Plant People Places final
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Hyphea
small, thread-like filaments that make up most visible fungi
Chitin
a nitrogen-containing polysaccharides that provides support to the cell wall of fungi
Mycelium
a collective mass of hyphae
Parasite
an organism that obtains nutrients from a living host, causing harm to the host
mutualistic symbiont
an organism that obtains nutrients from a living but provides a benefit to that host
saprobe
an organism that obtains nutrients by breaking down non-living organic matter; a decomposer
protoplasmic toxin
a chemical that destroys the liver and kidney cells
Neurotoxin
a chemical that negatively affects the central or atomic nervous systems
gastrointestinal irritant
a chemical that causes nausea, vomiting, cramps, or diarrhea
saturated sat
contains all single bonds between the carbon atoms of the lipid
Unsaturated fat
the carbon molecules of the lipid share some double bonds
Drying oil
an oil that reacts with the oxygen in the air to form a thin, waterproof elast
nondrying oil
An oil that reacts remains liquid for long time periods when exposed to air
semi-drying oil
an oil that dries slowly or only at high temperatures
Natural fibers
fibers with a plant or animal orgin
mineral fibers
fibers from rocks
synthetic fibers
Fibers created using technology
surface fibers
fibers that cover seeds, leaves or fruit
Bast or soft fibers
cluster of phloem within the periderm of dicot stems
leaf or hard fibers
Veins if monocot leaves
auxin
a class of plant hormones that control the growth and development of plants
phototripism
Growth toward a light source
Gravitropism
growth down in response to gravity
Gibberellin
a class of plant hormones that stimulate internode development to make plants larger
Cytokinin
a class of plant hormones that stimulate cell division and differentiation of plant organs
Ethylene
a gas that controls plant development
cell wall
encloses a plant cell
Cellulose
a complex carbohydrate that provides structural support to a plant
ligin
a complex carbohydrate that strengthens cell wall and reduces rot
Pectin
a complex carbohydrate that binds cells together
plasma membrane
a semipermeable barrier controlling the movement of molecules in and out of a cell wall
osmosis
the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from areas with more water to areas with less water
cytoplasm
composed of various organelle distributed in an inorganic matrix consisting mostly of water
Chloroplast
a double membrane organelle in which photosynthesis occurs, producing glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water
chlorophylls
a class of green pigments that allows for photosynthesis
carotenes
a class of orange pigments
Xanthophylls
a class of yellow pigments
mitochondria
a double membrane organelle in which cellular respiration occurs, producing energy, carbon dioxide, and water from the breakdown of sugar using oxygen
central vacuole
a membrane-bound organelle that contains cell sap-water and water-soluble molecules
Anthocyanin
a class of red blue or purple pigments
tannosome
An organelle found in the central vacuole that contains tannins
tannins
a class of dark brown protective molecules that ward off herbivory and provide UV protection
nucleus
stores genetic information as DNA which controls the production of proteins with cells
Hearthwood
the center of a trunk is made up of a secondary xylem and is darker in color than the sapwood
Sapwood
the lighter colored wood surrounding the heartwood that provides support and transport of nutrients
Pulp
a watery suspension of cellulose-rich plant material
resins
Chemical produced by plants as protection from herbivory and decomposition
Cork
material produced by the cork cambium of trees as the epidermis of the trunk is replaced by the periderm
vegetarian
a person whose diet that doesnt include any flesh ‘
vegan
a person whose diet that doesn’t include any animal products
macronutrient
a nutrient the body needs in large amount in order to supply energy and cellular building blocks
micronutrient
a nutrient the body needs in small amount to provide optimal cellular metabolism
nutrient
a component of food that performs a physiological function in the body l
essential nutrient
a nutrient the body needs in order to function but cant manufacture in adequate amounts and therefore must be part of the diet
carbohydrate
organic molecules that functions in energy stonage
monosaccharide
a single sugar molecule
disaccharide
a sugar molecule containing two monosaccharides
polysaccharide
a molecule containing hundreds to thousands of monosaccharides
glycogen
the short-term energy storage molecule of animals
