Psych-Soc MCAT (Milesdown)
1/427
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
428 Terms
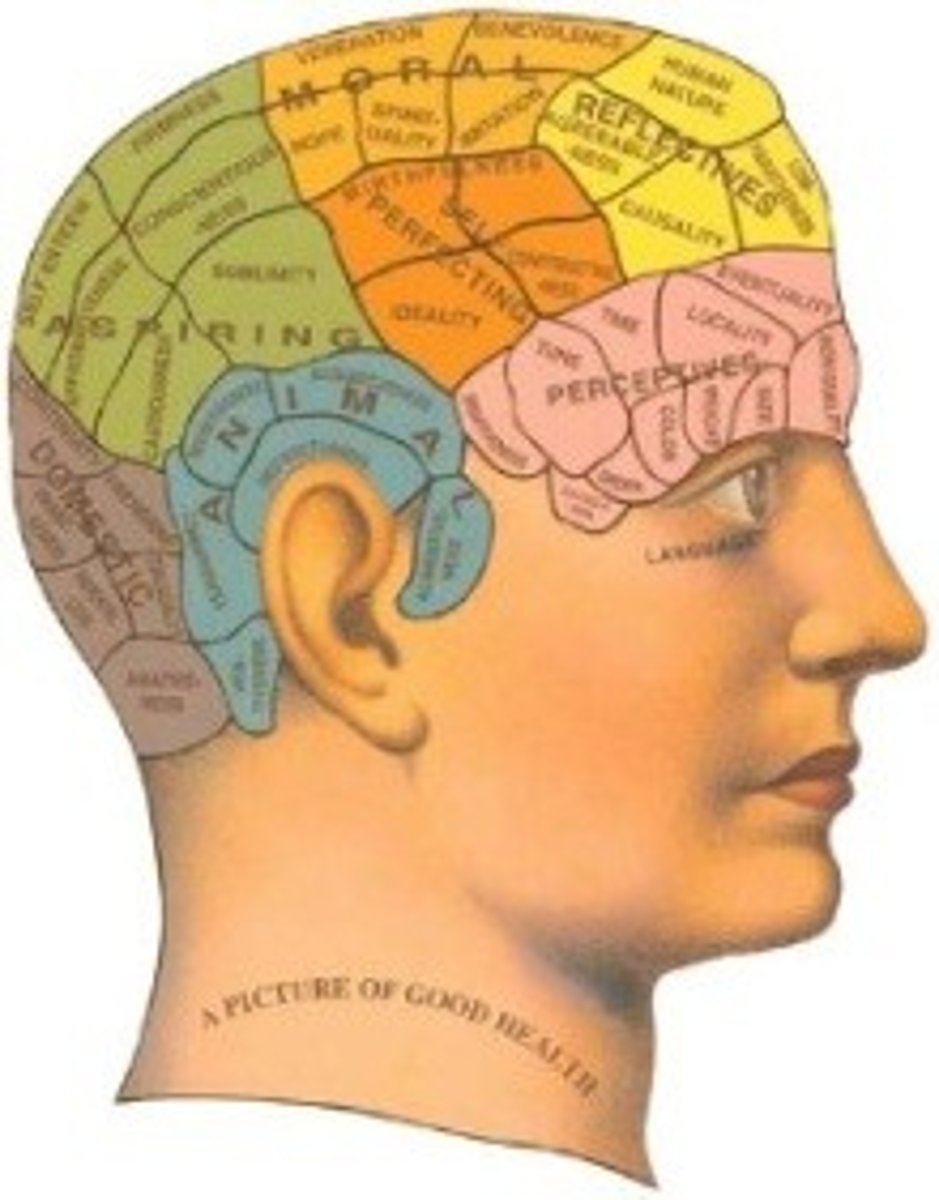
Franz Gall
phrenology
Pierre Flourens
functions of major sections of the brain;
used extirpation to study parts of the brain
William James
Functionalism, how mental processes help individuals adapt to the environement
John Dewey
Functionalism
Paul Broca
Studied people with legions in specific regions of the brain. Broca's area. Speech production
Hermann von Helmholtz
Speed of nerve impulse. Made psychology a science
Sir Charles Sherrington
Synapses
Sigmund Freud
Psychoanalytic perspective
Sensory neurons
Afferent, receptors --> spinal cord
Interneurons
Between other neurons. Mainly CNS
Motor neurons
Efferent, CNS --> muscles & glands
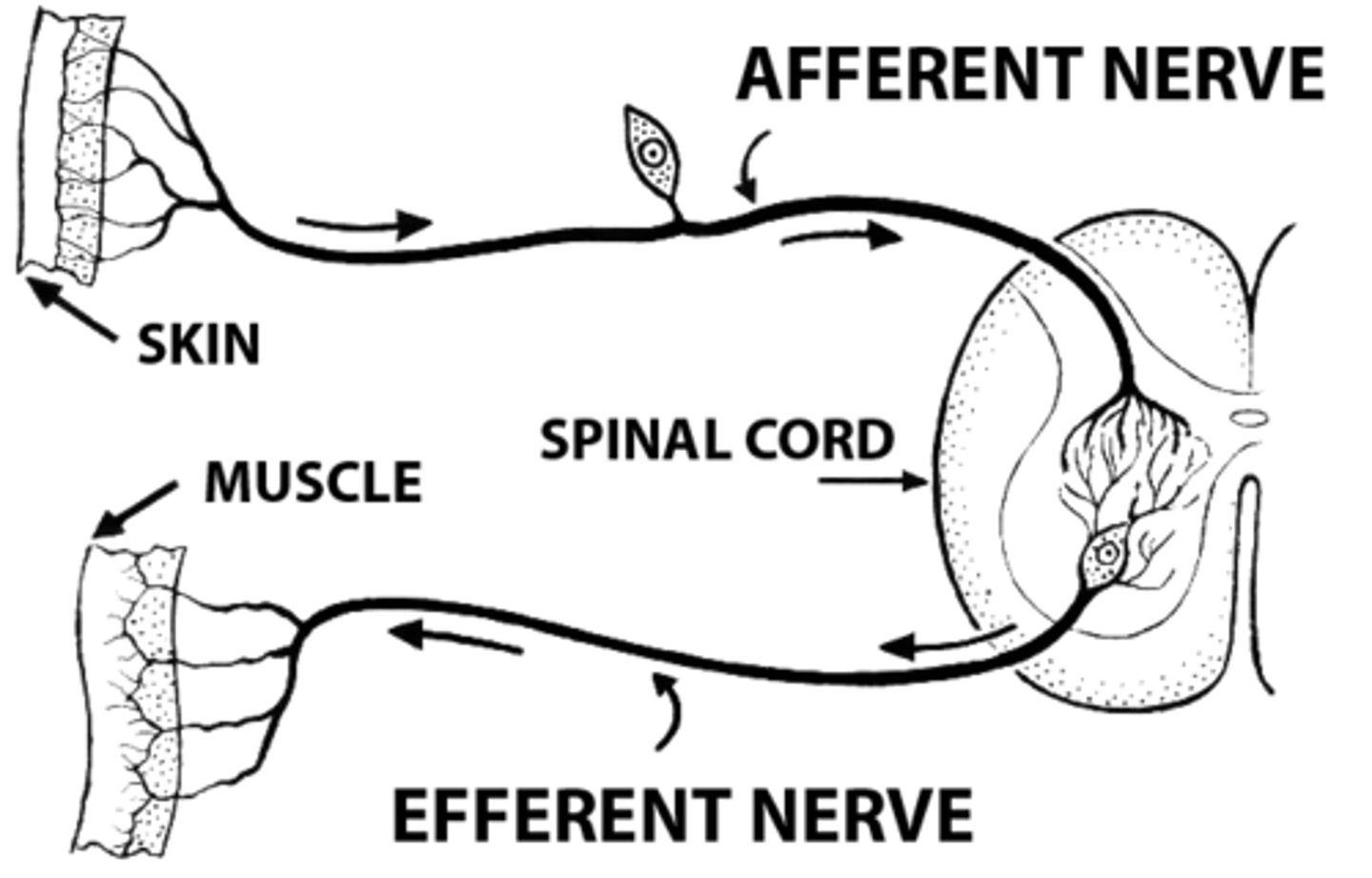
Reflex Arcs
interneurons in spinal cord relay info to the source of stimuli while simultaneously routing it to the brain
central nervous system
CNS. brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
