Patho- Genetics&Cancer
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pathophysiology Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
chromosomes
in the nucleus of every cell-the genetic material responsible for the structure+function of the body
– divided into Germline cells (gametes: sperm+egg cells) and Somatic Cells (all other cells)
Somatic cells
Every other cell besides sex sperm/egg cells. Contains 23 pairs of chromosomes—22 pairs of autosomes (nearly identical and homologous) and 1 pair of sex chromos (2 homo X or 1 nonhomo X and Y)
DNA
Contains deoxyribonucleic acid and histone proteins. __ provides the genetic code for the synthesis of proteins
– each strand is made up of 4 nucleotides
Nucleotide
Made up of a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose, and phosphate.
The 4 nitrogenous bases= 2 purines: Adenine and Guanine and 2 pyrimidines: Cytosine and Thymine
true
(T/F) Germline cells contain 23 single copies of chromosomes
true
(T/F) Adenine forms a bond w/ Thymine. Guanine forms a bond w/ Cytosine— the resulting structure is a double helix
Proteins
made up of sequences of amino acids (of which there are 20). Specific combination of amino acids creates a polypeptide, which form a __
transcription
step in protein synthesis:
— RNA polymerase binds to DNA at promoter
— DNA unwinds, RNA bases pair with DNA to form mRNA: A→U, C↔G. stops at termination sequence
— Introns are removed and mRNA moves to ribosome.
translation
step in protein synthesis:
- mRNA binds to ribosome, tRNA anticodons pair with mRNA codons
- each tRNA brings an amino acid and they link to form a polypeptide
DNA replication
process to preserve genetic info when cells divide:
1. DNA unwinds to expose the nucleotide bases
2. DNA polymerase moves along the template strand and creates a complementary strand of DNA nucleotides
– Cytosine + Guanine and Adenine + Thymine
3. DNA polymerase “proofreads” and excises+replaces not complementary bases
4. Now there are 2 identical pairs of chromosomes
Prophase
phase of mitosis
– the DNA coils+shortens, reveals two identical chromatids attached at a centromere, the nuclear membrane disappears
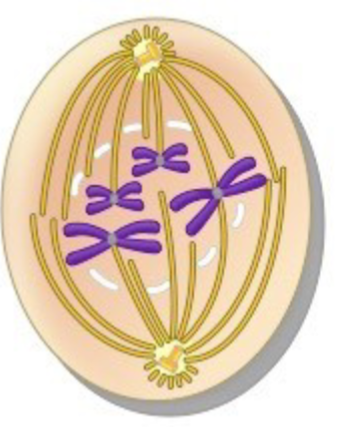
metaphase
phase of mitosis:
– the chromos line up at the cellular equator in the middle of cell, spindle fibers radiate from centrioles at each pole to the centromere
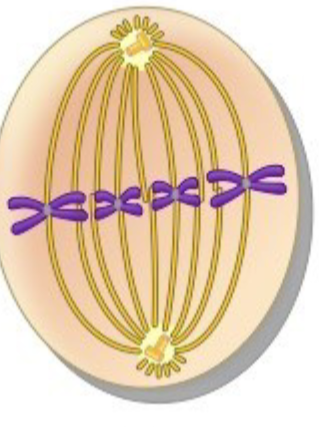
anaphase
phase of mitosis
– the centromeres split and the sister chromatids are pulled apart toward opposite poles
telophase
phase of mitosis
– the new nuclear envelope is formed, spindle fibers disappear and the cell divides
–result: 2 daughter cells w/ the same genetic info (diploid)
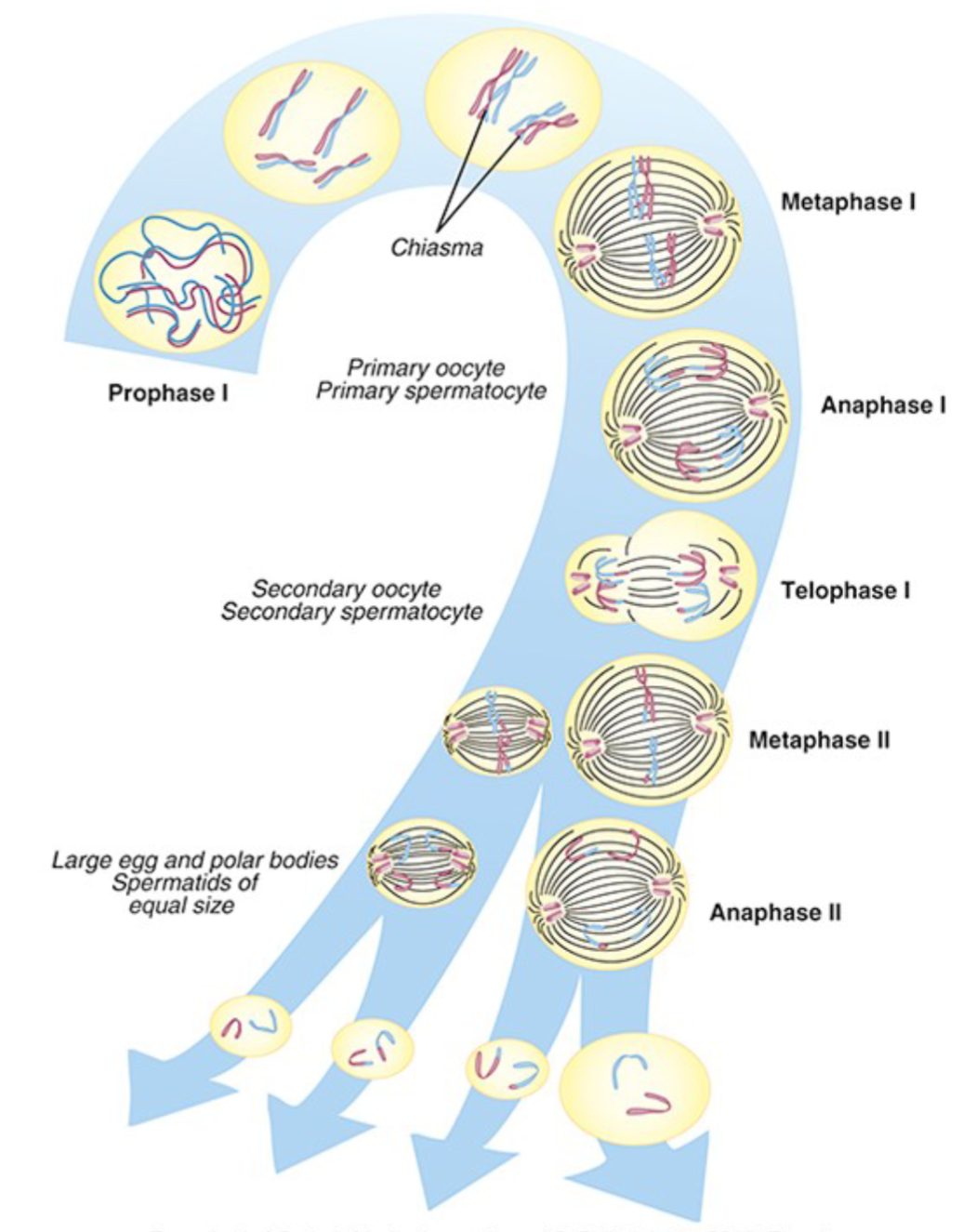
meiosis
