Energy Balance and Weight Control in Human Nutrition
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What percentage of American adults are overweight or obese?
Over 70% of American adults are overweight or obese.
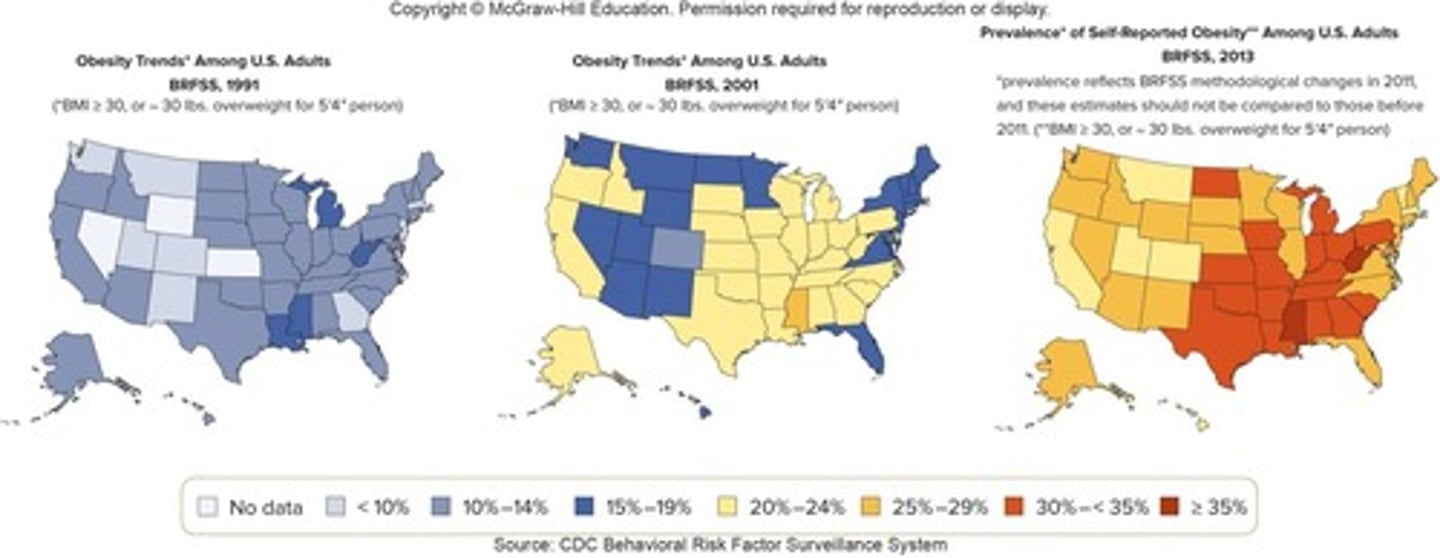
What dietary factors contribute to the increase in obesity rates in America?
Overconsumption of sugars, fat, and salt.
What is the relationship between body weight and health outcomes?
Maintaining a healthy body weight is associated with increased longevity and better health outcomes.
What is the most widely used measure of healthy body weight?
Body Mass Index (BMI).
