Biology Unit 6 test
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/62
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
1
New cards
What are restriction enzymes/what do they do?
Restriction enzymes are special proteins produced by bacteria to prevent or restrict invasion by foreign DNA. They act as DNA scissors, cutting the foreign DNA into pieces so that it cannot function.
2
New cards
What is a restriction site?
a “4” or “6” base pair sequence that is a palindrome. A restriction site is where the restriction enzymes cut along
3
New cards
What does DNA being palindromic mean?
A DNA palindrome is a sequence in which the “top” strand read from the 5’ end of DNA to the 3’ end is the same as the “bottom” strand read from the 5’ end of DNA to the 3’ end.
4
New cards
What is a sticky end cut?
A cut that leaves single-stranded “tails” on the new ends. This cut makes it easy to rejoin the DNA to complementary tails.
5
New cards
What is a blunt end cut?
a cut that goes through the sugar phosphate backbone only
6
New cards
What is selective breeding? (and examples)
allowing organisms with desired characteristics to reproduce.
Examples: Horses, cats, dogs, crop plants
Examples: Horses, cats, dogs, crop plants
7
New cards
What is hybridization and example?
Crossing two different species together and passing the best of both traits.
Ex. cotton candy grapes, zonkey’s, mules
Ex. cotton candy grapes, zonkey’s, mules
8
New cards
What are the benefits of hybridization?
To pass the best of both traits.
9
New cards
What happens to the offspring of hybridization?
They are infertile.
10
New cards
What is inbreeding?
Continual breeding of individuals with desired characteristics.
11
New cards
What are the benefits of inbreeding?
Desired characteristics will be passed on. It can concentrate the genes of a superior ancestor. It may be easier to predict which crosses will work well with an inbred animal when it is used for breeding.
12
New cards
What are the disadvantages to inbreeding?
Recessive alleles for a genetic disorder will be passed on, therefore increasing the risk of inheriting a genetic disorder.
13
New cards
What is polyploidy?
A mutation in some __**plant cells**__ that produce cells that have double or triple or more of the normal number of chromosomes
14
New cards
What are the advantages to polyploidy?
Organisms that are polyploid are larger and stronger than their diploid relatives.
15
New cards
Is polyploidy also good for animals?
No, polyploidy in animals is usually fatal
16
New cards
What can manipulating DNA be used for?
Identify individuals, Alter the DNA code of organisms, Create medicines
17
New cards
What is genetic engineering?
the process of modifying an organism's DNA to introduce new, desirable traits.