PNS. Nervous tissue and fibers outside CNS
Somatic nervous system
voluntary movements
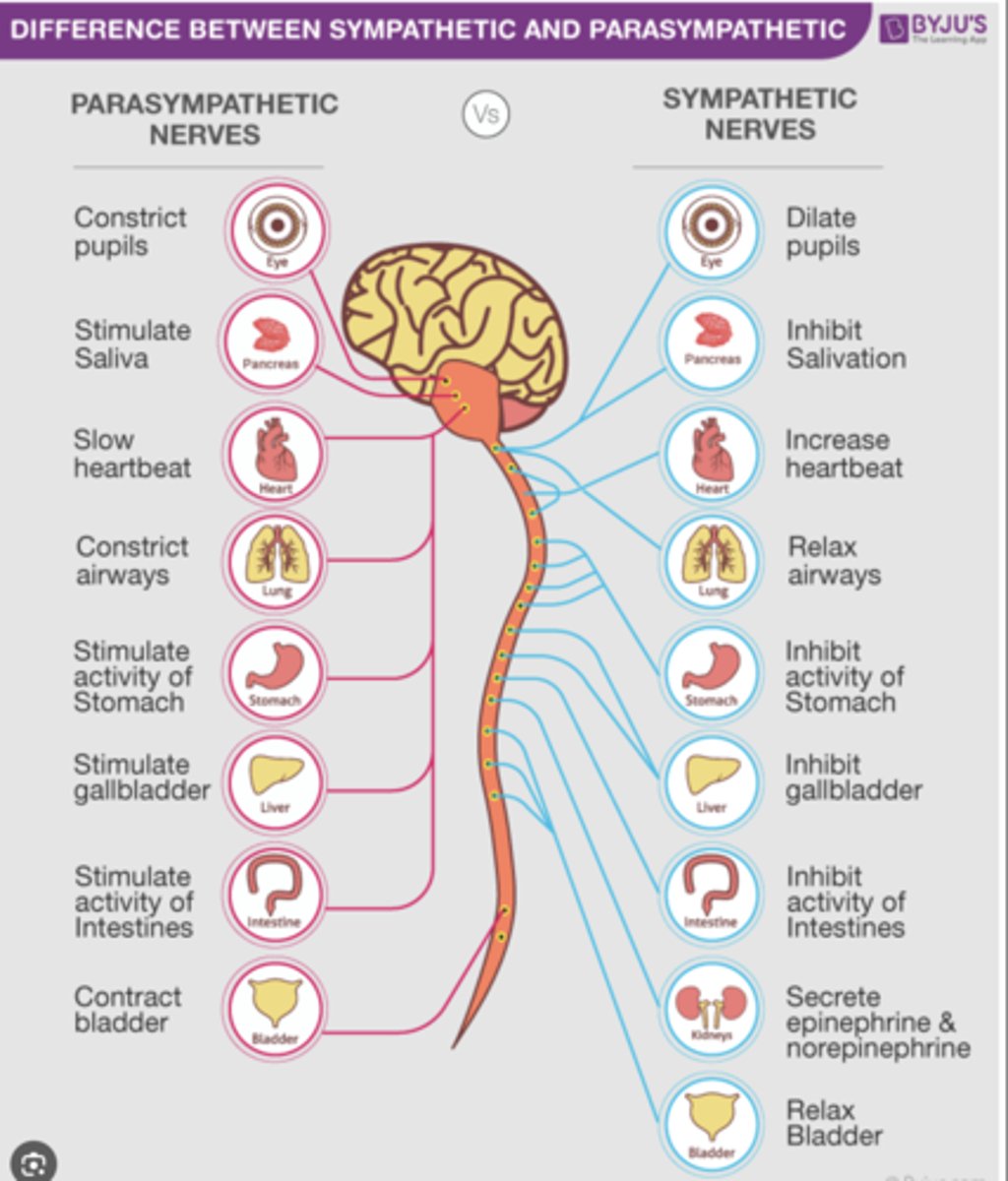
autonomic nervous system
sympathetic and parasympathetic
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
Parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest
Neurotransmitters
Released by neurons to carry a signal
Acetylcholine
used by the somatic nervous system (to move muscles), the parasympathetic nervous system, and the central nervous system (for alertness)
Dopamine
Maintains smooth movements and steady posture
Endorphins & Enkephalins
natural painkillers
Epinephrine & Norepinephrine
maintain wakefulness and alertness, and mediate fight-or-flight responses. Epinephrine tends to act as a hormone, and norepinephrine tends to act more classically as a neurotransmitter
GABA
Inhibitory neurotransmitter. Act as brain "stabilizers". Glycine serves a s similar function
Glutamate
Acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter
Serotonin
modulates mood sleep, eating, and dreaming
The endocrine system...