the process by which gametes are formed—will end up with half of the genetic info
• Prophase I: replicated chromosomes coil up
• Metaphase I: homologous chromosomes line up on equator
of cell opposite one another– Spindle fibers radiate from the centrioles and attach to centromere
• Anaphase I: homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles of the cell
• Telophase I: nuclear envelope forms and cell divides into two daughter cells
Metaphase II: chromosomes line up along the equator again– Spindle fibers radiate from the centrioles and attach to
centromere
• Anaphase II: Chromatids are pulled apart and move toward
opposite poles
• Telophase II: cell divides into two germ cells
Result: Each germ cell now has half the genetic information
(haploid)
polyploidy
cells that have a multiple of the normal # of chromosomes (23)
– triploidy- 2 copies of each chromos
– tetrapoidy- 4 copies of each chromosome
– nearly all triploidy+tetraploidy pregnancies are aborted
aneuploidy
cells that DONT have a multiple of 23 chromos (usually due to nondisjunction)
– Trisomy: 3 copies of 1 chromos (13,18, or 21 can survive)
– Monosomy- 1 copy of 1 chromos (lethal)
– fertilized eggs containing no X chromos (lethal)
nondisjunction
when the chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis I
– causes multiple mutations
trisomy 21
down syndrome - intellectually disabled
– 50% have congenital heart defects, 54-90% have obstructive sleep apnea, almost all develop symptoms of Alzheimers by 40
turner syndrome
syndrome characterized by presence of one x chromosome without a homologous X or Y chromosome
– pt usually AFAB and sterile
– short, webbing of neck, sparse body hair, normal intellect
klinefelter syndrome
syndrome characterized by 2 or more X chromos with a Y chromos (XXY)
– pts usually AMAB and sterile
– elevated stature, gynecomastia, small testes, sparse body hair, some intellectual disability
inversion
reversal of the order of the genetic code resulting from 2 breaks (insrevion)
translocation
interchanging of material from 2 non-homo chromos
– non-homologous chromosomes → non-homomosous chrologomes
fragile sites
microscopic breaks and gaps in DNA
cri du chat
syndrome w/ deletion of the short arm of chromosome 5
– high pitched cat-like cry, wide set eyes w prominent epicanthal fold, intellectual disability
fragile x syndrome
syndrome w multiple (>200) repeats of a 3 nucleotide sequence in long arm of X chromosome—silencing of the genes responsible for neuronal synaptic connections
– 2cd most common cause of intellectual disability & autism
– Face elongated,Repeats, ADHD, Giant genitals, Intellectual impairment, Large hands/feet, Ears protruding, X-tensible joints
true
(T/F) different forms of a gene are called alleles and a person receives one allele from each parent.
