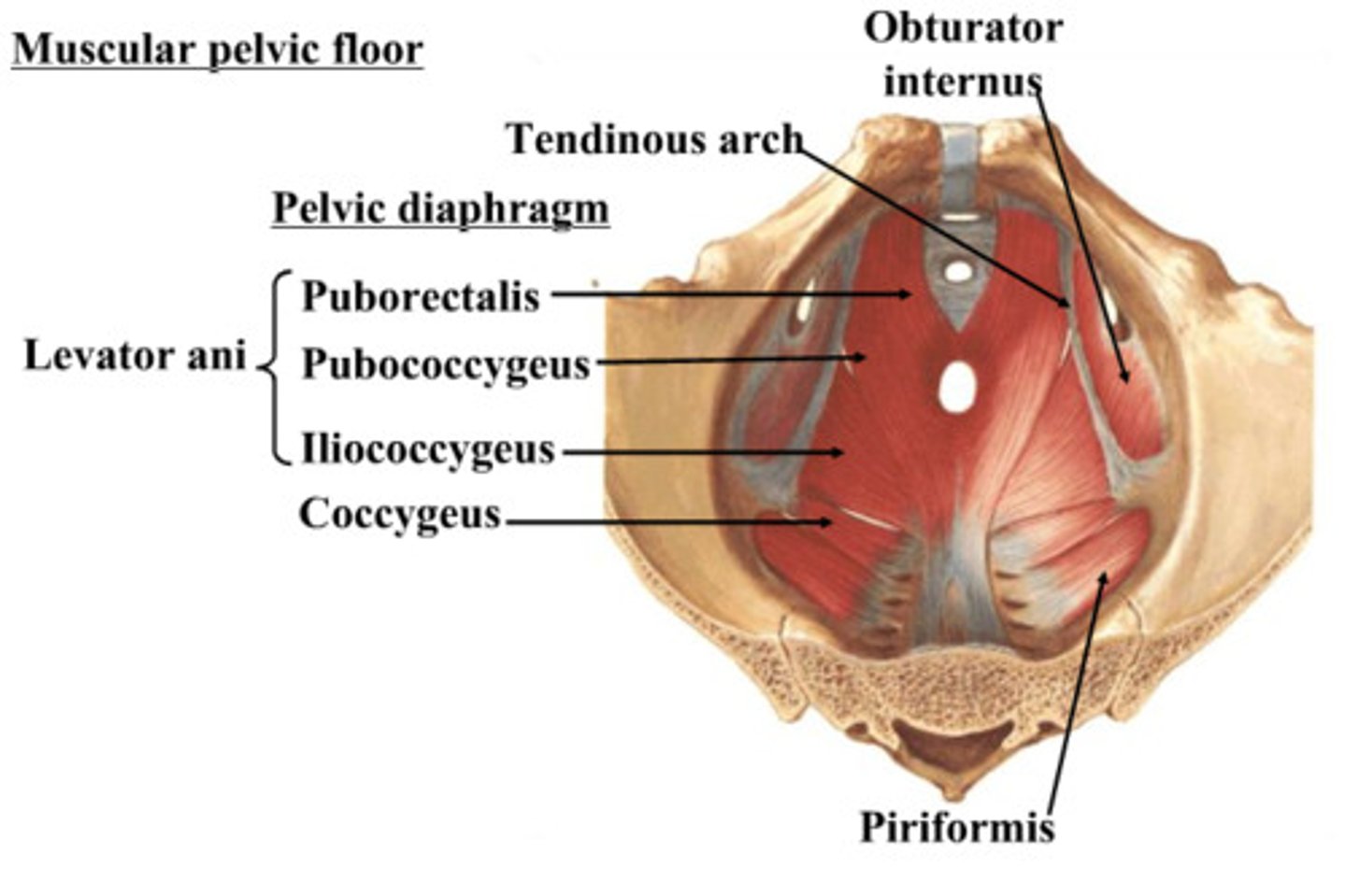
Obturator internus muscles line the ___ walls of the true pelvis
lateral
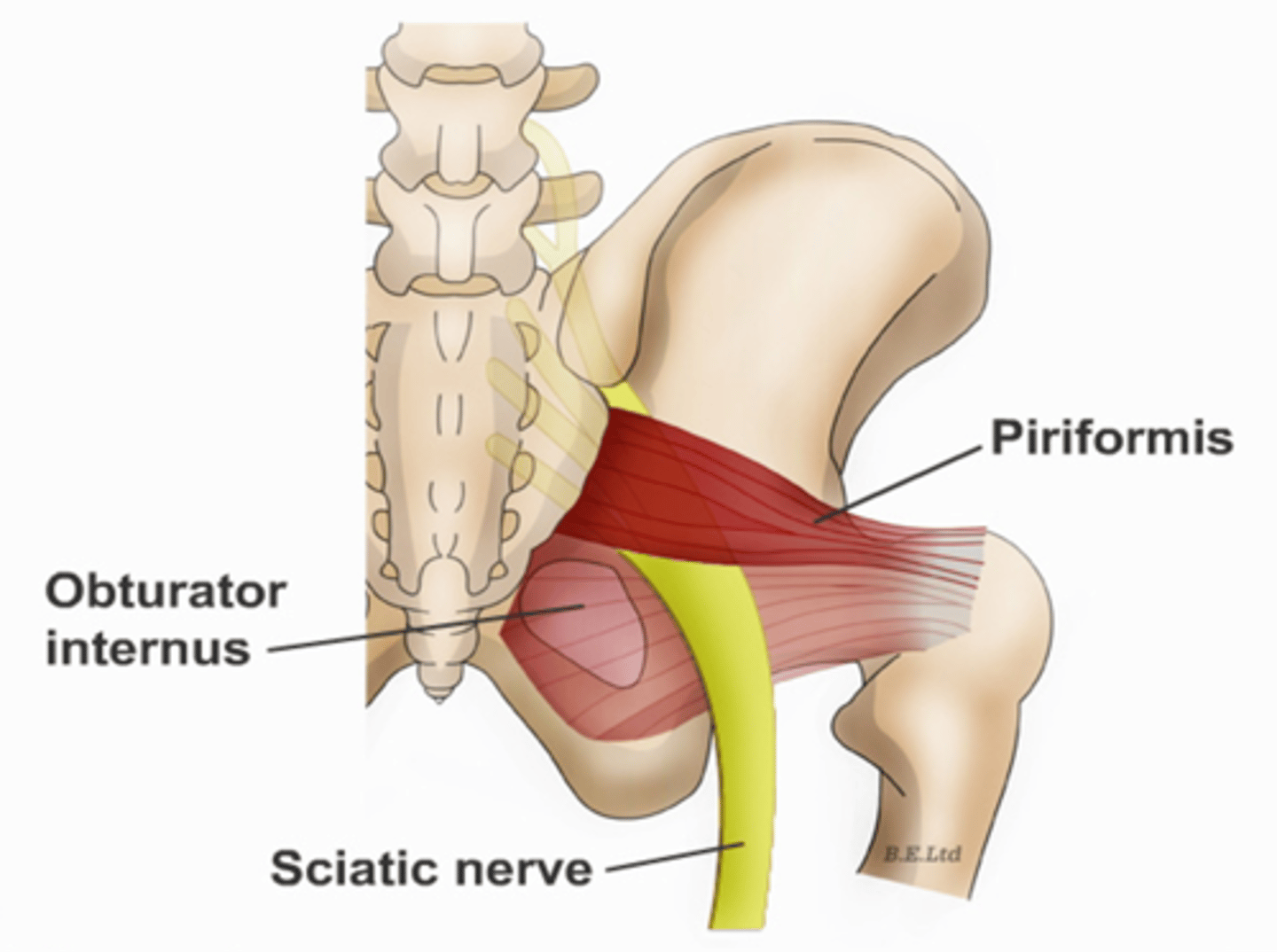
Piriformis muscles are in the ___ region of the true pelvis behind the ___
posterior; uterus
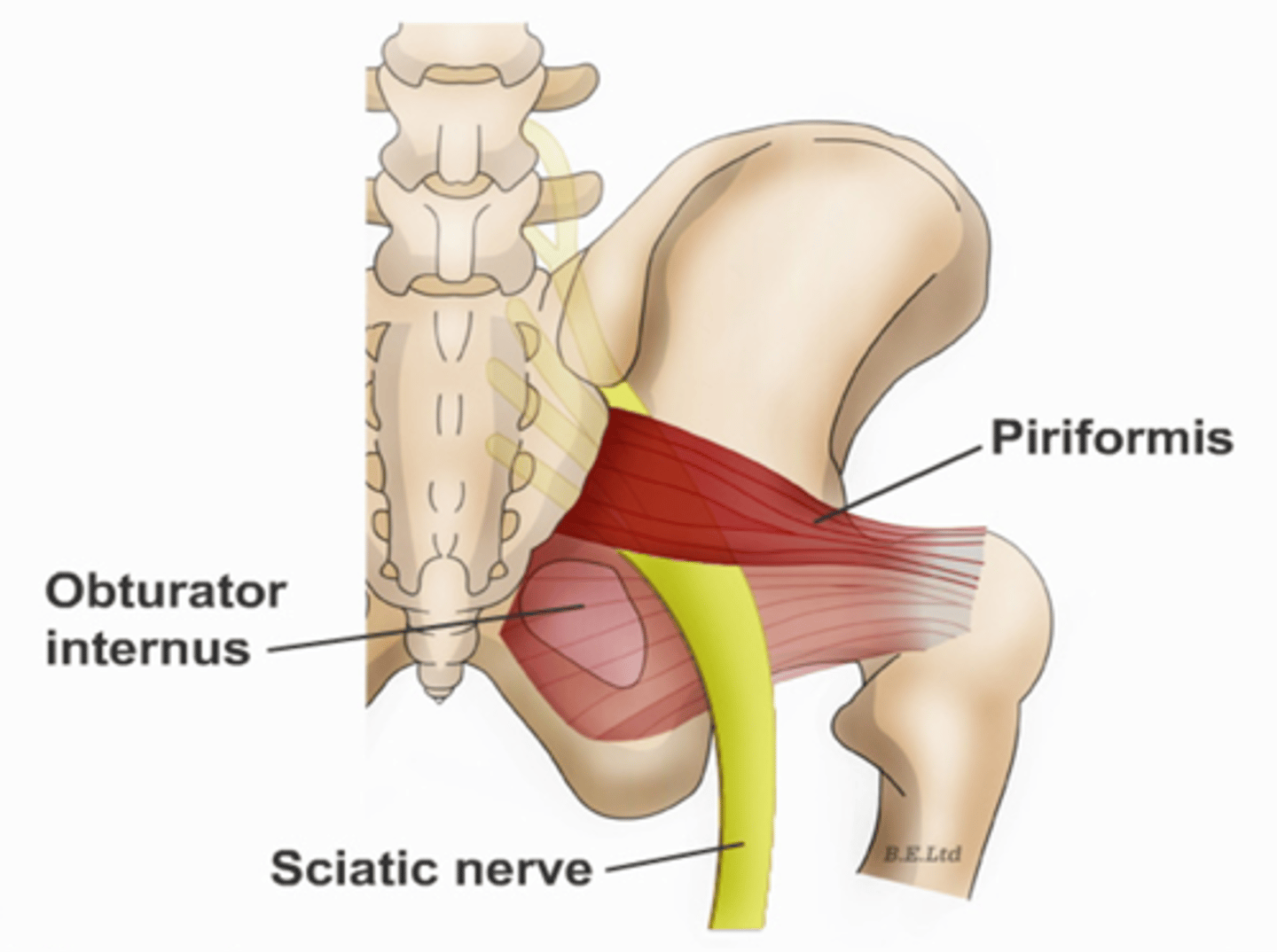
What muscle is often mistaken for ovaries?
