Session #27: Oxidative Phosphorylation and the Electron Transport Chain
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
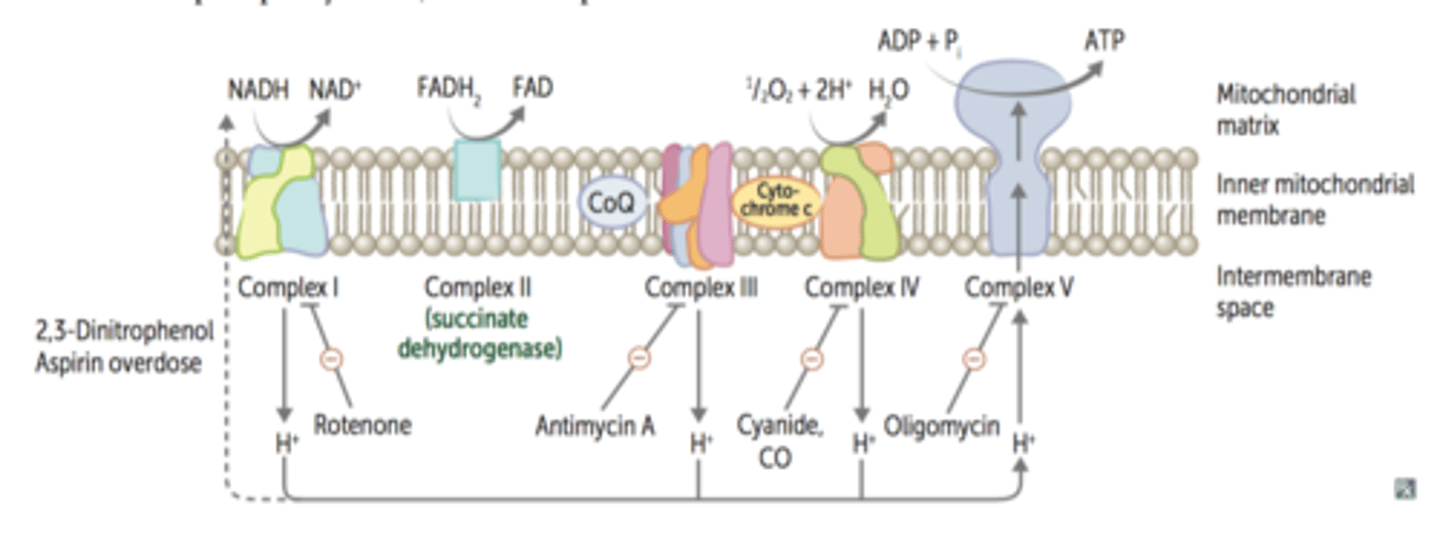
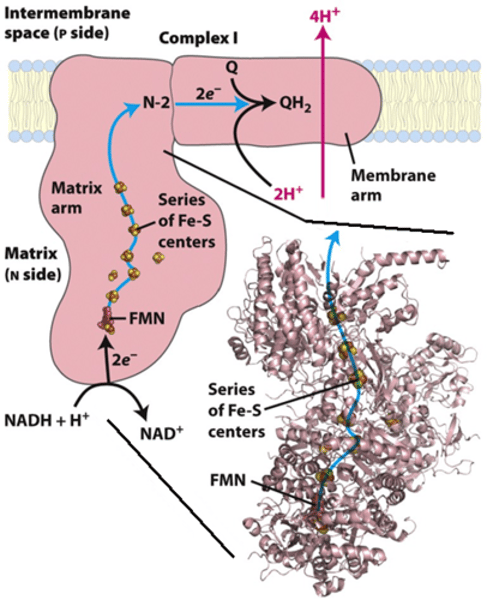
Complex I
- NADH Dehydrogenase
- Accepts 2 electrons from NADH
- Electrons donated to an acceptor group called Flavin Mononucleotide (FMN)
- FMN is reduced to FMNH₂
- The electrons move through the series of Fe-S clusters, which uses this electrical work to pump 4 H⁺ ions out of the matrix into the intermembrane space
- Electrons transferred to Coenzyme Q (ubiquinone), which takes two protons from the matrix to create Coenzyme QH₂ (ubiquinol)
Equation: NADH → NAD⁺ + H⁺ + 2e⁻
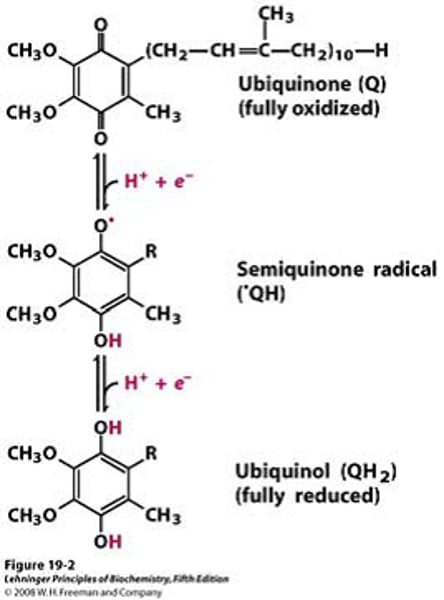
Coenzyme Q (Ubiquinone)
- Acts as an electron carrier and shuttle electrons from Complex I and II to Complex III
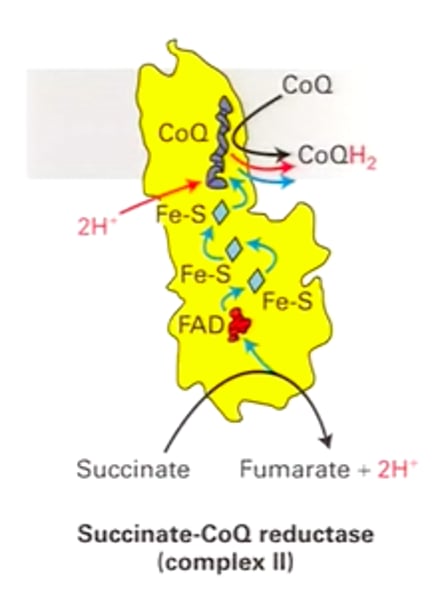