genetype
the genetic makeup of the alleles
carrier
a person is a __ for a disease if they have the allele for a disease but are phenotypically normal
– (often bc the disease causing allele is recessive-so to express the disease, both “bb” alleles have to be present)
cystic fibrosis
autosomal recessive — ↓ number and abnormal function of ion channel for Cl- and HCO3-
1. Thickening of mucus in lungs
– ↑ reabsorption of Na — airway obstruction→ recurrent infections
2. ↑ mucin production in GI→ tract disruption
3. ↓ absorption of Na+ and Cl- in sweat glands
huntington disease
autosomal dominant (regardless of hetero or homo), repeats of 3 nucleotide leading to extra long protein prone to fragment
– neuronal dysfunction and death
– onset age 45, involuntary+impaired movement, cognitive impairment, depression
true
(T/F) in cancer, repetition of certain gene sequences can increase expression of some genes (gene amplification)
true
(T/F) second leading cause of death in the us
neoplasm
new growth
differentiation
process by which cells become specialized
– regulated by genes and external stimuli (environment, cytokines, exposure)
– cells also lose ability to proliferate and tissues rely on progenitor/stem cells
-carcinoma
suffix meaning malignant neoplasm of epithelial tissue
– ex: adeno__= malignant neoplasm of glandular epithelial tissue
-sarcoma
suffix meaning malignant neoplasm of mesenchymal origin
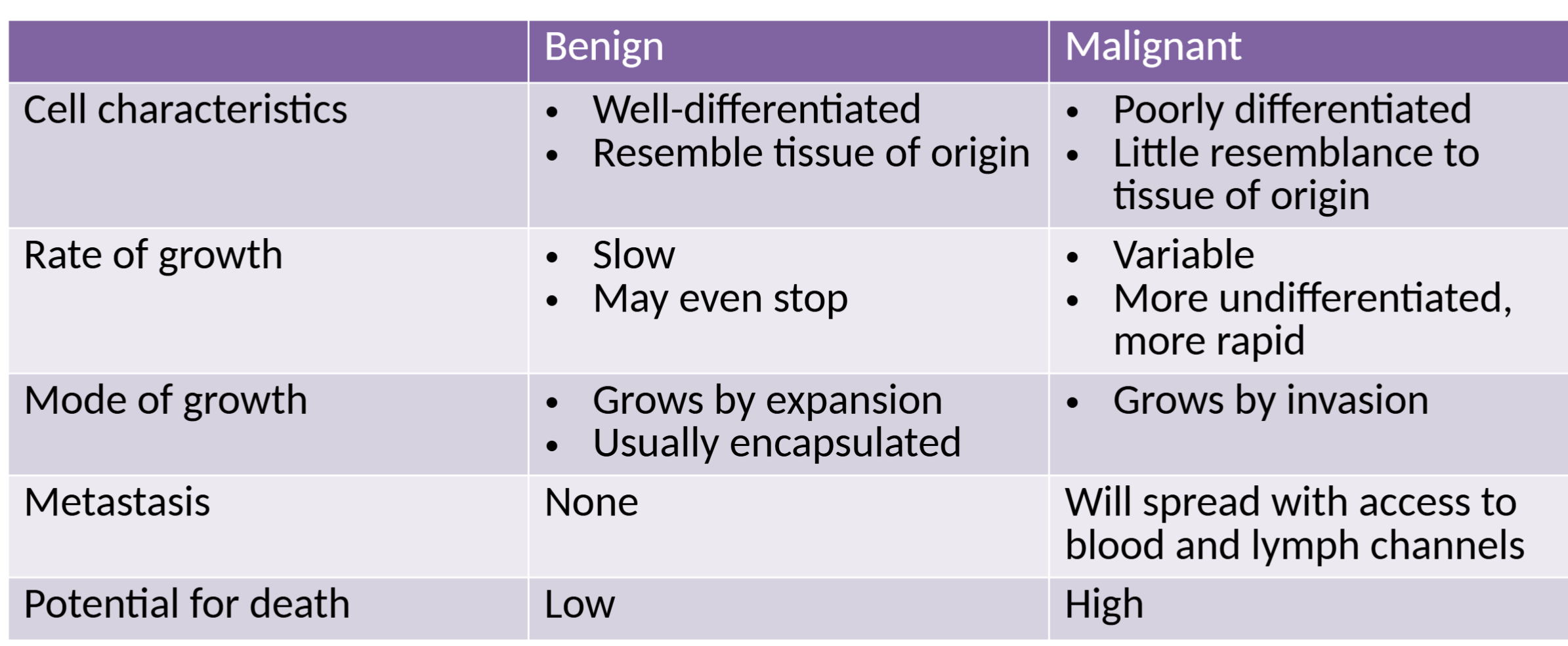
benign vs malignant
solid tumors
tumor confined to tissue or organ
– cells detach from original tumor, invade surrounding tissue, and enter bloodstream/lymphatic stream
hematologic cancer
