week 7 - statistical inference
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
statistic vs parameter
→ use statistics to estimate parameters
statistic: characteristics of a sample (population)
can change
parameter: characteristics of a population
describes the actual population
fixed value (whole population)
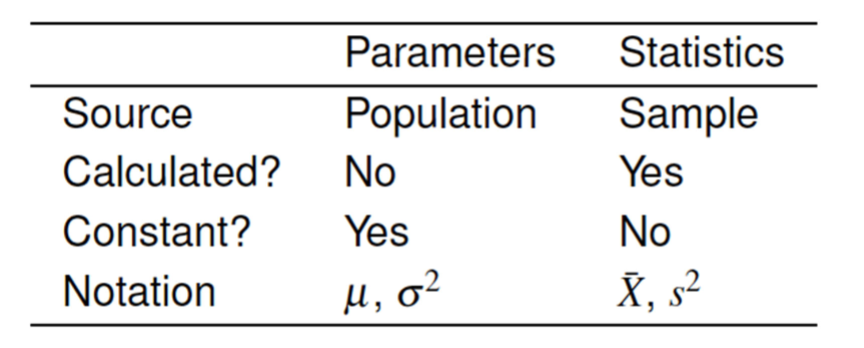
→ example:

sampling distribution and standard error
standard error: measures how much the sample statistic varies from sample to sample (smaller than the STD for the population)
population VS the sample:
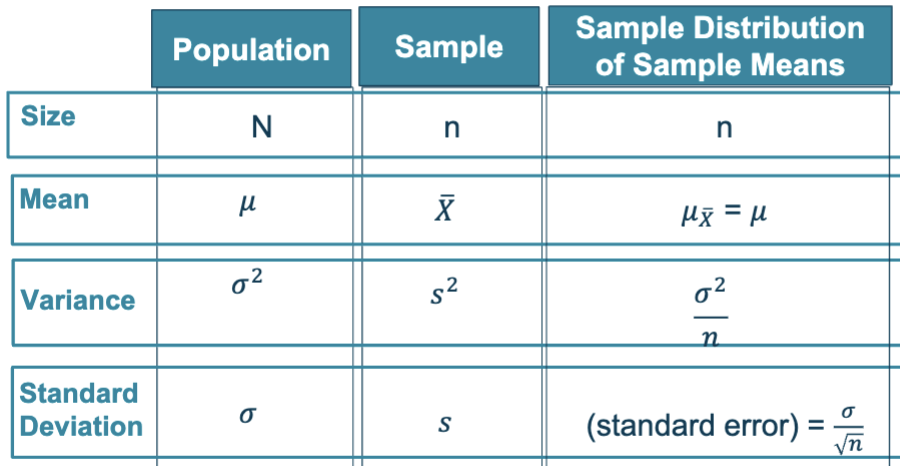
example:

large numbers:
When n is large enough:
the shape of the sampling distribution of the sample mean is approximately norma —- regardless of the original distribution
the sample mean more closely approximates the
population mean
increase sample size = mean decreases (error)
→ ex: n is increasing from 5 to 30 = error is decreasing
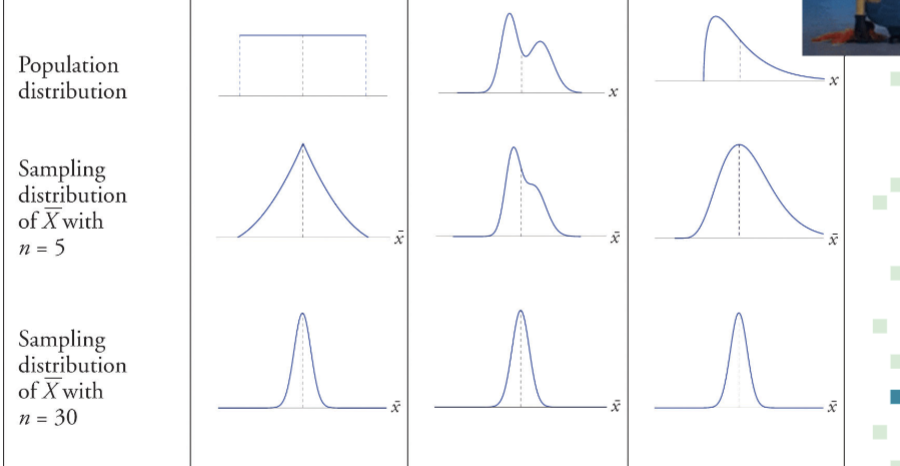
central limit theorem
If you have a population with mean μ and standard deviation σ and take large random samples from the population with replacement
the distribution of the sample means will be approximately normally distributed
we can calculate a Z-score (using STD error in the denominator)
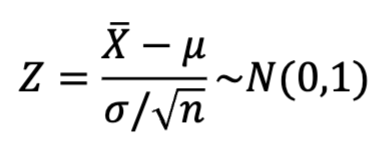
notation