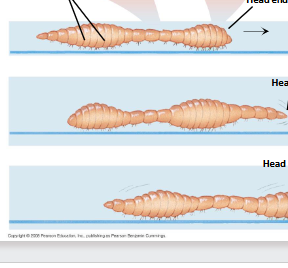
Phylum Nematoda ( Roundworms) Platyhleminthes (Planarians and Tape worms) and Annelids (Clamworm Earthworm Roundworm)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
who are the nematodes?
roundworms
are roundworms free living or parasistic
can be both
the cylindrical bodies of nematodes are covered by an exoskeleton called a
cuticle
do nematodea reproduce asexually or sexuallly
sexually
what is the symmetry, tissue organization, body cavity, and digestive opening for nematodes (roundworms)
symmetry: bilateral
tissue: triploblastic
body cavity: pseudocoelomate
digestive opening: tube within a tube (inner tube is lined w endoderm)
what type of circulatory system, habitat, respiratory organs, locomotion, excretory system, support system, segmentation, appendages and nervous system do nematodes have
circulatory: none really, transport nutrients in the pseudo coelom
habitat: parasitic, moist soil, bottom of lakes
respiratory organs: none, esentially anaerobic
locomotion: live in gut, limited in movement
excretory: two lateral lines
suppport: hydrostatic skeleton; external cuticle
segmentation: none
appendages: none
nervous system: dorsal and ventral nerve

Ascaris Nematode Anatomy
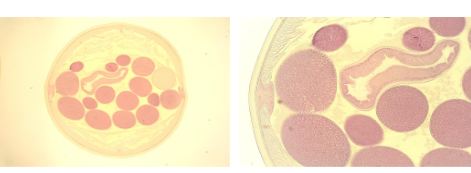
Nematode (MALE)
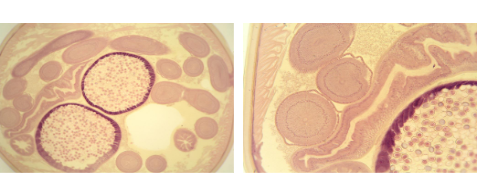
Nematode (FEMALE)
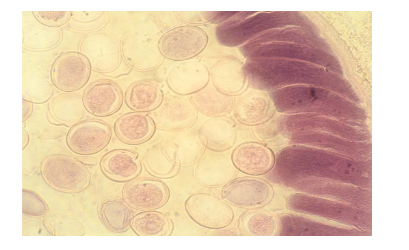
Nematode FEMALE EGGS
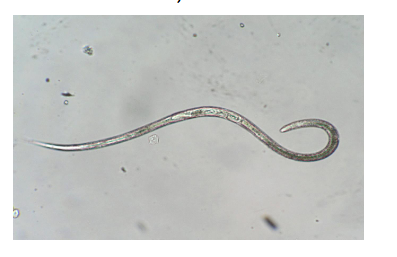
Vinegar Eels
who are part of the Phylum Platyhelminthes
Planarian and Flatworms
What is the symmetry, tissue organization, type of body cavity and digestive opening for Platyhlminthes (Planarians)
symmetry: first animal organization we have studied that has bilateral
tissue organization: triploblastic
body cavity: acoelomate
digestive opening: one opening sac like
what type of circulatory system, habitat, respiratory organs, excretory system do planarians/ Playthemites have
circulatory:none
habitat: aquatic
respiratpry organs: cells directly across membranes
excretory systems: flame cells; 2 lateral excretory canals. seperate organs a uterus and testes (involved in osmoregulation)
what type of locomotion, support system, segmentation, appendages, nervous systems do planarians/ Platyhleminthes have
locomotion: crawling, creep over
support: hydrostatic
segmentation: none
appendages: none
nervous system: brain, two ventral nerve cords; ladder like nervous system
do planarians(phlyum Platyhelminthes) exhibit cephalization
yes (organisms are able to asses the enviornment they are about to enter by going head first)
three tissue layers in flatworms (planarains)
inner layer- endoderm
outer layer- ectoderm
middle layer- mesoderm
what are the two types of parasitic worms of platyheliminthes
flukes nad tapeworms
definitive host vs intermediate host (planarians)
definitive: reprduces sexually on hosts digestive system
intermediate: found on muscle tissues or internal organs of host and reproduce asexually
reproduction in flatworms is (planarians)
monoecious (one individual has both sex)

Planarian (Flatworm)
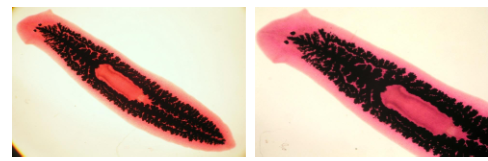
Planarian w Gut Injected
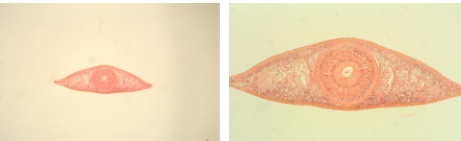
Planarain Cross Section at the level of Pharynx

