AP Chemistry | Unit 2 - Topic 2.2: Intramolecular Force and Potential Energy
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
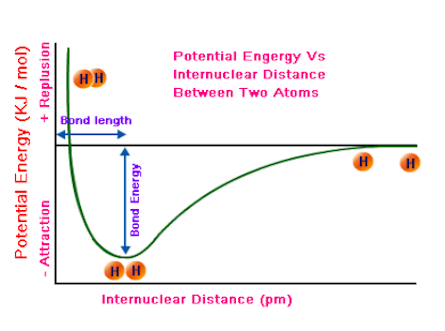
Potential Energy Graph
Covalent bonds occur at the lowest energy state. This happens when the attraction between the nuclei is greatest for the shared electrons, but the repulsion’s between electrons and between the nuclei is the least. If the atoms are too close together, the nuclei will repel each other and if they are too far apart the attraction will not be enough to hold them together. Bond length is affected by both the size of the atoms core (atomic radius, measured in picometers)
Covalent bonds
Occurs between two non metals when sharing valence electrons. Can be polar or non polar, depending on if electrons are shared equally or not. Covalent bonds can be single, double, or triple bonds or an average of those if there are resonance structures
Blank
Blank