piriformis
What are the 3 levator ani muscles?
pubococcygeus
iliococcygeus
puborectalis
The broad ligaments extend between the ___ and ___
uterine body; ovary
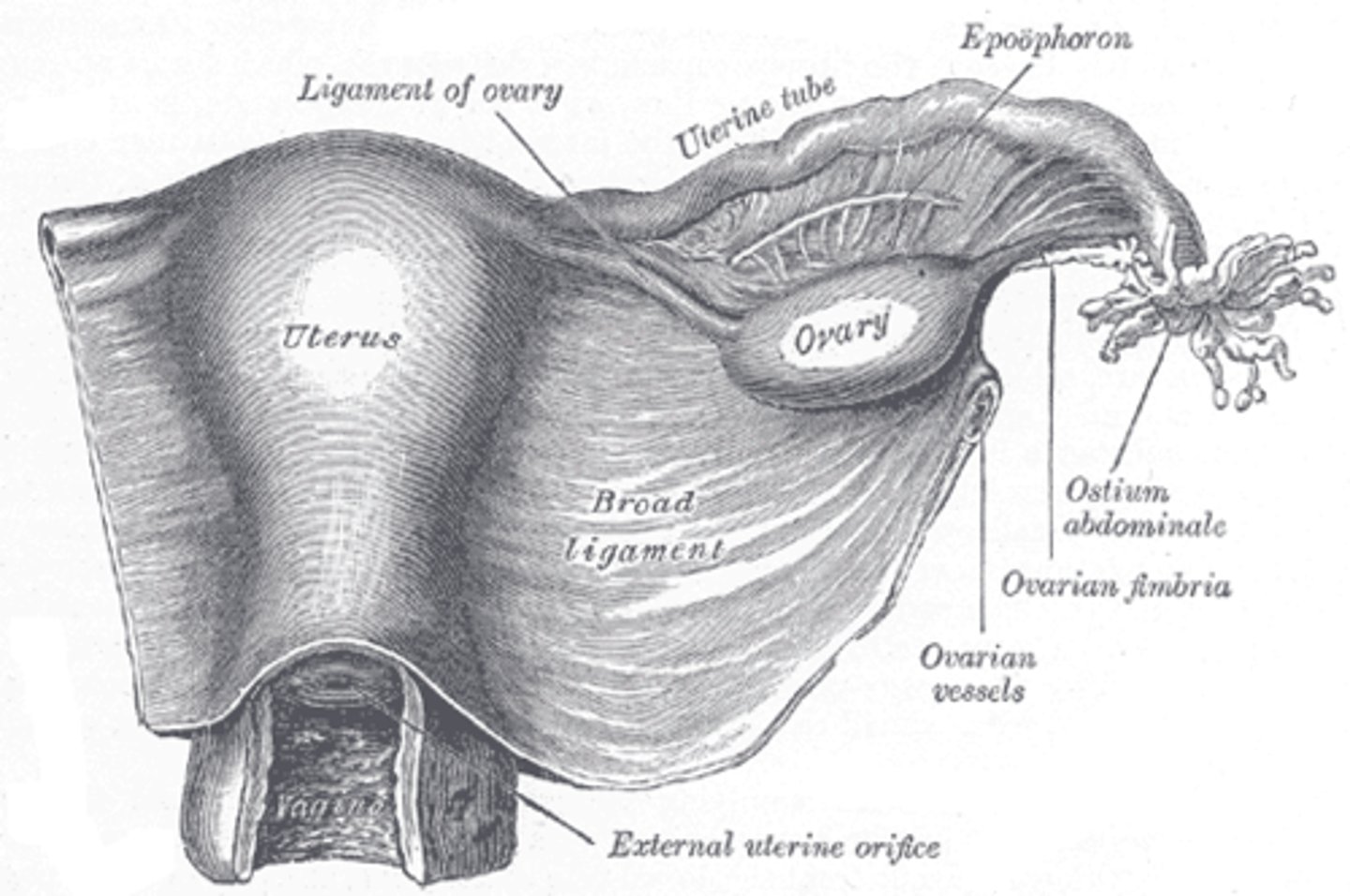
What is positioned between the 2 layers of the broad ligaments?
fallopian tubes
round ligament
ovarian ligament vascular structures
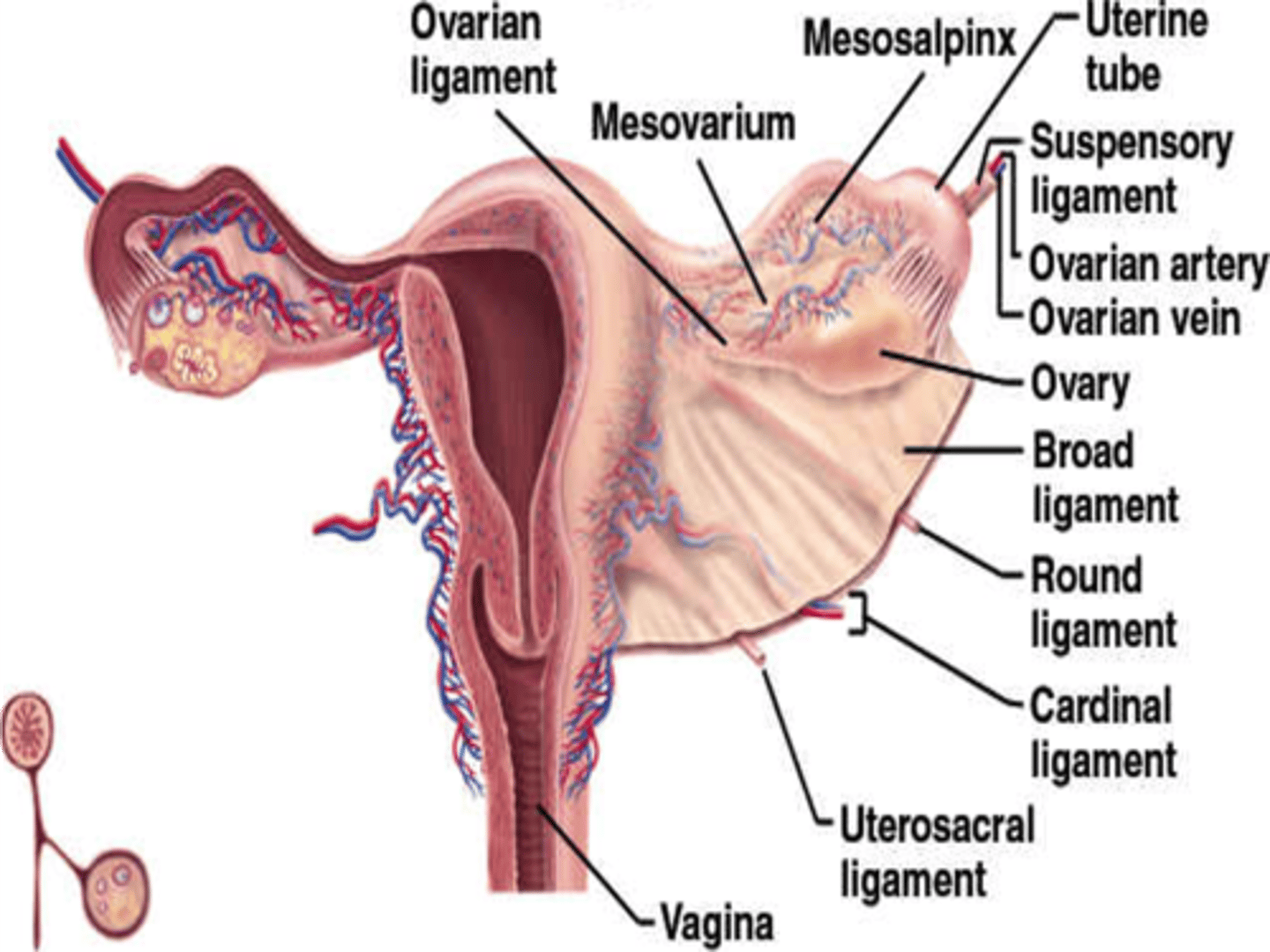
The round ligaments are located ___ to the fallopian tubes and insert into the ___ to help maintain the ___ of the uterus
anteroinferior; labia majora; position
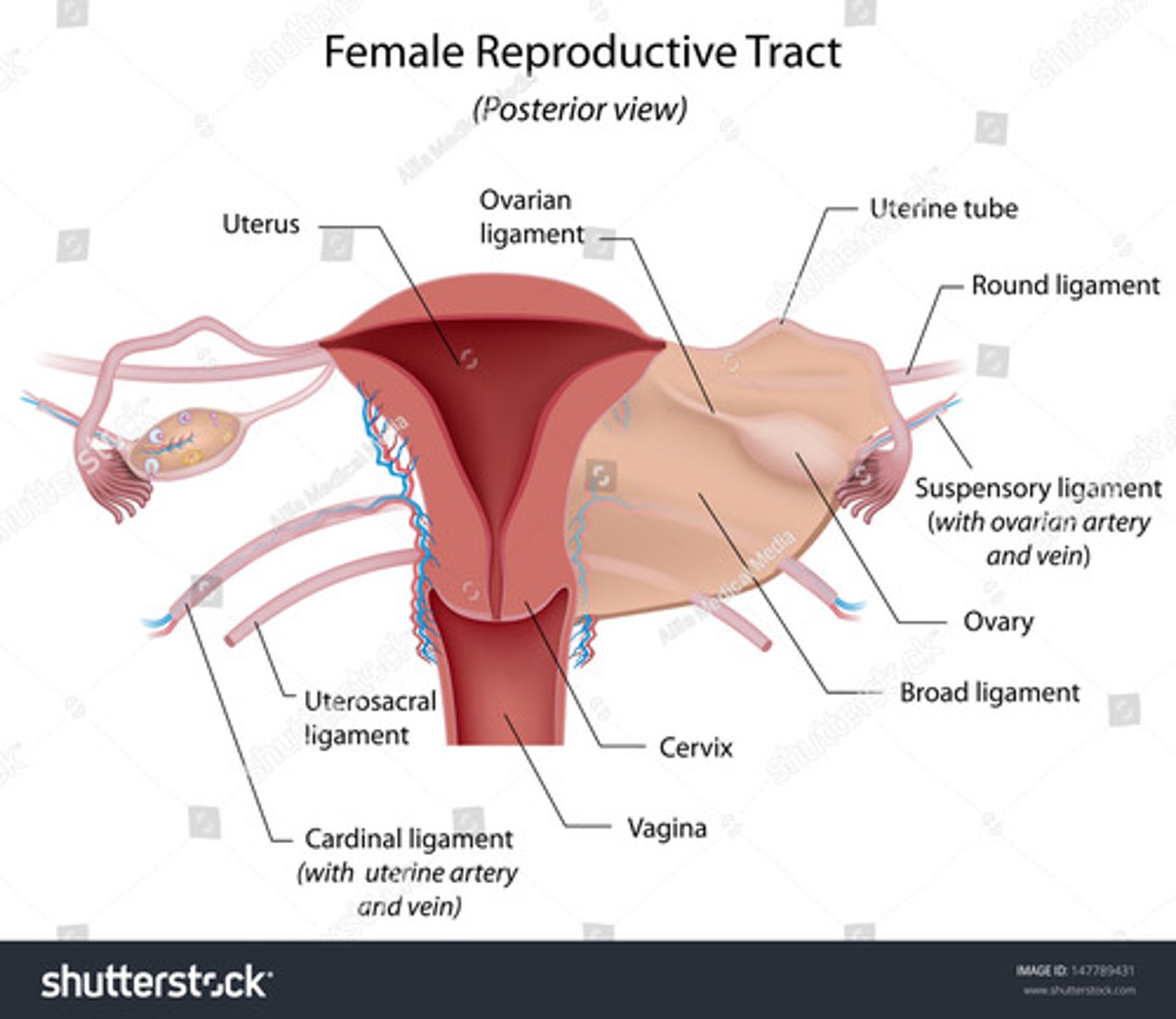
The ovarian ligaments are located ___ at the ___ of the uterus
bilaterally; cornua
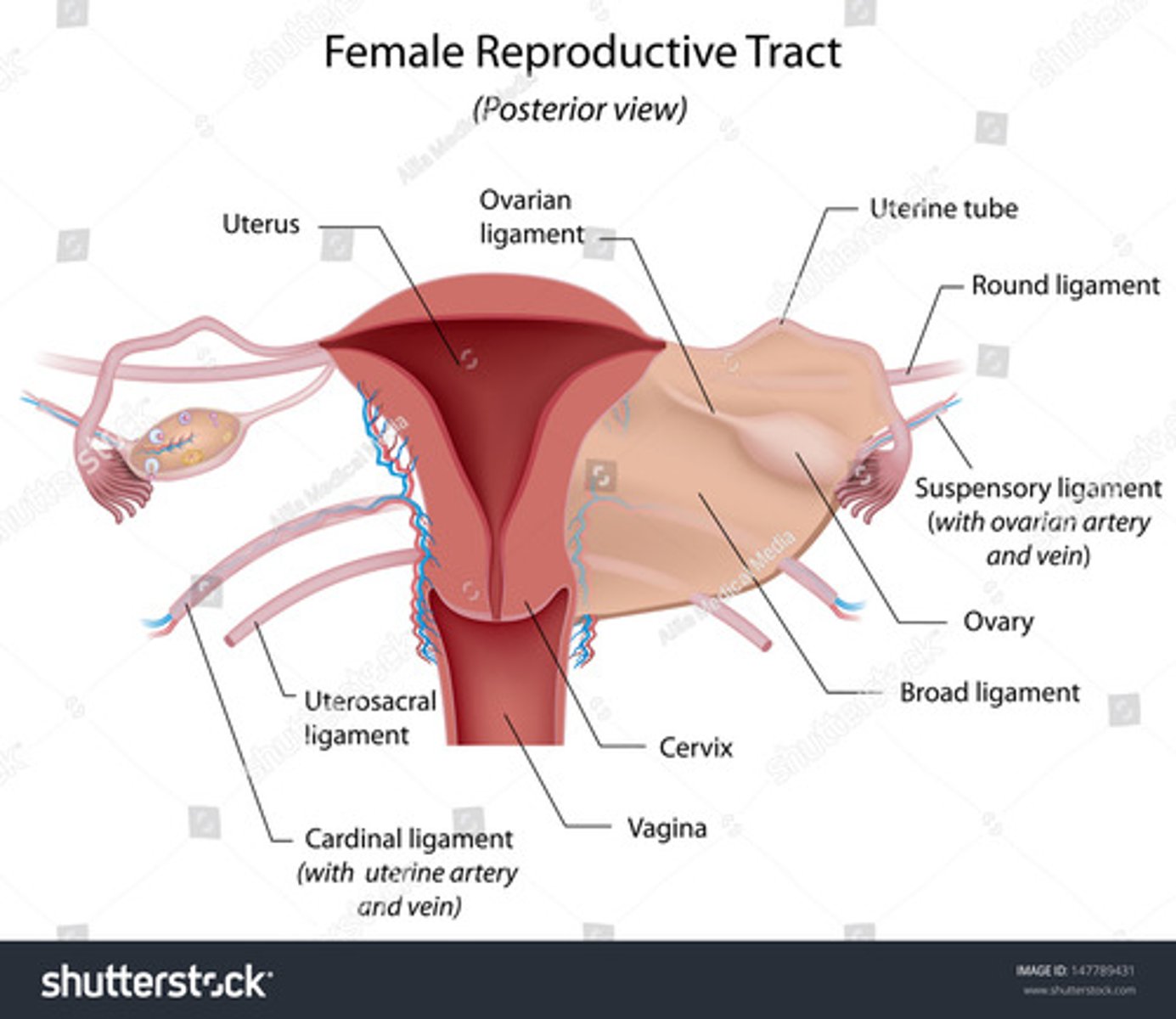
The suspensory ligaments extend from the ___ to the ___
infundibulum; pelvic sidewall
