Social Thinking and Social Influence Overview
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Person Perception
Process of forming impressions of others.
Appearance
Impressions based on physical characteristics.
Verbal Behaviour
Impressions based on what people say.
Actions
Impressions based on people's behaviors.
Nonverbal Messages
Facial expressions and body language convey emotions.
Situational Cues
Context of behavior influences interpretation.
Bad Impressions
Negative traits outweigh positive qualities in perception.
Snap Judgments
Quick, superficial assessments of others.
Systematic Judgment
In-depth evaluations requiring controlled processing.
Perceiver Expectations
Expectations influence perceptions of others.
Confirmation Bias
Favoring information that supports one's beliefs.
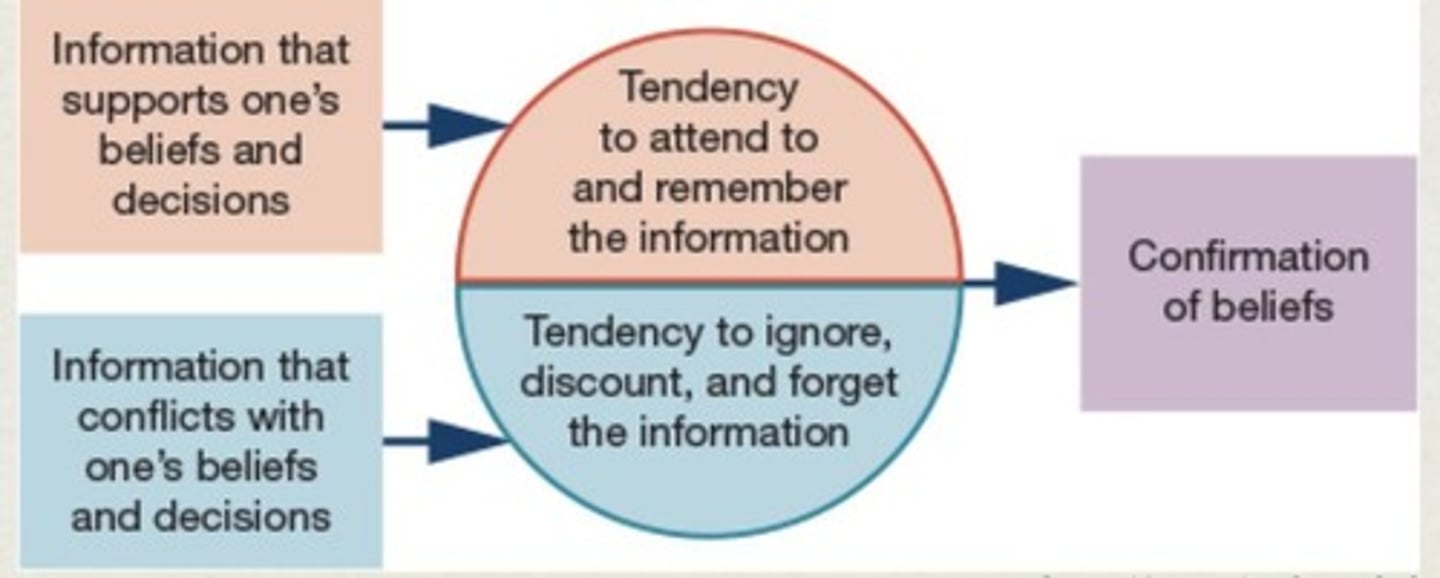
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
Expectations cause individuals to confirm those beliefs.
Initial Impression
First perception of a person's characteristics.
Behavioral Influence
Perceiver's actions shaped by their impressions.
Academic Performance
Influenced by teacher expectations in studies.
Weak Effects
Limited impact of expectations on performance.
Stigmatized Groups
More affected by self-fulfilling prophecies.
Detailed Questions
Encouragement based on positive expectations.
Praise
Positive reinforcement based on perceived abilities.
Memory Study
Research on recall influenced by stereotypes.
Cohen's Study
Examined memory for actions based on occupations.
Behavior Comparison
Observing actions across different situations.
Cognitive Distortions
Errors in perception affecting worldview accuracy.
