Complications associated with anaesthesia - how to respond and prevent them happening.
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Top 5 complications of anaesthesia
- hypotension
- hypothermia
- abnormal HR
- hypoventilation
- difficult recovery
What are some indications that an horse will have a poor anaesthetic recovery
- paddling of the front legs
- body condition - isoflurane stays in fat, and effects last longer
- completely unpredictable
why is it that horses can be ataxic on recovery
Still have iso in them -> incoordination due to its effects on sc and brain
what is there a risk of on recovery of horses from anaesthesia
fractures and serious damage
what is the minimum acceptable mean arterial blood pressure for a small animal under anaesthesia?
60 mmHg
can you list 2 drugs (apart from the volatile agents) most likely to result in hypotension.
acepromazine and propofol
You are undertaking dental radiographs under anaesthesia in a middle aged cross breed dog with halitosis and a history of rubbing its face. The oscillometric blood pressure machine generates a consistent MAP of 48mmHg. You have checked the cuff width and position. The plane of anaesthesia is adequate. You have decided to embark upon a tooth removal (404). What is the appropriate action before the tooth removal?
10ml/kg lactated ringers solution IV over 15 minutes
Which device would you select to use to reduce heat loss during anaesthesia?
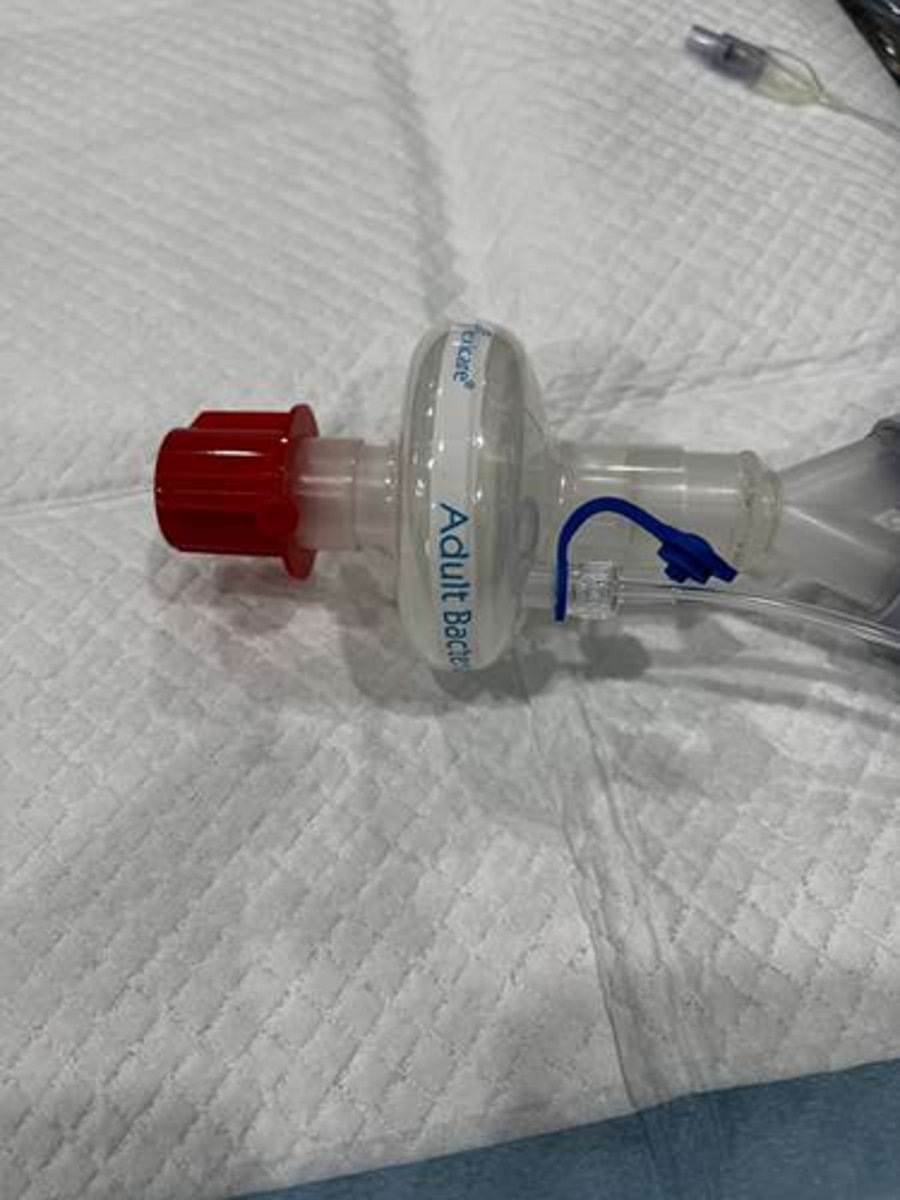
Consider that you have administered an alpha 2 agonist (medetomidine) and buprenorphine as a premed- your large dog (BMD) is now bradycardic (47bpm). He's quiet but rousable in the kennel, CRT is 2 seconds, peripheral pulses moderately strong and synchronous and his mucous membranes are light pink. What action is necessary?