Tapeworm
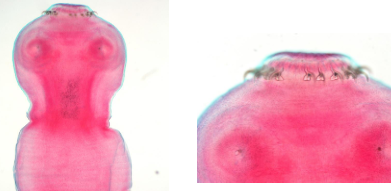
Tapeworm (notice hooks)
Tapeworm showing eggs in Uerus
Tapeworm cysts in meat
Life cycle of a beef tapeworm
mature progolottids are released from end of tapeworm and leave with the host’s feces.
• In one type of cycle, tapeworm eggs in contaminated food or water are ingested by
intermediary hosts, such as pigs or cattle.
• The eggs develop into larvae that encyst in the muscles of their host.
• Humans acquire the larvae by eating undercooked meat contaminated with cysts.
• The larvae develop into mature adults within the human.
posterior, ventral, dorsal, anterior
what are proglotidds in tapeworms platyhelminthes
sac of sex organs
who are part of the phylum annelida?
clamwor, earthworm, and the roundworm
what is the symmetry, tissue organization, type of body cavity, digestive opening and circulatory system for the annelidas?
symmetry: bilateral
tissue organization: triploblastic
body cavity: coelomate
digestive opening: two openings, tube within a tube
circulatory: closed circulation with blood vessels
what is the habitat, respiratory organs, excretory system, and locomotions of annelids?
habitat: clamworm is aquatic but earthworm is terrestrial
both respiratory organs are the skin and parapodia
the excretory system is the nephridia
locomotion for clamworms is swimming and parapodia, but with earthworm is setae and crawling
what type of support system, segmentation, appendages, nervous system do annelids have
support system: hydrostatic skeleton
segmentation : yes metameristem
appendages: clam worm has parapodia but earthworm has none
Nervous system: dorsal brain, ventral nerve cord
the first segmented worms to evolve were which ones?
annelid
what is parapodia?
paired of lateral appendages that some annelids have
how do earthworms crawl?
crawl by perstistalsis
what are the three clases for the phylum Annelids
1) oligochaeta earth worms (terrestrial)
2) polychaeta (many setae/chaeta) mainly marine
3) hirudinea (leeches)
why are earthworms part of class oligocaeta
have brsitles made of chitin present in each segment (chaetae), lack a head, monoecious, but can still exchange for fertilization
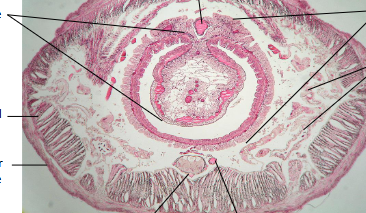
A- typhlosole
B- longitudinal muscle
C- circular muscle
D- nerve cord
E- ventral vessel
F- nephridium
G- intestine
H- dorsal vessel
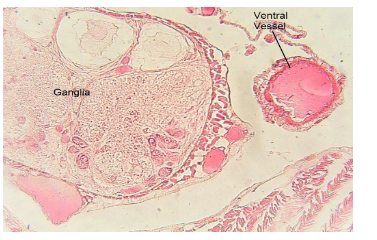
Earthworm cross section with ventral nerve and bloood vessel (label the ganglia and ventral vessel)
what is an example of class polychaeta
clamworm
most polychaetas are ____________. many crawl, or burrow on seafloor, while a few drift. They each have a lot of _______________ setae. They do have a ________ region.
marine
chitinous
head

Clamworm Dorsal view
A- Mouth
B- Jaw
C- Pharaynx
D- Eyes
E- Tentacles
F_ Chaetae
G- Parapodia
H- Bristles
I- Palp

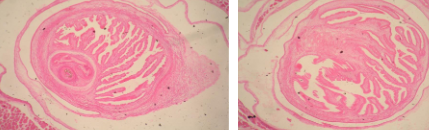
Clamworm cross section

Clamworm
Paddlelike Parapodia “almost feet”
function in locomotion
Nematodes such as roundworms reproduce
sexually and are dioceious
Are nematodes segmented?
NO

A- Bristles
B- Parapodia
C- Tentacles
D-Eyes
In planarians which organ system is the pharynx a part of?
digestive system, the pharynx is used to swallow prey
earthworms and nematodes both have cuticles what is the purpose of a cuticle?
the purpose of the cuticle is to be a protective layer. In nematodes the cuticle is part of their exoskeleton. The cuticle allows for gas exchange and helps these worms retain water, and prevents moisture loss
even tho clamworms and earthworms are both part of the annelid phlyum, why do clamworms not have a cuticle?
clamworms do not have a cuticle because they are commonly found in habitats that are aquatic therefore they do not need a cuticle to prevent moisture loss.
what is the difference between acoleomates and pseduocoloemtes ?
aceolomates lack a body cavity and they have no coelom such as flatworms. While pseudocoelomates have a body cavity, and their coloem is only partially lined with mesoderm, for example roundworms
why is the erathworm locomotion so unqiue
crawl by perstalsis, which means they contract their muscles. The longitudunal muscles thickens and shortens, but contractions of the circular muscles constricts and elongates the worms