5.1 Phospholipids
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 5 biology 1230
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is the main fabric of the cell membrane?
Phospholipids which are amphipathic
What makes up the hydrohilic head?
Glycerol
Phosphate group (polar)
What makes up the hydrophobic tail?
2 two fatty acid chains that are nonpolar, each fatty acid can be saturated or unsaturated
Carbons are saturated with H when…
There’s all single C-C bonds
Carbons are unsaturated when…
there’s atleast one double C=C bond occurs
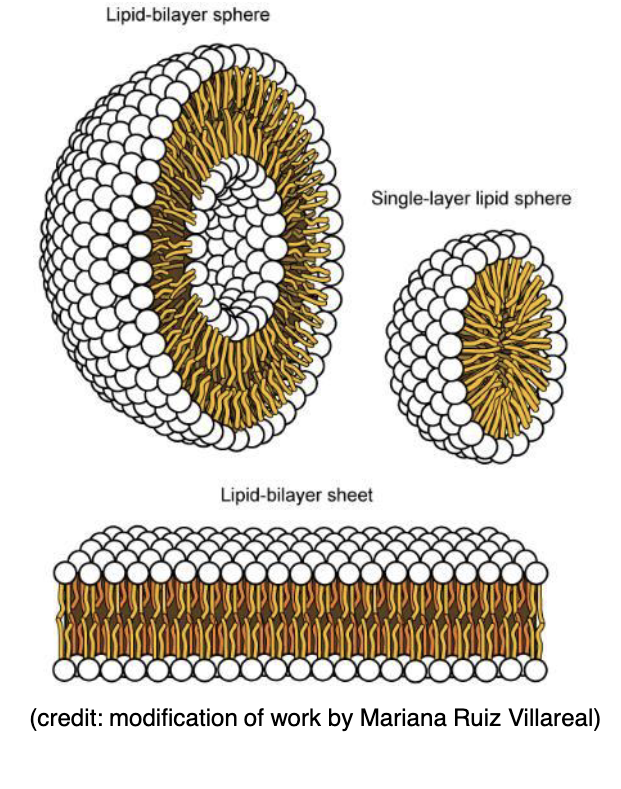
Phospholipid bilayers…
Polar heads face outward and hydrophilic tails face inward
What are proteins?
The second major component of membranes, they can be transporters, receptors, enzymes or function in binding and adhesion
Integral proteins…
Are integrated completely in the bilayer and have one or more regions that are hydrophobic and others that are hydrophilic
Peripheral proteins…
occur only on the surfaces
What are carbohydrates?
Third major component and are bound to either proteins or to lipids
What affects membrane fluidity?
Phospholipid type
Temperature
Cholestrol
What makes the cell membrane a fluid character?
A mosaic of components of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins and carbohydrates
What are transmembrane proteins?
Integral proteins that pass completely through the phospholipid bilayer
When carbohydrates are bound to proteins what’s formed?
Glycoproteins
When lipids are bound to carbohydrates what’s formed?
Glycolipids
What is membrane fluidity?
When the membrane needs to be flexible but not so fluid it cannot maintain it’s structure