roceed with induction of anaesthesia
Which induction drug causes sinus tachycardia?
Ketamine
You are undertaking a mammary strip on husky dog with no previous history of cardiac problems. Your RVN reports the dog is having VPCs 1-2 per minute. The dogs blood pressure is 112/64, and SPO2% is 96. What do you suggest?
No action required
Your Husky dog is recovering from anaesthesia. A methadone 'top up' (IM) was given 30 minutes ago as you finished the long surgery (mammary strip). The dog is extubated and recovering but howling very loudly in the kennels, everyone in the practice can hear her noise, even the clients in reception are looking concerned! What do you suggest?
IV dexmedetomidine
You are undertaking a cat spay and the RVN asks you to take a look at the capnograph as he's worried it has changed recently. What do you suggest?
Suggest the endotracheal tube is suctioned or replaced
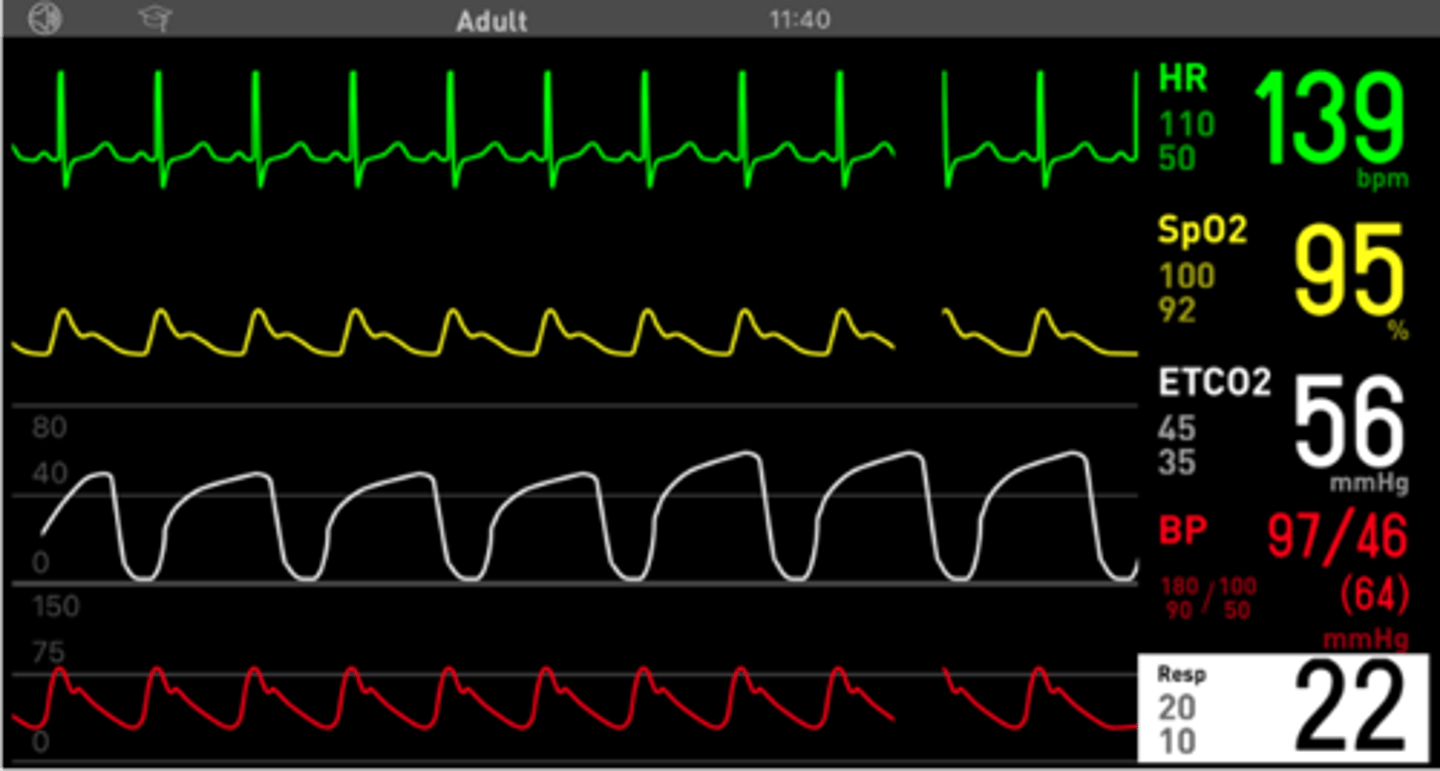
A large obese labrador is undergoing a scrotal ablation for a testicular tumour. He is anaesthetised on sevoflurane (vaporiser setting 3.5%) delivered in oxygen (1L/min) via a circle system. His HR, ABP, SPO2% are within normal limits. His ET CO2 has been increasing (61mm Hg) and his respiratory rate is 2bpm. What do suggest?
Reduce the vaporiser setting, increase fresh gas flow, and start IPPV
Reduce the vaporiser setting and start IPPV - This is ok, but the better answer would be also to increase the fresh gas flow for a short period of time too, in order to speed up the change the sevo concentration in the circle
Your team reports a mistake has been made and a 3kg cat has just received 6mg of methadone rather than 0.6mg methadone. The cat is bradycardic, pale, and breathing very slowly and on an oxygen mask. Which drug(s) would be suitable to antagonise the overdose?
Butorphanol
Naloxone - Yes this would be my first choice, and several doses may be required as it is shorted acting than methadone and the cat can become re-narcotised