Complex II
- Succinate Reductase/Dehydrogenase
- FAD is reduced to FADH₂ and transforms succinate into fumarate
- The FADH₂ remains attached to the complex and gives off the 2 electrons to a series of Fe-S clusters
- Electrons transferred to Coenzyme Q (ubiquinone), which takes two protons from the matrix to create Coenzyme QH₂ (ubiquinol)
- Does not pump protons
Equation: FADH₂ → FAD⁺ + 2H⁺ + 2e⁻
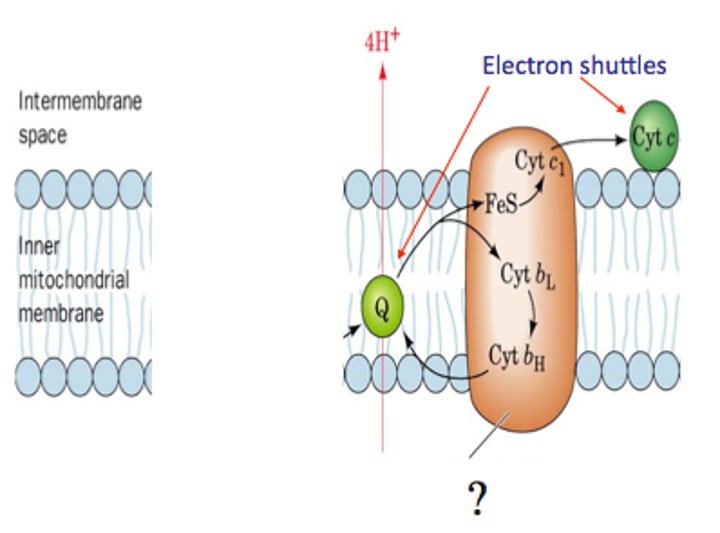
Complex III
- Cytochrome Reductase
- QH₂ binds to this complex and two electrons follow different paths:
1. One electron moves unto the Fe-S group of the Rieske Center and transfers to (Cytochrome C₁), which is then picked up by Cytochrome C and travels to Complex IV
2. One electron moves onto the heme groups of Cytochrome B and gets picked up by Q
- 4 H⁺ ions are pumped out of the matrix into the intermembrane space
