Assessment of Pregnancy and Fetal Well-Being
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Ultrasonography indications
Fetal heart activity, growth, anatomy, genetic disorder
Placental position and functioning
Adjunct to other invasive tests
Cervical thickness and length
Doppler blood flow analysis
use of ultrasound for noninvasive measurement of blood flow in the fetus and placenta
Oligohydramnios
Too little amniotic fluid (AFI <5)
- Baby swallows fluid but maybe isn't peeing enough back out
- Could indicate kidney insufficiency or fluid leakage
Polyhydramnios
Too much amniotic fluid (AFI >25)
- Blockage in baby's GI so it can't swallow the fluid
Biophysical profile
A test that assess five variables; fetal breathing, fetal movement, fetal tone, amniotic fluid volume, and fetal reaction
Normal fetal breathing movements
At least one episode of fetal breathing movements
Normal muscle tone
1 or more episodes of active extension/flexion of limbs, etc. (i.e. opening and closing a hand)
Normal fetal movement
at least 3 trunk/limb movements in 30 minutes
Normal amniotic fluid
1 or more adequate pockets of fluid
Normal non-stress test
reactive
Daily Fetal movement count (kick count)
maternal assessment of fetal movement by counting fetal movement in a period of time to identify
- movement is generally a sign of health
- once a day for 60 min or count until 10 movements (should be within 2 hours)
- Less than 3 movements per hour warrants further evaluation
- No movement in 12 hours = fetal alarm system (call provider)
Amiocentesis
a procedure in which a syringe is inserted through a pregnant female's abdominal wall into the amniotic fluid surrounding the developing fetus to obtain fluid for testing
- Genetic disorders
- Congenital anomalies
- Assessing lung maturity
Can be done after 14 weeks
amniocentesis maternal complications
Hemorrhage
Infection
Labor
Abruptio placentae
Damage to intestines or bladder
Amniotic fluid embolism
amniocentesis fetal complications
Death, hemorrhage, infection, direct injury from needle
Chorionic villus sampling
removal of a small piece of chorion for genetic analysis
Percutaneous Umbilical Blood Sampling (cordocentesis)
Insert needle into fetal umbilical vessel for fetal blood sampling and transfusion
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
screens for neural tub defects between 14-34 weeks
Multiple marker screens
detects chromosomal abnormalities
increased risk for trisomy 21
Coombs' test
Rh incompatibility
Detects other antibodies for incompatibility with maternal antigens
Electronic fetal monitoring
To determine if the intrauterine environment is supportive to the fetus
Nonstress test
Determines fetal activity
-FHR monitored for 20-30 and tracing is observed for signs of fetal activity and concurrent acceleration in FHR
-Makes sure baby is getting enough oxygen from placenta
reactive nonstress test
2 accelerations in 20 minutes each lasting 15 secs and 15 bpm above baseline
-Accelerations happen when baby moves
Contraction stress test
Identify jeopardized fetus that is stable at rest, but compromised with stress
-Contractions stimulated with nipple stimulation or oxytocin until 3 contractions lasting 40-60 sec in 10 mins)
-FHR monitored
-Toco (contraction monitor) senses when mom contracts
-Tracing observed to see how baby responds to contractions
Negative contraction stress test
(Normal) A negative result is represented by no late decelerations of fetal heart rate (FHR).
