4) Sonography presentation (doubt we'd need to know) (lil info)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is diagnostic medical sonography?
or rephrased:
Describe what ultrasound it (EXAM).
use sounds waves via tranducer/probe → investigate different tissues in the body
-sound beams reflect off tissues called echos
—
Maryna:
1) Use sound waves sent into body via transducer/probe
2) Manipulate probe to investigate different tissues in body
3) Sound beams reflect off tissue in the body = Echos
→ echos return back to transducer
4) US machine uses this reflective info
→ produce 2D image of 3D structure (that we are investigating)
What does anechoic mean (EXAM)?
-black
-fluid filled (blood urine, serous cyst)
What is echogenic (EXAM)?
(more echos coming back/more dense)
-bright
-white (bone, lipoma, calcifications)
What is homogenous?
-smooth
-uniform texture (normal liver)
What is heterogenous?
-coarse
-irregular texture
What’s the purpose of GEL in ultrasound? (EXAM)
has low acoustic impedance compared to tissue
→ allows sound waves to travel far
—-
Maryna:
- gel acts as connection b/w skin & tissue
→ allows sound to transfer from probe into body
→ and back again via echoes
How does frequency affect ultrasound?
high frequency = better resolution/detail
- good for superficial
low frequency = travels deeper
- less resolution
*note: shitty for fat people b/c sound waves can’t travel far
Ultrasound is unique because it is __
OPERATOR DEPENDENT
General info: (nope)
1) Need empathy
- sick, worried
- fear of unknown
- life changing dx
2) they are detectives
- differential dx
- modification of exam (looking for more stuff aside from physician note)
- change patient positional
- adding additional exams

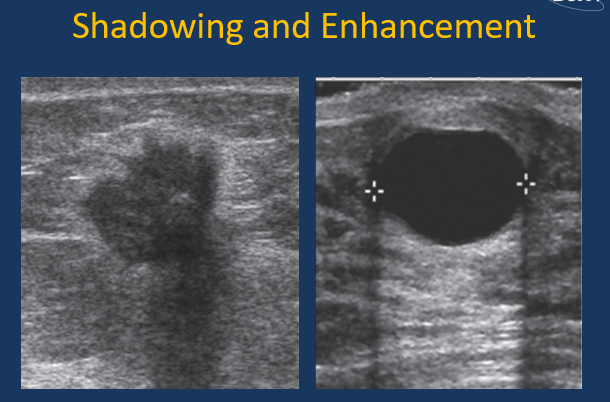
Difference b/w SHADOWING & ENHANCEMENT (nope)
(right image) enhancement = travels very well through fluid = benign
(left image) shadowing = sound beam tries to get through very dense → dense masses in breast likely cancerous
What comes after sonography (doubt you need to know) (nope)

What is PARACENTESIS? (nope)
tube inserted through abdominal wall → drain fluid to relieve pressure
(using needle + ultrasound)
What is THORACENTESIS (nope)
tube inserted in lower chest → drain fluid out of lung space
= easier to breathe
(using needle + ultrasound)
What are the PROS of ultrasound? (EXAM)
-safe (no radiation)
-inexpensive
-realtime imaging
-portable
-accessible
-US can distinguish b/w benign and malignant lesions
What are the CONS of ultrasound? (EXAM)
-operator dependent
-limitations w/ sound
-high injury rate for worker (repetitive movements)
Describe the role of US in cancer detection (EXAM).
1) Survey anatomy
- sweep though + scann organs for structural abnormalies/tumor detection
2) Guidance - real time (i.e., needle biopsy)
3) Followup
- check to see if change in tumor size/quality
- effectiveness of treatment
4) Detect evidence of:
- regression or
- progression