What is another name for anterior cul de sac?
vesicouterine pouch
What is another name for posterior cul de sac?
pouch of douglas
rectouterine pouch
What is another name for space of retzius?
prevesical
retropubic space
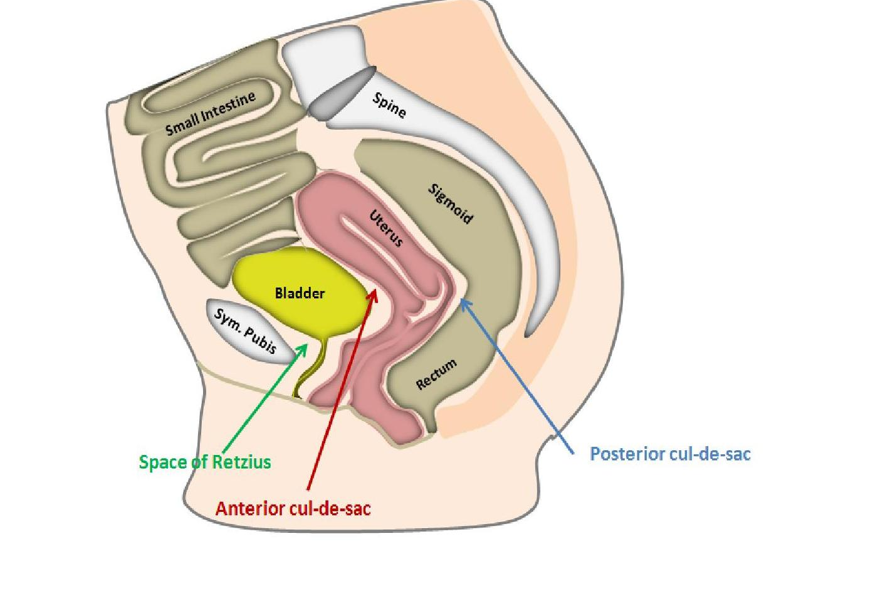
The space of retzius is located between the ___ and ___
pubic symphysis; bladder
Menstrual cycle phases:
Days 1-5
Days 6-13
Day 14
Days 15-28
menstrual phase
proliferative phase (preovulatory)
ovulation
secretory phase (postovulatory)
Days 6-13 of the menstrual cycle
- endometrium thickens to prepare for implantation
- estrogen rises
- FSH rises
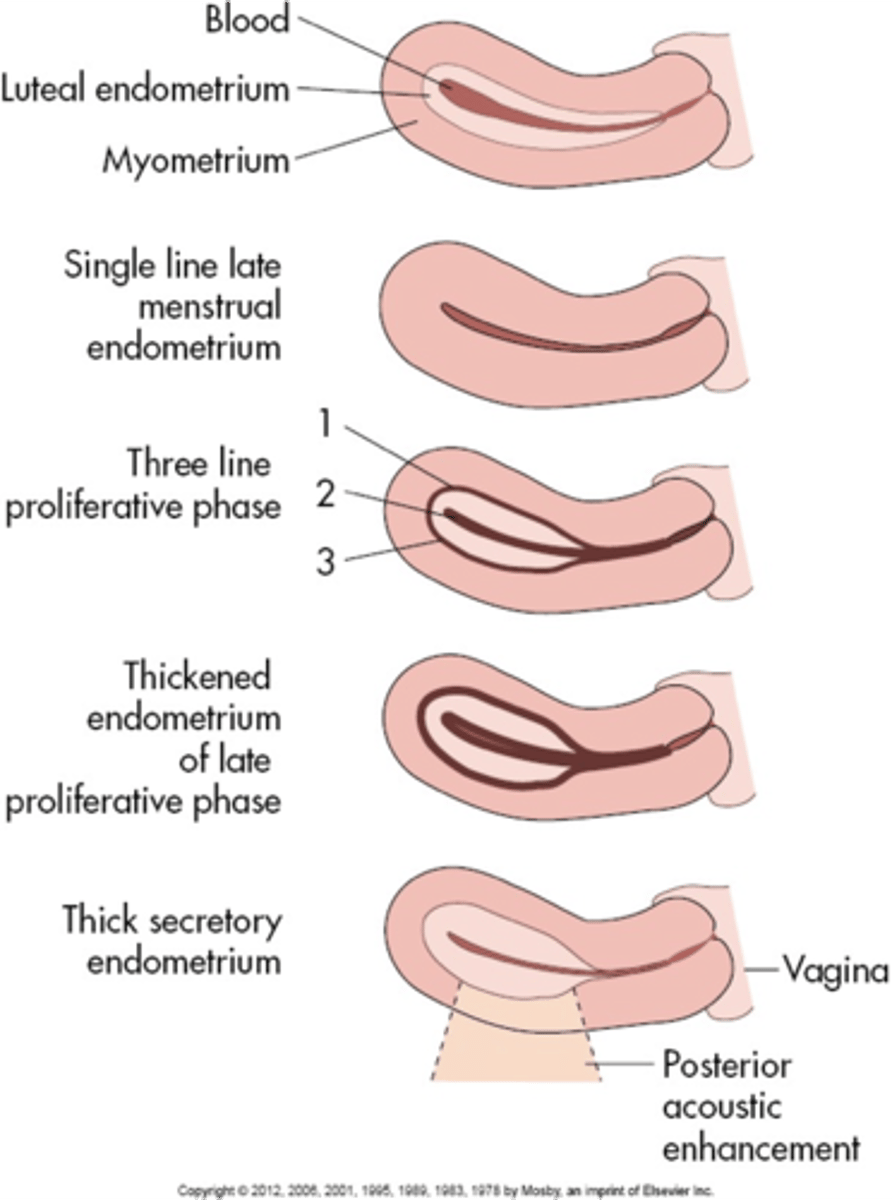
During the menstrual phase, the endometrium appears ___ and ___
thin; bright
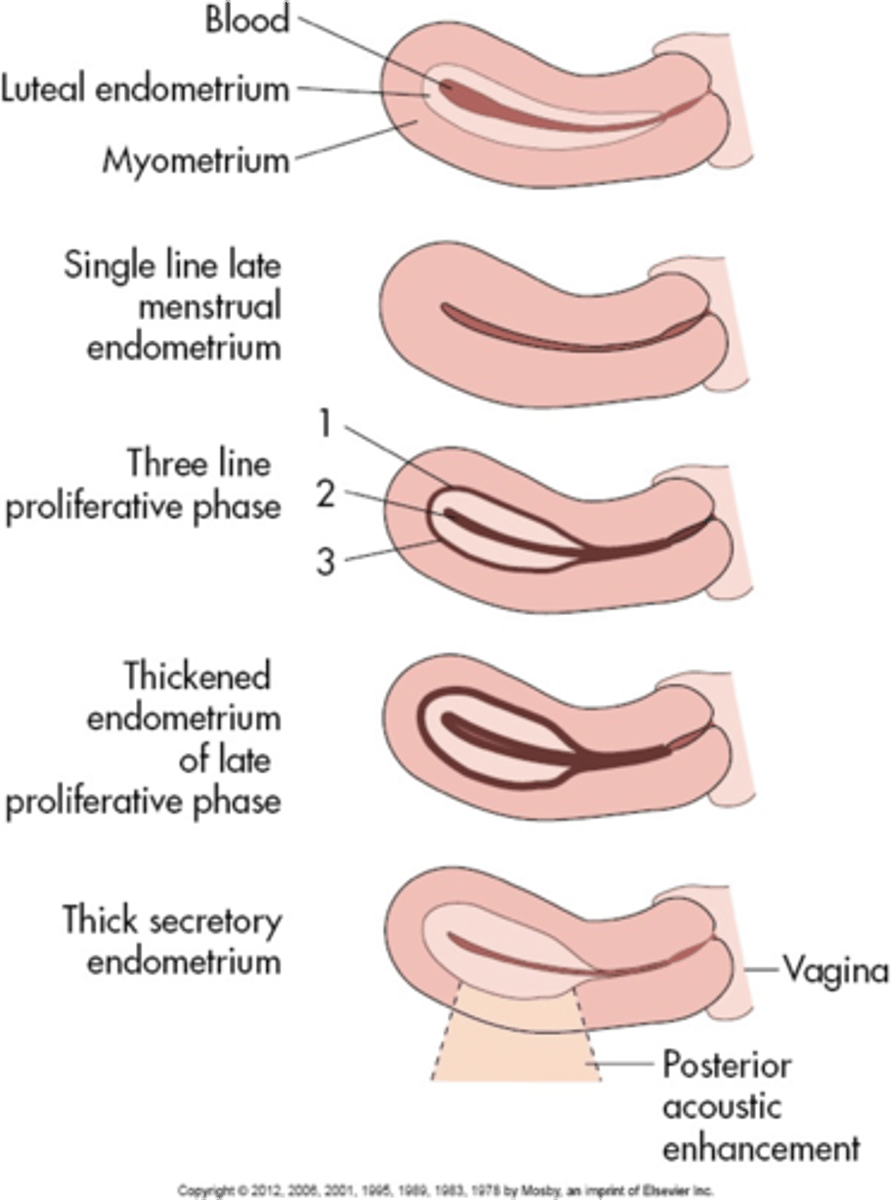
