Chemical Equilibria
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Finals
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Sulfuric acid, ammonia, ethylene, propylene, phosphoric acid, chlorine, nitric acid, urea, benzene, methanol, ethanol, and ethylene glycol
are examples of chemicals produced at scales of many billions of kg per year worldwide.
a major industry synthesis.
The transformation of raw materials into products of greater value by means of chemical reaction
Chemical Kinetics
Study of reaction rates and
Besides information about the speed at which reactions occur, kinetics also sheds light on the reaction mechanism (exactly how the reaction occurs).
SIGN CONVENTION
positive (+) for a product and negative (−) for a reactant
∣νi∣
is a stoichiometric coefficient
Ai
represents a chemical formula
νi
itself is called a stoichiometric number, and by the sign convention
zero
inert species
dε
a single variable representing the extent to which the reaction has proceeded,
ε
called the reaction coordinate, characterizes the extent or degree to which a reaction has taken place.
Collision Theory
When two chemicals react, their molecules have to collide with each other (in a particular orientation) with sufficient energy for the reaction to take place
There must be enough activation energy (Ea).
The reactant particles must collide with proper orientation.
TEMPERATURE
INCREASES
At higher temperatures, reactant molecules have more kinetic energy, move faster, and collide more often and with greater energy.
CONCENTRATION
INCREASES
As the concentration of reactants increases, so does the likelihood that reactant molecules will collide
CATALYST
INCREASES
Speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
SURFACE AREA
INCREASES
More area for reactants to be in contact.
CATALYST
A substance that fastens the reaction without getting consumed in the reaction.
Provides an alternative pathway that has a lower activation energy.
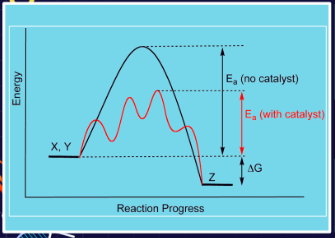
Label all the Parts
Energy
X, Y, Z
Ea (no catalyst)
Ea (with catalyst)
Delta G
Reaction Progress