Cytochrome C
- Transfers electrons between complex III and IV
- Bound to the intermembrane complex of Complex III
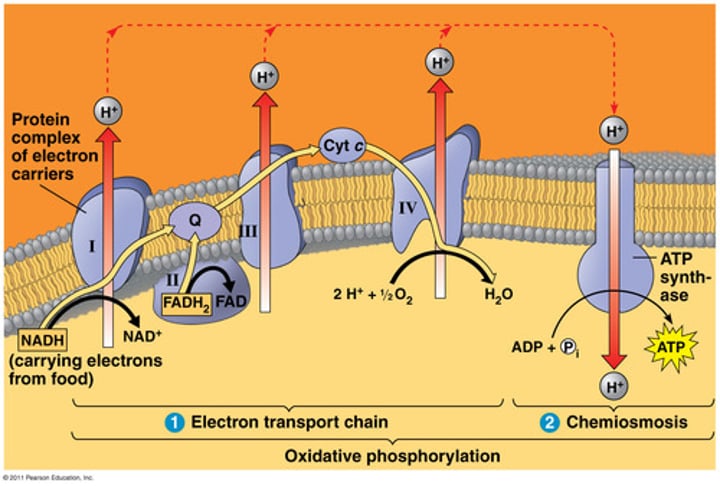
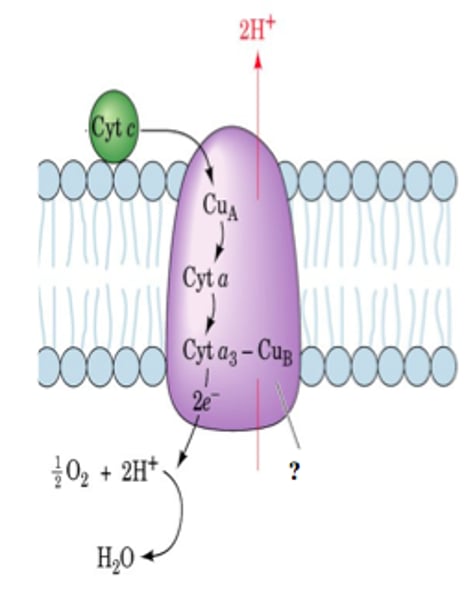
Complex IV
- Cytochrome C transfers two electrons to the Cytochrome AA3 complex, which transfers electrons oxygen, reducing it to water
- 2 H⁺ ions are pumped out of the matrix into the intermembrane space
Equation: 2e⁻ + 2H⁺ + ½O₂ → H₂O
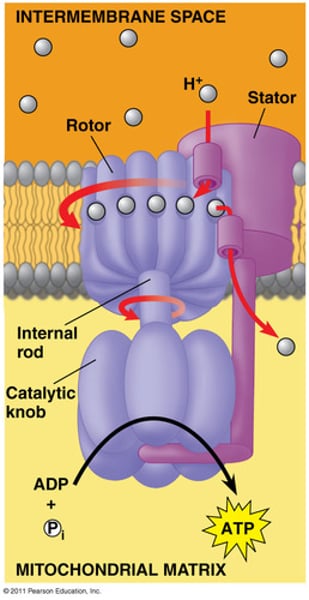
ATP Synthase (F₀F₁ ATPase)
- Protons flow down their electrochemical gradient
- Allows the enzyme to synthesize ATP
- F₁ → Headpiece that contains the catalytic center that synthesizes ATP
- F₀ → the rotor; contains the motor which is driven to rotate by the proton flow
For every mole of NADH that is oxidized...
- 0.5 moles of O₂ is reduced to H₂O
- Approximately 2.5 moles of ATP are produced.