During the early proliferative phase, the endometrium appears ___ and measures ___
bright; 4-8 mm
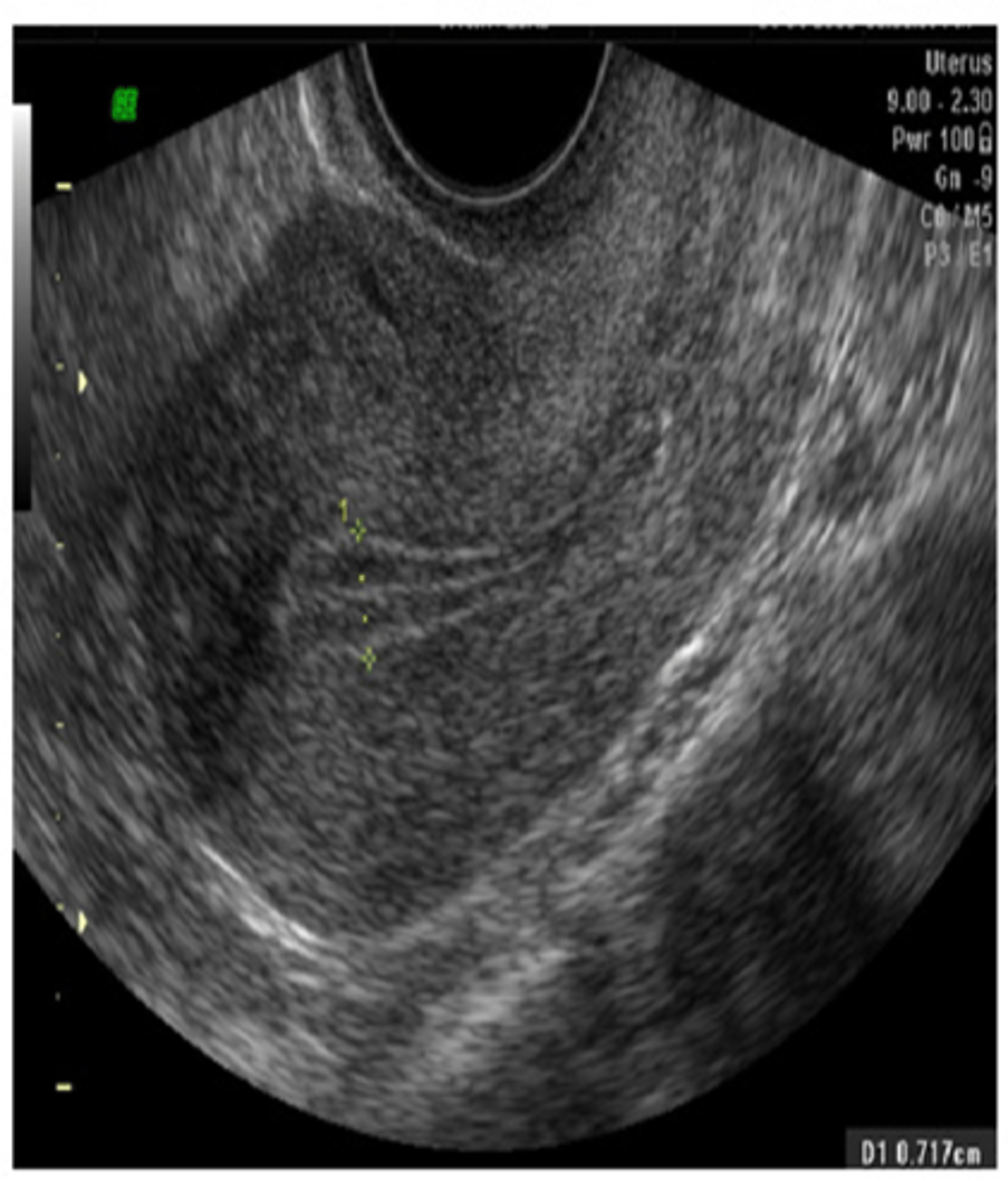
During the late proliferative phase, the ___ is visible and endometrium thickens to ___
3 line sign; 6-10 mm
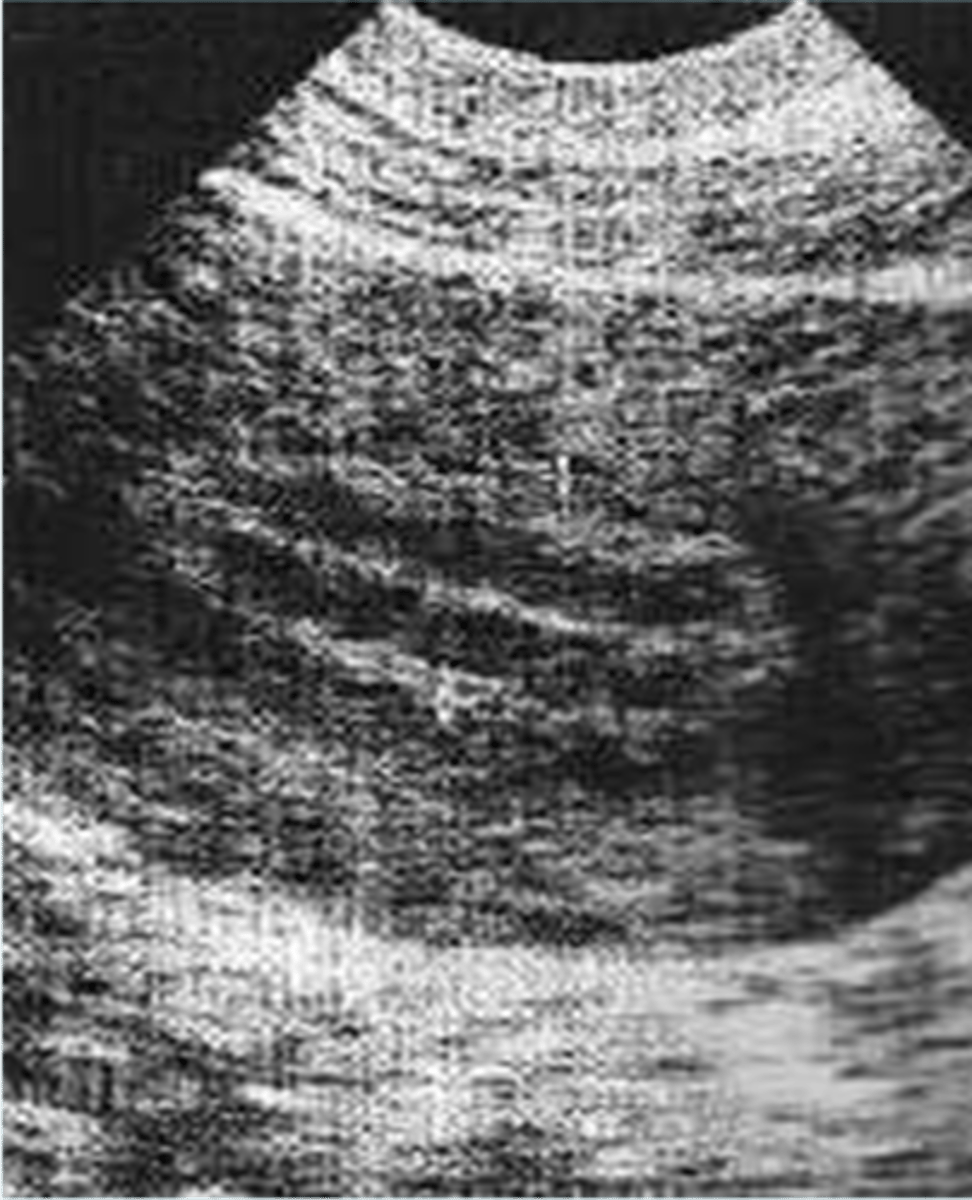
During the secretory phase, the endometrium appears ___ and ___ and measures ___
thick; echogenic; 7-14 mm
Days 15-28 of the menstrual cycle
- endometrium is at its thickest
- ruptured dominant follicle (Graafian) becomes corpus luteum
- estrogen and progesterone decrease
When a ruptured dominant follicle becomes corpus luteum:
- with pregnancy, it remains and secretes ___
- without pregnancy, it becomes ___
progesterone; corpus albicans
How long does the corpus luteum persist?