18
New cards
What does PCR stand for and what does it do?
Polymerase chain reaction, the process of creating new strands of DNA
19
New cards
Steps of PCR
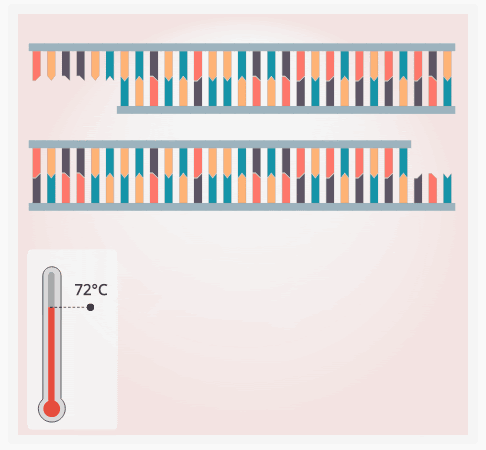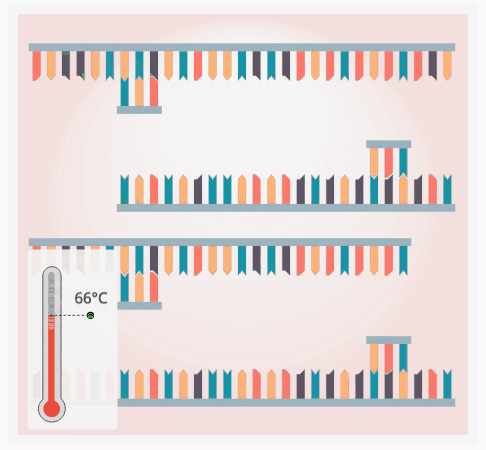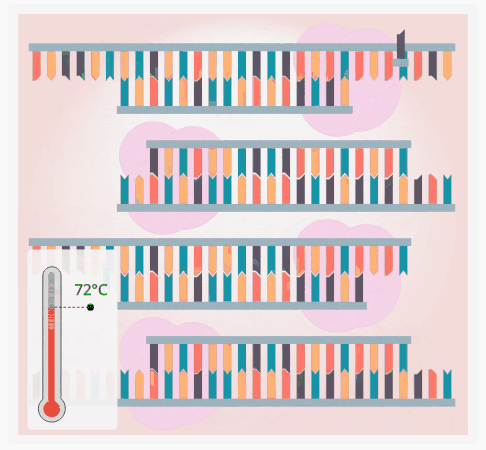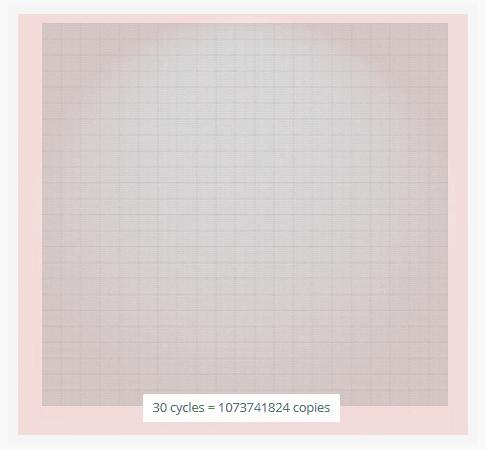
1. Can be performed with a thermal cycler
1. Raises and cools the temperature of DNA
2. Used in crime labs
3. Steps:
1. DNA is heated to 94℃ to unwind the DNA strands
2. DNA is then cooled to 55℃ to allow DNA primers to bind to the DNA
3. DNA is heated to 74℃ so the DNA Polymerase can create the new strand of DNA
20
New cards
What is a recognition sequence?
Different from a restriction site, a recognition sequence is a sequence that can occur multiple times and tells restriction enzymes where to cut (Ex. AAGGA)
21
New cards
How do Restriction Enzymes know where to cut?
It goes to the specific restriction site, and mostly there is just 1 restriction site per enzyme.
22
New cards
What is gel electrophoresis?
A method for the separation of DNA.
23
New cards
What is passed through a gel plate filled with DNA? What does this do to the DNA fragments?
DNA fragments are passed through a gel plate, and electricity causes the fragments to separate.
24
New cards
Steps of Gel Electrophoresis
1. Introduce restriction enzymes to cut DNA into fragments
2. Pour the DNA fragments into wells on the gel
3. Apply an electric current to the gel
25
New cards
In what direction will the DNA fragments travel?
Negative to positive
26
New cards
Based on how the DNA will travel what charge does DNA have?
Negative
27
New cards
What type of fragments move faster and farther in the gel?
Smaller fragments
28
New cards
Is gel electrophoresis used in RFLP, STR, or both?
Gel electrophoresis is used for both methods:
RFLP - separates the DNA fragments
STR Analysis - expands repeated sections
RFLP - separates the DNA fragments
STR Analysis - expands repeated sections
29
New cards
What is done in DNA fingerprinting?
analyzes sections of DNA that vary widely between individuals.
30
New cards
Where can you get DNA samples from?
Cheek cells, blood, or hair strands with tissues at the base
31
New cards
How can repeats help identify individuals?
The length and the number of repeats are unique
32
New cards
How are Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) and Short Tandem Repeat (STR) Analysis different?
1. RFLP - Uses enzymes to cut DNA
2. STR Analysis - analyzes the length of repeated sections of DNA
33
New cards
What does STR look like?
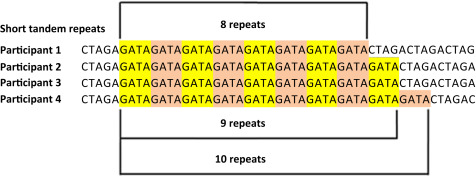
34
New cards
What does RFLP look like?
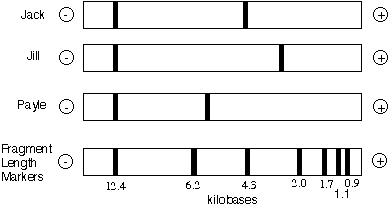
35
New cards
Why is RFLP not used anymore?
