med micro microbial diseases of the skin and eyes
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
what 2 things in the skin contain nutrients?
perspiration and sebum
what inhibits microbes in the skin?
salt
what hydrolyzes peptidoglycan in the skin?
lysozyme
what inhibits some pathogens in the skin?
fatty acids
what are antimicrobial peptides in the skin?
defensins
mucous membrane
line body cavities; epithelial cells are attached to an extracellular matrix
in mucous membranes cells secrete. __________
mucous
mucous is often basic or acidic
acidic
1 multiple choice option
in mucous membranes, some cells have cilia t/f
true
1 multiple choice option
in the eyes, tears contain _________
lysozyme
what is a normal, gram +, salt tolerant bacteria found on the skin?
Staphylococci spp.
normal microbiota of the skin grow on ________
olis
what is an aerobe found on the surface of the skin?
Corynebacterium xerosis (G+)
what is an anaerobe found in hair follicles?
Propionibacterium acnes (G+)
what are normal yeasts found on the skin?
Malassezia furfur and Candida albicans
what are the 4 types of skin lesions?
vesicle, bulla, macule, pustule
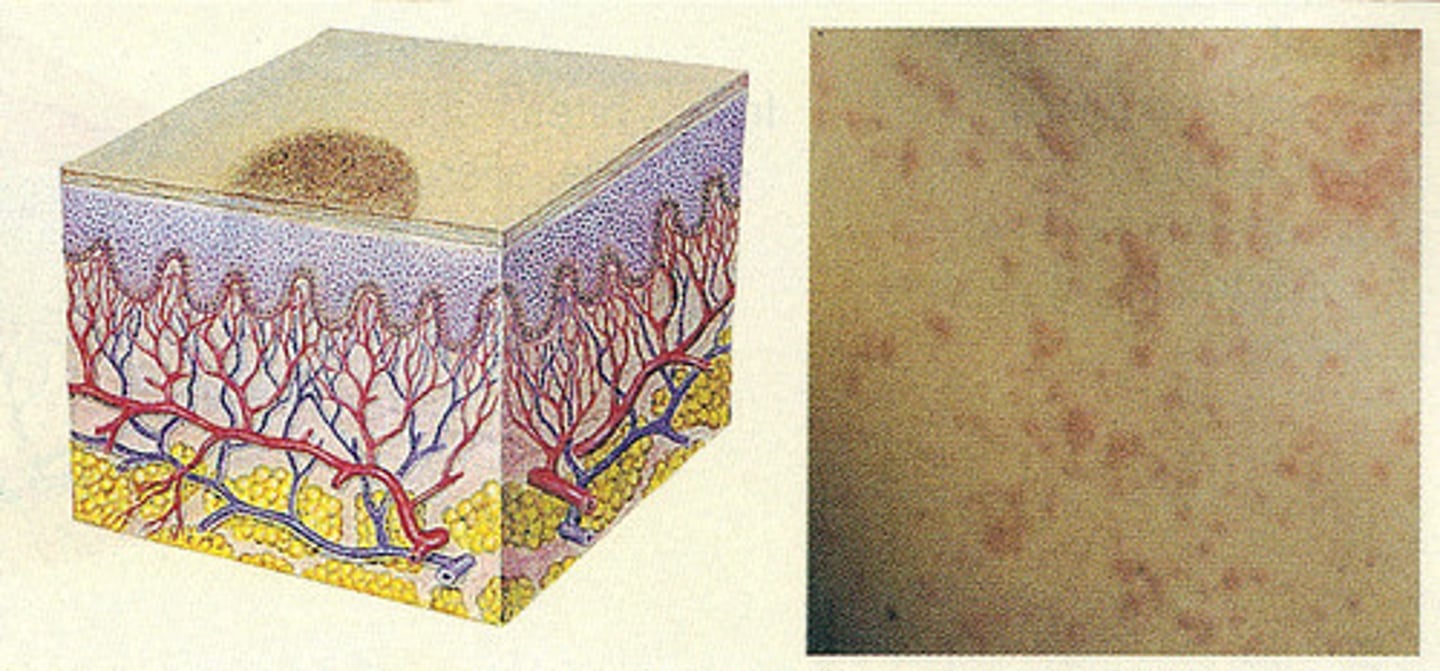
vesicle
small, fluid-filled raised spot on the skin; blister
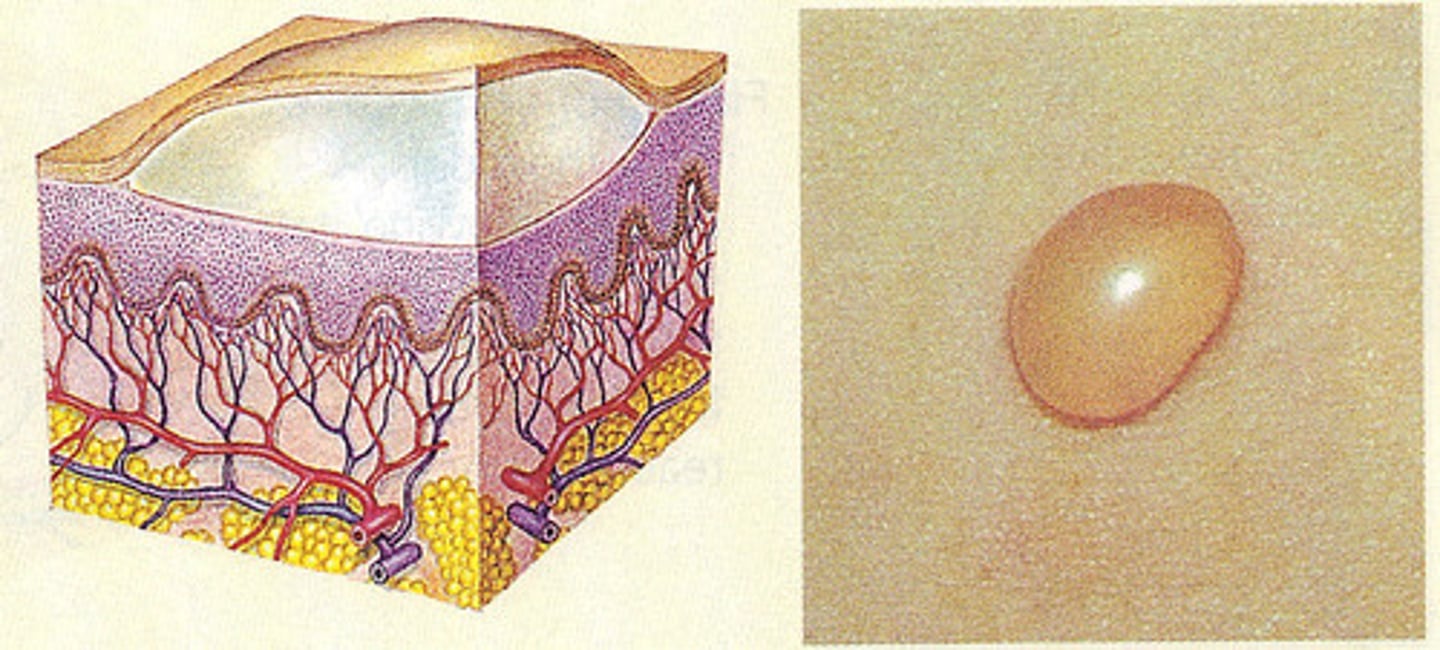
bulla
large blister containing watery fluid
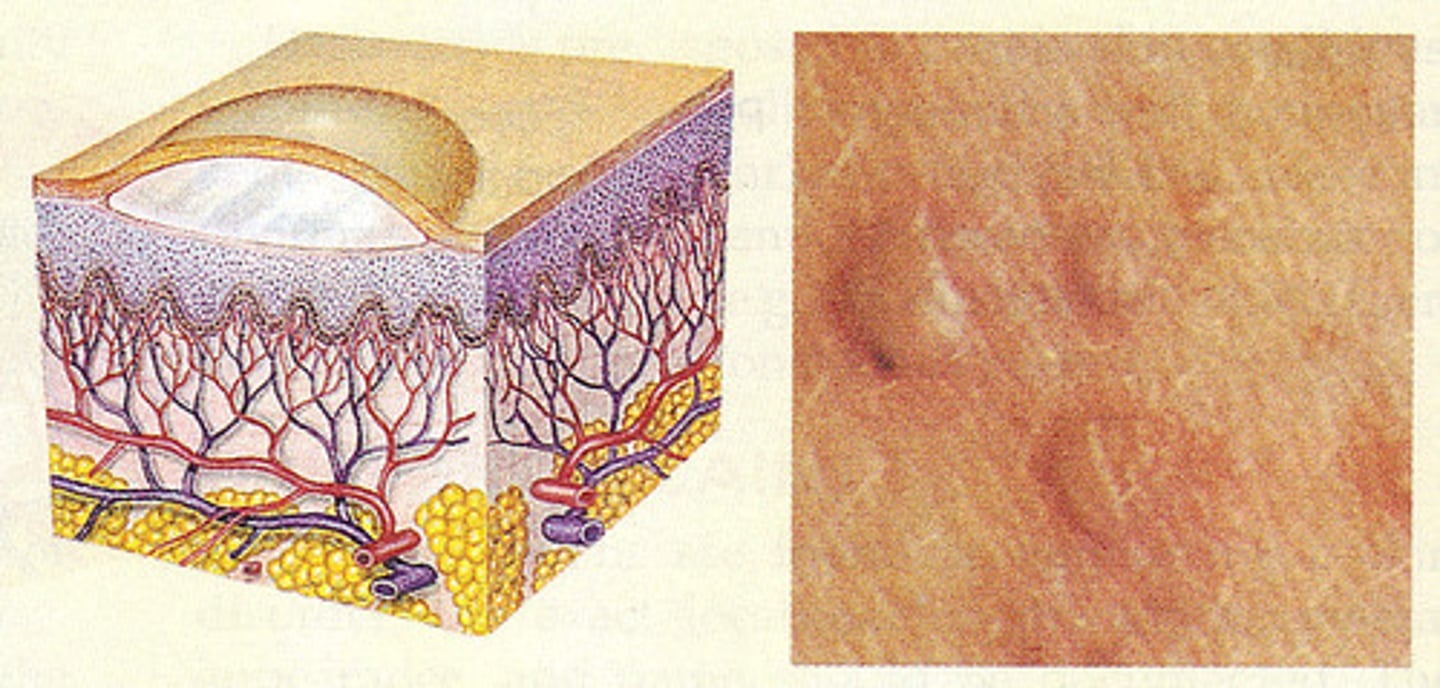
macule
flat, colored spot on the skin (freckle)
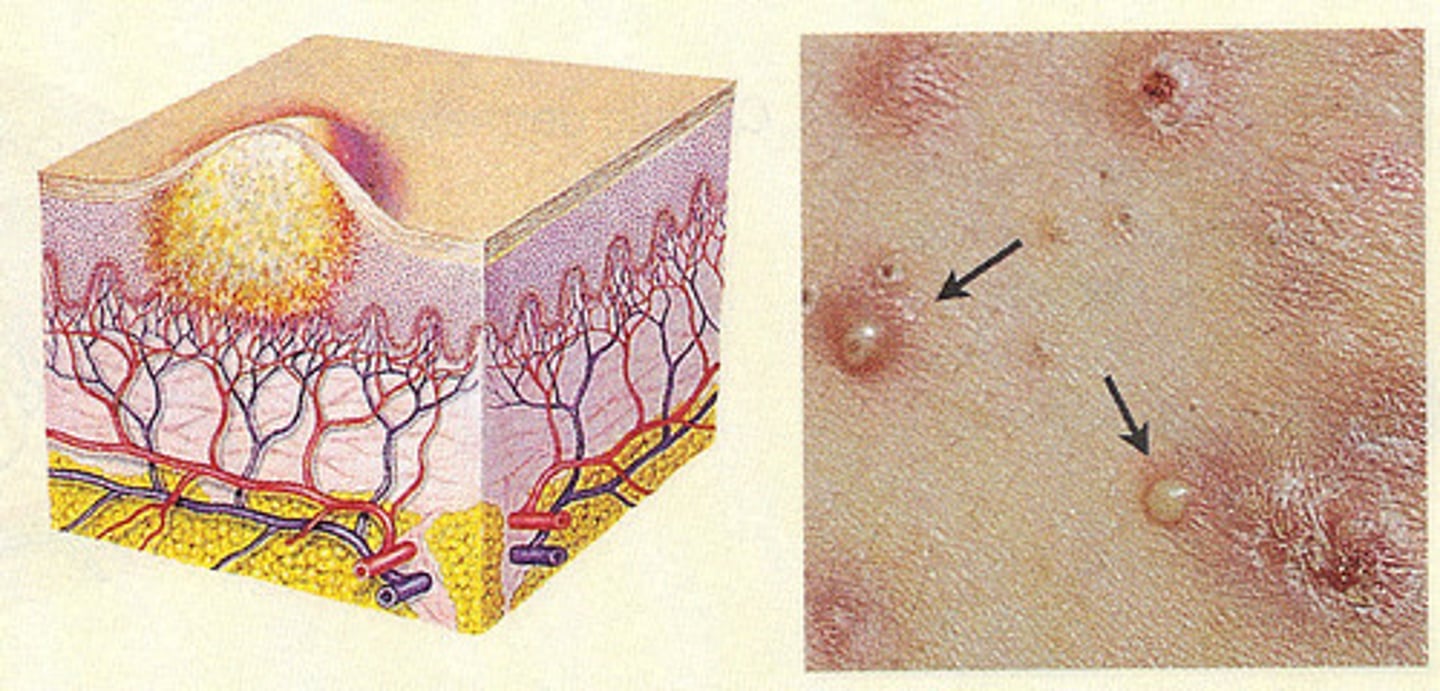
pustule
raised spot on the skin containing pus
exanthem
skin rash
enanthem
mucous membrane rash
what are 2 staphylococcal skin infections?
Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
opportunistic, gram + cooci, coagulase negative
Staphylococcus aureus
gram + cocci, coagulase positive, multi drug resistant
Staphylococcus aureus resists ___________
opsonization
Staphylococcus aureus survives in ____________
phagolysosome
leukocidin
kills leukocytes
coagulase
coagulates plasma
hyaluronidase
digests extracellular matrix
staphylokinase
digests blood clots
exfoliative toxin
digests epithelium
superantigen
drives anaphylactic shock
folliculitis
infections of the hair follicles
sty
folliculitis of an eyelash
furuncle
abscess; pus surrounded by inflamed tissue
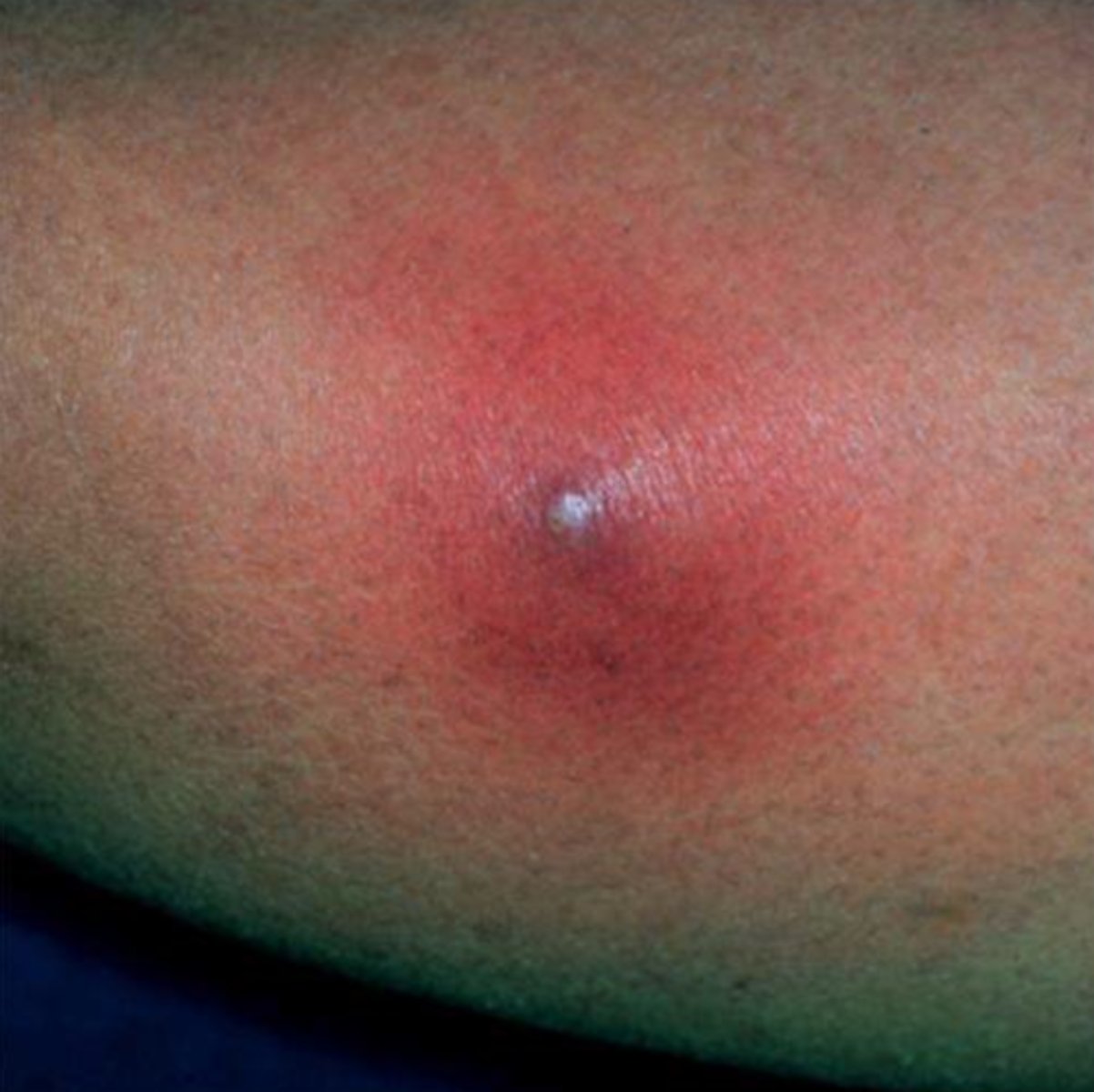
carbuncle
inflammation of tissue under the skin
what involves a single follicle and what involves multiple follicles?
single: furuncle
multiple: carbuncle