until the end of the 1st trimester
Ovarian cycle phases:
Days 1-5
Days 6-13
Day 14
Days 15-28
follicular phase
follicular phase
ovulatory phase
luteal phase
TV sagittal image orientation
TV coronal image orientation
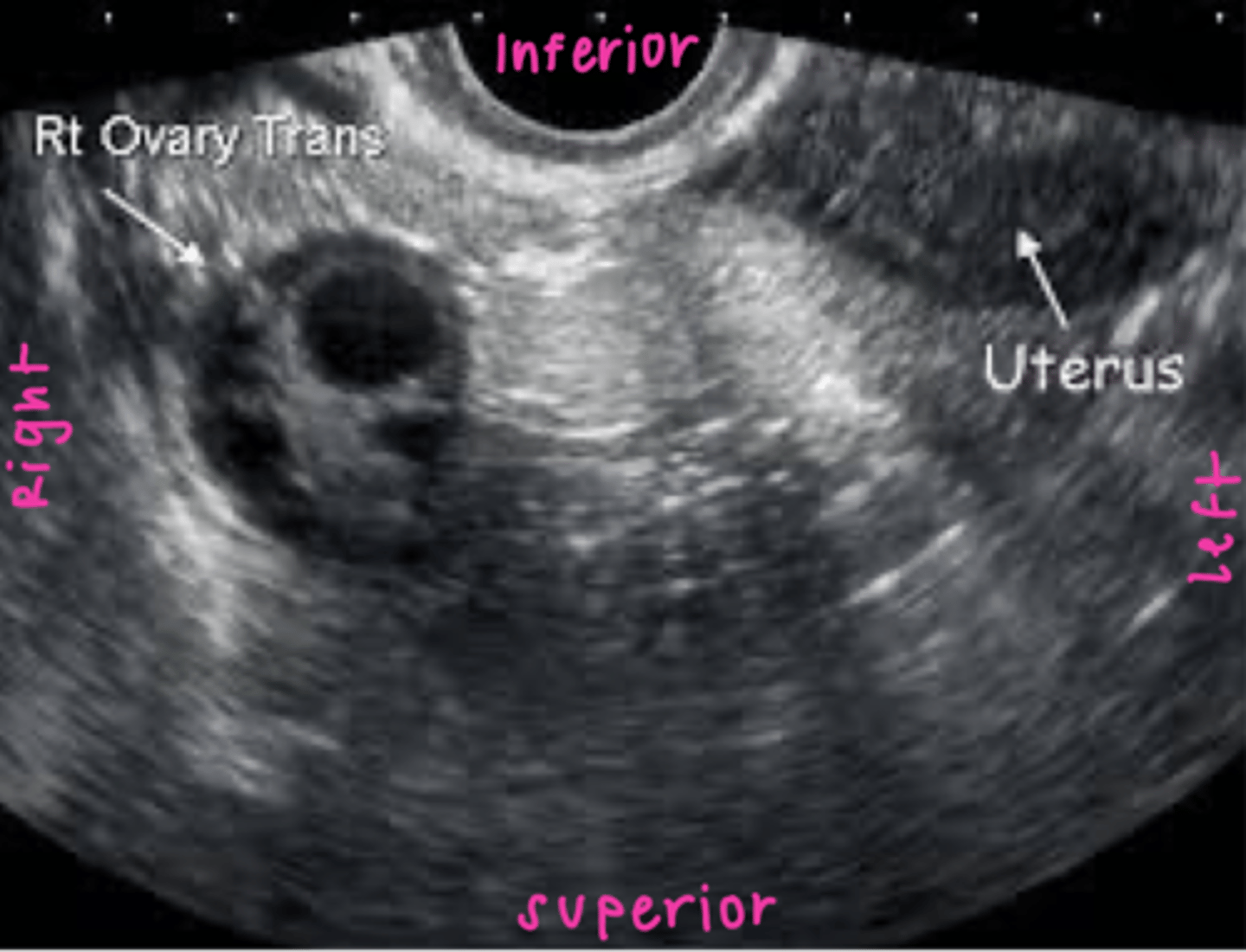
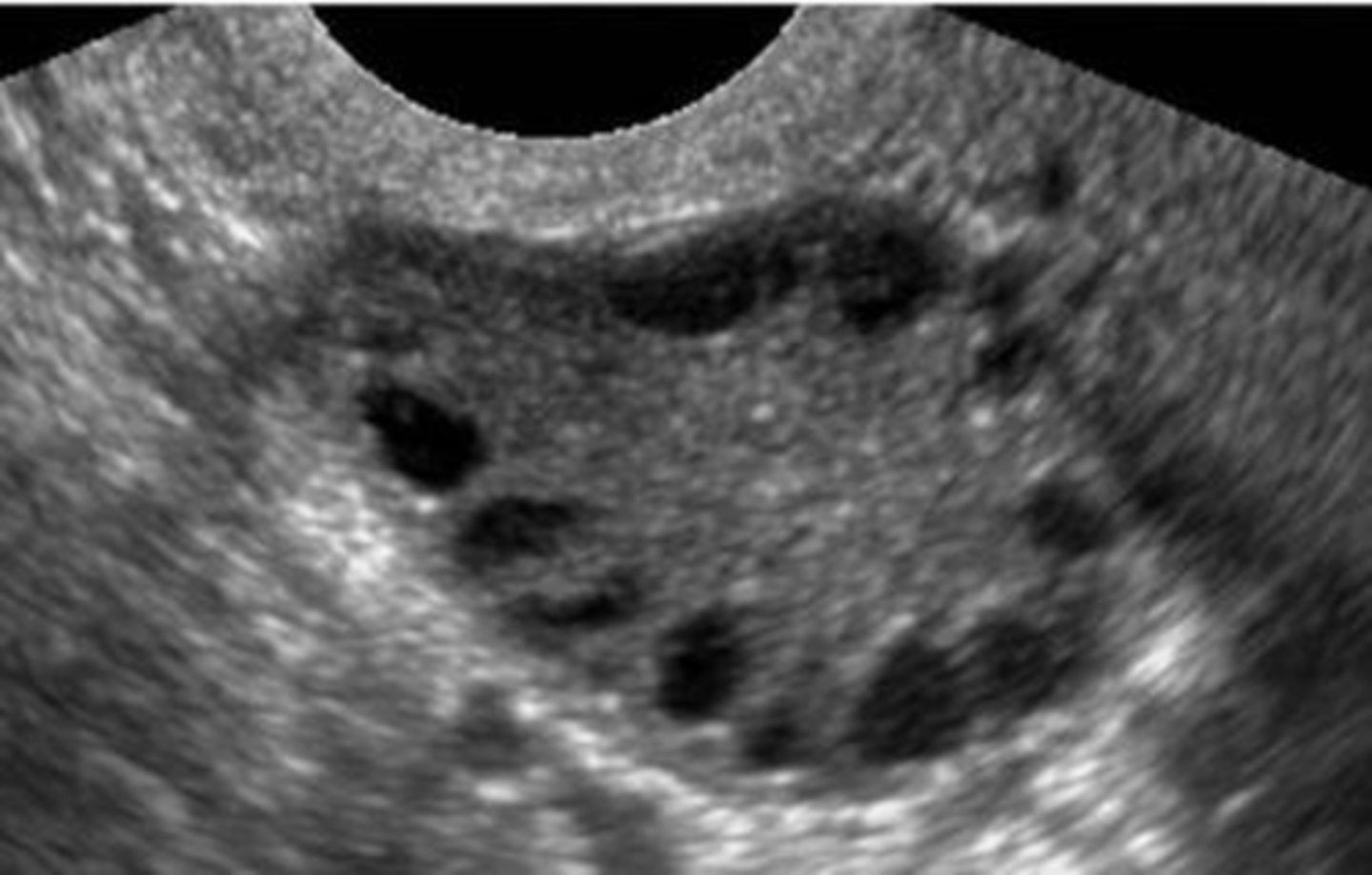
In polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) ___ do not develop normally preventing normal ___
follicles; ovulation
How does PCOS appear sonographically?
normal ovary with multiple small immature follicles; "string of pearls"
What are symptoms of PCOS?
1. oligomenorrhea
2. hirsutism
3. obesity
What is gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT)?
ovum inserted into fallopian tube and fertilized inside woman's body
What is zygote intrafallopian tube transfer (ZIFT)?