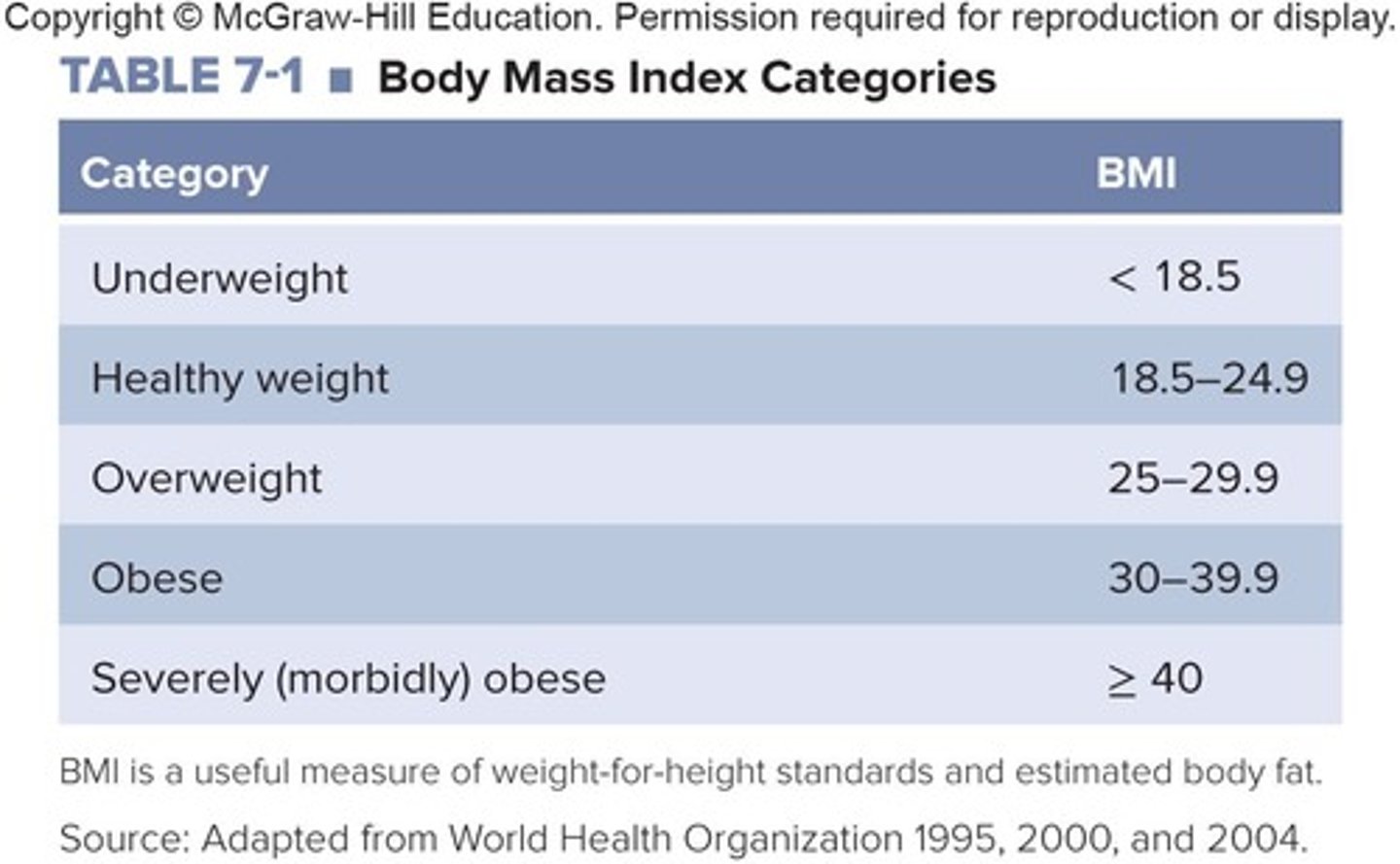
What are the pros of using BMI as a screening tool?
BMI is easy to obtain, noninvasive, and gender neutral.
What are the cons of using BMI as a measure of body fat?
BMI is a crude measure for athletes and short individuals and cannot be applied to children, the elderly, and pregnant or lactating women.
How is body mass calculated?
Body mass is calculated by dividing body weight by height.