is tied to the nervous system through the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary
cortisol
stress hormone released by the adrenal cortex
Testosterone & Estrogen
mediate libido; ----------- also increases aggressive behavior. both are produced in gonads and released by adrenal cortex
Location of epinephrine & norepinephrine
released by adrenal medulla and cause physiological changes associated with the sympathetic nervous system
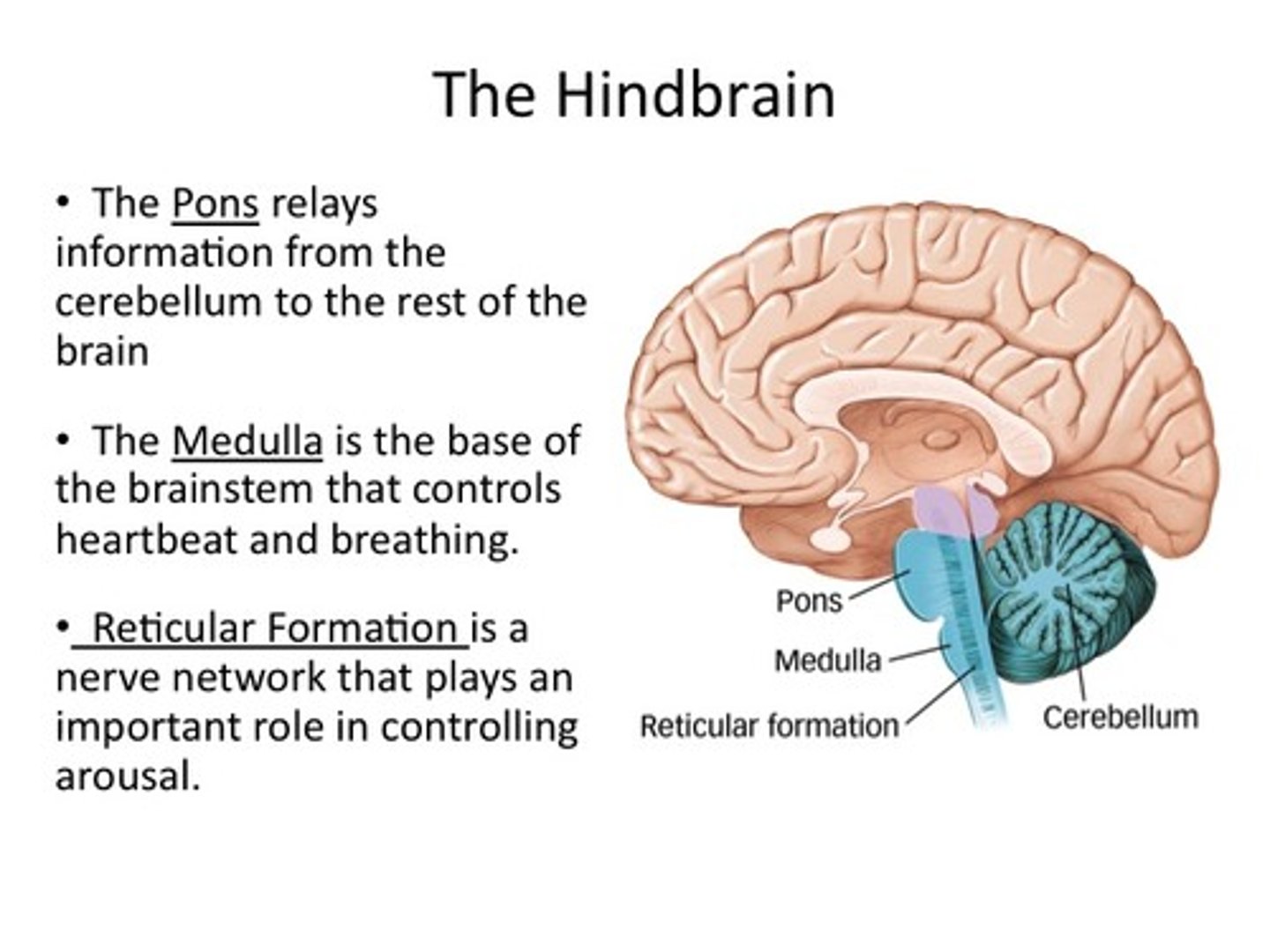
Hindbrain
cerebellum, medulla oblongata, reticular formation
Midbrain
inferior and superior colliculi
Forebrain
thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, limbic system, cerebral cortex
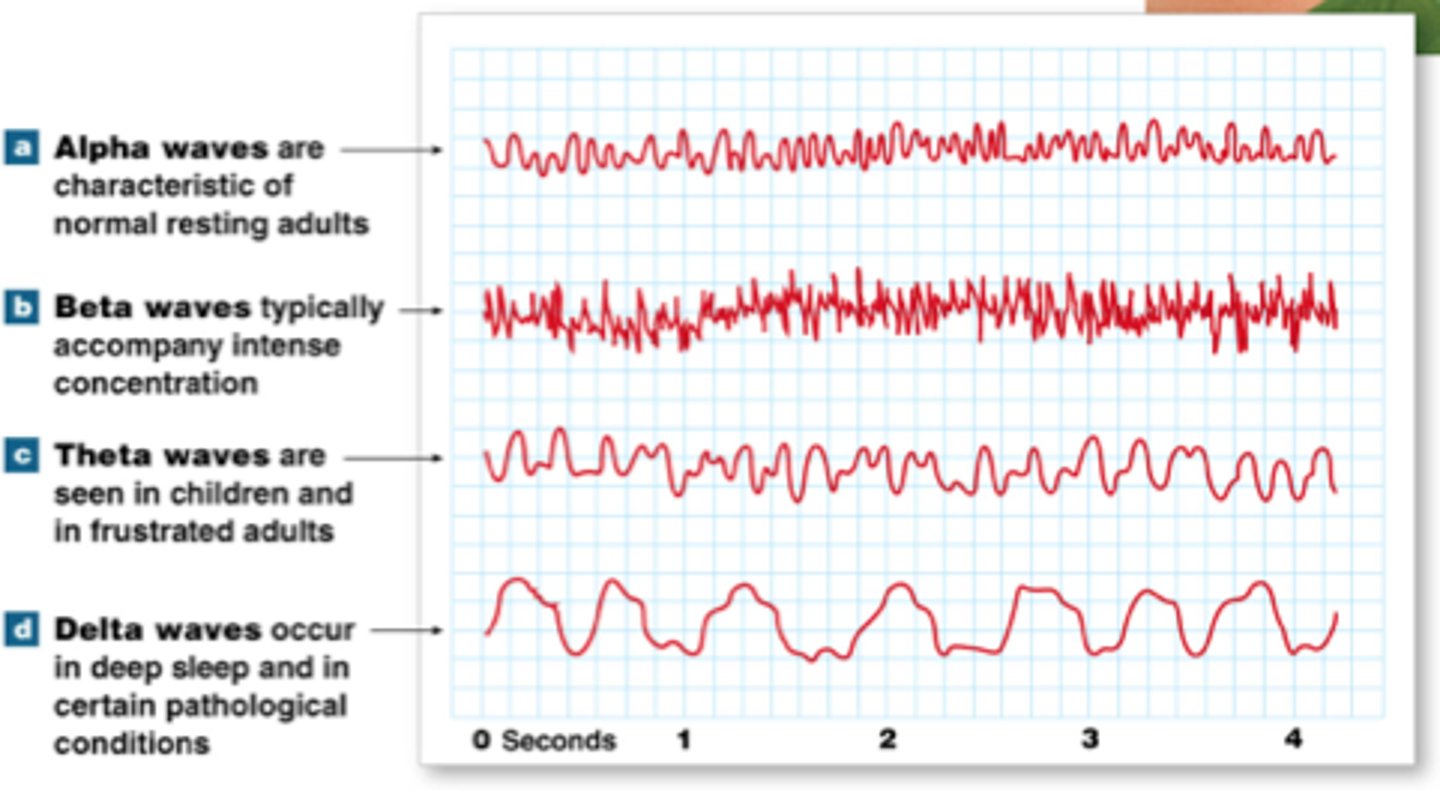
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
Thalamus
Relay station for sensory information
Hypothalamus
Homeostasis & the 4 F's.
Integrates with endocrine system. Hypothalamus --> hypophyseal portal --> anterior pituitary
Basal ganglia
