Final Exam Study Material for MMET 207 - Texas A&M University - Course Overview
1/476
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
477 Terms
Types of Hardness Testing (3)
Rockwell, Brinell, Vickers or Knoop
Can FCC or BCC hold more carbon?
FCC
Are Hardness Rockwell B (HRB) and Hardness Brinell (HB) the same or different tests?
Different
(more/less)
___ grains = ____ ductility = ____ slip
smaller grains = more ductility = more slip
vice versa
(higher/lower)
___ temp --> ___ grain size
higher temp --> larger grins size
(higher/lower)
___ MoE --> ___ deflection
higher MoE = less deflection (droop)
MoE of: (all x 10^6)
Carbon Steel
Titanium
Aluminum
Plastics
Carbon Steel: 30
Titanium: 20
Aluminum: 10
Plastics: .5
What is the microstructure of the Delta Iron Triangle?
BCC
Is grain size a determining factor in if a material is BCC/FCC or Austenite/Ferrite/Pearlite?
No, you can have any grain size of the same material
What motion is used for wear testing?
Rubbing
What heat treatments soften a material?
Tempering, annealing, stress relieving, and normalizing
Rockwell Hardness Testing (process)
Apply minor load, apply major load, remove loads, calculate the difference of the indentions
Rockwell Hardness Testing (Indentors)
1/16" Tungsten Carbide Ball for B&T
120 degree Diamond Cone or Brale for C, A, & N (EX: HRC)
Rockwell Regular loads
Minor: 10 kg
Major: 60kg, 100kg, 150kg
Rockwell Superficial loads
Minor: 3kg
Major: 15kg, 30 kg, 45kg
What does a major load mean?
Load that makes the second indention
Differences between regular and superficial loads
regular - prefer to use this
superficial - use if material is really thin or soft
Rockwell: difference between Beuler and Wilson?
They are just different brands, same type of rockwell hardness test
Brinell Hardness Test
Uses 10mm ball as indentor
Smash ball into metal surface and measure diameter of the indention
What are the mechanical properties of metals?
- strength
- formability
- stiffness
- toughness
- durability
Strength
The max load a material can take before fracture
Properties of Strength (6)
- tensile
- yield
- compression
- flexural
- shearc
- creep
Formability
The easiness to shape a metal; can I bend this w/o breaking it?
Properties of Formability (3)
- % elongation
- % reduction in area
- bend radius
Toughness
The energy required to fracture the volume of a material (measured in foot pounds)
Properties of Toughness (2)
- impact strength
- notch sensitivity
Durablilty
Wear resistance
Properties of Durability
- Hardness
- Wear resistance
- Fatigue strength
Stress
-A force distributed over an area or object
-Stress = F/Ao
-Units: (lb/in2) or (psi or ksi) or (N/m2)
Strain
-Percentage size change of a material in a particular direction when subjected to a force in that direction