External fetal monitors
Ultrasound transducer: monitors fetal heart rate
Uterine Tocotransducer: monitors uterine contractions
- Cannot report strength of contractions
Internal monitors
fetal scalp electrode: pokes into baby's head to collect heartbeat
intrauterine pressure catheter: similar to TOCO but can tell us contraction strength
- Membranes must be ruptured and cervix must be dilated enough
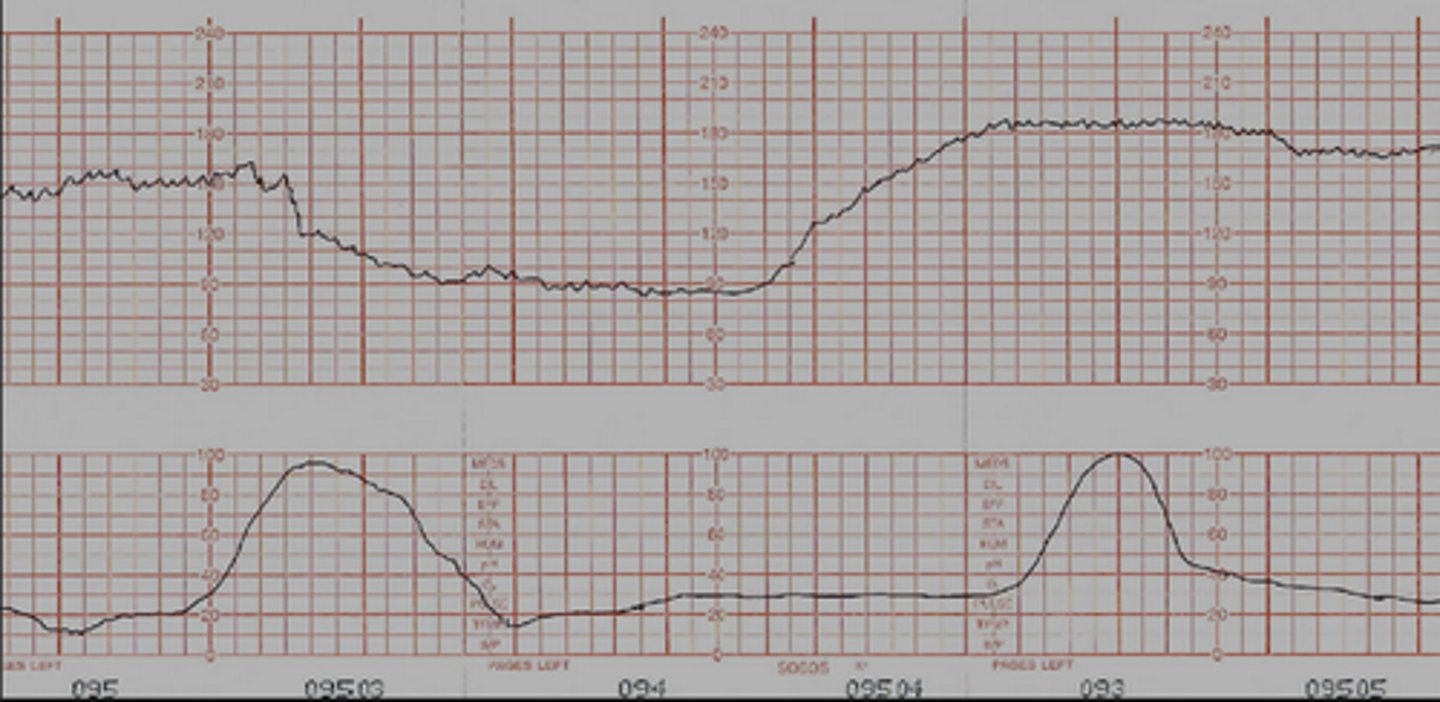
fetal heart rate
Baseline heart rate = 110 - 160 bpm (for full term fetus)
Variability - irregular fluctuations (normal)
- Moderate variability fluctuates 6-25 bpm
Acceleration
abrupt increase in FHR above baseline
- Positive thing to tell us baby is moving and placenta is working
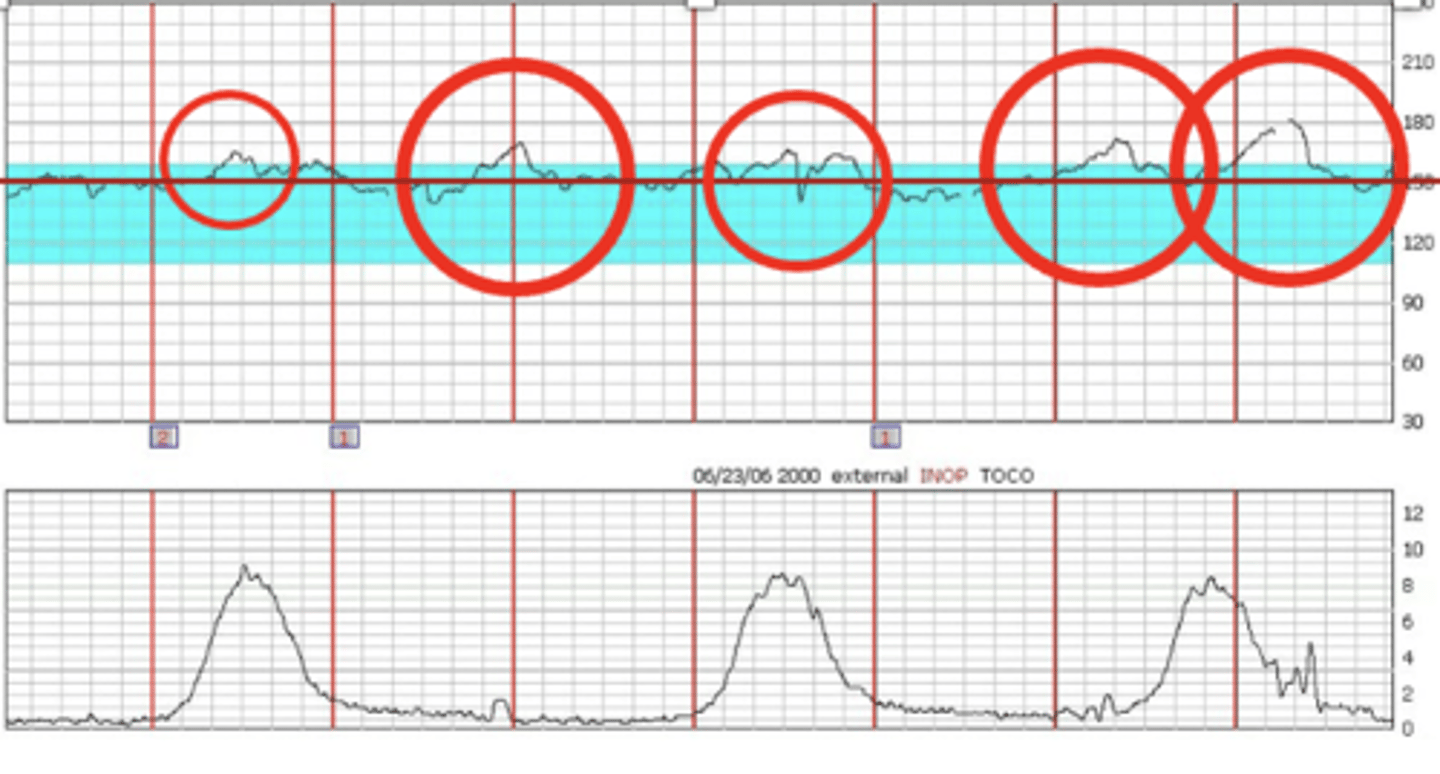
Early decelerations