structures in the forebrain that help to control smooth movements and postural stability
Limbic system
septal nuclei, amygdala, hippocampus
Concerned with instincts and mood.
septal nuclei
pleasure and addition
Amygdala
fear and aggression
Hippocampus
emotion and memory
cerebral cortex
4 Lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
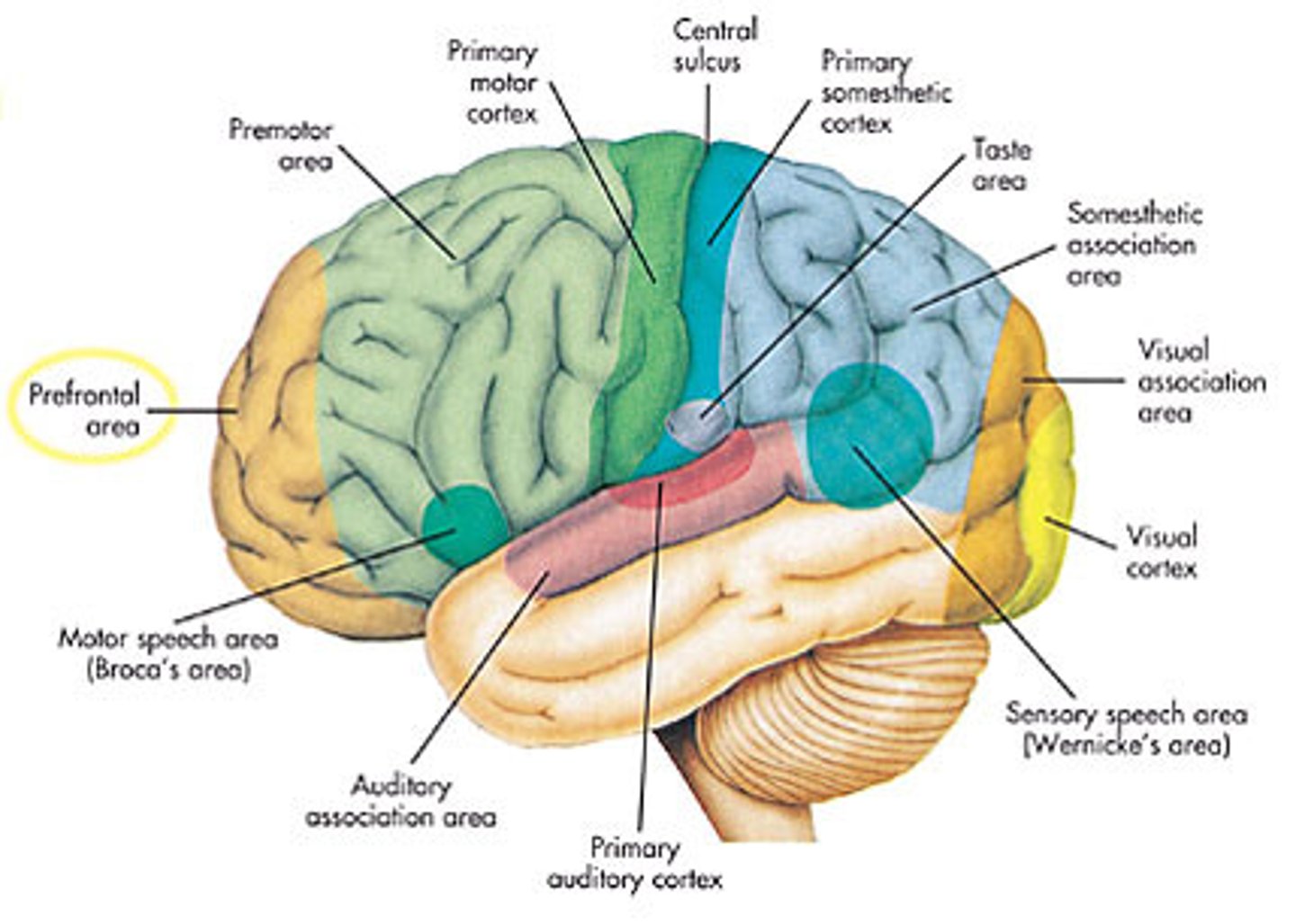
Frontal lobe
executive functions, impulse control, speech, motor
Parietal lobe
Touch, pressure, temperature, pain, spatial processing
occipital lobe
visual
Temporal lobe
sound, speech perception, memory, emotion
left cerebral hemisphere
analytic, language, logic, math
usually dominant
right cerebral hemisphere
intuition, creativity, spatial processing
Neuralation
The formation of the nervous system during weeks 5-8 of gestation. ------------ begins when a section of the ectoderm invaginates and pinches off to form the neural groove, which ultimately forms the neural tube, from which the brain and spinal cord develop.