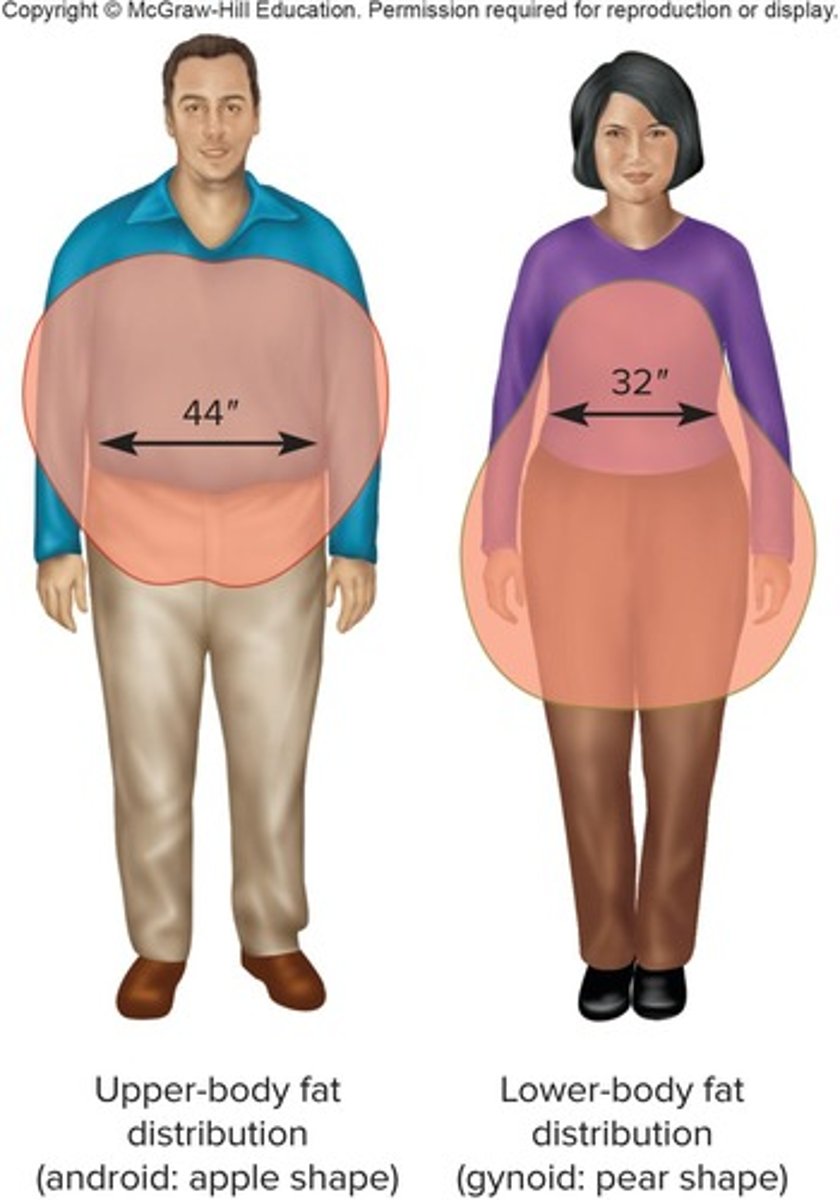
What type of fat distribution is common in women, and is it a risk factor for obesity-related disorders?
Excessive fat in thighs and buttocks is common in women and is not a risk factor for obesity-related disorders.
What type of fat distribution is common in men, and what are its associated risks?
Excessive fat in the abdomen is common in men and is a significant risk factor for obesity-related disorders.
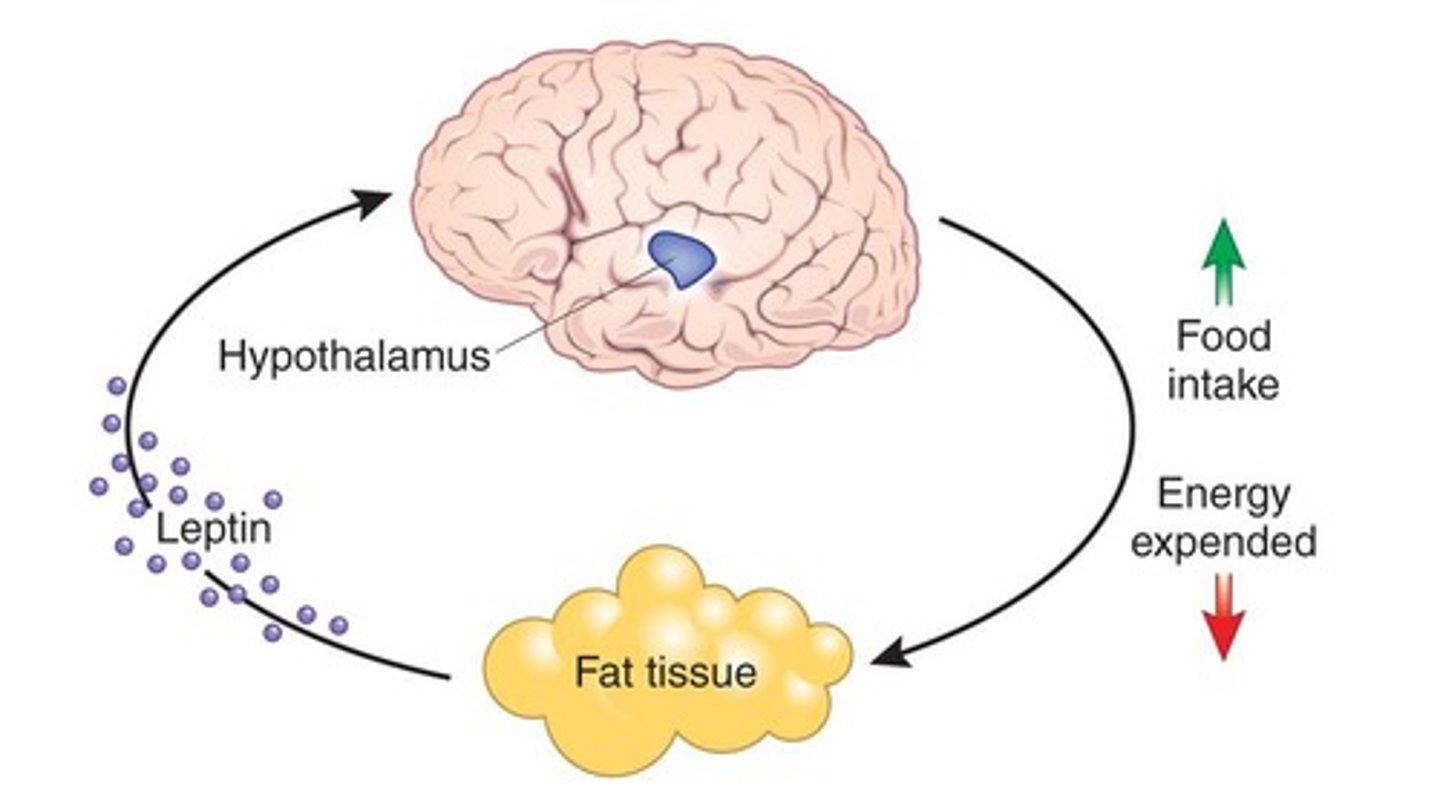
What does the set point theory propose about body weight?
The set point theory states that each person has a genetically predetermined body weight regulated by the nervous and endocrine systems.
What role does leptin play in appetite regulation?
Leptin promotes satiety and reduces appetite when levels are high, while low leptin levels stimulate hunger.
What is ghrelin and how does it affect hunger?
Ghrelin is a hormone that stimulates hunger and is also released when the stomach is empty.
How does weight gain or loss affect energy expenditure?
Weight gain initially increases physical activity and resting metabolic rate, but these rates decrease sharply after weight loss.