1. Large, non contaminated sample required
2. Subject to degradation (when the DNA is broken)
3. The DNA needs to be cut
36
New cards
Does everyone have a unique DNA fingerprint?
All individuals, __**except**__ identical twins, will have a unique DNA fingerprint
37
New cards
How should you analyze a DNA fingerprint?
Look at the similarities between the fingerprints.
38
New cards
What is CODIS?
A system set up by the FBI to be able to match DNA with other DNA. CODIS sites are the locations that you look for the repeating sequences of DNA
39
New cards
The repeating nucleotides used in STR are what?
Introns
40
New cards
How many sites need to match to convict someone in codis?
20
41
New cards
What is the probability of one CODIS site versus 20 CODIS sites matching?
1/10 vs one in one hundred quintillion
42
New cards
What is AMEL?
Not a CODIS, but is used to determine the sex of a person
43
New cards
What is recombinant DNA?
The combination of DNA from different organisms
44
New cards
How do you make recombinant DNA?
Using restriction enzymes, desired DNA is cut out of one organism’s genome and into incorporated the DNA of another organism that has been cut by the same restriction enzyme.
\
The result is recombinant DNA.
\
The result is recombinant DNA.
45
New cards
Would DNA with sticky ends or blunt ends be used to make recombinant DNA?
Sticky ends, so that you can attach the new DNA to the old one.
46
New cards
What is a plasmid?
Circular DNA in bacteria
47
New cards
What are transgenic organisms?
organisms that contain recombinant DNA
48
New cards
Uses for transgenic bacteria
to make insulin, growth hormones, and clotting factors.
49
New cards
Reasons to create transgenic plants
prolong the life of plants, increase size, protect against disease or promote growth in changing environmental conditions.
50
New cards
Uses for creating transgenic animals
to create environmentally friendly livestock or treat food allergies or produce more food
51
New cards
What is gene therapy?
1. A **faulty** gene is replaced by a normal gene
2. The organism will produce the right **protein**
3. This __**IS NOT**__ a permanent fix
52
New cards
Gene therapy gene replacement process
Step 1: A virus is engineered with the gene of interest. The virus is also modified to not cause harm to host cell.
Step 2: The virus is inserted into host cell for replication. Cells will replicate the gene of interest
Step 3: The cells are injected into the bone marrow where they will continue to produce more cells with the corrected gene
Step 2: The virus is inserted into host cell for replication. Cells will replicate the gene of interest
Step 3: The cells are injected into the bone marrow where they will continue to produce more cells with the corrected gene
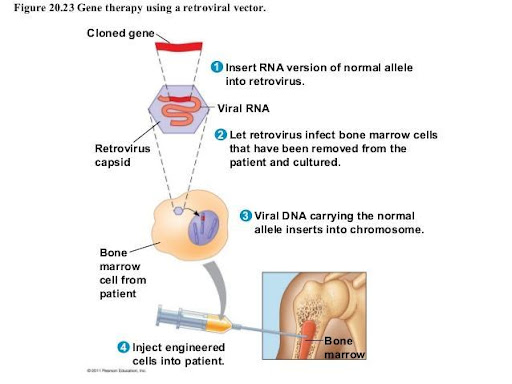
53
New cards
Examples of disorders that can be treated with gene therapy
sickle-cell disease, AIDS, cancer, hemophilia
54
New cards
Gene therapy knock out method steps
1. Recombinant DNA is introduced outside of cell
2. DNA is absorbed
3. Recombinant DNA can knock out (replace) a gene
55
New cards
What is CRISPR?
* Discovered in bacterial immune systems to protect against viruses
* Can cut DNA at specific sequences when combined with CAS proteins
* Works on any organism’s genetic material
* Can cut DNA at specific sequences when combined with CAS proteins
* Works on any organism’s genetic material
56
New cards
How does CRISPR and CAS9 work?
