Biomechanics Unit 1 exam
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Biomechanics
Application of mechanical principles to living organisms.
Kinesiology
Study of human movement.
Sports Medicine
Clinical and scientific aspects of sports and exercise.
Occupational Biomechanics
Prevention of work-related injuries and performance improvement.
Kinematics
Study of motion description (sequence and timing).
Kinetics
Study of forces involved in motion.
Statics
Systems with no acceleration (can be stationary).
Dynamics
Systems with acceleration.
Anatomical Reference Position
Standing upright, arms at sides, palms facing forward.
Sagittal Plane
Divides body into left and right, involves flexion and extension.
Frontal Plane
Divides body into front and back, involves hip abduction and adduction.
Transverse Plane
Divides body into top and bottom, involves rotation, pronation, and supination.
Mass
Amount of matter in an object, measured in kilograms (kg).
Weight
Gravitational force acting on a body (wt = ma).
Inertia
Resistance to change in motion; higher mass equals higher inertia.
Force
A push or pull acting on a body (F = ma).
Center of Gravity
Point where body weight is equally balanced.
Pressure
Force per unit area (P = F/A).
Stress
Distribution of force within a body (Stress = F/A).
Volume
3D space occupied by a body (V = l × w × h).
Density
Mass per unit volume (Density = Mass/Volume).
Torque
Rotational effect of an eccentric force (T = F × d).
Impulse
Force applied over time (J = F × t).
Compression
Pressing force through the body.
Tension
Stretching force through the body.
Shear
Force parallel to the body (e.g., ACL tear).
Bending
Tension on one side, compression on the other.
Torsion
Twisting force (e.g., snake bite).
Combined Loading
Multiple forces acting together.
Vector
Has both magnitude and direction.
Scalar
Has only magnitude.
Biomechanics
Application of mechanical principles in the study of living organisms
Kinesiology
Study of human movement
Sports medicine
Clinical and scientific aspects of sports and exercise
Kinematics
Study of the description of motion
Kinetics
Study of forces associated with motion
Statics
Branch of mechanics dealing with systems at Constant state of motion
Dynamics
Branch of mechanics dealing with systems subject to acceleration
Occupational biomechanics
Field focused on preventing work-related injuries and improving work conditions and performance
Formal problem
A problem with a mathematical equation and specific components
Informal problem