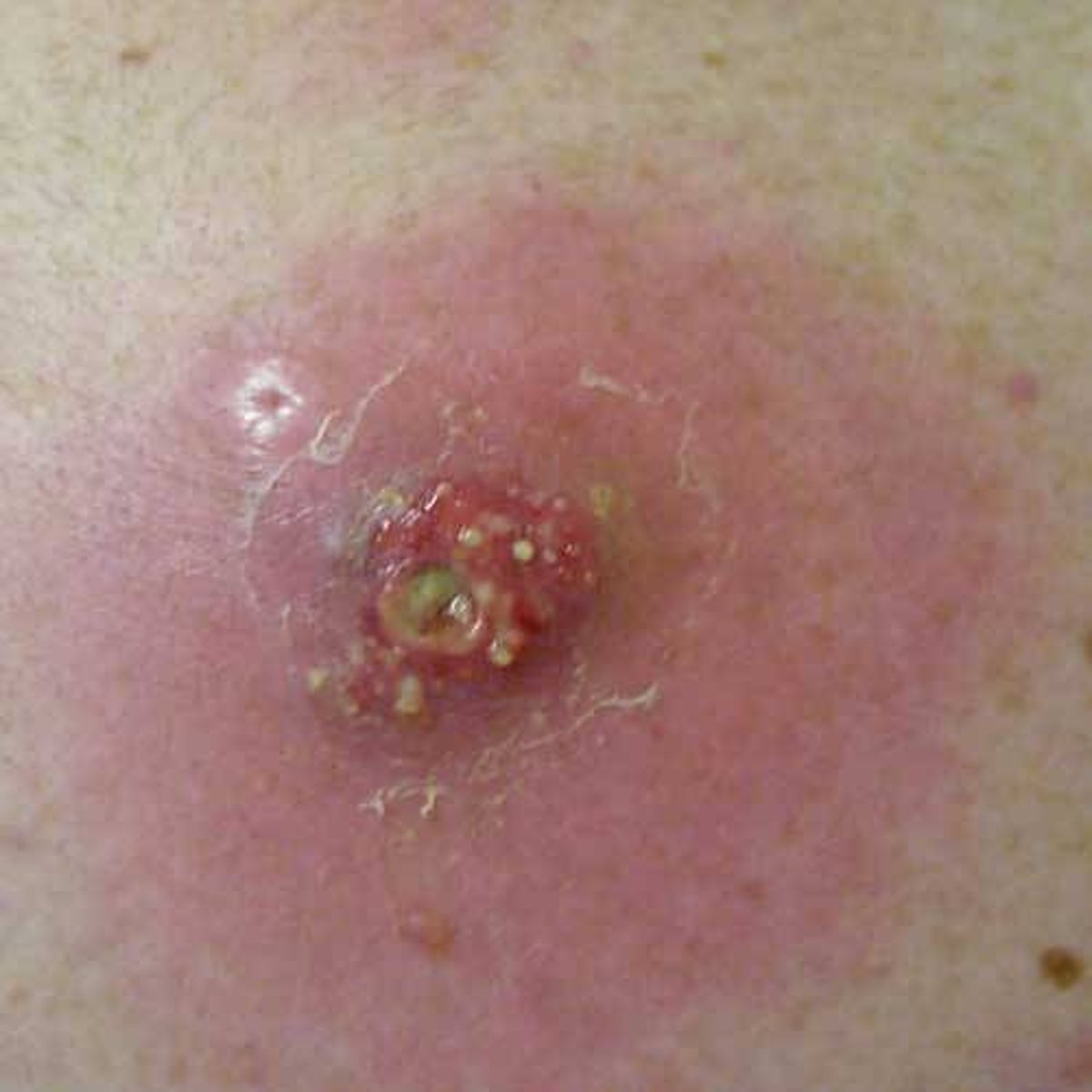
impetigo
crusting (nonbullous) sores, spread by autoinoculation
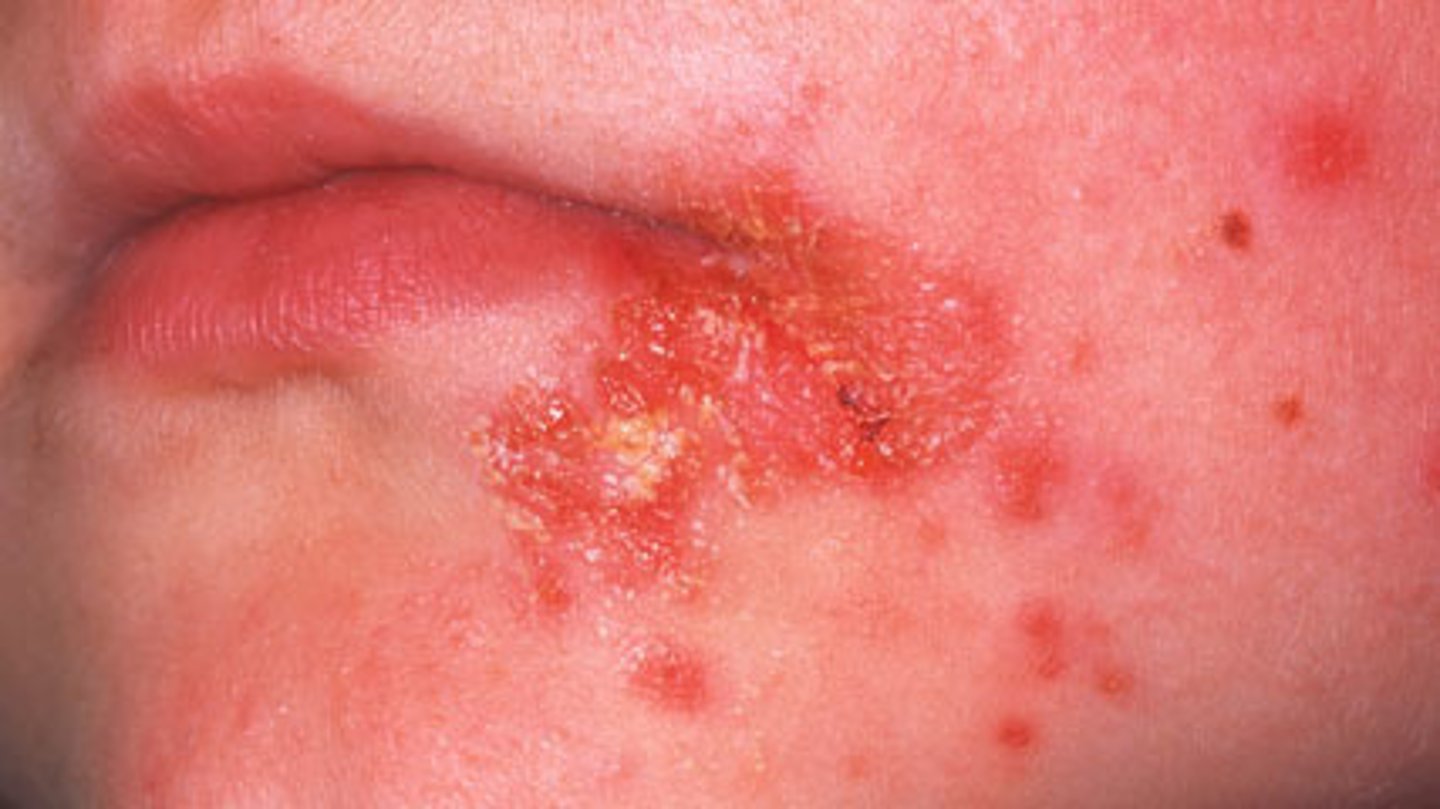
Staphylococcus aureus intoxication causes what 2 syndromes?
toxic shock syndrome and scaled skin syndrome
toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
due to superantigen toxin (TSS toxin)
scaled skin syndrome (SSS)
bullous lesions; impetigo of the newborn; due to exfoliative toxins A and B
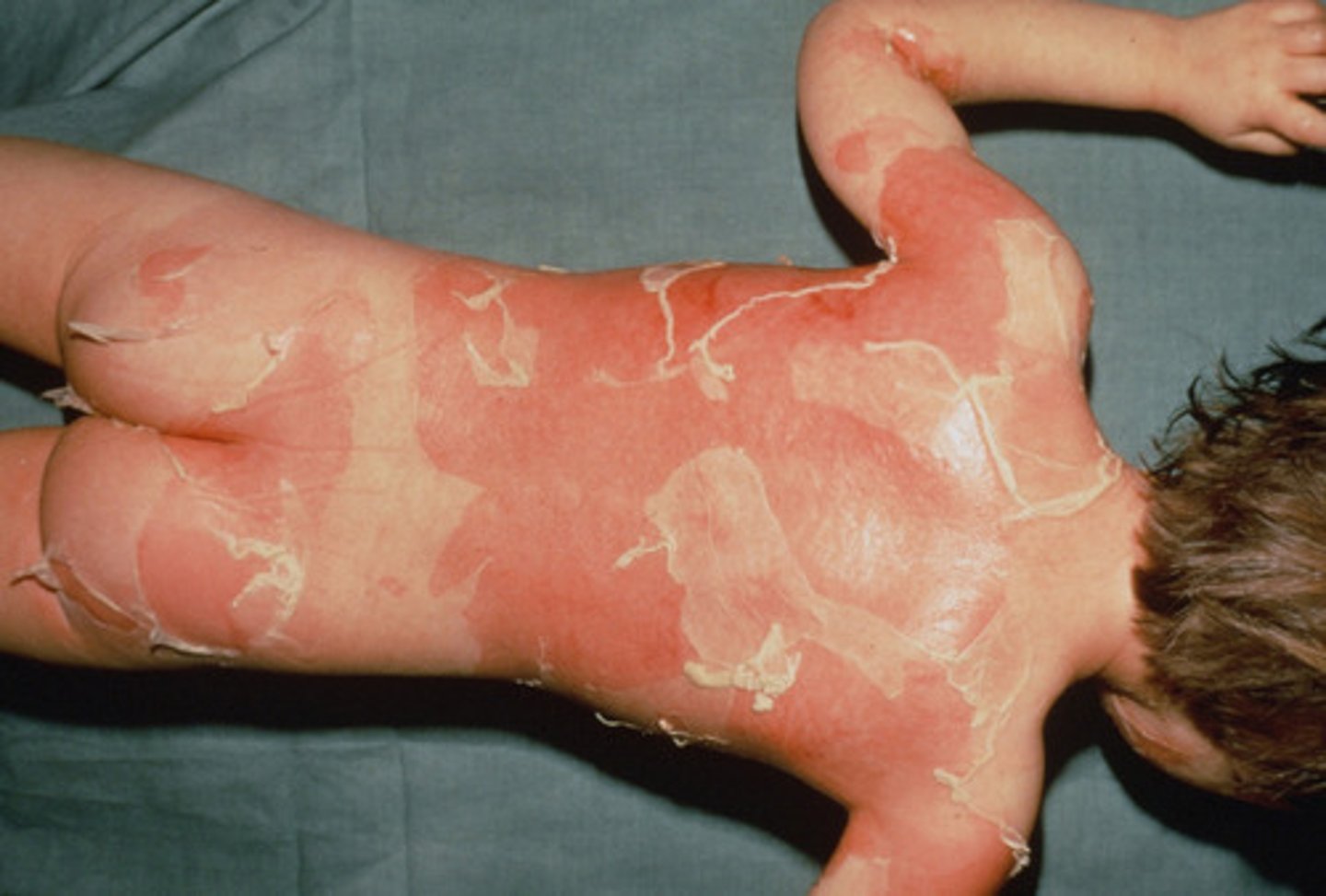
scaled skin syndrome (SSS) % mortality
50%
Streptococcus pyogenes
beta hemolytic
hemolysins
digest RBCs
hyaluronidase
digest ECM
streptolysins
digest RBCs
M proteins
blocks opsonization and phagocytosis
erysipelas
blisters or swollen lesions
necrotizing fasciitis
flesh eating disease
necrotizing fasciitis caused by
superantigen exotoxin
M protein = _______ factor in ?