Caused by head compression usually as head gets lower in cervix: typically a good sign
- Mirror image of contraction
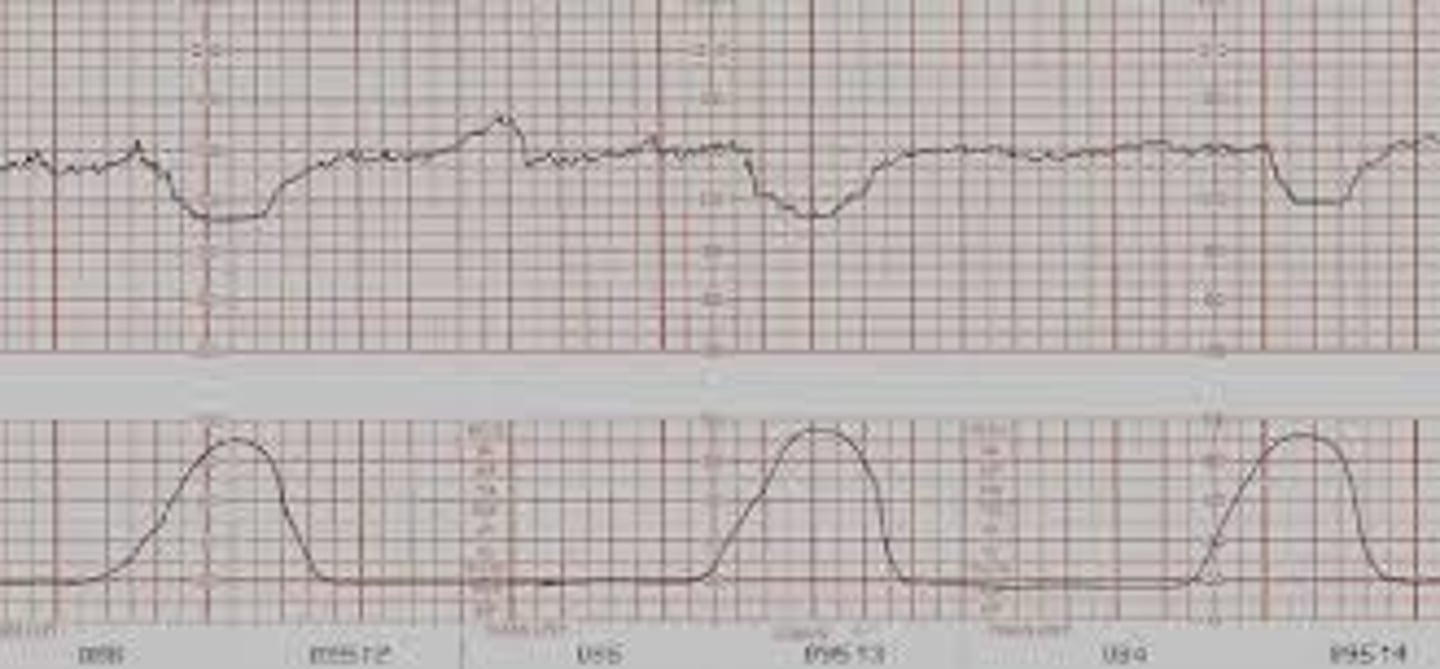
Variable decelerations
Caused by cord compression: more than 1 not good
- Happen with or without contraction
- Abrupt deep and wide section below baseline
- Give O2, fluid, and change position
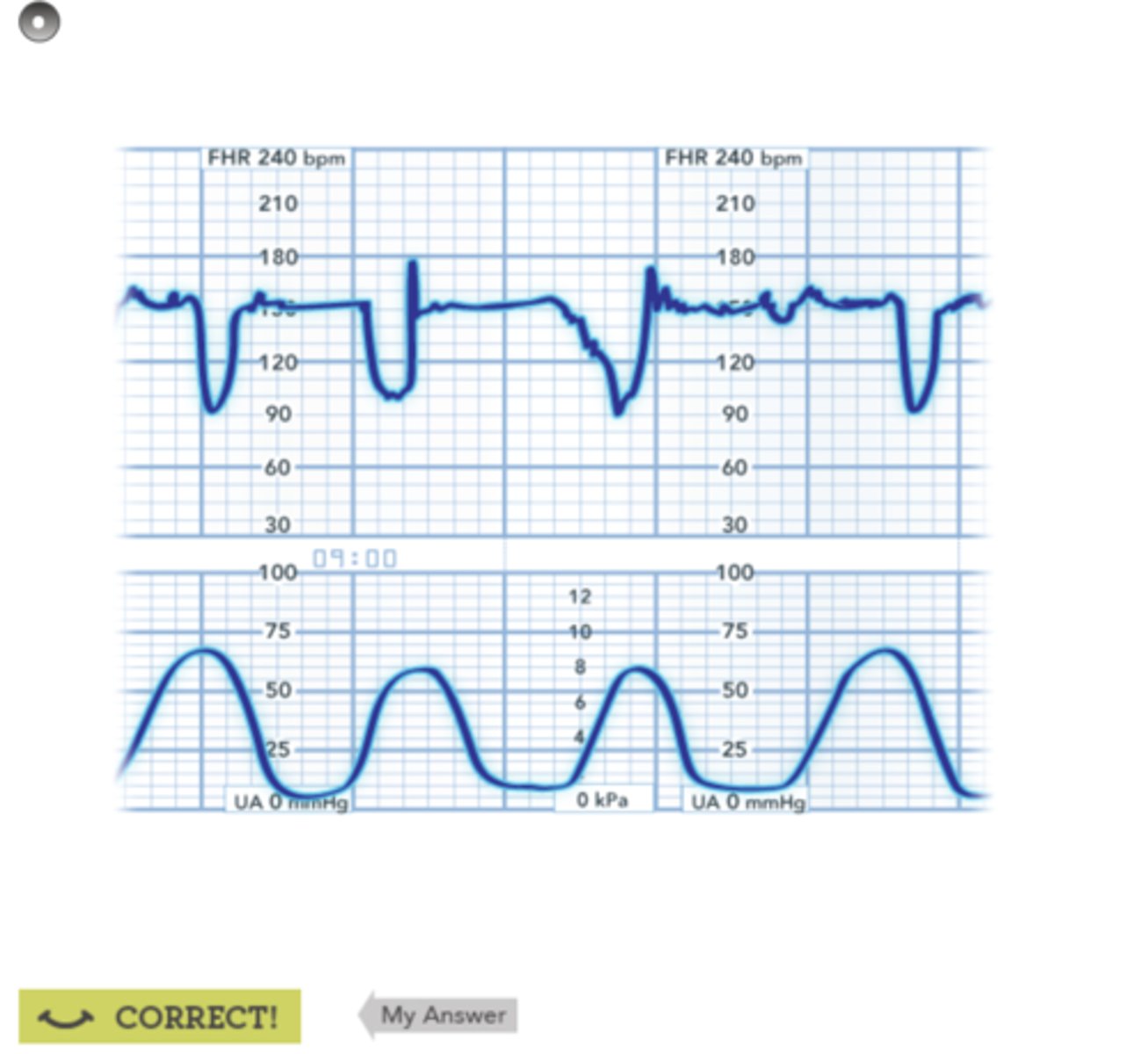
Late decelerations
caused by uteroplacental insufficiency: NOT GOOD