CRISPR consists of a guide RNA (RNA-targeting device) and the Cas enzyme
\
1. The guide RNA of CRISPR finds the target sequence in DNA and bind to it
2. Once bound to the target DNA, Cas 9 cuts the DNA
3. After the DNA is cut, a new segment of DNA can be added.
\
1. The guide RNA of CRISPR finds the target sequence in DNA and bind to it
2. Once bound to the target DNA, Cas 9 cuts the DNA
3. After the DNA is cut, a new segment of DNA can be added.
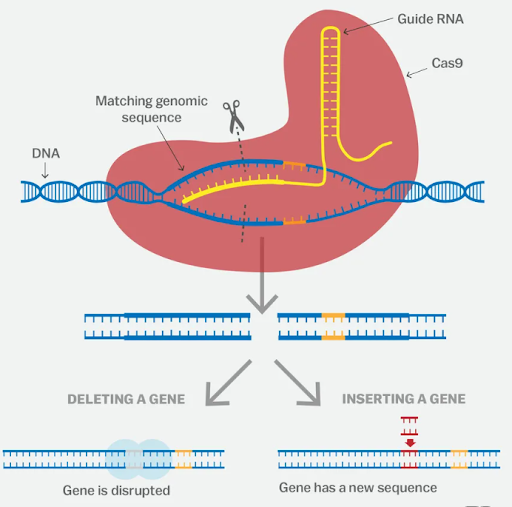
57
New cards
Cloning process
1. A donor diploid body cell is taken from the cloning specimen
2. An egg cell is taken from an adult female
organism
3. The nucleus from the egg cell is removed.
4. The two cells are fused together through an electric shock to form a fused cell
5. The embryo is placed in the uterus of a foster mother.
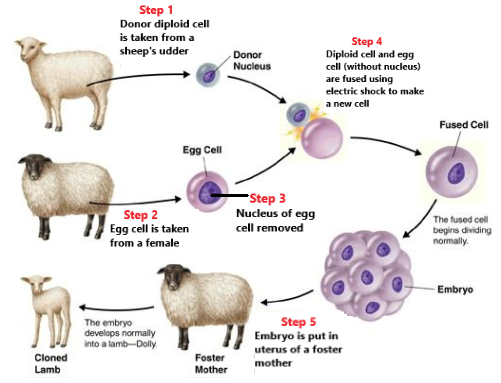
58
New cards
Cloning possibilities
* Possible Benefits:
* Can revive extinct animals.
* Some believe clones may have genetic defects.
* Can be used to grow organs.
* Highly controversial
* Bioethics
* Can revive extinct animals.
* Some believe clones may have genetic defects.
* Can be used to grow organs.
* Highly controversial
* Bioethics
59
New cards
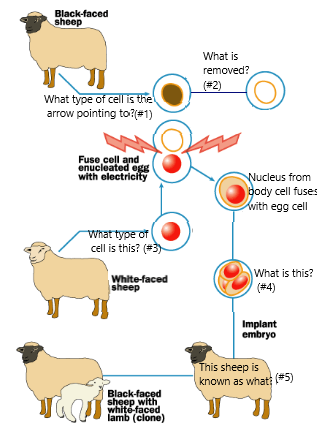
Answer the number questions
1. Egg Cell
2. Nucleus
3. Body Cell
4. Embryo
5. Foster Mother
60
New cards
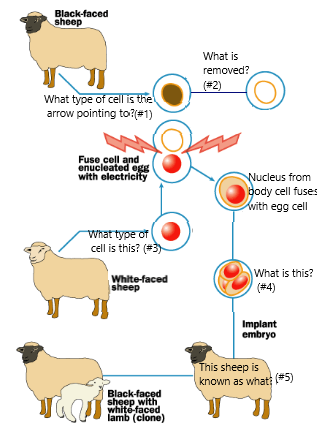
Why does the cloned lamb have a white face and not a black face like the foster mother?
The genetic information comes from the white-faced sheep.
61
New cards
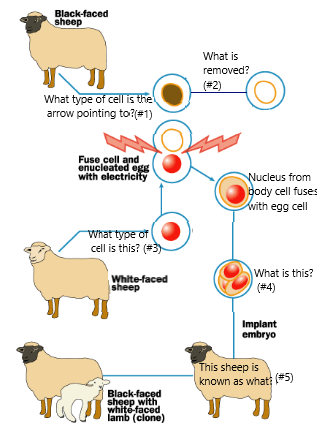
Does the donor nucleus have to be from a female sheep?
No, the nucleus can be from a male or a female
62
New cards
What was the human genome project?
an international scientific research project with the goal of determining the base pairs that make up human DNA, and of identifying, mapping and sequencing all of the genes of the human genome from both a physical and a functional standpoint
63
New cards
How long was the project supposed to take and how long did it end up taking?
It was supposed to take 15 years and ended up taking 13.