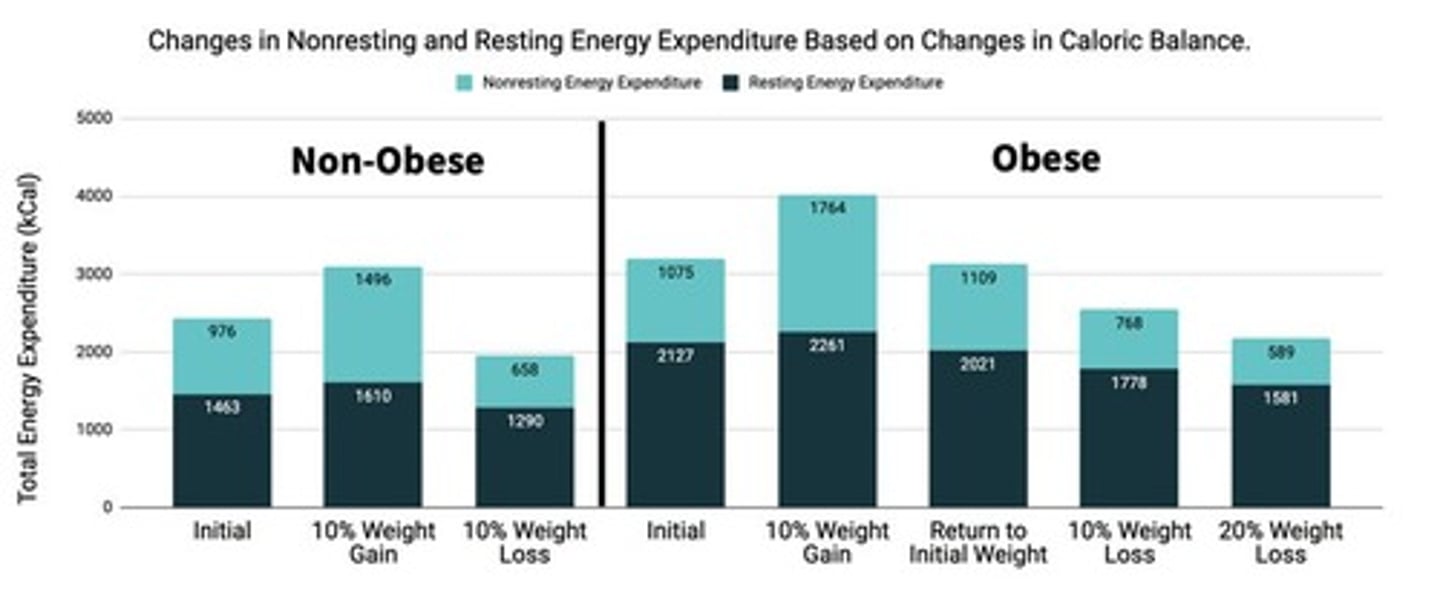
What genetic factors contribute to obesity?
Genes affect metabolic rate, fuel use, brain chemistry, and body weight, including the thrifty metabolism gene.
How do environmental factors influence obesity?
Environmental factors such as physical inactivity, poverty, limited access to healthy foods, and dietary habits influence weight.
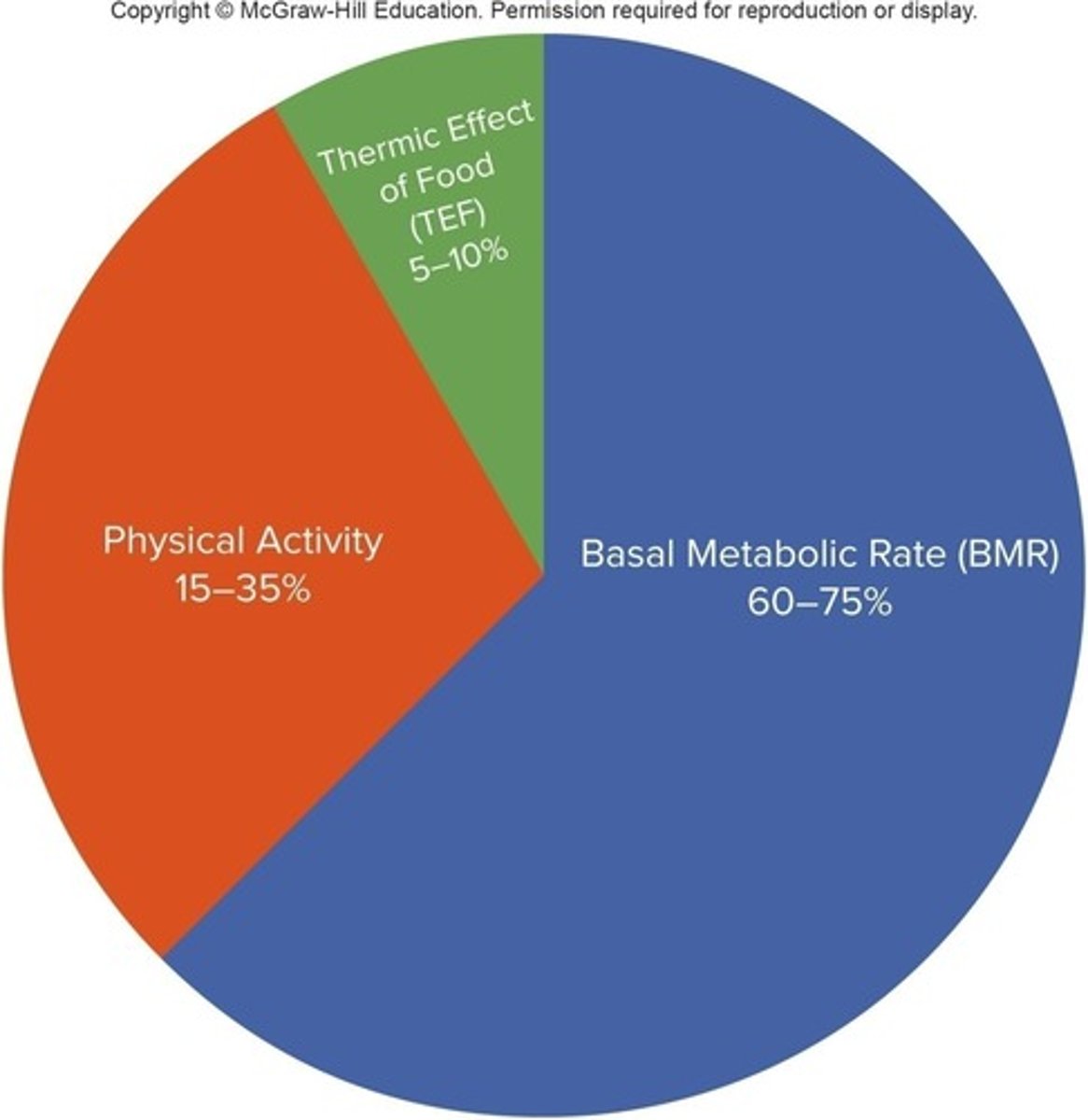
What is the Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)?
BMR represents the minimal amount of calories needed to sustain life, measured in a waking state with no food or movement.
What is the significance of identical twins in obesity studies?
Identical twins tend to have similar weights even if raised apart, indicating a genetic influence on body weight.
How does childhood obesity relate to adult obesity in females?
Female obesity is often related to childhood obesity.
At what age does male obesity typically appear?
Male obesity tends to appear after age 30.
What is a food desert?
A food desert is an area with limited access to fresh fruits and vegetables.
What is the impact of fast food on obesity rates?
Frequent meals from fast food or takeout restaurants are linked to higher obesity rates.
What hormonal changes are associated with abdominal fat in men?
Abdominal fat in men is linked to high testosterone and cortisol levels.
What does Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) represent?
The amount of calories the body burns at rest, usually higher than Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR).

What is the Thermic Effect of Food (TEF)?
The calories burned to digest and absorb nutrients from food, with protein and alcohol having a high TEF compared to fats and sugars.
What is the Estimated Energy Requirement (EER)?
The average amount of calories required to maintain health and weight, based on energy intake, expenditure, age, sex, weight, height, and physical activity level.
