Microbiology: Chapter 6 - Microbial Metabolism: Fueling Cell Growth
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Metabolism
Sum total of all the enzymatic chemical reactions in a cell
Anabolism (Biosynthesis)
set of chemical reactions that requires the energy (ATP) to assemble compounds
Catabolism
the set of chemical reactions that degrade (breakdown) compounds, releasing their energy
Energy
the capacity to do work; can exist as either potential (stored) or kinetic (motion)
Exergonic Reactions
a chemical reaction that releases energy because the starting compounds have more free energy than the products
Endergonic Reactions
a chemical reaction that requires a net input of energy because the products have more free energy than the starting compounds
Metabolic Pathways
series of sequential reactions that converts starting compound to an end product; allows cells to better regulate reactions
Enzyme
a molecule, usually a protein, with complex 3-D shape that functions as an organic catalyst, speeding up reaction rates; lowers the activation energy
Substrate
Substance on which an enzyme acts to form products; surface on which an organism will grow; each enzyme only works with one of these due to its shape
- High Temperature
- Changes in pH
- Inhibition
What factors effect enzyme function?
High temperature
Changes in pH
What factors can denature an enzyme?
Cofactor
non-protein portion of an enzyme required for some enzymes to function; (ex: coenzymes)
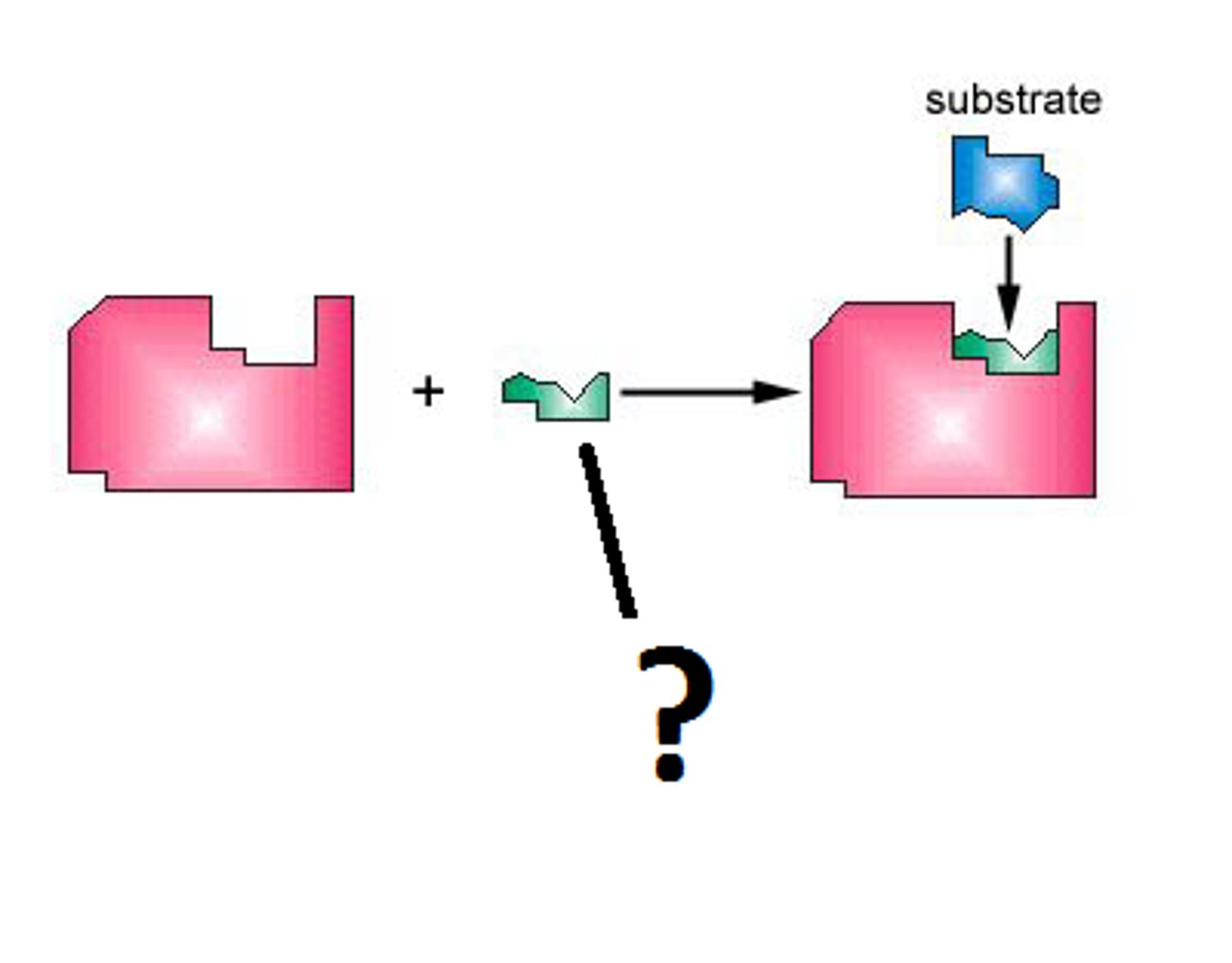
Coenzyme
Non-protein organic compound that assists some enzymes, acting as a loosely bound carrier of small molecules or electrons
Competitive Inhibition
inhibitor binds to active sight of enzyme, blocking access of the substrate to that site; does not denature enzyme
Noncompetitive Inhibition
inhibitor binds to site on the enzyme other than the active site (allosteric site), changing the shape of the enzyme; does not denature enzyme; (ex- feedback inhibition: E. coli and production of isoleucine)
ATP
Energy in an organic compound is converted to _____.
Electrons
Energy production involves the transfer of ________.