zygote (fertilized egg) inserted into fallopian tube
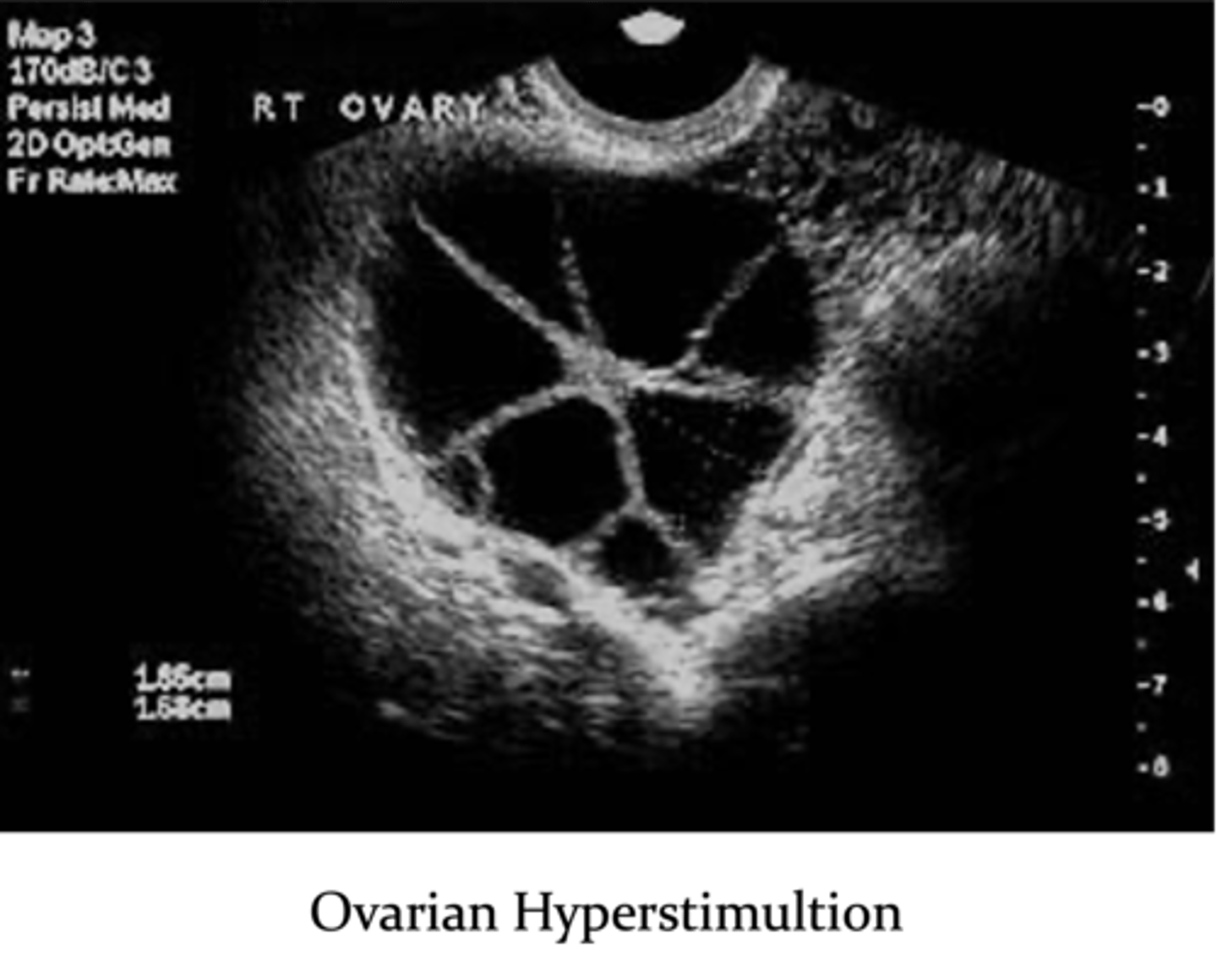
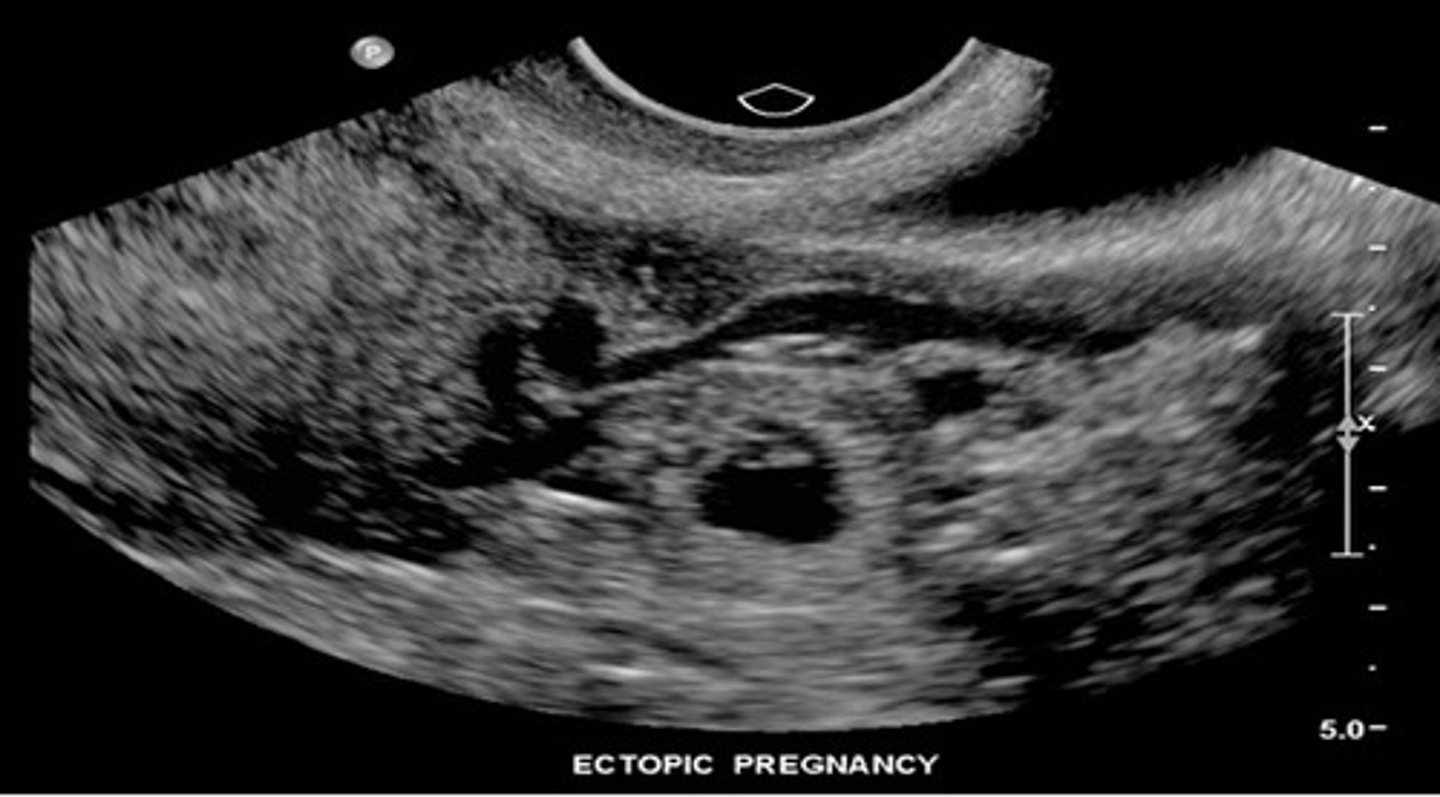
What are complications with assisted reproductive technology?
1. ovarian hyperstimulation
2. multiple gestations (25% chance)
3. ectopic pregnancy
After ___ weeks, hCG levels off and then ___ while the gestational sac and embryo continue to grow
9-10; declines
A normal gestational sac can be seen transabdominally when the hCG level is ___ or ___ weeks
greater than or equal to 1800 mIU/mL; 6-7
A normal gestational sac can be seen transvaginally when the hCG level is ___ or ___ weeks
500 mIU/mL; 4.5-5
An hCG of ___ indicates pregnancy should be seen transvaginally OR transabdominally
1000 to 2000 mIU/mL
If hCG is 1000 to 2000 mIU/mL and pregnancy is not seen within uterus, rule out ___
ectopic pregnancy
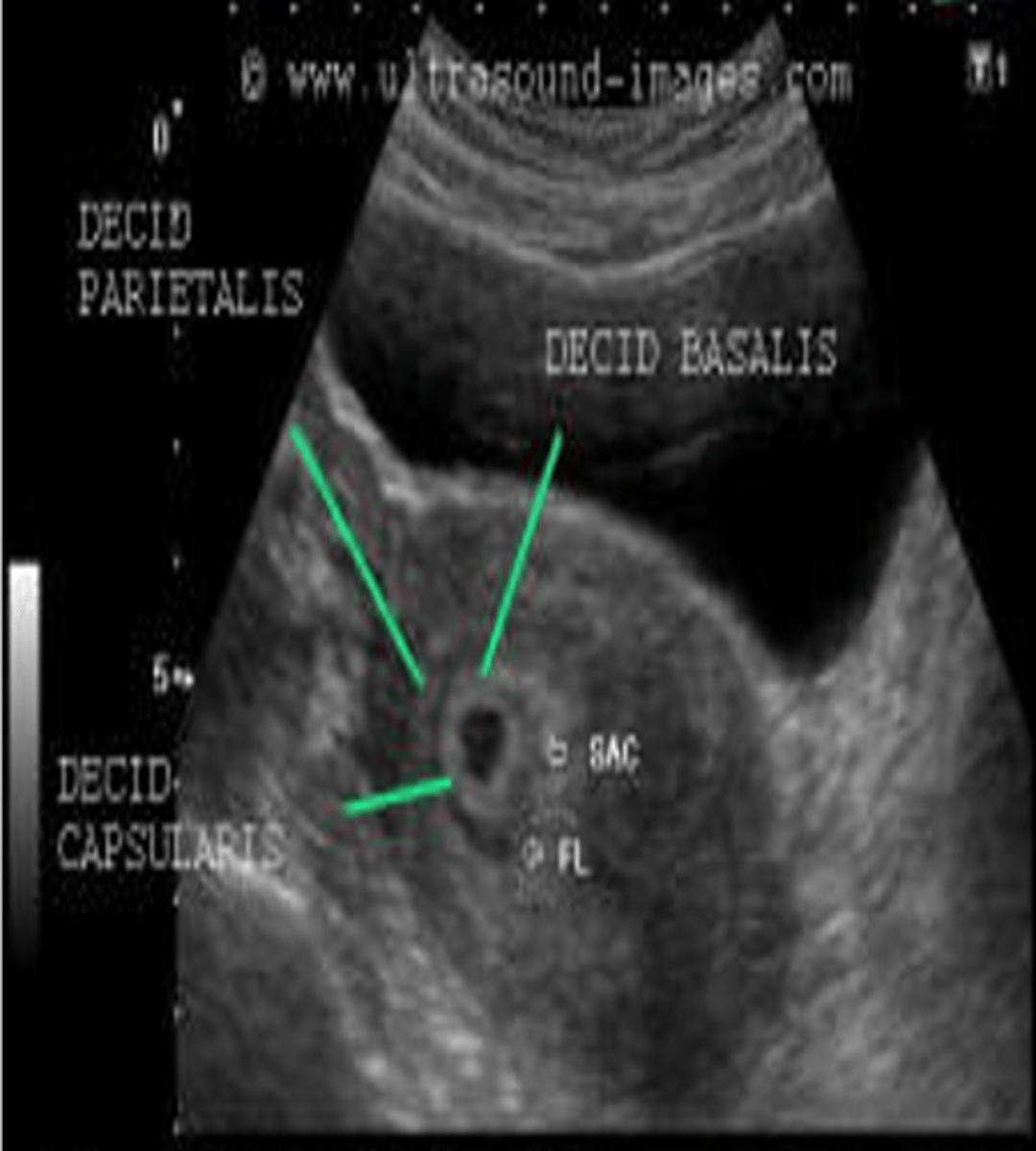
What components can the echogenic ring around the gestational sac be divided into?