neural tube
becomes the CNS
neural crest cells
spread out throughout the body, differentiating into many different tissues
primitave reflexes
exist in infants and should disappear w/ age.
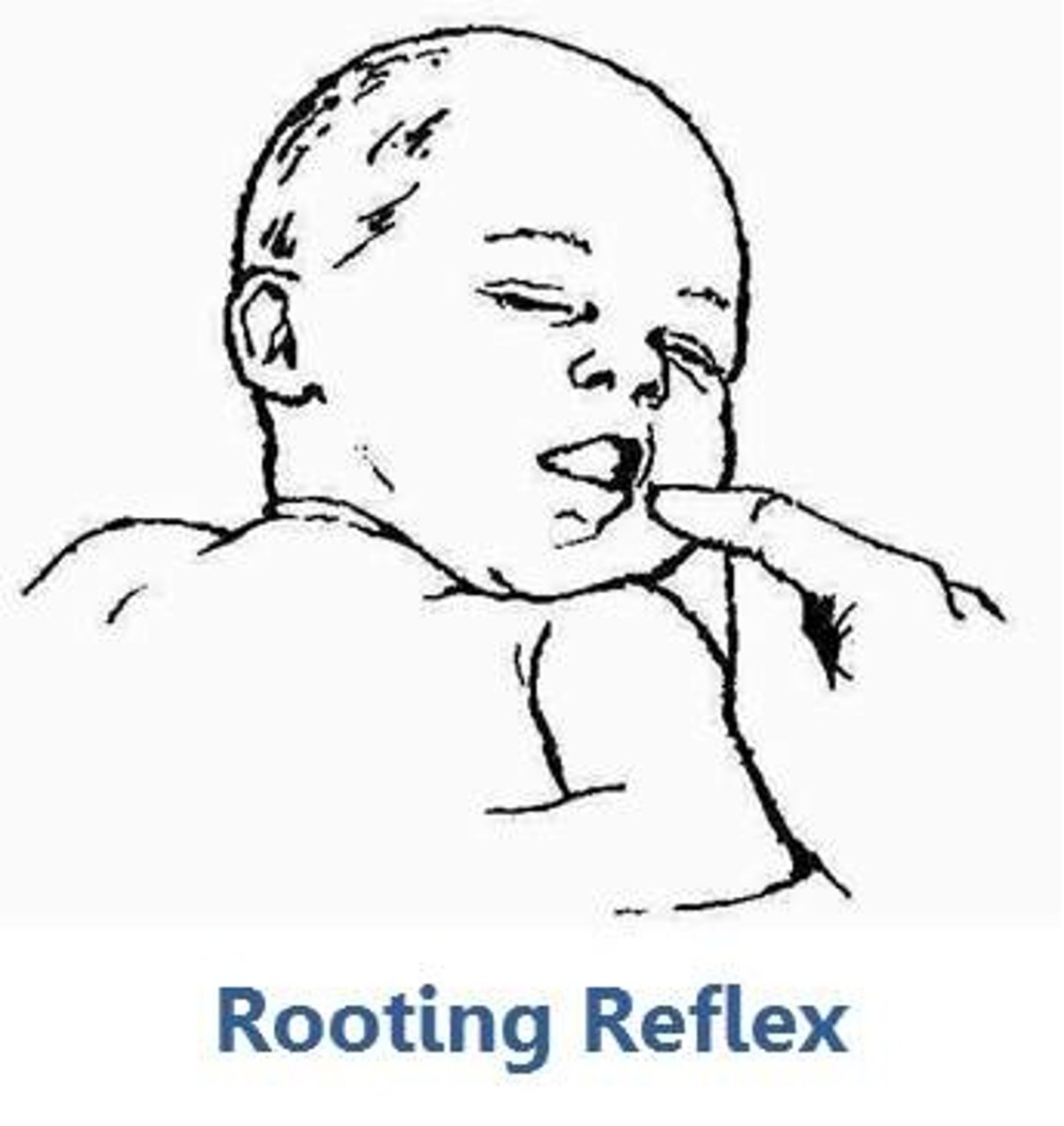
rooting reflex
turns head toward stimulus
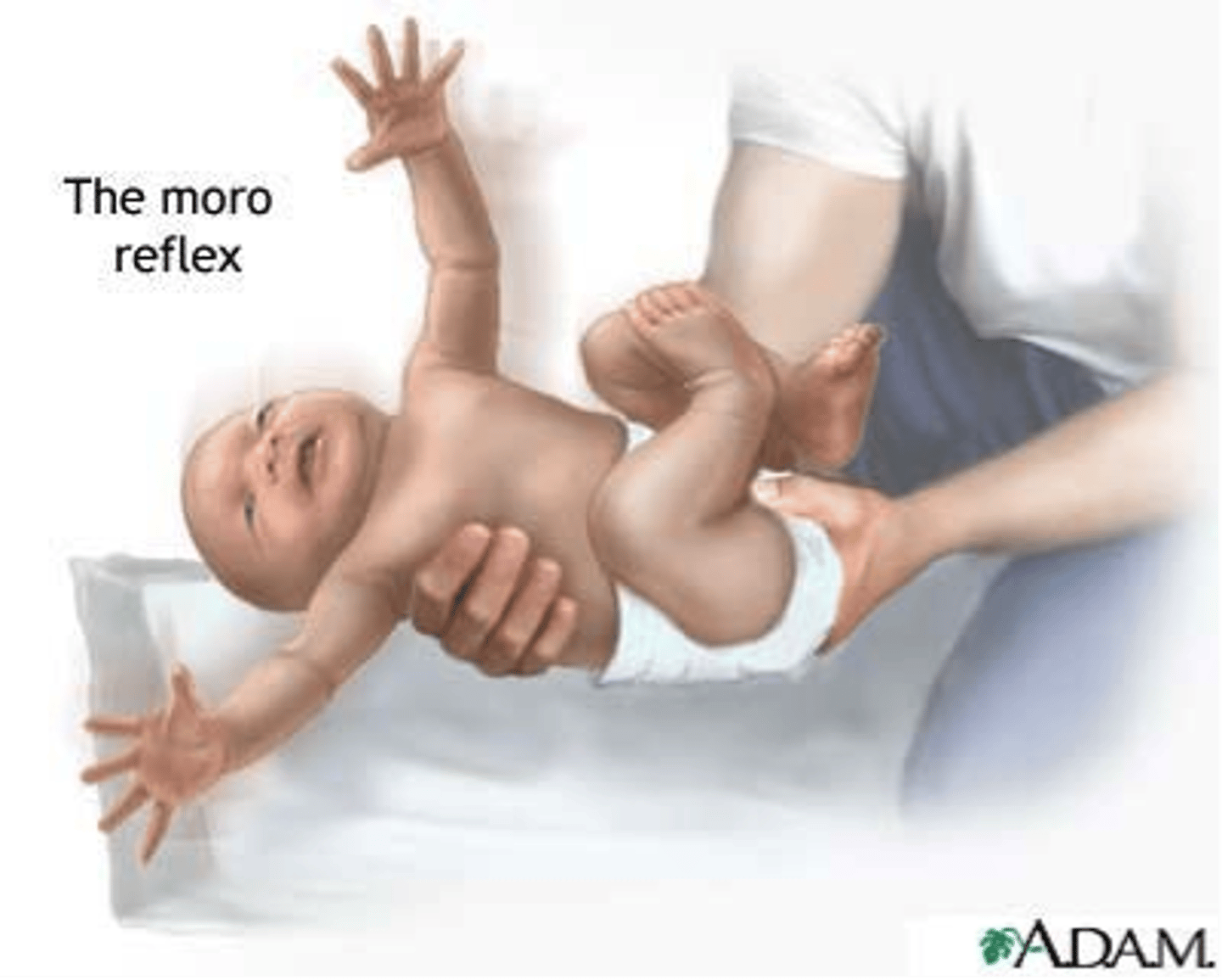
Moro reflex (startle reflex)
extends arms, response to falling sensation

Babinski reflex
big toe extended and other toes fan in response to brushing of sole of foot
grasping reflex
grasping objects that touch the palms
gross motor skills
motor skills that involve large-muscle activities, such as walking
fine motor skills
use of muscles in fingers, toes, and eyes to coordinate small actions