-Strain (Es) = Lf - Lo / Lo
-Units: none or (in/in) or (m/m)
What does the size of the area under the stress-strain curve indicate about a metal?
How much energy is absorbed when the material breaks
Draw and label a stress-strain curve

What is the difference in stress/strain diagram for ductile and brittle materials?
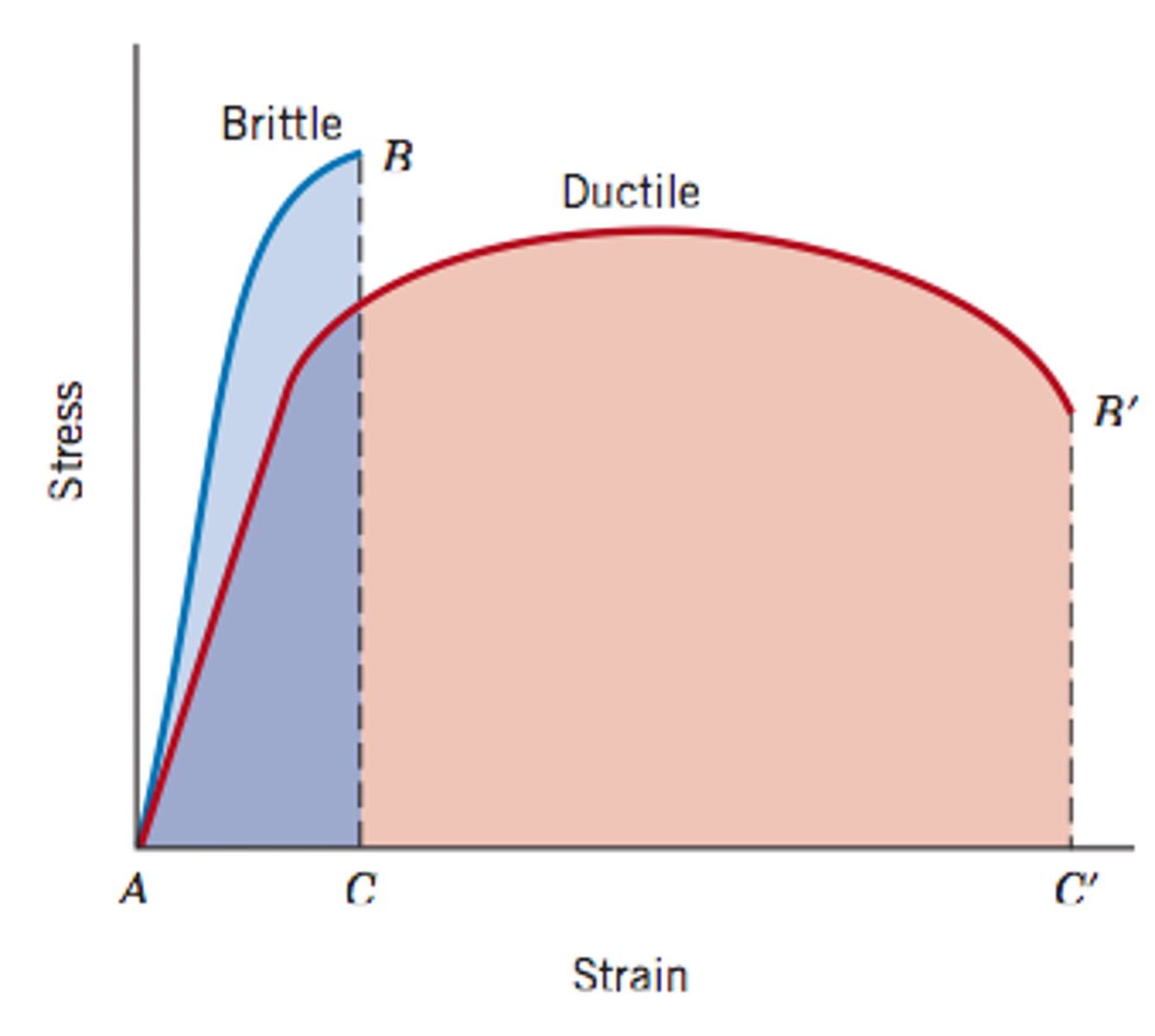
Ultimate tensile strength
The maximum stress that can be applied to a material before it breaks
Elastic limit/Yield Point
point where a material goes from elastic to plastic; last point on linear part of graph
Break point
End of plastic behavior; where a material breaks
What is 0.2% offset yield (Engineering yield strength)
the stress at which a material exhibits a specified deviation from proportionality of stress/strain. Also, it hard to determine precisely so yield point is considered at an offset strain of 0.2%
How to find 0.2% offset yield
determining .002 strain and traveling parallel to modulus of elasticity
Modulus of Elasticity
(What is it?, formula, where on stress/strain curve, tell about the material?)
-A measure of rigidity ( or stiffness)
- Slope of linear line
- delta stress/ delta strain (Es)
- tells a material's stiffness
Modulus of Elasticity of Steel
E(steel) = 30x10^6 psi
Standard gauge for tensile specimens
2 inches
Elastic Behavior
returns to original shape
Plastic Behavior
Does not return to original shape... permanent deformation
Necking
Tensile deformation where relatively large amounts of strain localize disproportionately in a small region of the material (post UTS an about to break)
Impact testing (what for)
Tests toughness; measures a materials ability to with stand a shock load
- Temperature also has a huge impact on it
Impact Testing (how)
Take a material that is NOTCHED, whack it with pendulum or hammer; Charpy Vee or Izod
Charpy Impact Testing
- Has a notch in it and is facing away from impact
- Done more often, easier, faster
what does the difference between Charpy and Izod impact testing look like
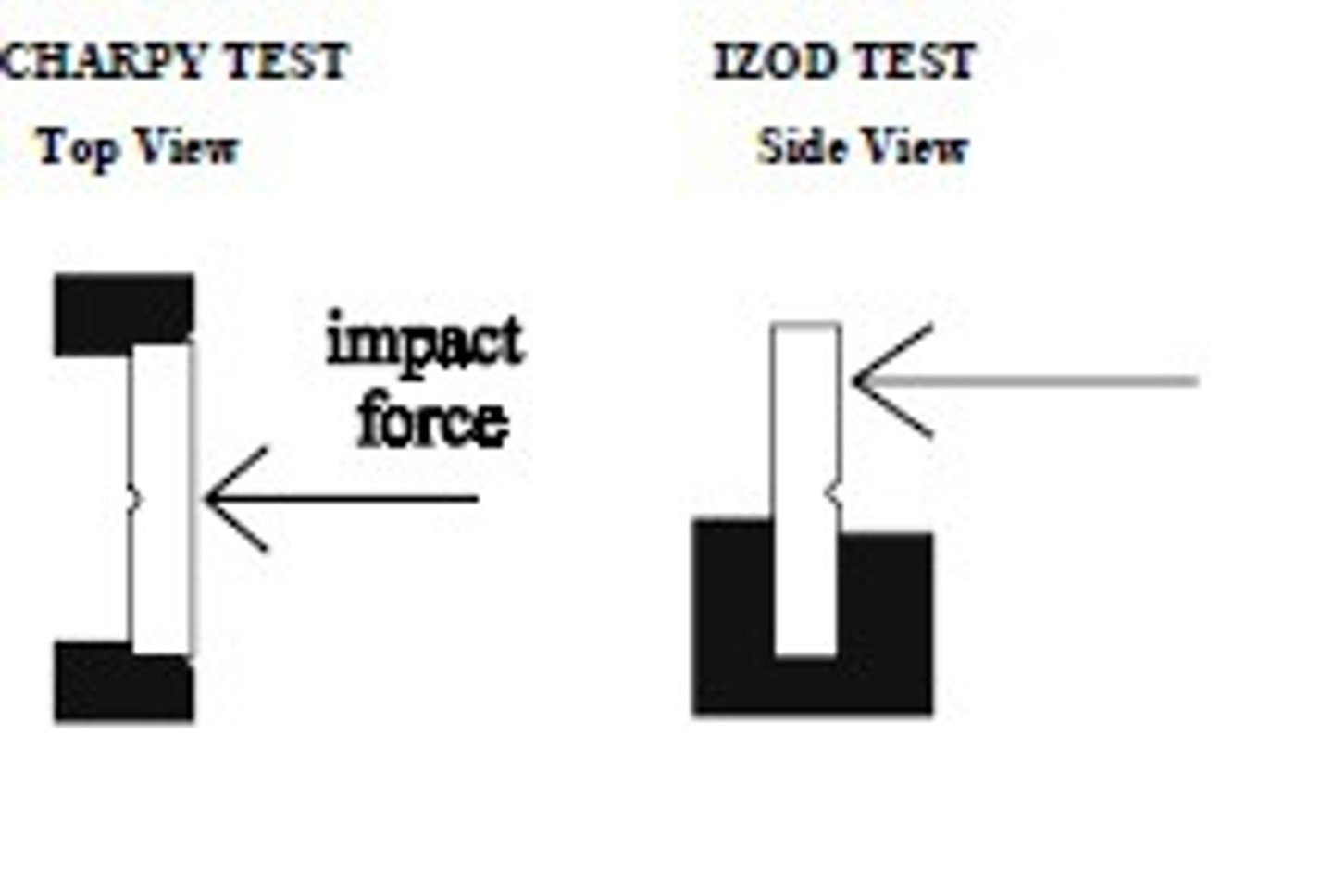
Nil Ductility Temp
the temp at which the toughness of a material drops below the DBTT
DBTT
Ductile to Brittle Transition Temperature
Fatigue Strength
The highest stress that a material can withstand for a given number of cycles without breaking
Fatigue Strength/ Endurance Test
Continuously loading (bending back and forth) a material at given stress levels until it breaks
Endurance Limit/ fatigue strength
The point where you can bend a metal back and forth infinite times and it never breaks
Creep Strength
the resistance of a material to plastic deformation under a sustained load
Creep units
% deformation at a given stress
TRUE/FALSE: a Creep testing temperature must be shown
