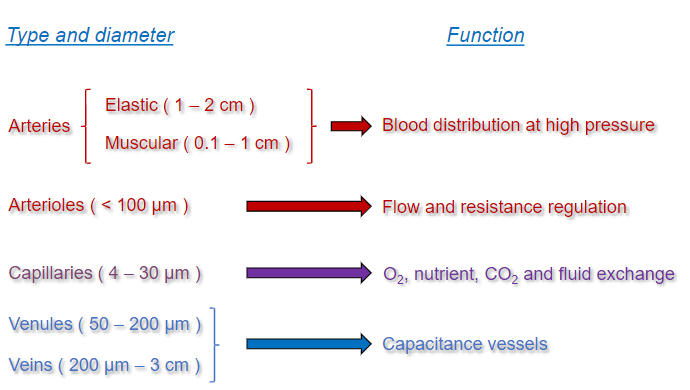
Blood vessels
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Cardiovascular system function
A transport system of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Blood vessels contribute to perfusion and homeostasis according to structure, location and functional changes due to vasoactive molecules and the local microenvironment
(e.g. pH, CO2, O2, Cytokines etc.)
Histology
The study of tissues and cells under a microscope
Blood vessel histology
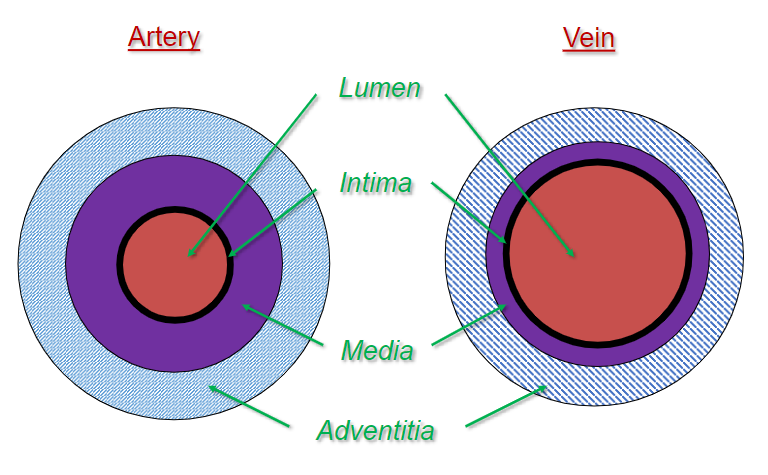
Vascular differences: artery vs vein diagrams
Endothelium
Single layer of polygonal, flattened epithelial cells. Elongated in the direction of blood flow
Basement membrane
Sub-endothelium contains loose connective tissue and fibroblasts
Collagen and Elastin fibers
Longitudinal arrangement
Autonomic innervation
Vasa vasorum ‘vessels of the vessel’
Provide O2 and nutrients to the cells in the vessel wall; more frequent in larger vessels than in arteries
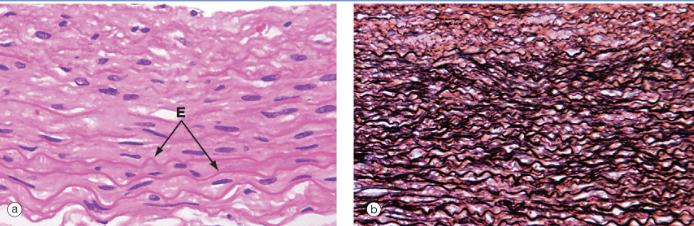
Elastic arteries
It contains alternating layers of smooth muscle cells and elastic laminae
Left (H&E) shows SMCs and elastic fibers (E); right, elastin staining (black)
Right out of the ventricles
Function is to receive energy from when the heart contracts, stores it and releases the energy to pump the blood around the body.
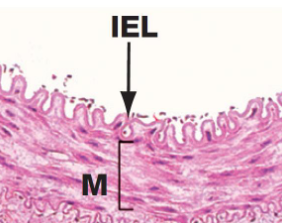
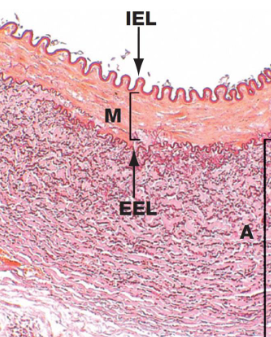
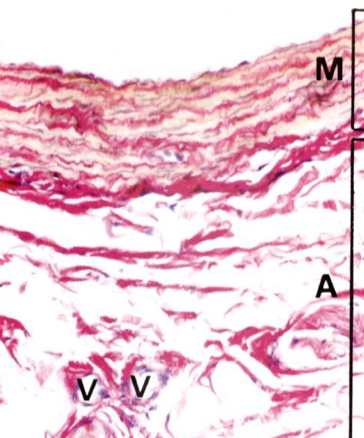
Muscular arteries
It contains layers of smooth muscles cells and some elastic fibers
Prominent internal elastic lamina (IEL) and less accentuated external elastic lamina (EEL, absent in smaller muscular arteries)
M, tunica media
A, tunica adventitia
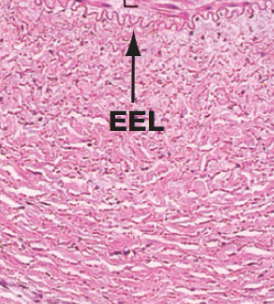
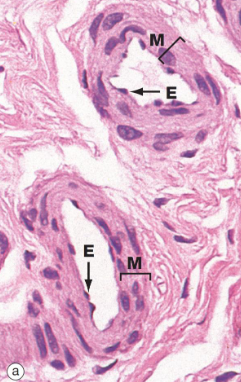
Arterioles
Contains 1 - 2 layers of smooth muscle cells
Elastic fibers limited to internal elastic lamina (IEL)
No external elastic lamina (EEL)
The transition from large to small arterioles is indicated by the loss of IEL
Tunica adventitia is very thin
E, endothelium
M, tunica media
Venules
Capillaries drain into postcapillary venules, similar in structure to capillaries: bearing endothelium and pericytes, larger diameter = 15 - 20 um.