sensory receptors
sensory nerve endings that respond to stimuli
sensory ganglia
collections of cell bodies outside the CNS
projection areas
Areas in which the brain tissue seems to form a "map" of sensory information.
absolute threshold
the minimum stimulus energy needed to detect a particular stimulus 50 percent of the time
threshold of conscious perception
minimum of stimulus energy that will create a signal large enough in size and long enough in duration to be brought into awareness
Difference (Just noticeable difference) threshold
the minimum difference in magnitude between two stimuli before one can perceive the difference
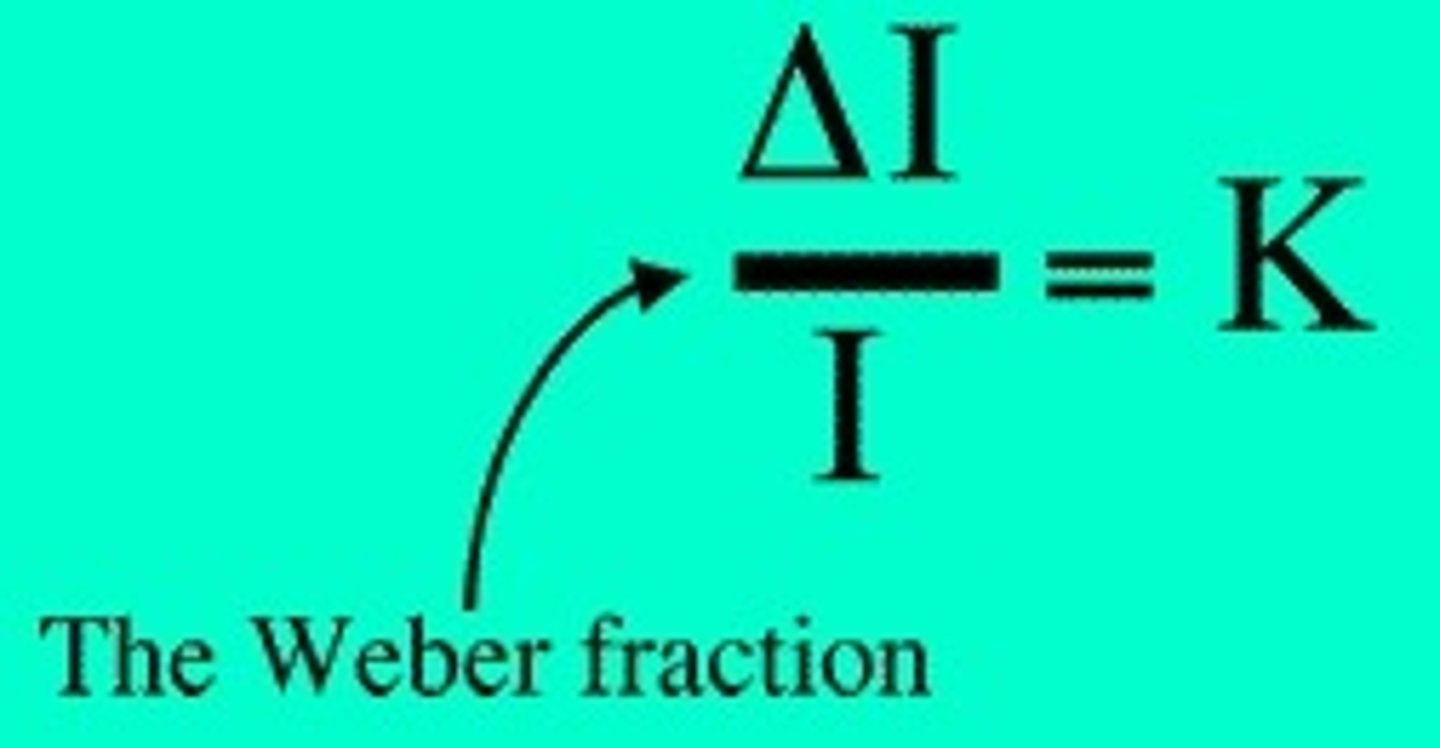
Weber's Law