TRUE
Creep Testing
Used to rate the resistance of a material to plastic deformation under a sustained load and temp; a load is put on a material and when load is taken off, did it retain elasticity
- EX: Fan blade in container
Factors involved in material selection
Chemical, Mechanical, and Physical properties
Melting Point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid
Specific Heat
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celcius
Magnetic (Ferritic)
ferrous based material; retention and strength of magnetic field
Electrical Property
Conductivity and resistivity
Optical Property
Is it reflective
Acoustic Property
speed of sound traveling through a metal; used un ultrasonic inspection
Gravimetric Property
Density, weight
Color
Shiny, dull, light or dark; metals often used for decorative purposes
What is limestone used for
acts as flux (purifier) that removes impuritites
Coke
Used as a heat source to deoxidize; reduces gases that will detach from the oxygen
Blast Furnace
Furnace charged with iron ore, limestone, and coke
Heat melts iron, limestone forms slag, slag and metal separate, liquid is poured into molds, makes pig iron
Pig Iron
Has 3-5% carbon, good for being made into steel
Reduction Reaction formulas
1. C (coke)+ O_2 (air) → 〖CO〗_2 (carbon dioxide)
2.〖CO〗_2+C (excess coke) → 2CO (carbon monoxide)
1. 2〖Fe〗_2 O_(3 ) (ore)+3C (coke) → 4Fe+3CO_2
2.〖Fe〗_2+3CO → 2Fe+3〖CO〗_2
What is reduction
The process of removing iron ore to produce iron; limestone and coke remove oxygen
Types of steel refiners
Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)
How is steel refined
Converts pig iron, scrap, or ore into steel
Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) Process
Charged with molten pig iron → oxygen is blown into the furnace to bring molten slag pool to the top = steel and slag is separate (ITS LIKE BLOWING BUBBLES IN MILK)
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Process
Charged with solid pig iron → arc is struck and melts the metal → oxygen lance is brought in and arc pulls impurities to the top → slag and steel are separated
- Circular furnace shape
What do iron sulfides do to steel
- Create soft spots in steel
- Silican improves the fluidity of molten metal
- adding Manganese (MnS) keeps iron sulfides from being harmful to steel
Primary steel refining
Removing Carbon from Pig Iron
Secondary steel refining
is aimed at altering chemical composition and reducing non-metallic inclusions; produces higher quality steels and alloys
Continuous casting
Continuously pouring metal through a tundish into an open ended mold to make simple, various slab shapes
- End up with semi finished billet, bloom, or slab
- Only uses killed steels
Vacuum Degassing