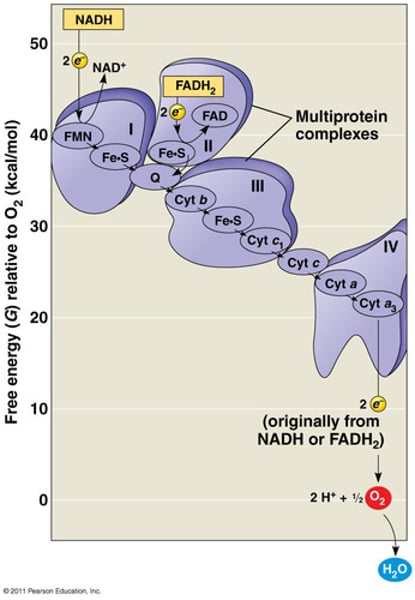
For every mole of FADH₂ that is oxidized...
approximately 1.5 moles of ATP are generated
Regulation - ADP Concentration
- The ADP level increases when ATP is consumed, and so oxidative phosphorylation is coupled to the utilization of ATP
- As the concentration of ADP increases, the rate of oxidative phosphorylation increases
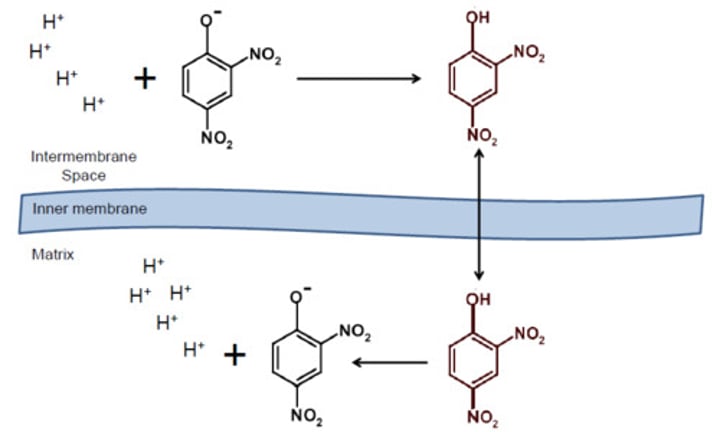
Regulation - DNP
- 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) is a small lipophilic ionophore molecule that can easily diffuse through the inner mitochondrial membrane
- Allows protons to travel down their gradient and back into the mitochondrial matrix without passing through ATP synthase
- Binds to H⁺ ions in the inner membrane space
- Dissociates from H⁺ ions in the matrix
- Dissipates the proton gradient collapsing the proton motive force that the cell uses to produce most of its ATP chemical energy
- Reduces ATP production
- The energy that should have been converted to chemical energy in the form of ATP is then released as excess heat, raising body temperature
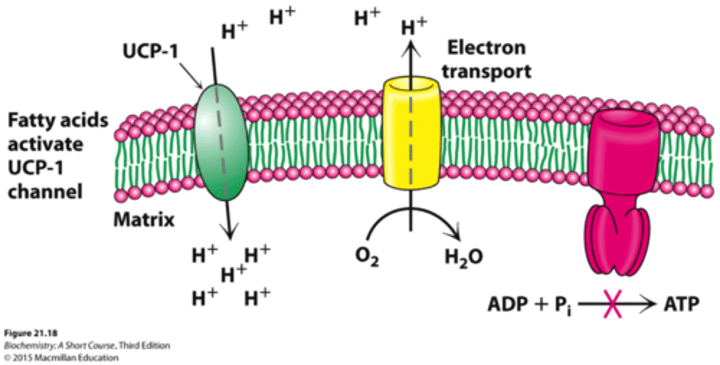
Regulation - Uncoupling Proteins
- A means of generating heat to maintain body temperature in the process of nonshivering thermogenesis
- UCP-1 or thermogenin generates heat by allowing the flow of proton into the matrix
- Activated by free fatty acids liberated from
- Reduces ATP production
If there is a block at any point in the electron transport chain...
all carriers before the block will accumulate in their reduced states, whereas those after the block will accumulate in their oxidized states.