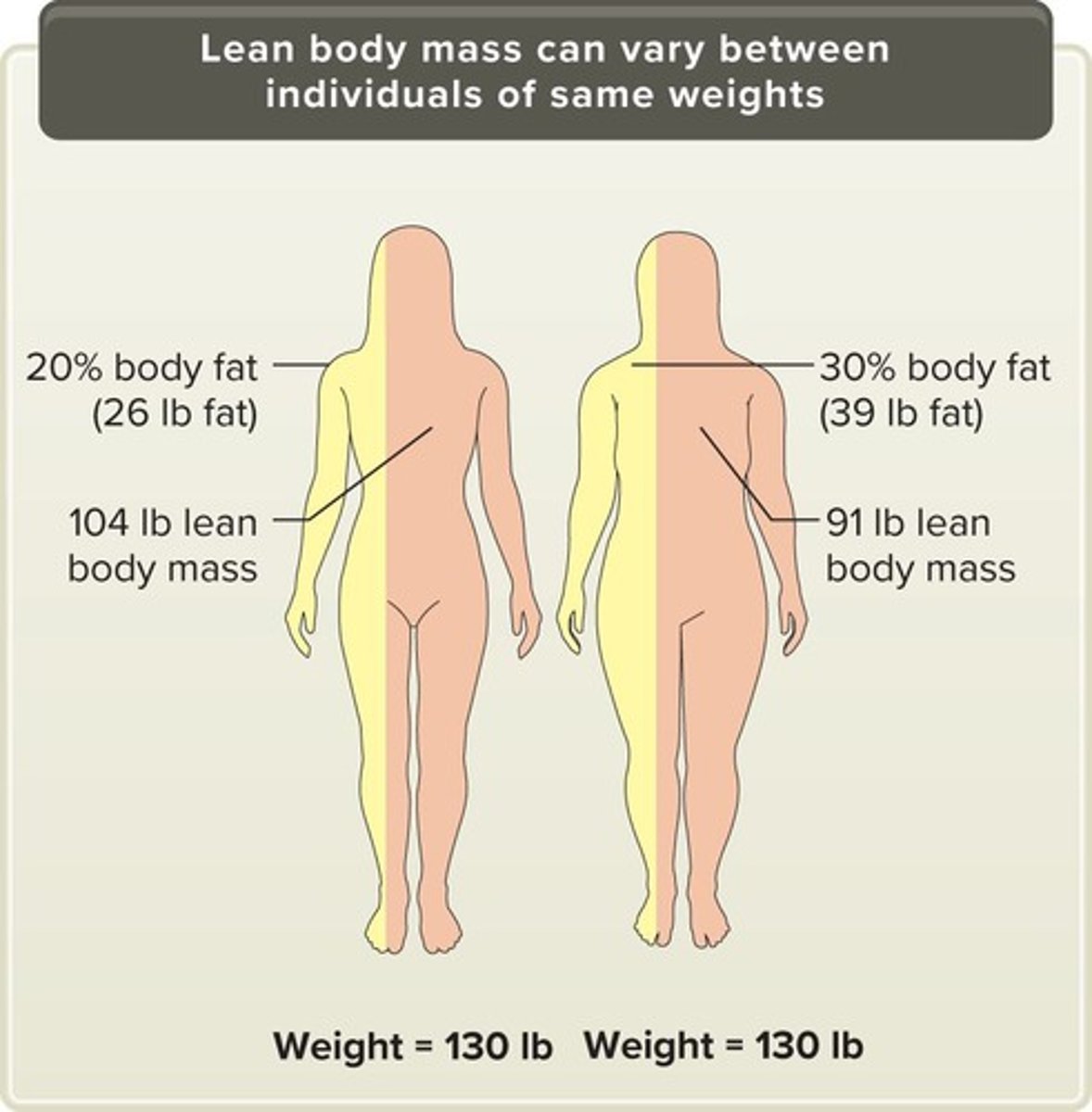
What is Lean Body Mass (LBM) and its significance?
LBM is the most significant contributor to basal metabolic rate and varies greatly between individuals, affecting energy needs.
What is Exercise-Induced Thermogenesis (EAT)?
The energy burned during intentional exercise, which can increase energy expenditure by 15% to 30%.
What is Nonexercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT)?
The energy expended for non-exercise activities, including body posture, ambulation, and spontaneous movements like fidgeting.
What is the range of TEF as a percentage of total calories consumed?
Approximately 5% to 10% above the total calories consumed.
How does TEF vary among macronutrients?
TEF is highest for protein, followed by carbohydrates, and then fats.
What is the weight loss triad for a sound weight loss plan?
Decrease calorie intake by approximately 500 kcal per day, increase physical activity to over 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, and make positive behavior changes.

What are some characteristics of fad diets?
Fad diets promise short-term weight loss with minimal effort, often lack a physical activity component, use celebrity testimonials, promote quick weight loss, recommend expensive supplements, and may limit or exclude food items.
What are some examples of popular diet approaches?
High protein, low carbohydrate diets; carbohydrate-focused diets; low-fat approaches; novelty or fad diets; meal replacements.
What is a common issue with very-low-carbohydrate, high-protein diets?
They typically leave a person fatigued and wanting more variety in meals, leading to abandonment of the diet.