virulence; S. pyogenes
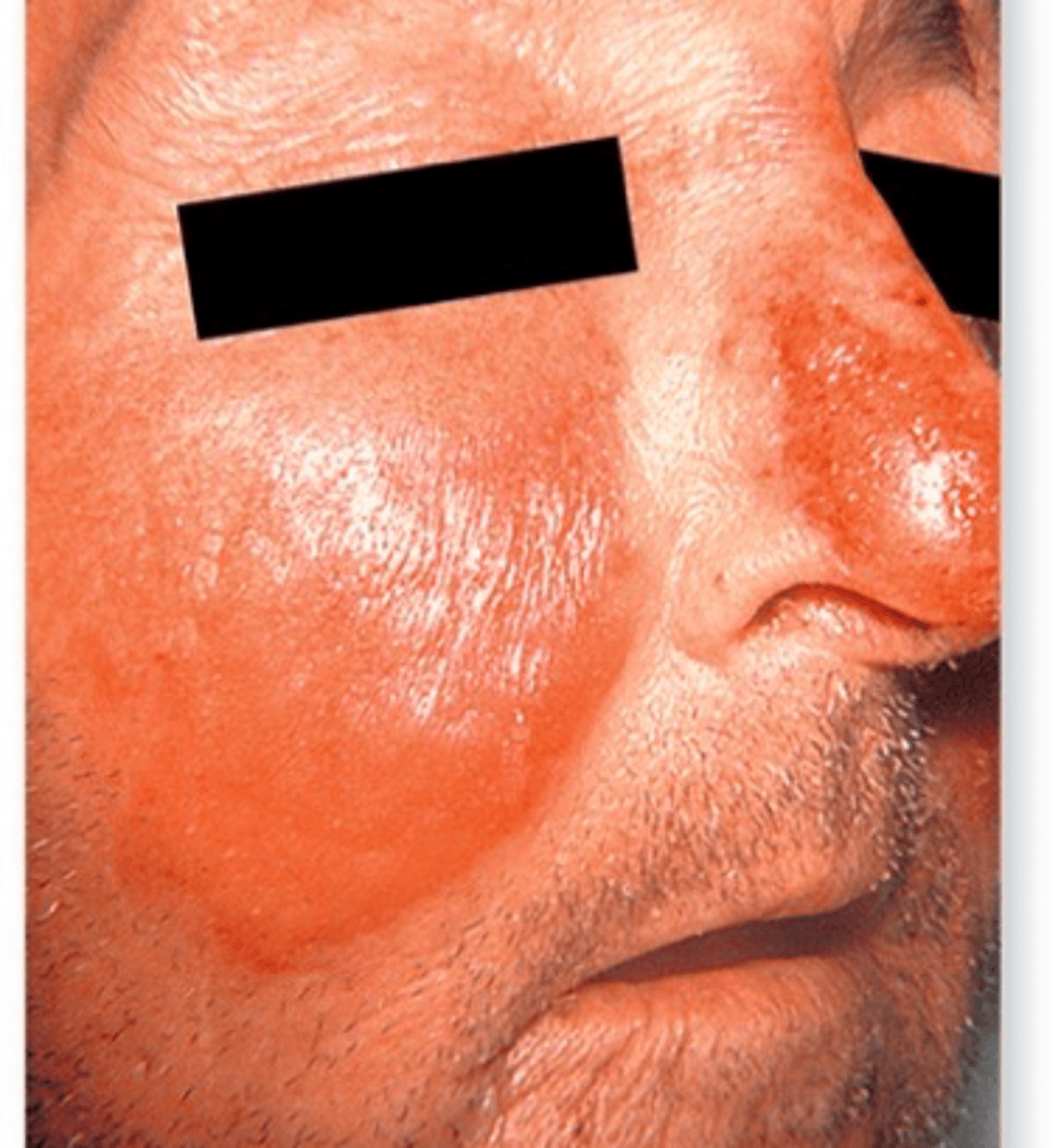
lesions of erysipelas caused by B-hemolystic streptococcal toxins
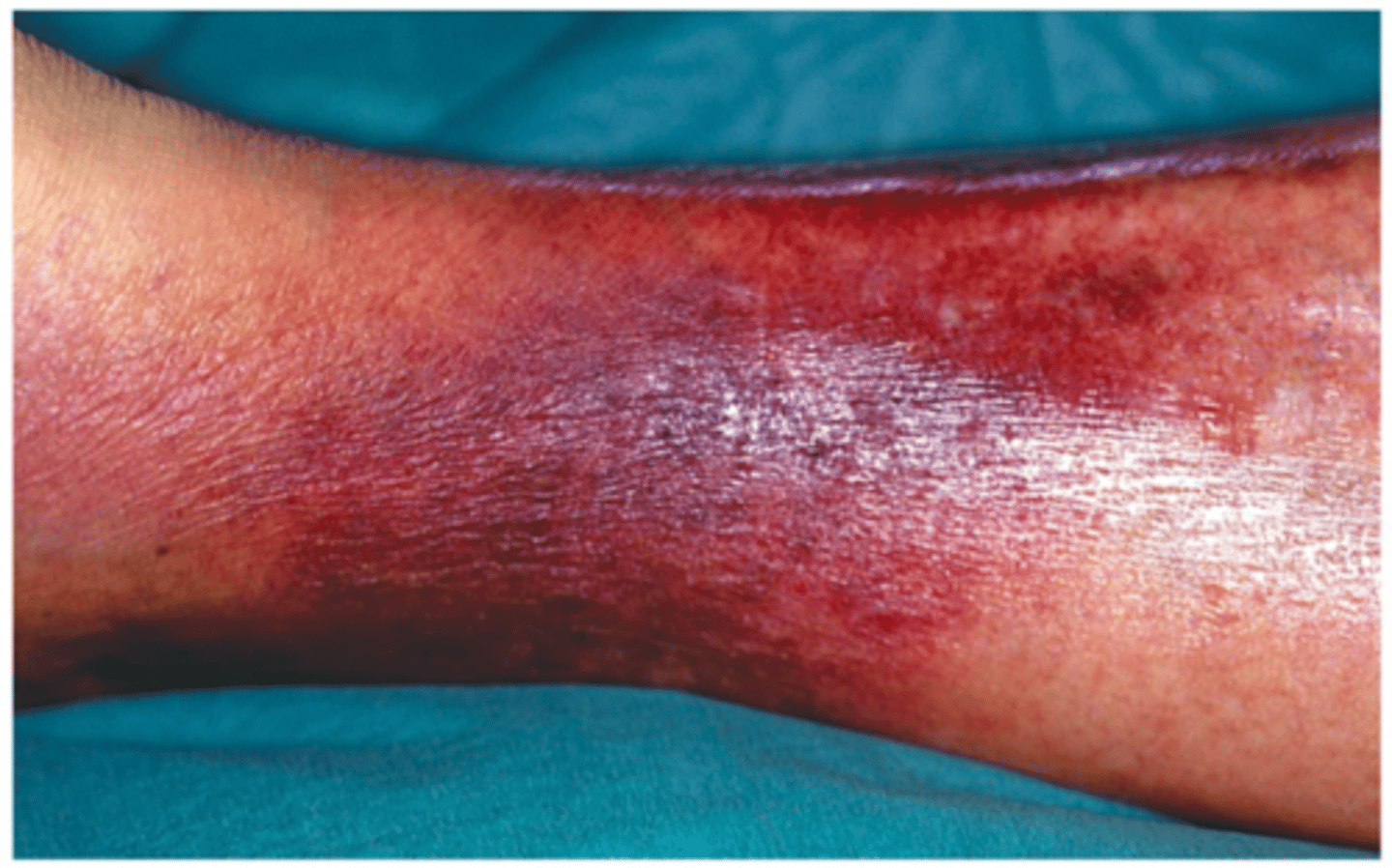
lesions of facial erysipelas caused by hemolytic streptococcal toxins
necrotizing fasciitis due to Streptococcus pyogenes
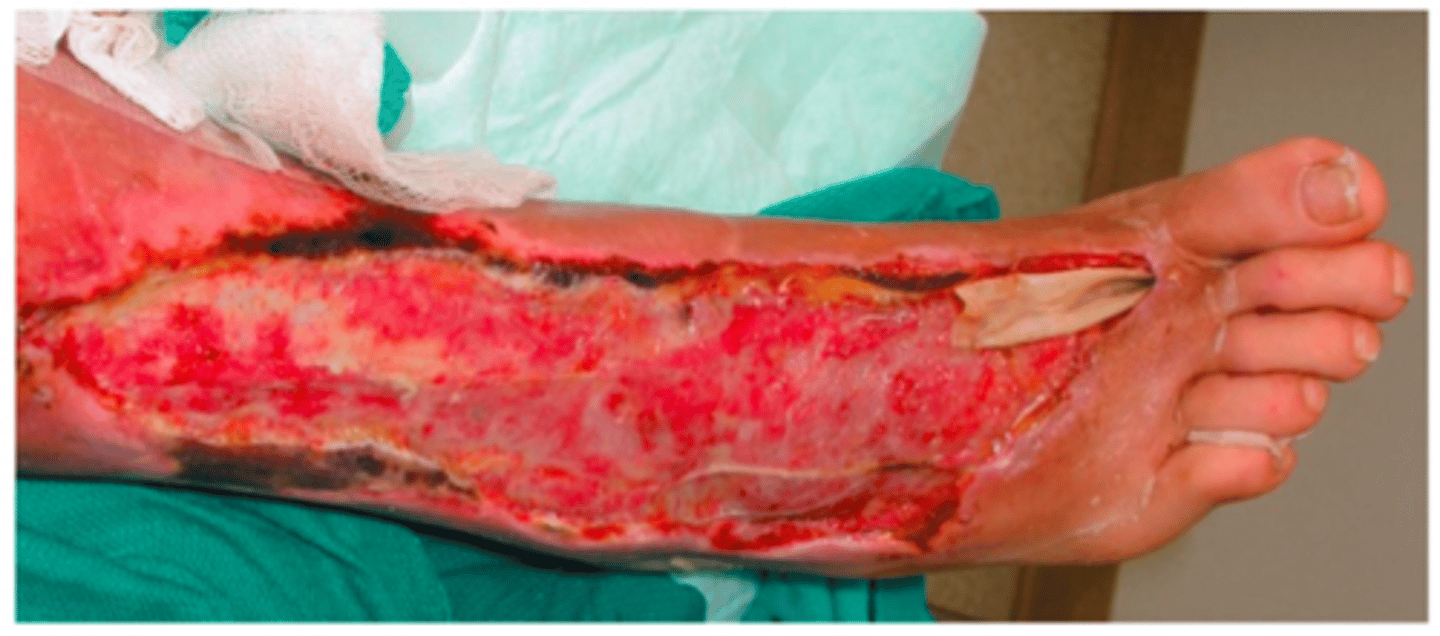
necrotizing fasciitis due to Streptococcus pyogenes

infections by Pseudomonas aeruginosa
pseudomonas dermatitis, otitis externa, post burn infections, common nosocomial agent