ingot mold is melted in an evacuated chamber and then is poured through a vacuum to suck out dissolved gases; makes very flat steel
Vacuum Arc Furnace (VAR)
Ingots are melted in a vacuum by making an arc b/w each ingot and water-cooled copper mold; as the arc picks up the inclusions they're sucked out by the vacuum
- used for super alloys and extra clean steel
Electroslag Melting (ESM)
Similar to VAR but w/o vacuum; melting metal from ingot passes through flux that acts as an electrode slag to remove impurities
Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM)
Charge is melted in a crucible → causes convection current stirring → inclusions go to the top and are sucked out by a vacuum ; used to melt solid scrap or liquid charges
- used for specialty alloys
Electron Beam Refining
Molten metal is poured down a tundish → as it flows down an electron beam vaporizes (zaps) impurities out of the metal
- used for aerospace kind of materials
Ladle stirring injection
Bubbling argon through the melt from a port in bottom of ladle → desulfurization and deoxidation
Ladle Furnace Heating
Used to restore heat to the metal in the ladle; electric arc heats melt at the top
Oxides
Non metallic inclusions, doesnt have strength of metals
Cleanliness
How many inclusions, porosity....
Tapping the Furnace
Take liquid steel out of furnace
Rimmed Steel
Ingots that solidify with a skin that is purer than the center; lots of chemical segregation
- Only slightly deoxodized
- low carbon surface layer very DUCTILE
- HAS A VERY NICE SURFACE LAYER
Capped Steel
Have a thin low-carbon rim; semi killed steel with similar characteristics to rimmed steel
- greater use of capped steels overs rimmed steels lately
- more expensive but stronger than rimmed
Semi-Killed Steel
- Intermediate in deoxidation b/w killed and rimmed; has less killing agents
- composition more uniform than rimmed
- used when cold-forming, surface char, or uniformity is NOT essential
Killed Steel
strongly deoxidized; chemical segregation is minimized b/c dissolving elements are added to remove oxygen
- high degree of uniformity in composition and properties
- Cost more, but have better properties
- continuous cast steels
Galvanized
Zinc-coated steel products. The zinc is applied by hot dipping.
Galvannealed
Zinc-coated and heat-treated steel. The heat treatment given to galvanneaied steels creates an oxide layer that allows better paint adhesion.
What/How are ingots made
They are a cast shape that will undergo further finishing
Molten metal is poured into large molds of basic shapes
Non-metallic inclusions
Oxides, sulfides, or alumina that form during conventional melting and refining
Forms of semi finished steels
Billet, bloom, slabs
Billet
Bars, Rod, Tube rounds, Cold-drawn bars, wire, seamless pipe