ECOLOGY-adaptations/food chains/trophic levels /pyramids of biomass/biomass transfer
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Adaptations
Adaptations allow organisms to survive. There are three types of adaptations.
Structural
Behavioural
Functional
What are structural adaptations
Structural, adaptations are features of an organisms, body structure, such as shape or colour. Examples include
Arctic fox have white fur so they camouflage against snow which helps them avoid predators and allows to sneak up and pray.
Animals that live in cold places like whales Have a thick layer of blubber and a low surface area to volume ratio to help them retain heat
Animals that live in hot places like camels, have a thin layer of fat and a large surface eras of volume ratio to help them lose heat
What are Behavioural adaptations
Behavioural adaptations are ways that organisms behave many species like swallows migrate to warmer climates during winter to avoid the problems of living in the colder. harsher conditions
Other examples could include playing dead, or an animal being nocturnal
What is functional adaptation?
Functional adaptations are things that go on inside of an organisms body that can be related to processes, like reproduction or metabolism For an example
Desert, animals, conserve water by producing very little sweat and small amounts of concentrated urine
Brown bears hibernate over winter. They lower their metabolism which conserves energy, so they don’t have to hunt when there’s not much food about.
It could also be the late implantation of embryos, such as when elephants have a long pregnancy and keep their baby for over a year in the womb, which means that the baby will be stronger and has a better chance of survival
What are extremophiles?
Extreme files are organisms that live in very extreme conditions such as high temperatures, high pressures and high salt concentration
Organisms that live in deep sea vents are extremophiles
Food chains
Food chains show what’s eaten by what in an ecosystem
Food chains always start with a producer and end with the Tertiary consumers or the Apex predator
What is a Producer
A producer is usually the first step of the free chain they make their own foods using energy from the Sun produces are usually green plants or algae they make glucose by photosynthesis
When the green plant produces glucose, some of it is used to make other biological molecules in the plant. These biological molecules are the plants biomass – the mass of living materials.
What are primary consumers?
Primary consumers eat, the producers and primary consumers are usually fish, herbivores, or insects
What are secondary consumers?
Secondary consumers eat the primary consumers, secondary consumers tend to be Birds or carnivores. Sometimes you get a tertiary consumer that eats the secondary consumer. These are always carnivore.
What is an Apex predator?
Secondary consumers eat the primary consumers, secondary consumers tend to be Birds or carnivores. Sometimes you get a tertiary consumer that eats the secondary consumer. These are always carnivore.
What are secondary consumers?
Between each trophic level energy is transferred through living organisms in an ecosystem when an organism eats other Organisms
What is an Apex predator?
An Apex predator cannot be prayed on, and it is at the top of the food chain. These are all usually carnivores.
Formula to calculate the efficiency of biomass transfer

What happens when living organisms eat other organisms?
Between each trophic level energy is transferred through living organisms in an ecosystem when an organism eats other Organisms
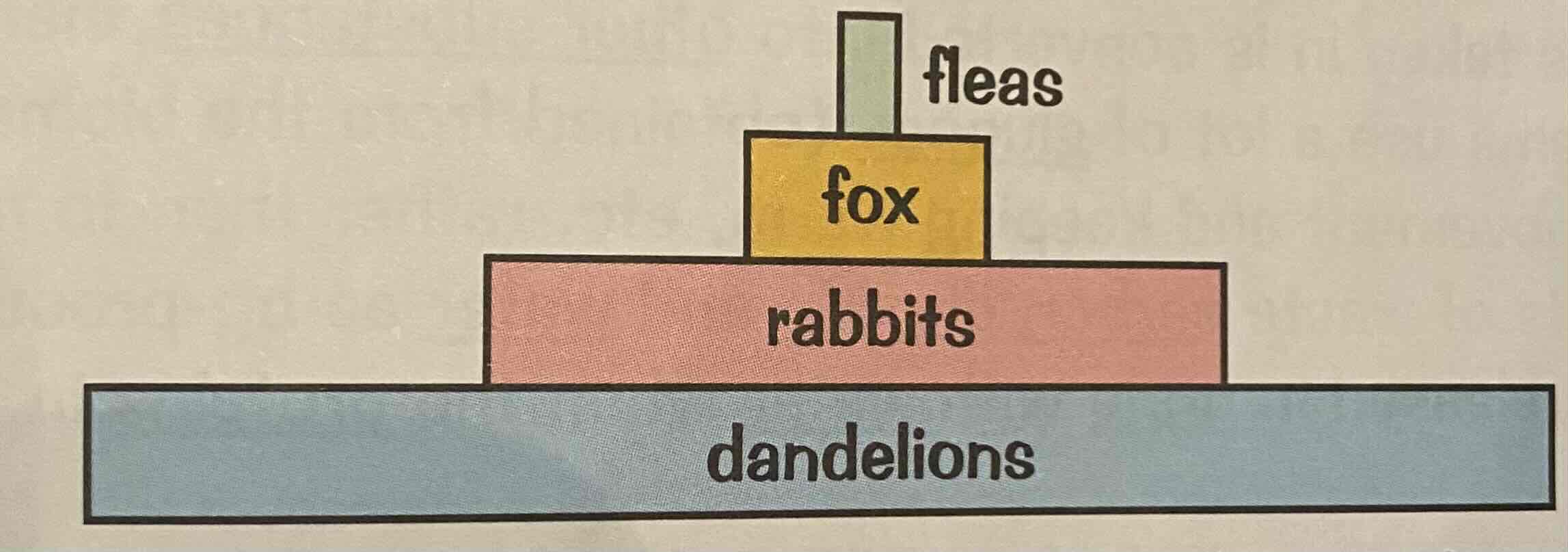
Why are food chains not that long?
Biomass is usually lost between each trophic level organisms organisms, don’t always get all of the energy/biomass from the food that they ingest
Biomass is lost through the trophic levels due to respiration/growth and repair/faeces or urea
Usually the amount of biomass available to the next level decreases by 10% in each trophic level
And because of the fact that the biomass decreases every trophic level, this means that the food chain cannot go on forever as the amount of energy/by mass transfers decreases the point where it’s not even worth The hunt
What is a trophic layer?
Food chains can be divided into trophic levels. This just organises the different stages of a food chain.
Trophic level one contains a producers which make their own food by photosynthesis Using energy from the Sun, these are usually plants and algae
Trophic level two contains a primary consumers. These are herbivores that eat the plants and algae.
Trophic level three contains the secondary consumers. These are carnivore that eat the primary consumers.
Trophic level four contain a tertiary consumers. These are always carnivals that eat other carnivore. The highest trophic level is the Apex predator
What are decomposers?
Decomposes breakdown uneaten remains and waste decomposers such as bacteria and fungi. They decompose any dead plant or animal material left and environment and they do this by secreting enzymes that break the dead stuff down into smaller soluble food molecules. These then diffuse into microorganisms.
What is the relationship of prey and predators?
The relationship for pray And predators are not instantaneous They are out of phase with each other, and this is because it takes awhile for one population to respond to the changes of another population
What is a quadrat?
A quadrat is a square frame enclosing a known area. It is 1 m x 1 m. They are placed at random points within the first sample area
Quadrats are good because they are random no biases
What is a transect?
A transect can be used to map out an area that you are going to collect data in
These are good because it keeps it a fair test if you repeat at different times of the year, but it could be biased and unrepresentative of a whole field