decidua basalis
decidua capsularis
double decidual sac sign
The decidua basalis is the ___ on the ___ or burrowing side of the embryo
villi; myometrial (mother's side)
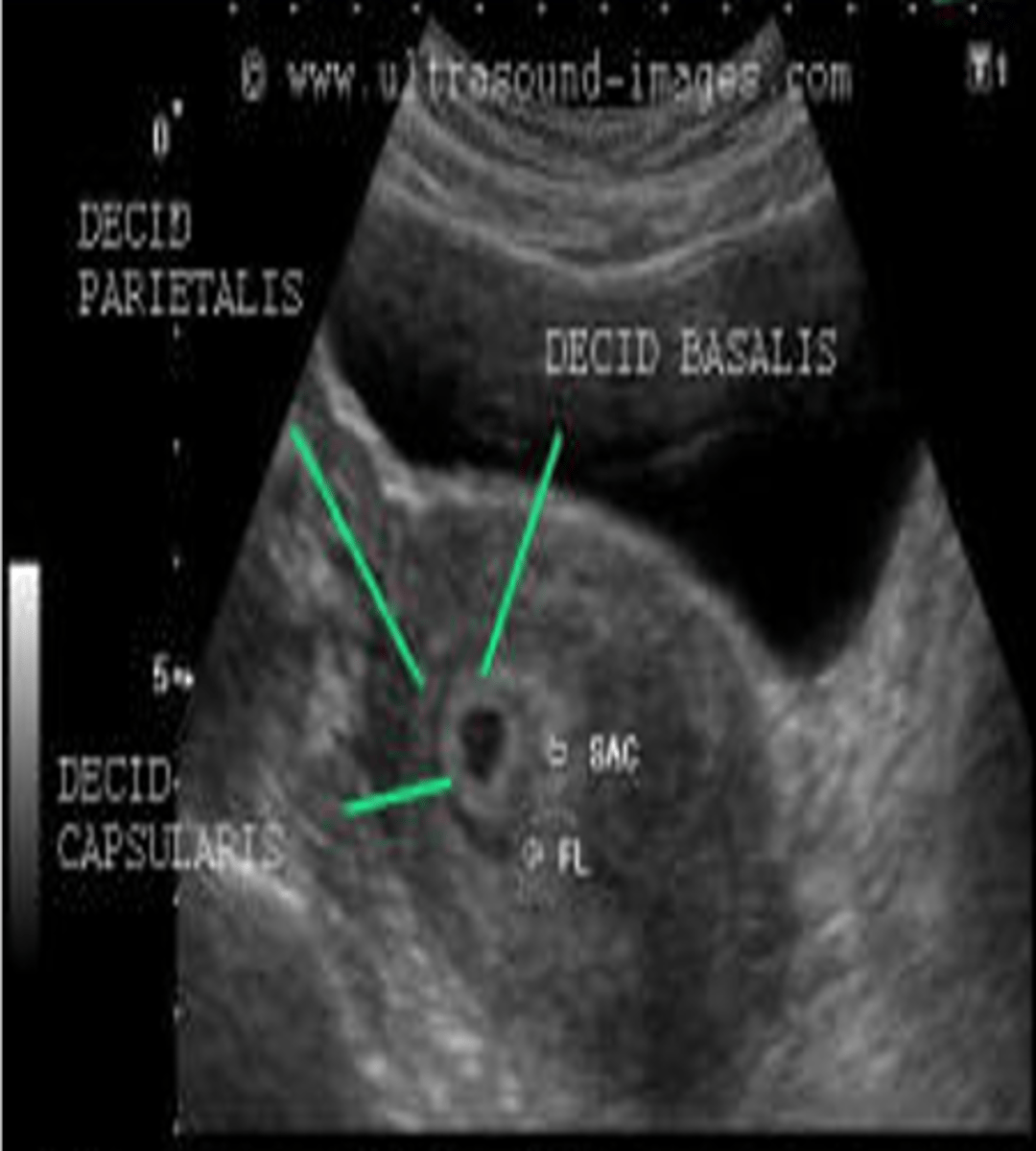
The decidua capsularis is the ___ covering the rest of the ___
villi; developing embryo (baby side)
The double decidual sac sign is an interface between the ___ and the ___
decidua capsularis; endometrium
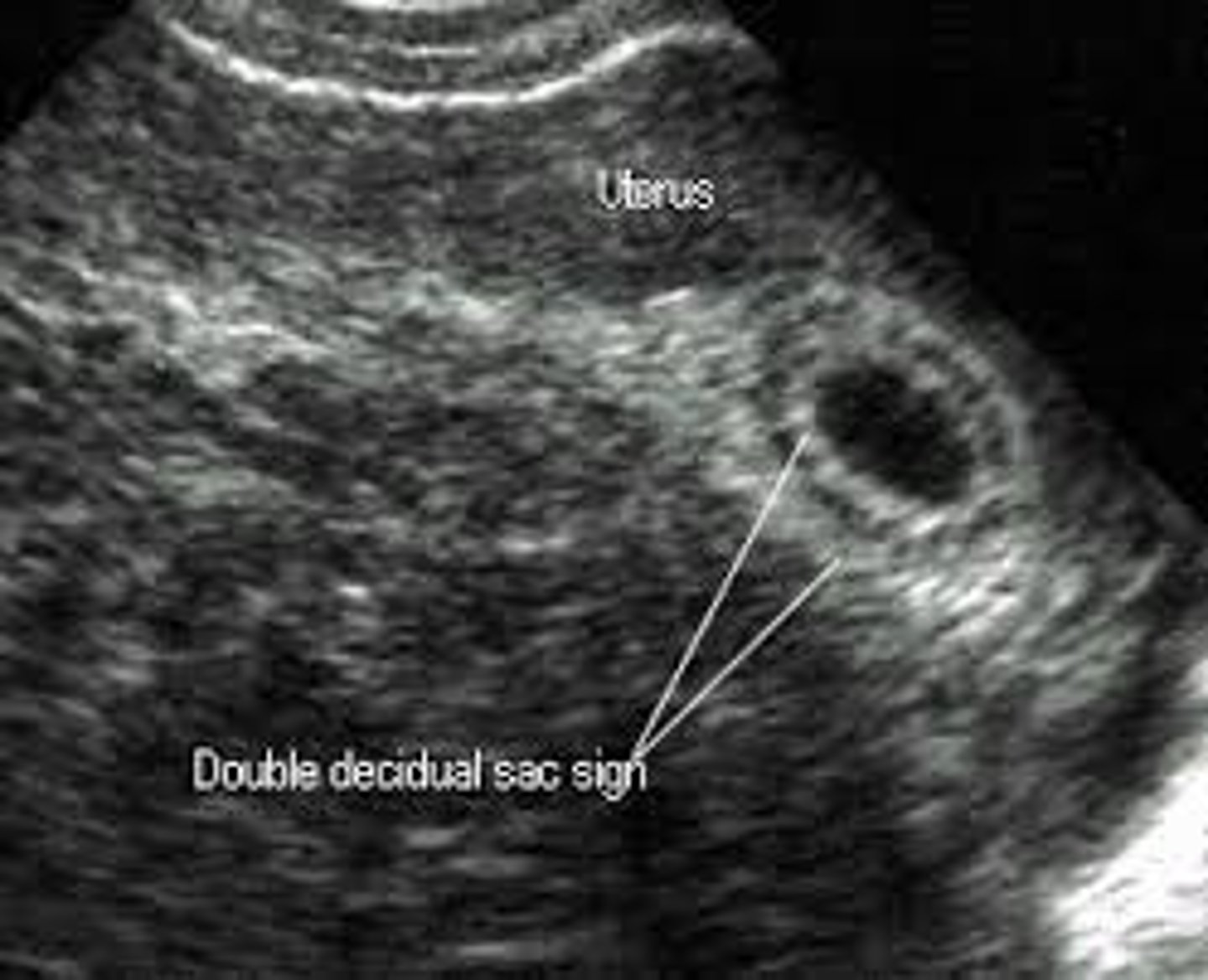
The double decidual sac sign is a reliable sign of ___
viable gestation
During the 5th week, what is decidua wall thickness?
greater than 3 mm
The yolk sac is seen on ultrasound when the gestational sac measures ___
greater than 8 mm
In early pregnancy, the gestational sac grows ___ a day
1 mm
What is gastroschisis?
herniation of intestines, not encapsulated
At what stage does the normal bowel herniation (gastroschisis) resolve?
12 weeks
What is omphalocele?
herniation of intestines and other organs, encapsulated
Once the rhombencephalon divides with its corresponding flexure, the ___ forms
cystic rhomboid fossa
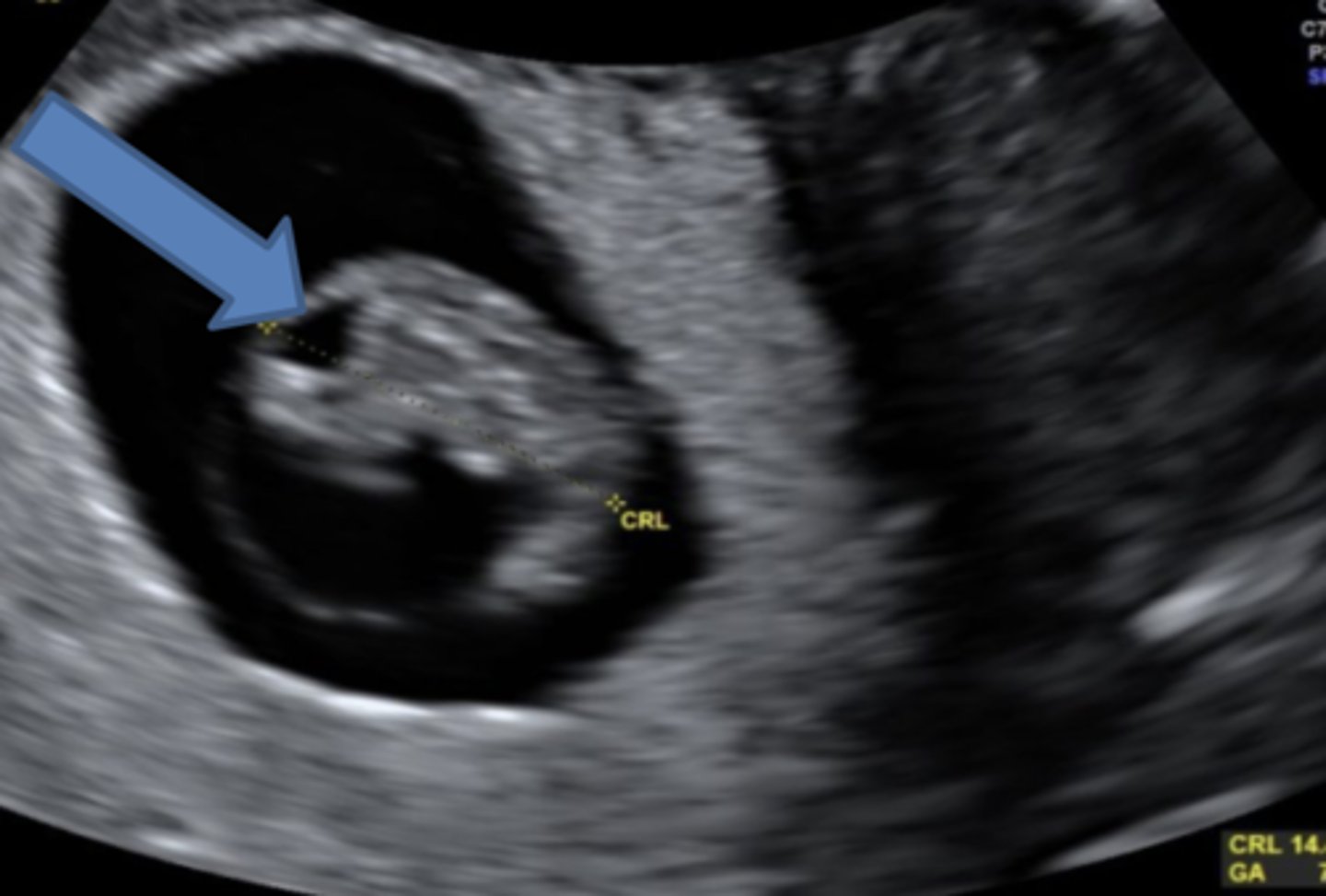
When is the cystic rhomboid fossa seen on ultrasound?