tumor involving cells already in circulation (ex:leukemia)
carcinoma in situ
localized, pre-invasive lesion
– has not broken through the basement membrane of the tissue and more easily treated
cancer cell
characteristics of __ __
– Abnormal+Rapid Proliferation, Loss of Cell Differentiation (similar to embryonic cells rather than origin), Genetic Instability, Growth Factor independence, Failure of Cell density-dependent inhibition, Loss of Cell Cohesiveness+Adhesion, Loss of Anchorage Dependence, Loss of Cell-to-Cell Comms, Antigen Expression (different than host or cytokines that suppress immune response), Production of Enzymes/Hormones, Cytoskeletal Changes, or Unlimited Life Span (prolonging telomeres)
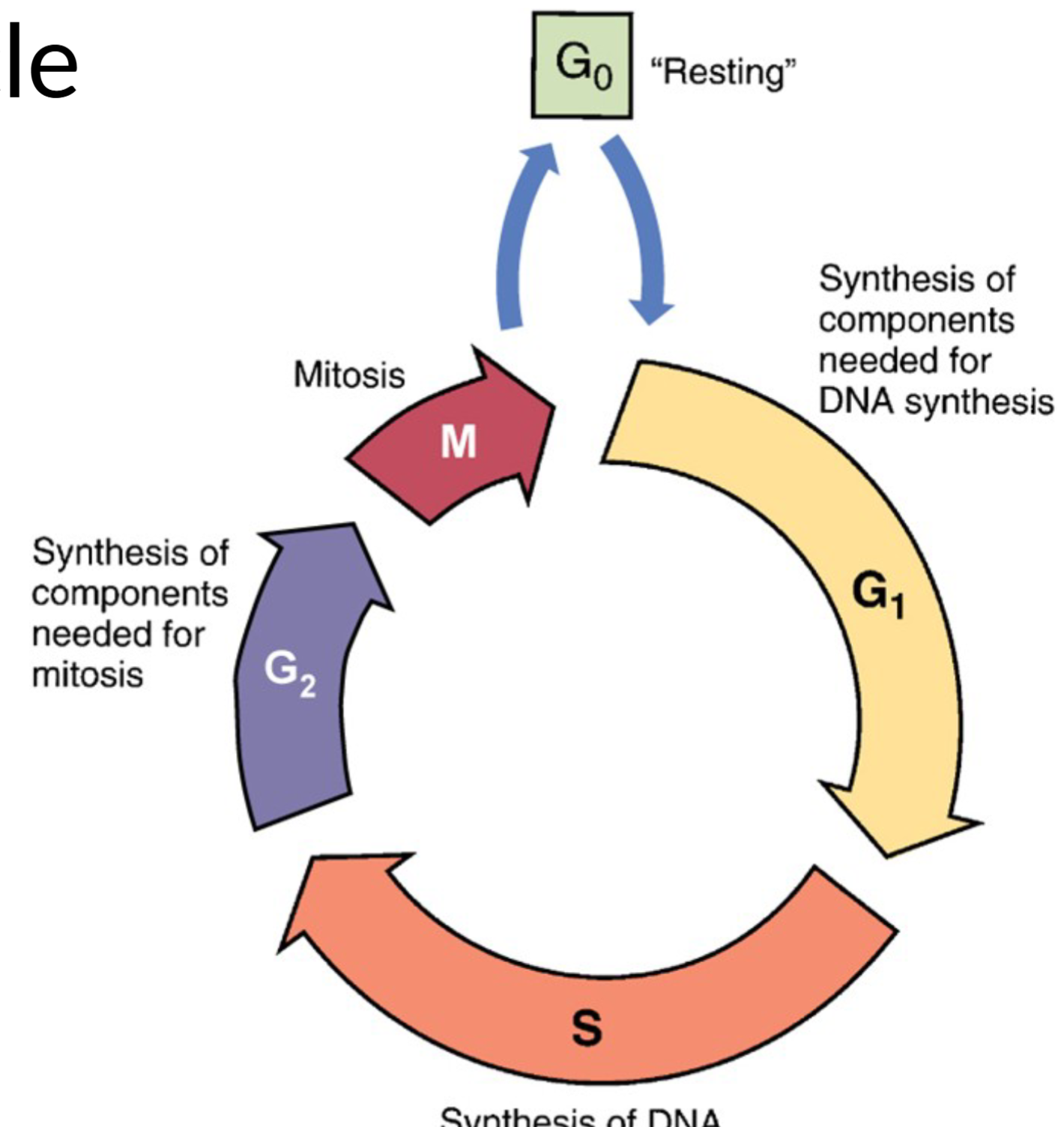
cell cycle
cycle-
– G0: the resting and repairing phase
– G1: cell is preparing for DNA synthesis
– S: DNA synthesis
– G2: cell is preparing for mitosis
– M: mitosis
growth fraction
we measure the activity of a tumor by evaluating the __ __:
# of cells actively dividing / # of cells in G0
Proto-oncogenes overactivity
etiology for cancer-
– mutations increase activity of what-would-be normal genes coding for normal cellular growth+development
– ex: overexpression of ras leads to colorectal and lung cancer. overexpression of HER-2 leads to breast cancer
underactivity of tumor supressing genes
mutation prevents activation of genes that would normally block cell division when DNA is damaged and induce apoptosis
– cancerous cells are not removed and allowed to grow
– ex: BRCA-1 and 2 defect promotes breast and ovarian cancer
telomerase
__ promotes synthesis of telomere and prevents the chromosome from shortening+unraveling
– cancer cells secrete this