Categorization
Grouping people to save cognitive resources.
Outgroup Homogeneity Effect
Perceiving outgroup members as more similar.
Ingroup
Group of people perceived as similar to oneself.
Outgroup
Group of people perceived as different from oneself.
Stereotypes
Beliefs about characteristics based on group membership.
Prejudice
Negative attitudes towards members of a group.
Discrimination
Unfair behavior towards members of a group.
What-is-beautiful-is-good Stereotype
Belief that attractive people possess positive traits.
Defensive Attribution
Blaming victims to feel less vulnerable.
Just World Hypothesis
Belief that people get what they deserve.
Spontaneously Triggered Stereotypes
Automatic activation of stereotypes upon encountering groups.
Outgroup Perception
Viewing outgroup members as more alike than they are.
Ingroup Perception
Seeing ingroup members as more unique than they are.
Attractiveness Bias
Belief that attractive individuals are more capable.
Social Influence
Impact of others on individual behavior and thoughts.
Cognitive Resources
Mental capacity available for processing information.
Diversity
Variety within groups, contradicting stereotypes.
Split-Second Decisions
Quick judgments often based on stereotypes.
Perceiver's Actions
Behavior influenced by the perceptions of others.
Social Competence
Ability to interact effectively in social situations.
Efficiency
Preference for minimal cognitive effort in impressions.
Selectivity
Seeing what one expects to see.
Primacy Effect
Initial information weighs more than later information.
Ableism
Prejudice against individuals with disabilities.
Old Fashioned Racism
Outward discrimination against underrepresented groups.
Modern Racism
Private negative attitudes expressed when justified.
Systemic Racism
Societal practices favoring certain groups unfairly.
Robbers' Cave Experiment
Study of intergroup conflict and prejudice reduction.
Subordinate Goals
Common goals that require cooperation between groups.
Intergroup Contact
Contact that reduces prejudice through cooperation.
Persuasion
Changing attitudes through communication.
Source Credibility
Trustworthiness and expertise of the communicator.
Need for Cognition
Desire to engage in thoughtful activities.
One-Sided Argument
Ignores opposing viewpoints in persuasion.
Two-Sided Argument
Acknowledges and downplays opposing viewpoints.
Elaboration Likelihood Model
Two routes to process persuasive information.
Peripheral Route
Persuasion via superficial cues, not message content.
Central Route
Persuasion through logical evaluation of the message.
Motivation
Desire to analyze persuasive messages carefully.
Ability
Capacity to understand and grasp the message.
Conformity
Yielding to real or imagined social pressure.
Normative Influence
Conforming to avoid negative social consequences.
Informational Influence
Conforming based on others' behavior in uncertainty.
Asch Study
Demonstrated conformity through visual perception tasks.
Compliance
Yielding to social pressure in public behavior.
Obedience
Following direct commands from authority figures.
Milgram Experiment
Study on obedience involving electric shocks.
Authority Figure
Person in a position of power or control.
Bystander Effect
Reduced likelihood of helping when others are present.
Diffusion of Responsibility
Feeling less responsible when others are around.
Evaluation Apprehension
Fear of embarrassment affecting helping behavior.
Consistency Principle
Sticking to commitments even with changed terms.
Foot in the Door Technique
Agreeing to small requests increases larger request compliance.
Lowball Technique
Committing to an attractive offer before hidden costs.
Self-Perception Theory
Inferring attitudes by observing one's own behavior.
Reciprocity Principle
Expectation to return favors or kindness received.
Door in the Face Technique
Large request followed by a smaller request for compliance.
Scarcity Principle
Desire for items perceived as limited or exclusive.
Law as Policy Instrument
Law is one of many tools for social change.
Moral Development
Stages of moral reasoning proposed by Kohlberg.
Obedience and Punishment Orientation
First stage of moral development focused on authority.
Instrumental Relativism
Second stage characterized by naive reciprocity.
Personal Concordance
Third stage based on approval from others.
Law and Order Stage
Fourth stage emphasizing societal rules and order.
Ethnocentrism
Belief in superiority of one's own group.
Fatalism
Feeling of resignation or powerlessness.
Economic Factors
Limited resources can resist social change.