A problem without a mathematical equation and more observational in nature
Inference
Process of forming deductions from available information
Qualitative analysis
- identify major question
-determine optimal perspectives
-determine the viewing distance
-number of trials/executions
-performer's attire and nature surrounding equipment
-visual observation, video camera, other tools
Optimal viewing perspectives
-Determining the best perspectives to view human motion
-finer movements ->gross movements
-closeup, medium, distant view
Linear motion
Motion along a straight or curved line with all parts of the body moving in the same direction at speed
Angular motion
Rotation around a central axis of rotation
Axis of rotation
Imaginary line perpendicular to the plane of rotation
General motion
Combination of translation and rotation
Frontal axis
Axis of rotation for movements in the sagittal plane
Sagittal axis
Axis of rotation for movements in the frontal plane
Longitudinal axis
Axis of rotation for movements in the transverse plane
Compression
Pressing or squeezing force directed axially through a point
Tension
Pulling or stressing force directed axially through a point
Shear
Force directed parallel or tangent to a surface
Bending
Asymmetric loading that produces tension on one side and compression on the opposite side
Torsion
Load producing twisting of a body around its longitudinal axis
Combined loading
Simultaneous action of more than one form of loading
Stress
Distribution of force within a body
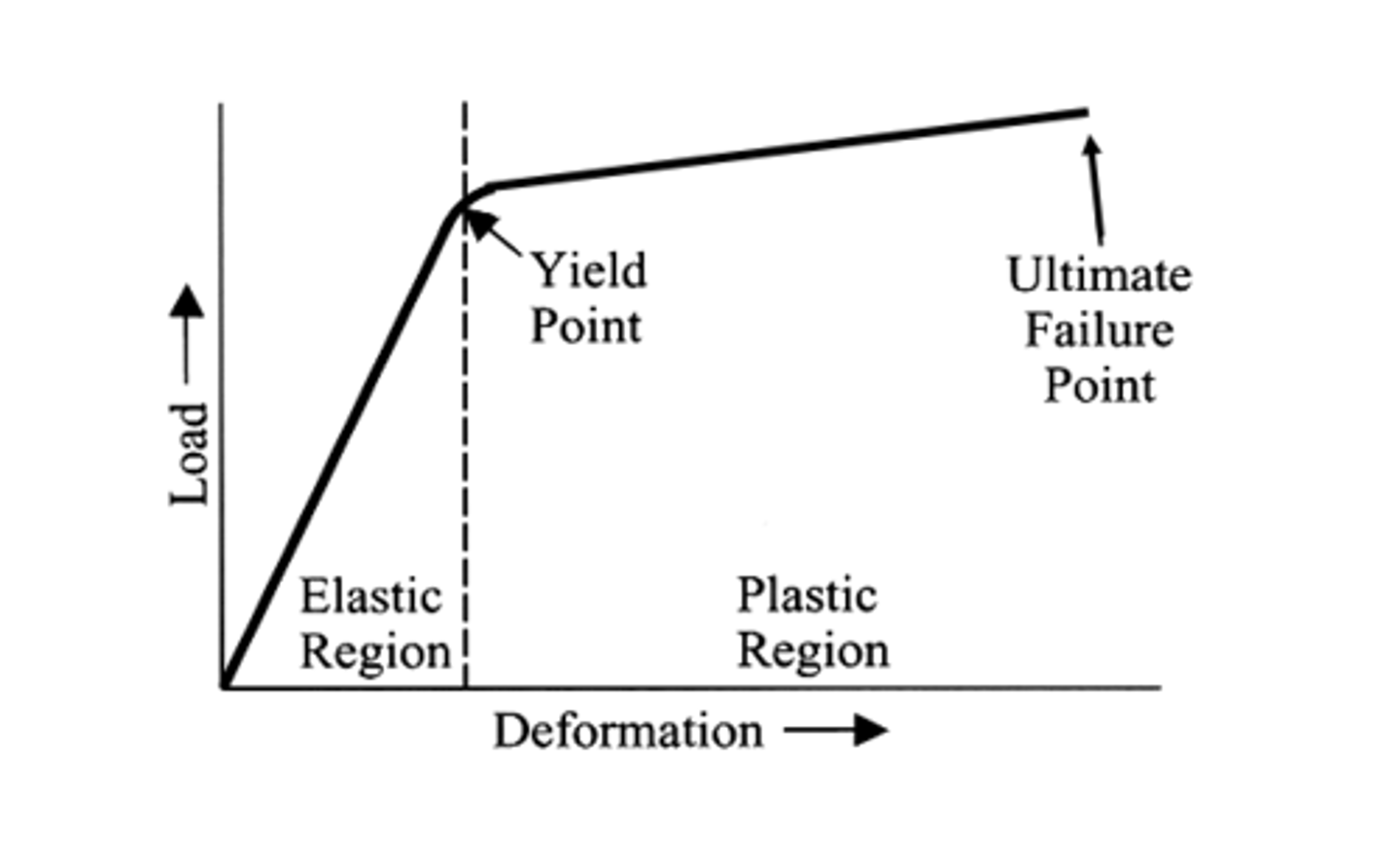
Yield point
Point on the load-deformation curve where deformation becomes permanent
Failure
Loss of mechanical continuity
Force plates
Devices that measure ground reaction forces
Pressure platforms
Platforms that provide graphical or digital maps of pressures
Dynamometers
Devices used to measure forces
Vector
A quantity with magnitude and direction: SIZE AND DIRECTIONS
Scalar
A quantity with magnitude but no direction
acute loading
application of a single force of sufficient magnitude to cause injury to a biological tissue
-tearing meniscus
repetitve loading
repeated application of a subacute load that is usually of relatively low magnitude
-running on bad ankle
Deformation curve
x = deformation, y = load. Shows us where the elastic region vs plastic region are
elastic - back and forth
plastic - permanent
deformation - change in shape
yield point - deformation now permanent
failure point - "breaks"
* ex: ACL
qualitative analysis
describing without numbers
quantitative analysis
involving use of numbers
-