- happens after contraction
- need to give O2, fluid, and change position
- notify provider
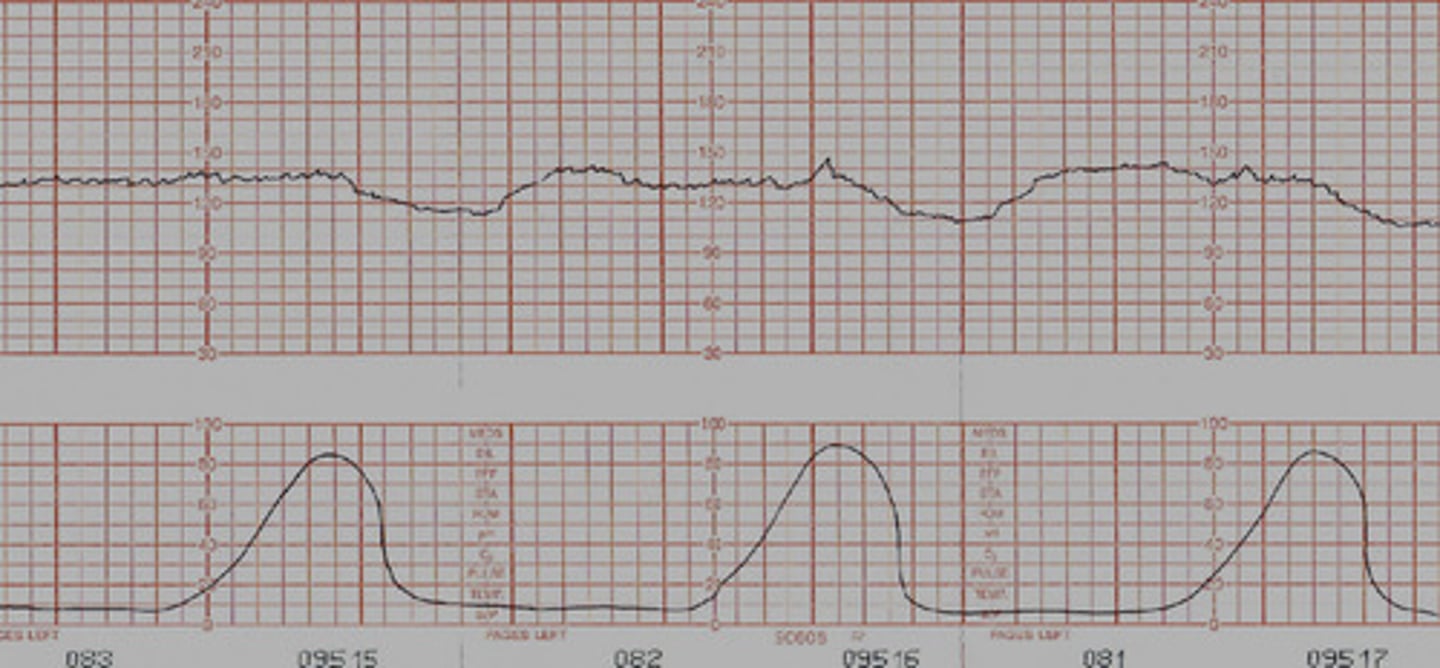
Prolonged decelerations
Dips down and stays down with decreased variability
- After a few minutes of this, usually head to C-section
VEAL CHOP
V- Variable C- Cord Compression
E- Early Decels H- Head Compression
A- Accelerations O - OK
L-Late Decels P - Placental insufficieny