Starch
the energy storage molecule of plants
cellulose
a carbohydrate that provides structural support to plants
ketosis
a metabolic state that occurs when the body burns fat for energy instead of glucose
fiber
indigestible carbohydrates
protein
an organic polymer composed of amino acids important to the structure and function of cells
complete protein
a protein that contains all 20 essentials amino acids
incomplete proteins
a protein that lacks an essential amino acid
kwashiorkor
a severe form of malnutrition caused by a lack of protein chatacterized by fluid retention
lipids
a diverse category of hydrophobic molecules
hydrophobic
doesn’t mix with water
saturated fat
a triglyceride that contains all single bonds between the carbon atoms
unsaturated fat
a triglyceride that has some double bonds between carbon atoms
trans fat
acts like saturated fats but are chemically unsaturated
vitamin
an organic compound the body need for metabolic purpose but cant manufacture in adequate amounts
pellagra
a disorder brought on by a niacin deficiency characterized bu skin lesions and mental confusions
mineral
inorganic compounds the body needs for metabolic purpose
what two molecules make up a plant cell wall
composed of cellulose and lignin
cellulose function
used to produce paper products, textiles, and as a potential base for biofuels
lignin function
found in cells providing support, protection, and water conductions
what does the cell wall enclose
the plasma membrane
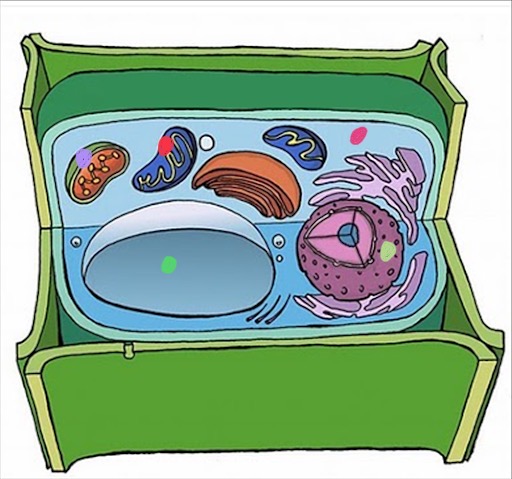
What do the dots respresent
dark green drop- central vacuole
purple dot- chloroplast
Red dot- mitochondria
pink dot- cytoplasm
light green dot- nucleus
what are the four groups of gymnosperm
Gnetophytes, ginkgo, cycads, and conifers
what are the uses of wood
wood provides strength, insulation, versatility, and aesthetic appeal, and must harvest trees sustainably. The hardness of wood is determined by the strength of the cell walls and tied to lignin levels. Most softwood is uses for lumber
wood as lumbar
fell the trees, take to a sawmill, debark the log, lock for metal, cut into lumbar, and then dry lumbar. The grain of wood depends in the thickness of the cell walls.
wood as fuel
a primary source of fuel up until the Industrial Revolution. Burning wood is not very energy-efficient. Energy content can be increased if wood is turned into charcoal, and can be turned into pellets
wood as pulp
used to produce paper, cardboard, fireboard, rayon, cellphone, cellulose acetate
Wood products
Resins- are produced by trees as protection
Cork- is produced by the cork cambium as the epidermis of the trunk is replaced by the periderm
what are fungi mostly composed of?
hyphea
what are fungal cell walls composed of?
chitin
What may hyphae form?
mycelium
what are three methods fungi use to get nutrients?
from the environment, may be parasites, and may be mutualistic symbionts
Fungi produce food
can be used to ferment food (pickles), and can produce alcohol. Yeast produces alcohol and carbon dioxide breaking down sugar in the absence of oxygen
Fungi produce drugs
produces a chemical that inhibits the growth of bacteria, most wisely used as antibiotics today, and the first effective antibiotic was developed from penicillium.
What are the three different types of toxins produced in fungi
Protoplasmic toxins, Aflotoxins, and neurotoxins
Fungi can cause plant disease
80% of all plant diseases are caused by fungi, American chestnut. Blight, Dutch elm disease, Irish potato famine
How does fungi infect people?
It mostly affects the hair, skin, and nails. Ringworm is caused by fungi that break down kertain. Yeast infections occur in warm, moist locations on the body.
Fungi may be used as building materials
use mycelium to produce bricks or packaging, bicycling of demolition waste, and use mycelium to produce clothing.
where was coffee domesticated?
Native to the mountains of Ethiopia
what part of the coffee plant do we use? Is it a monocot or a dicot? How is it harvested?
We use the cherries produced by the plant. Coffee is a dicot. Coffee is made on a plant for decades, cherries from the plant are often picked by hand, and the cherries go through a wet or dry process.
where was cotton domesticated?
Domesticated multipiule times. First harvested in Peru 10,000 years ago, then domesticated in Sudan and India 7,000 years ago
what are the uses of cotton?
Cotton is spun into yarn or thread and then woven or knit into clothes; bleaching, mercerization to improve the strength and luster of fibers and affinity for dyes, applications of sizing to make fabric smoother and improve sheen, and applying finishes like permanent press.