Inhibitor - Rotenone
- Fish poison
- Blocks the transfer of electrons from complex I to coenzyme Q
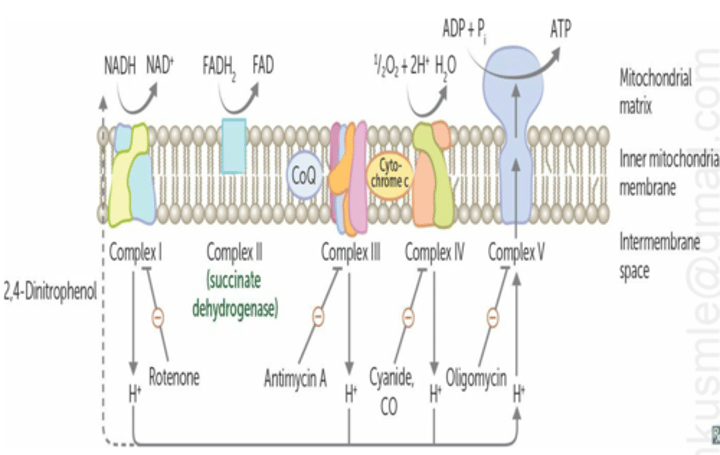
Inhibitor - Antimycins
- Antibiotics
- Blocks the transfer of electrons from complex III to cytochrome c
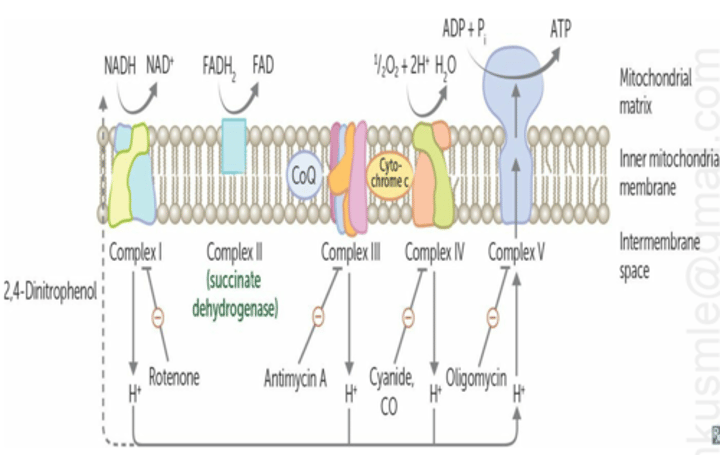