What should you be cautious of in diet plans that do not follow MyPyramid guidelines?
They may be suspect if they lack a physical activity component, use celebrity testimonials, promote quick weight loss, or recommend expensive products.
What is weight cycling, also known as yo-yo dieting?
The cycle of losing weight and then regaining it, often associated with diets that encourage reverting to unhealthy eating habits.
What is a strategy to promote positive behavior in weight management?
Keep sweets hidden in the home.
What is the role of physical activity in maintaining energy balance?
Physical activity contributes to energy expenditure and helps prevent obesity.
What is the impact of lack of activity on obesity?
A major cause of obesity is a lack of physical activity.
How does body weight relate to Lean Body Mass and energy needs?
Individuals with the same body weight can have different amounts of LBM and body fat, leading to varying energy needs.
What is the significance of dietary choices like celery in terms of energy density?
While no food is calorically negative, low energy-dense foods like celery are still excellent dietary choices.
What is the approximate calorie count for TEF if the calorie intake is 3,000 kcal?
TEF would account for approximately 150 to 300 kcal.
What are the three main components of Nonexercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT)?
Body posture, ambulation, and other spontaneous movements.
What is the relationship between energy expenditure and physical activity?
More physical activity leads to higher energy expenditure.
How much more do people who keep desserts visible tend to weigh compared to those who hide them?
About 10 pounds more.
What effect does matching the color of your plate with your food have on consumption?
Subjects consume up to 30% more food.
What is the benefit of keeping a fruit bowl on the counter?
It serves as a reminder to snack healthy and families with a fruit bowl weigh 8 pounds less.
How much can shifting from a 12-inch plate to a 10-inch plate reduce caloric intake?
By 22%.
What is the BMI criteria for candidates eligible for weight loss medications?
BMI ≥ 30 or BMI ≥ 27 with at least one obesity-associated comorbid condition.
What is the mechanism of action of Orlistat (Xenical®)?
It blocks fat digestion by about 30% by inhibiting lipase enzyme action.
What are two medications for weight loss mentioned in the notes?
Semaglutide (Ozempic® and Wegovy®) and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro® and Zepbound®).
What are the criteria for surgical treatment of severe obesity?
BMI ≥ 40 or BMI ≥ 35 with obesity-related comorbid conditions.
What is the purpose of AspireAssist®?
It is a surgically placed tube that drains a portion of stomach contents after a meal.
What does bariatric surgery entail?
A surgical procedure to reduce stomach capacity.
What is a very-low-calorie diet (VLCD)?
A diet known as protein-sparing modified fast (PSMF) with 400 to 800 kcal intake per day, often in liquid form, administered under strict medical supervision.
What is liposuction?
A surgical procedure known as lipectomy that involves the removal of fat through a tube inserted under the skin.
What is intermittent fasting?
A method that cycles days of normal eating with days of eating little to nothing.
What are the two main effects of Semaglutide (Ozempic® and Wegovy®)?
Increases insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity, and suppresses appetite.
What percentage of body weight can individuals expect to lose while taking semaglutide over a 2-year period?
About 15%.
What are some side effects of semaglutide?
Nausea, vomiting, tiredness, and potential loss of fat in the sagging skin of the face (referred to as 'ozempic face').
What is the difference between Ozempic® and Wegovy®?
Ozempic® is approved for type II diabetic patients at a lower dose, while Wegovy® is approved for weight loss in children and adults at a higher dose.
What are the BMI requirements for a patient to be approved for semaglutide?
BMI ≥ 30 or BMI ≥ 27 with at least one obesity-related condition such as high blood pressure, type II diabetes, or dyslipidemia.
What is the market difference between Mounjaro and Zepbound?
Mounjaro is marketed to anti-diabetic patients, while Zepbound is marketed for weight loss patients.
How do Ozempic® and Wegovy® work?
They bind to the GLP-1 receptor, increasing satiety, decreasing appetite, reducing visceral fat, and increasing insulin secretion and sensitivity.
Why is Mounjaro generally more expensive than Ozempic and Wegovy?
Because it is newer and more effective for blood sugar control and weight loss.