the just noticeable difference of a stimulus is proportional to the magnitude of the stimulus
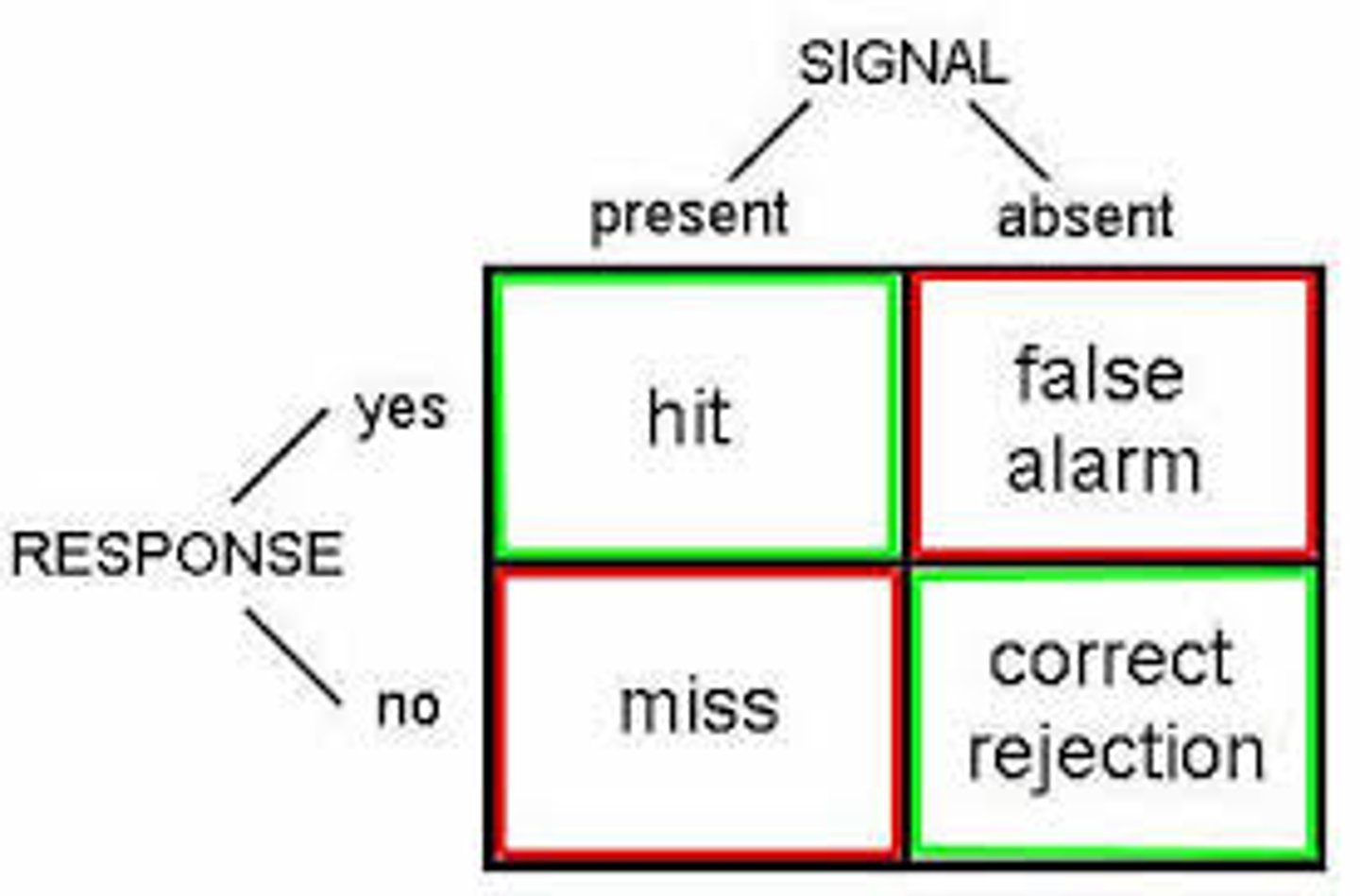
signal detection theory
refers to the effects of nonsensory factors, such as experiences, motives, and expectations, on perception of stimuli
Adaptation
Refers to the increase or decrease in sensitivity to a stimulus
Cornea
gathers and filters incoming light
Iris
controls the size of the pupil, divides eye into anterior & posterior chamber. dilator and constrictor pupilae
Lens
refracts incoming light to focus it on the retina
Aqueous humor
Produced by the ciliary body. Nourishes the eye and gives the eye its shape. Drains through the canal of Schlemm.