8-11 weeks
The cystic rhomboid fossa appears in the ___
posterior cranium
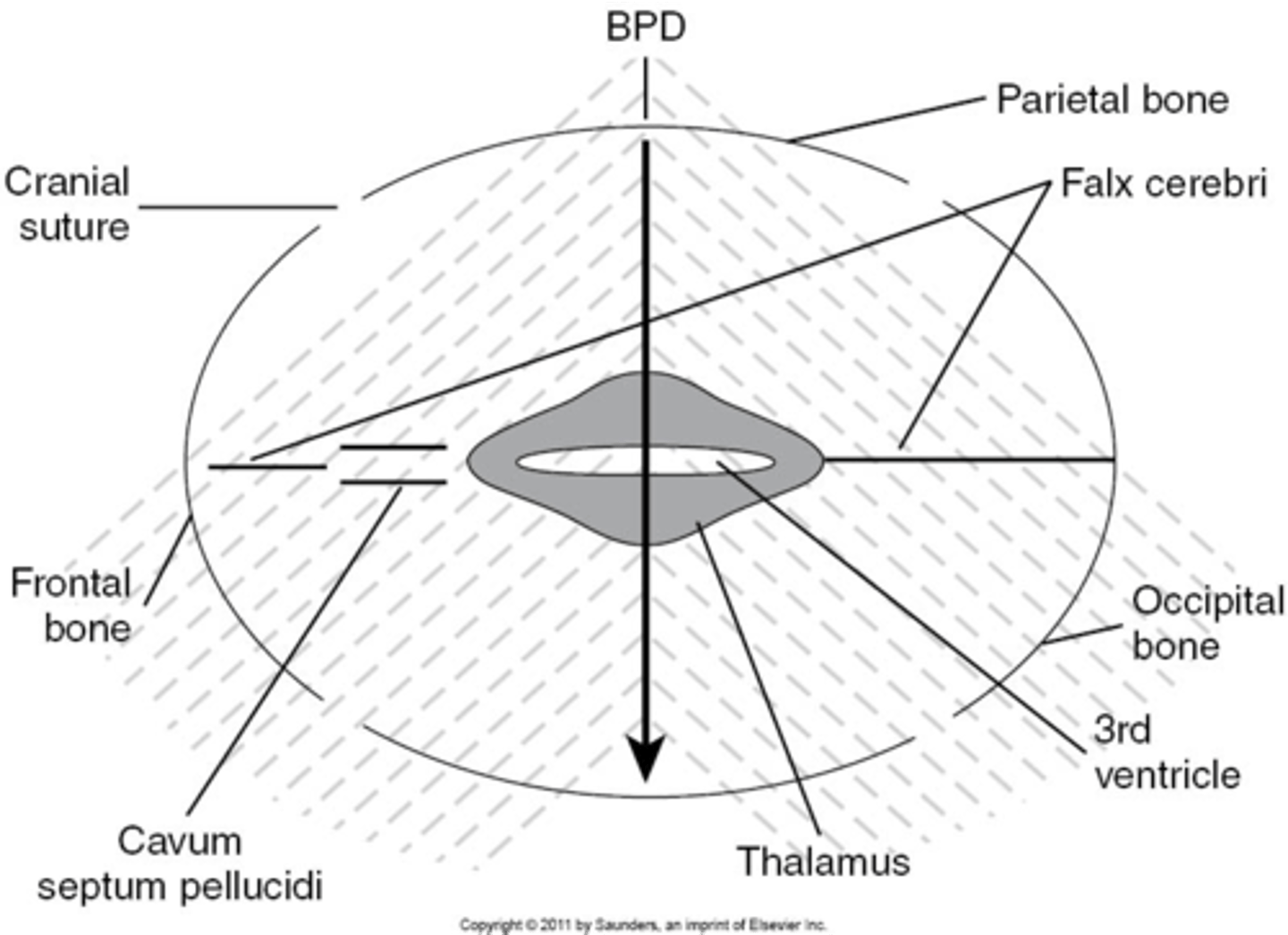
What is the most widely accepted means of measuring fetal head and estimating fetal age?
BPD
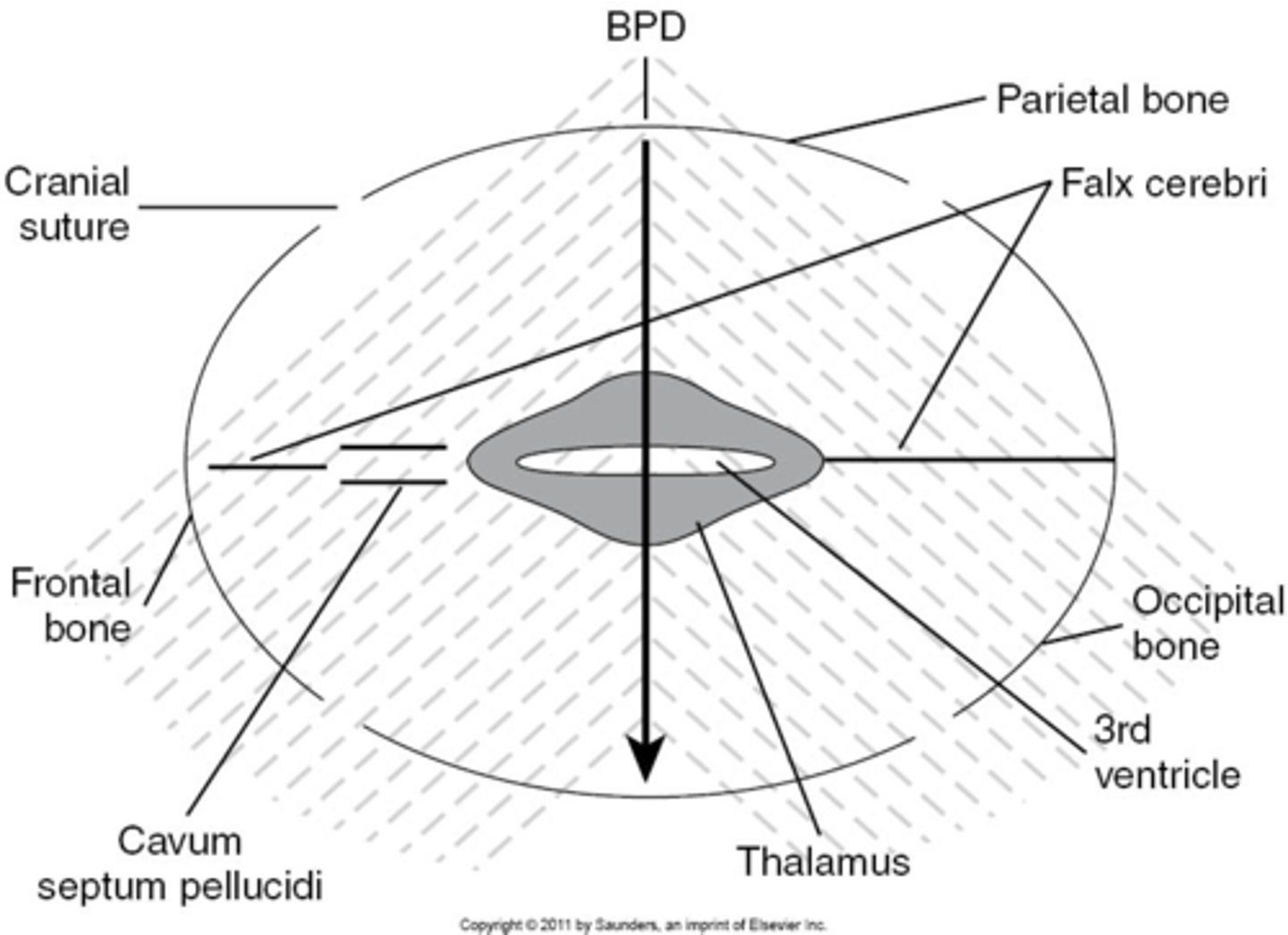
What part of the skull do you measure BPD?
midline echo complex
How do you find midline echo complex on ultrasound?
move the transducer caudally from lateral ventricles
When measuring BPD, paired ___ will be seen on either side
thalamus
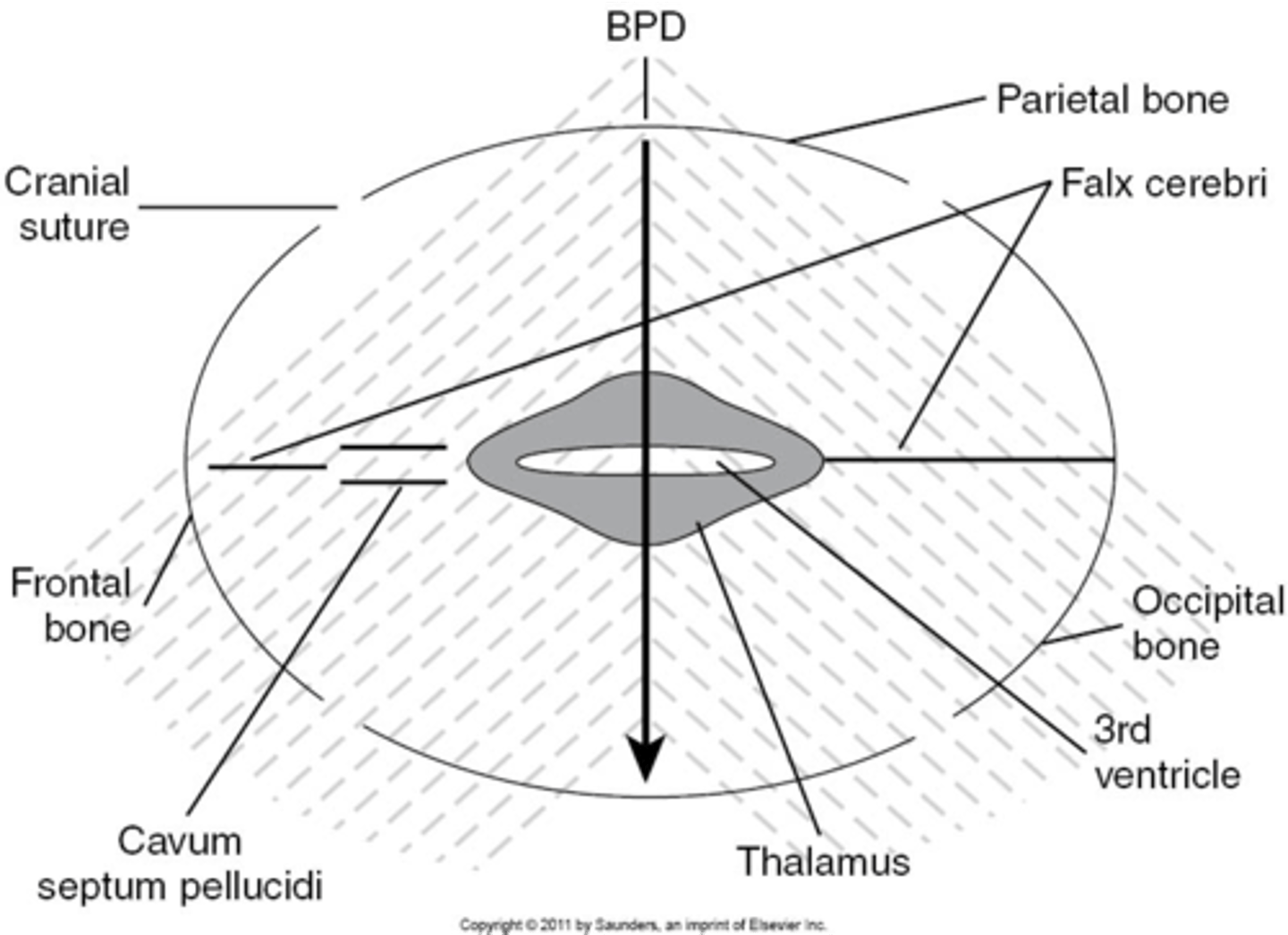
When measuring BPD, what is located between the thalamus?
3rd ventricle