VEGF
cellular pathway promoting cancer survival: cancer cells produce vascular endothelial growth factor which promotes production of new blood vessels→ increased blood supply to cancer site
heredity, hormones, immunology
host factors that promote cancer growth and survival
carcinogens, radiation (ionizing/ultraviolet), bacteria, viruses
environmental factors that promote cancer growth and survival
anorexia-cachexia syndrome
an energy imbalance disorder in which energy intake is decreased and energy usage is increased
– loss of appetite and impaired taste, hypermetabolic state, muscle wasting
– clinical manifestation of cancer
gi disturbances
clinical manifestations of cancer- diarrhea (decreased ability to absorb) and stomatitis (mouth full of sores)
– due to chemotherapy destroying highly proliferative cells
screenings
secondary preventions:
– tumor markers
– papanicolaou test (microscopic exam for abnormal cells)
– tissue biopsy
– immunohistochemistry (use of antibodies to detect cell products/surface markets on cancer cells)
cancer staging
3 factors used to determine how advanced cancer is:
– Size of tumor (T)
– degree of local spread to lymph nodes (N)
– extent of metastases (M)
cancer-4 stage system
– Stage 0: carcinoma in situ
– Stage 1: cancer confined to organ or origin
– Stage 2: starting to show signs of local spread within local tissue
– Stage 3: cancer that has spread to regional nodes
– Stage 4: cancer that has spread to distal organs (liver, brain, bone, etc.)
cancer spread
two methods of __ __:
– direct invasion and metastasis (cancer cell breaks loose and accesses distant regions [blood or lymph nodes])