Oxidation-reduction Reactions
Chemical reactions in which one or more electrons is (are) transferred from one molecule, atom, or ion to another; one substance in the reaction becomes reduced and the other becomes oxidized
Oxidized
refers to loss of electrons
Reduced
refers to the gain of electrons
Glucose
What is a common energy source for cells?
Aerobic
uses oxygen; involved in cellular respiration
- Glycolysis
- Transition Step (preparatory reaction)
- Krebs Cycle
- Electron Transport Chain
What are the 4 stages of cellular respiration?
Anaerobic
without oxygen; involved in fermentation
NAD+/NADH
Abbreviations for the oxidized/reduced forms of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, an electron carrier
NADP+/NADPH
Abbreviations for the oxidized/reduced forms of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, an electron carrier
FAD/FADH2
Abbreviations for the oxidized/reduced forms of flavin adenine dinucleotide, an electron carrier
Glycolysis
Metabolic pathway that oxidizes glucose to pyruvate, generating ATP and reducing power;
- produces 2 pyruvate
- occurs regardless of oxygen
- glucose is split into two
- produces 2 ATP
Transition Step
also referred to as preparatory reaction; produces...
- 2 pyruvate
- 2 acetyl coenzyme A
- 2 NADH
Krebs Cycle
In this stage...
- acetyl coenzyme A enters to become citrate
- 6 NADH and 2 FADH2 are produced
- 4CO2 is produced
- 2 ATP produced
Electron Transport Chain
a series of membrane-embedded electron carriers; NADH and FADH2 transfer their electrons; produces 32-34 ATP
mitochondria; plasma membrane
The electron transport chain occurs in the _____ of eukaryotes and the _______ of bacteria.
Chemiosmosis
A process for synthesizing ATP using the energy of an electrochemical gradient and the ATP synthase enzyme;
- 32-34 ATP produced
- oxidative phosphorylation
- oxygen is the final electron acceptor (6H2O)
Fermentation
- Occurs without oxygen
- Glycolysis occurs as normal
- NADH dumps it's electrons back on pyruvate or a derivative (this recycles the NAD; produces various end-products)
- Net gain of 2 ATP