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
gram - aerobic rod; pyocyanin; opportunisitc
pyocyanin
produces a blue-green pus
Pseudomonas dermatitis
2 week rash
otitis externa
swimmers ear; inflammation of the outer ear
intoxication by Clostridium perfringens
gas gangrene, phospholipase exotoxin, requires early treatment otherwise fatal
Clostridium perfringens
gram + anaerobe, can form endospores, commonly found in soil
gas gangrene
myonecrosis
phospholipase exotoxin
alpha toxin
what is a treatment for Clostridium perfringens?
hyperbaric oxygen therapy
"trench foot" from Clostridium perfringens
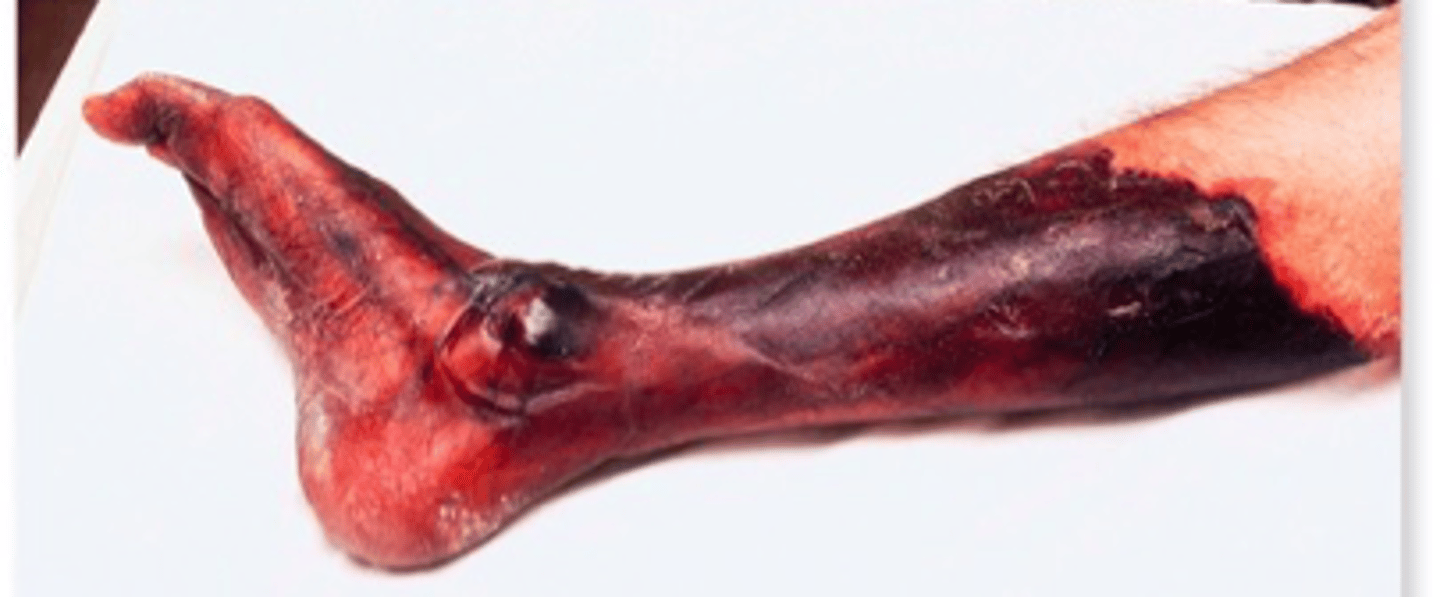
necrotic blisters from Clostridium perfringens
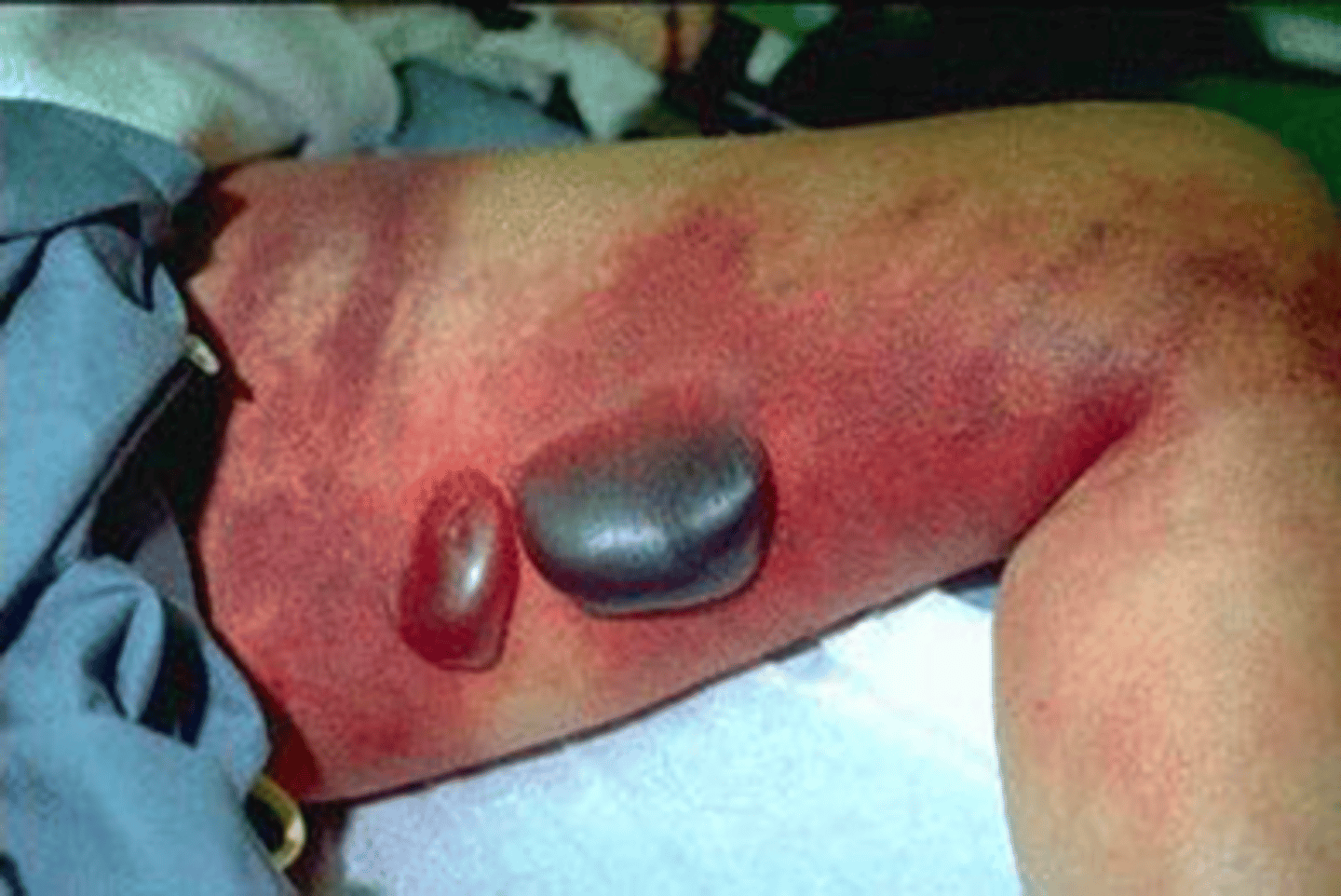
buruli ulcer
caused by Mycobacterium ulcerans; deep, damaging; exceeds incidence of leprosy
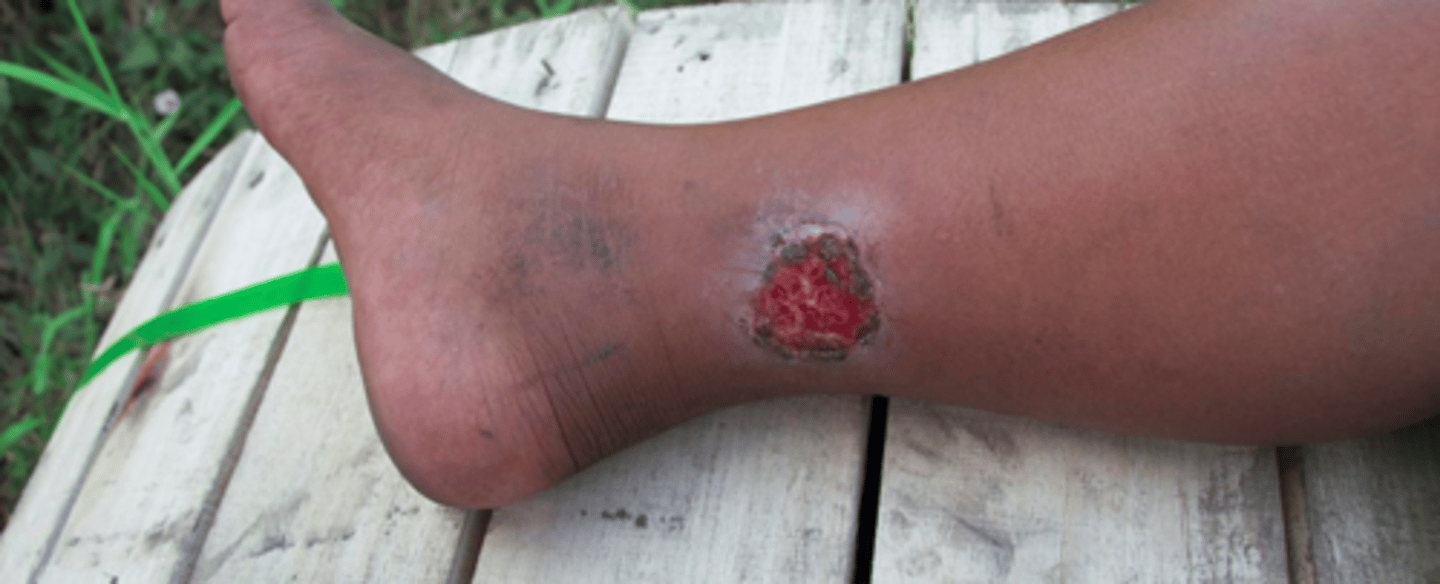
what are the 3 classifications of acne?