Retina pathway
rods and cones --> bipolar cells --> ganglion cells --> optic nerve
Rods
detect light and dark, contain rhodopsin
Cones
in the fovea, detects color
retinal disparity (binocular disparity)
space between eyes; allows for binocular vision and depth
horizontal & amacrine cells
integrates signals from ganglion cells and performs edge sharpening
Eye structure and support
virtuous on inside. sclera and choroid on outside
parallel processing
color, form and motion at same time
magnocellular cells
motion. high temporal resolution
parvocellular cells
shape. high spatial resolution
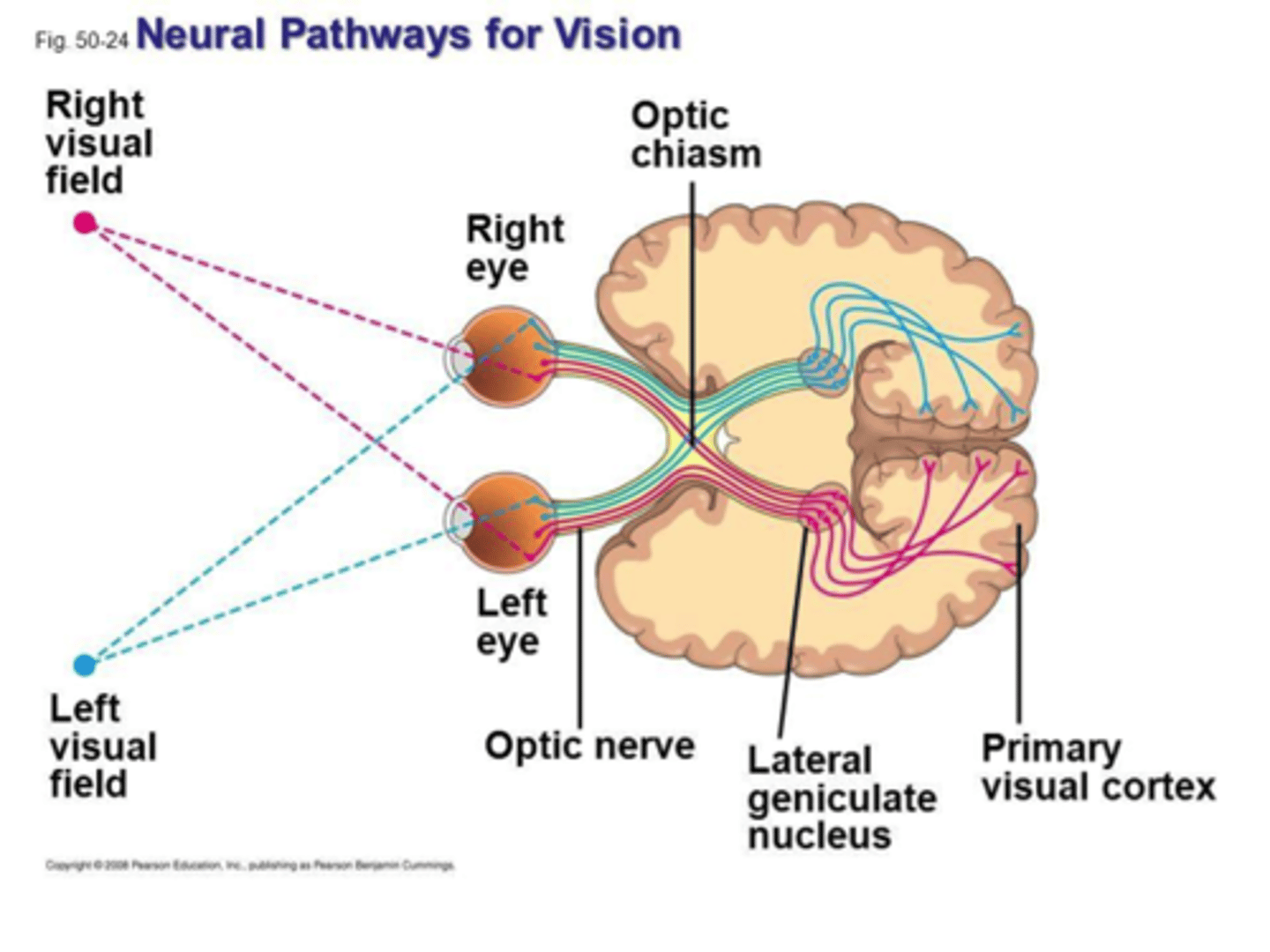
visual pathway
retina -> optic nerve -> optic chiasm -> optic tracts -> lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of thalamus -> visual radiations -> visual cortex
outer ear
pinna (auricle), external auditory canal, tympanic membrane
Middle ear
connected to nasal cavity by Eustachian tube
Ossicles
MIS
Malleus
Incus
Stapes
HAS
Hammer
Anvil
Stirrups
Malleus
a small bone in the middle ear that transmits vibrations of the eardrum to the incus.
incus
a small anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear, transmitting vibrations between the malleus and stapes.
Stapes
stirrup; last of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear, rests in the oval window of the cochlea
inner ear (labyrinth)
bony labyrinth (perilymph) and membranous labyrinth (endolymph)
membraneous labyrinth
filled with endolymph, sound
utricle and saccule
detect linear acceleration and the effects of gravity
semicircular canals
rotational acceleration and balance
Superior olive
localizes sound
inferior colliculi
Startle reflex- Turn head towards unexpected sound; also vestibulo-ocular reflex- keeps eyes fixed while head rotates
Auditory pathway
cochlea --> vestibulocochlear nerve --> medial geniculate nucleus (MGN) of thalamus --> auditory cortex
smell
detection of volatile or aerosolized chemicals by olfactory chemoreceptors (olfactory nerves). Bypasses the thalamus
Pheromones
chemicals given off by animals that have an effect on social foraging, and sexual behavior in other members of that species
taste
detection of dissolved compounds by taste buds in papillae: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, uramami
somatosensation
refers to the four touch modalities: pressure, vibration, pain, and temperature
two-point threshold
minimum distance necessary between two points of stimulation on the skin such that the points will be felt as two distinct stimuli
physiological zero
the normal temperature of the skin to which objects are compared to determine if they feel warm or cold