Inhibitor - Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Blocks the transfer of electrons from complex IV to oxygen
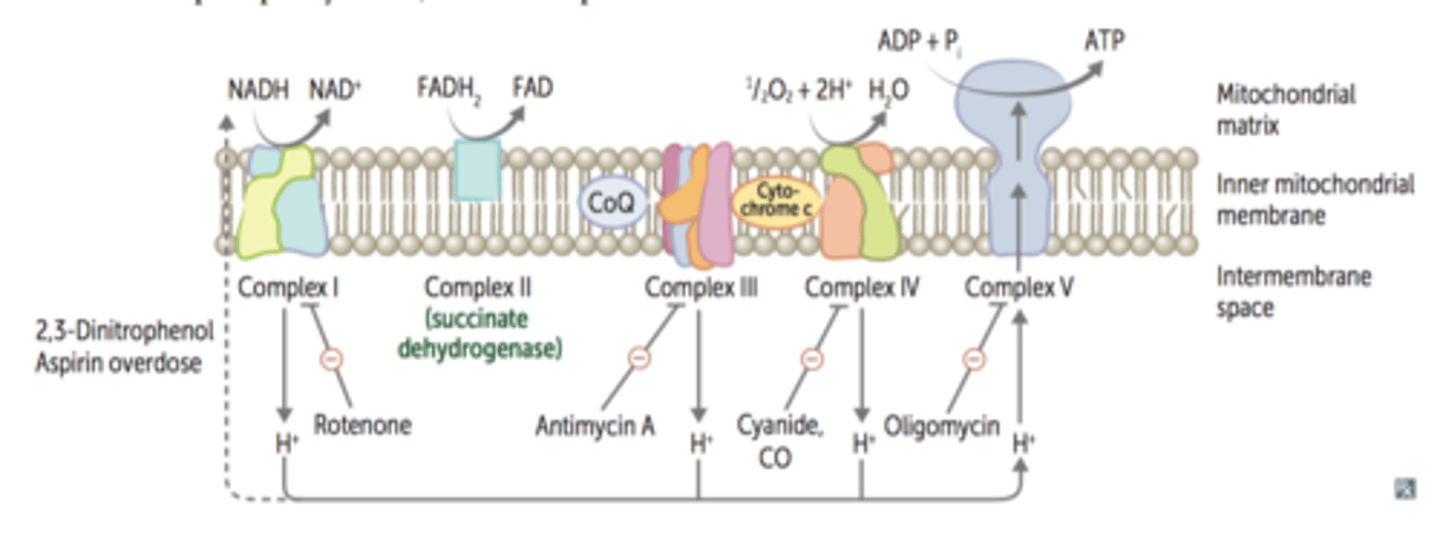
Inhibitor - Cyanide (CN)
Blocks the transfer of electrons from complex IV to oxygen
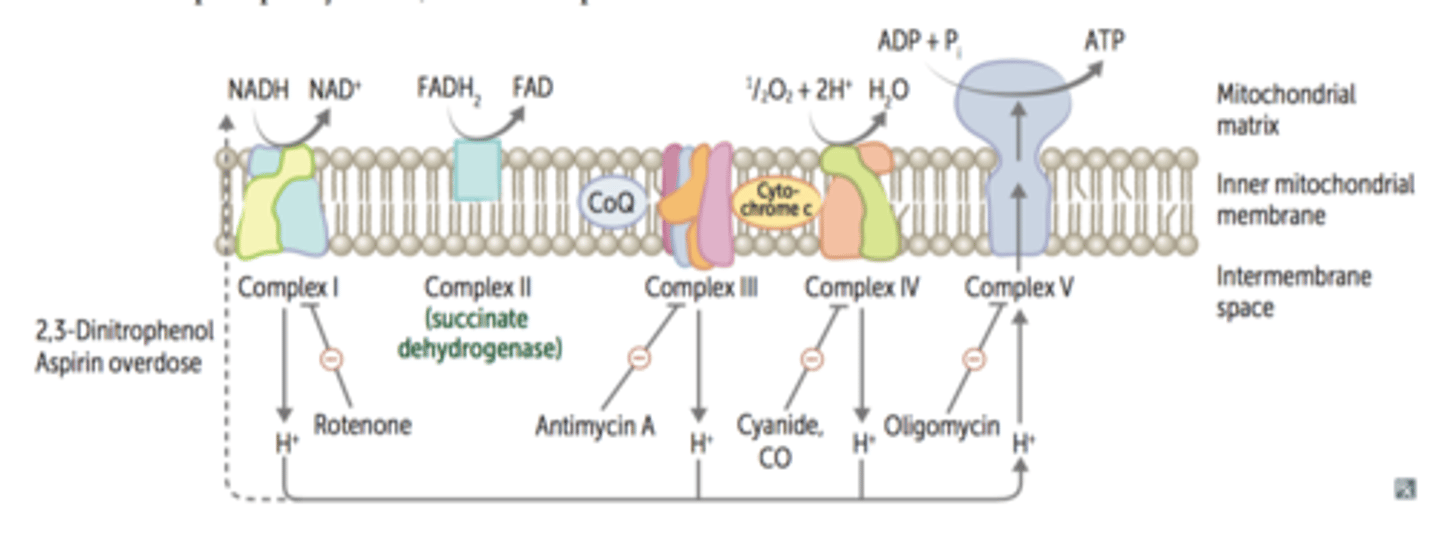
Inhibitor - Oligomycin
Inhibits proton flow through F0 component of the ATP synthase