Postcapillary venules drain into collecting venules: larger diameter with an increase in pericyte density
Collecting venules drain into muscular venules: media layer with 2 - 3 layers of smooth muscle cells.
Pericytes
cells present at intervals along the walls of capillaries (and post-capillary venules).
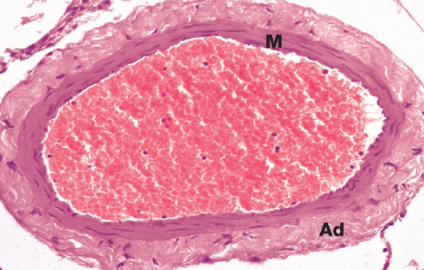
Small and medium veins
Tunica media contains a few layers of smooth muscle cells
Tunica adventitia contains some elastin and collagen fibers arranged, longitudinally
No elastic laminae
M, tunica media; Ad, tunica adventitia
Large veins
Tunica media contains a few layers of smooth muscle cells
Tunica adventitia contains some elastin and collagen fibers, arranged longitudinally
No elastin laminae
M, tunica media; A, tunica adventitia
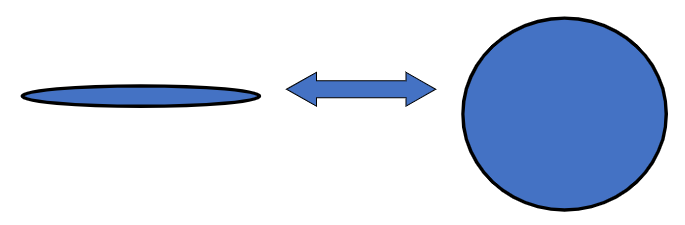
Vein structure allows fluid capacitance
Significance of thin wall and wide lumen
Easily collapsed and expanded
Facilitates function as capacitance (storage) vessels
Structural comparison among arteries and veins
Arteries are characterised by:
A narrow lumen
A thicker wall and media layer
Greater wall-to-lumen and media-to-lumen ratios.
Greater elastin content of the arterial media layer:
Especially in elastic arteries (windkessel effect)
Dampens pulse pressure
Veins possess valves (intimal projections) that prevent backflow, facilitating venous return
Capillaries
A single layer of endothelial cells located upon a basement membrane
Diameter 4 - 10 um
Three forms of capillary classified according to the nature of the endothelium:
Continuous
Fenestrated
Discontinuous (sinusoids)
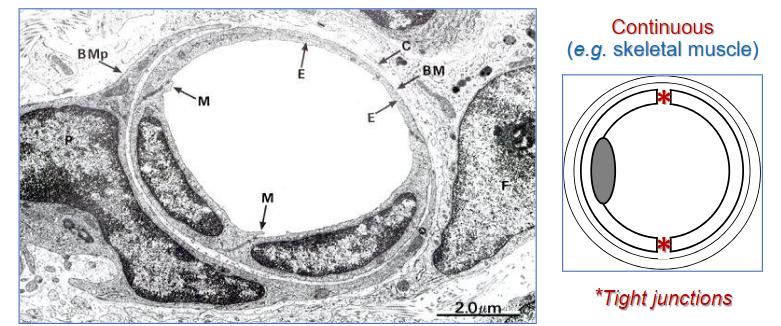
Continuous capillaries (electron micrograph)
M, marginal fold
P, pericyte (partly surrounds endothelial cell layer, endowed with limited contractile ability; contributes to basement membranes protein secretion)
Fenestrate capillaries
Small circles are the transportation of lipids and others.
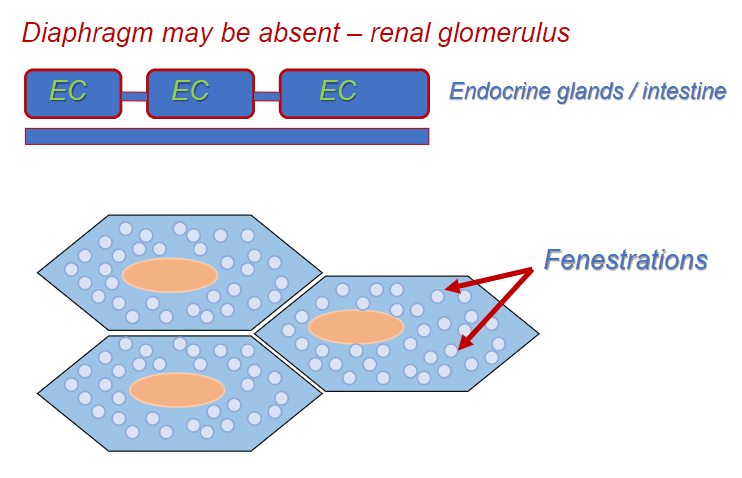
Sinusoids
Large intercellular gaps
Large fenestrations (no diaphragms)
Discontinuous basement membrane
Diameter = 30 - 40um: liver, bone marrow, spleen.
Summary: structure follows function