comedonal (mild), inflammatory (moderate), nodular cystic (severe)
comedonal acne
mild; sebum channels are blocked with shed cells
comedonal acne treatment
salicylic acid preparations and retinoids
inflammatory acne
Propionibacterium acnes
Propionibacterium acnes
gram +, anaerobic rod
inflammatory acne treatment
preventing sebum formation (isotretinoin), antibiotics, benzoyl peroxide to loosen clogged follicles, visible (blue) light (kills P. acnes)
isotretinoin
prevents sebum formation but teratogen
nodular cystic acne
severe
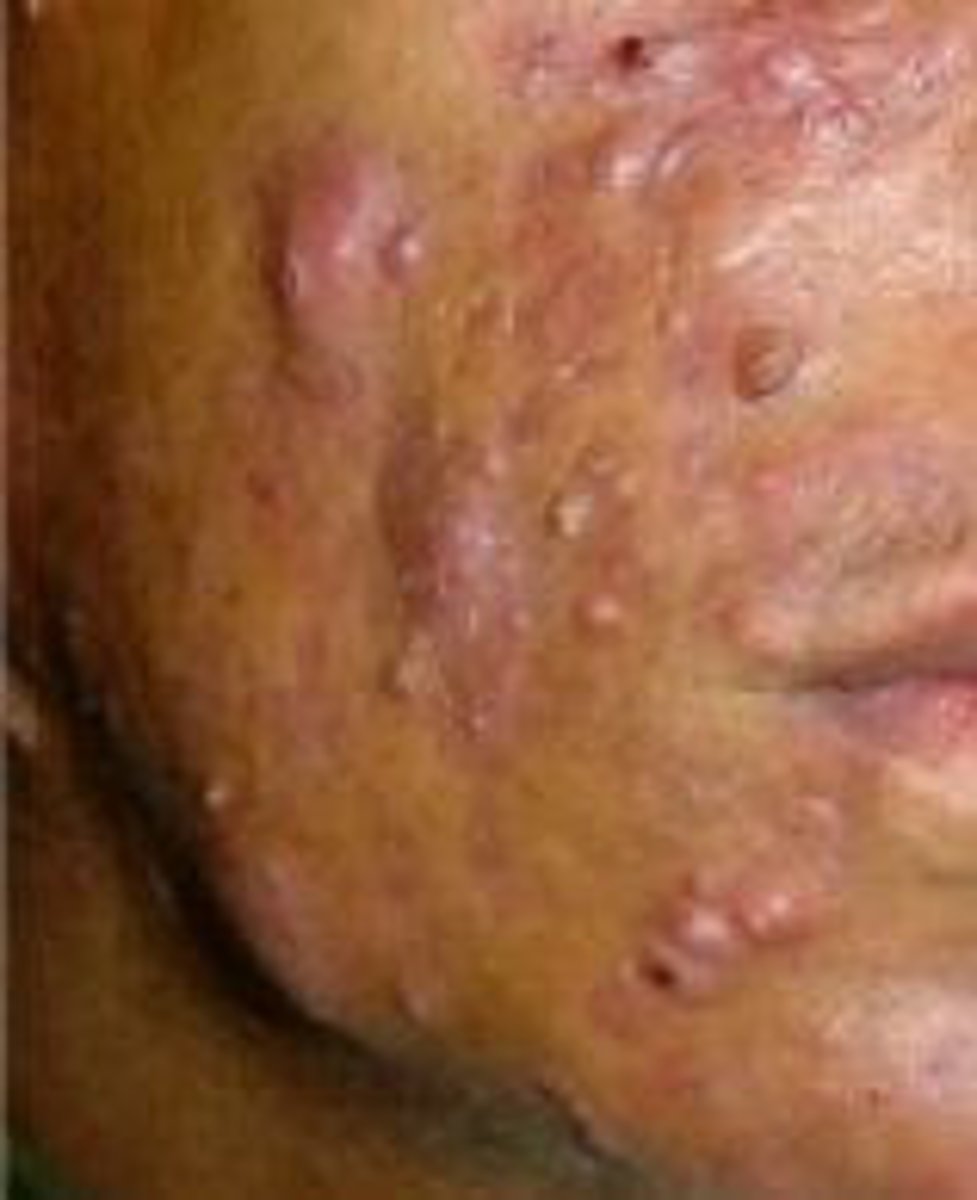
nodular cystic acne treatment
isotretinoin
treatment for bacterial conjunctivitis (possibly bonus cause Gary had it)
ofloxacin and cephalosporin
warts
papillomaviruses
treatment for papillomaviruses
removal and imiquimod
what are 3 ways to remove warts?
cryotherapy, electrodesiccation, salicyclic acid
cryotherapy
cold treatment
electrodesiccation
tissue is destroyed by burning with an electric spark
imiquimod
stimulates interferon production
interferon signaling drives _________ ________ expression
antiviral peptide
smallpox
variola
variola major mortality rate
20%
variola minor mortality rate
less than 1%
smallpox was eradicated t/f
true (1979)
1 multiple choice option
a single case of smallpox is considered a health emergency why?
very communicable
who discovered the smallpox vaccine and with what?
Edwen Jenner; discovered that vaccina virus or cowpox has a similar structure to smallpox and was not deadly to humans (discovered this when milk maids were not getting sick/were not dying)
centrifugal lesions
more on periphery, less in body center
centripetal lesions
moves toward the center
smallpox lesions
extremely itchy which can cause secondary infection of other microbes getting in (like MRSA under fingernails)
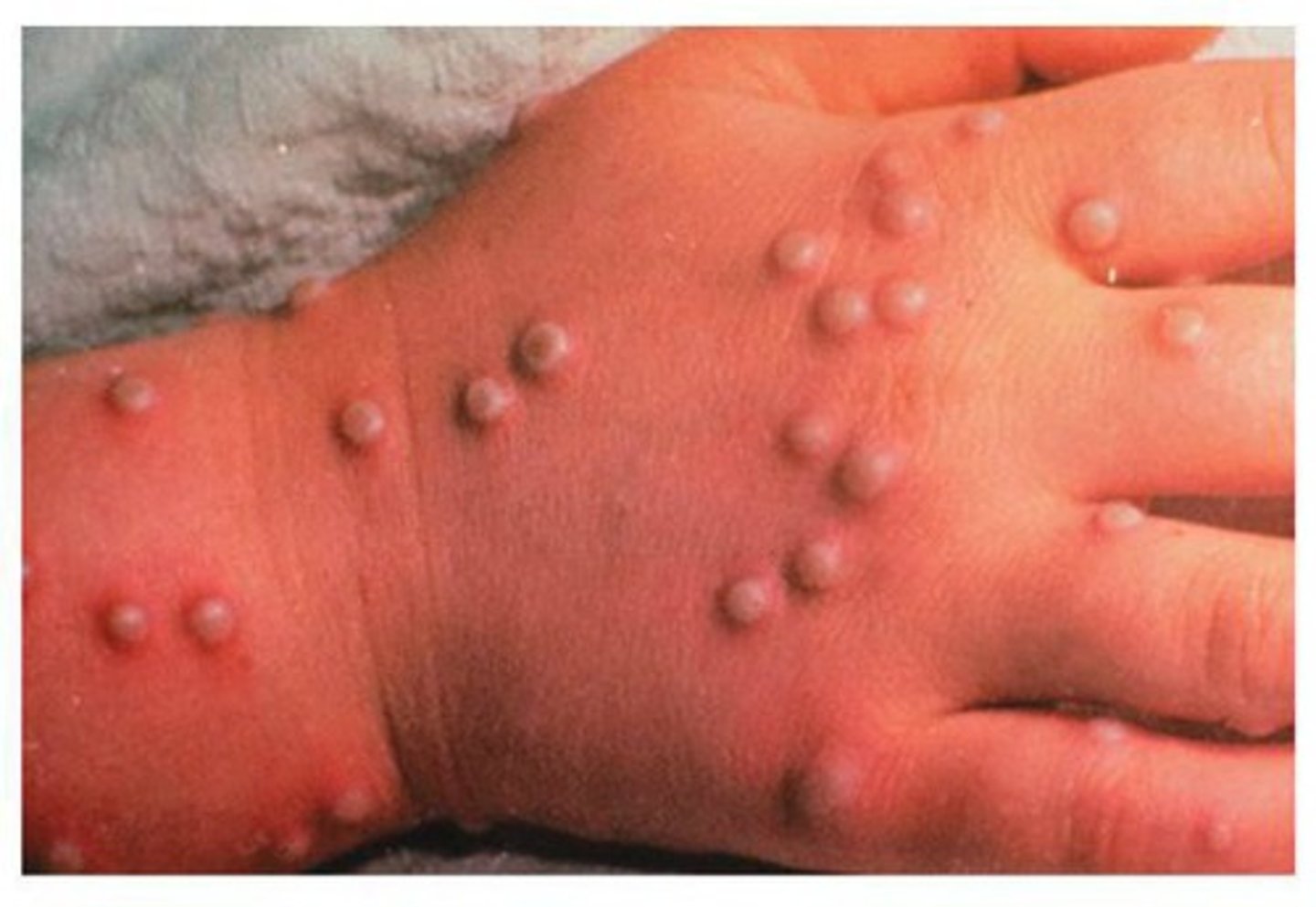
smallpox centrifugal or centripetal lesions?
centrifugal
chickenpox centrifugal or centripetal lesions?
centripetal
varicella-zoster virus
chicken pox; humam herpesvirus 3
how is chickenpox transmitted?
by respiratory route