How would you arrange the ECG on a horse in right lateral recumbency?
Base-Apex
Einthoven triangle
2 electrodes spanning the heart
3 electrodes in triangle
You have just induced anaesthesia in a horse and are about to place an endotracheal tube.... what can be used to help
A mouth gag is used to prevent damage and occlusion of the tube
An endoscope can be used in the case of difficult intubation
You have been asked to induce anaesthesia in a 450kg gelding for joint arthroscopy with ketamine and midazolam. He has been given acepromazine, romifidine and morphine. He is not quite as sedated as you expected and is lifting his head and responding to noises outside the knockdown box. What do you want to do
Wait a bit longer - Good idea, if you've been impatient! Although intravenous romifidine works quite quickly, it will still take a few minutes
Give more romifidine
Which of the following would be suitable for assisting a 650kg horse during induction of anaesthesia
A squeeze door
Free drop
Manual restraint
Use a sling
Use head and tail ropes
A squeeze door
Free drop
You are about to place a jugular catheter in a colicking horse prior to induction of anaesthesia. In which direction do you place the catheter and can you explain this?
Pointing down the neck
Catheters pointing down the neck are suitable for longer term fluid administration and cause less turbulence. You should make sure they are well secured though as disconnection can result in an air embolus with catastrophic consequences.
You are an equine intern, and are responsible for the anaesthesia for a 520kg ISH undergoing colic surgery for a large bowel torsion. You've been switching the isoflurane up, as the heart rate has been increasing. The vaporiser is on 4%, and your ET reading is 3.6% (you have a fancy monitor with ET volatile agent).The horse is spontaneously breathing. The dobutamine was switched off 20 minutes ago. You are pleased with the blood pressure. What should you do next?
Instigate IPPV
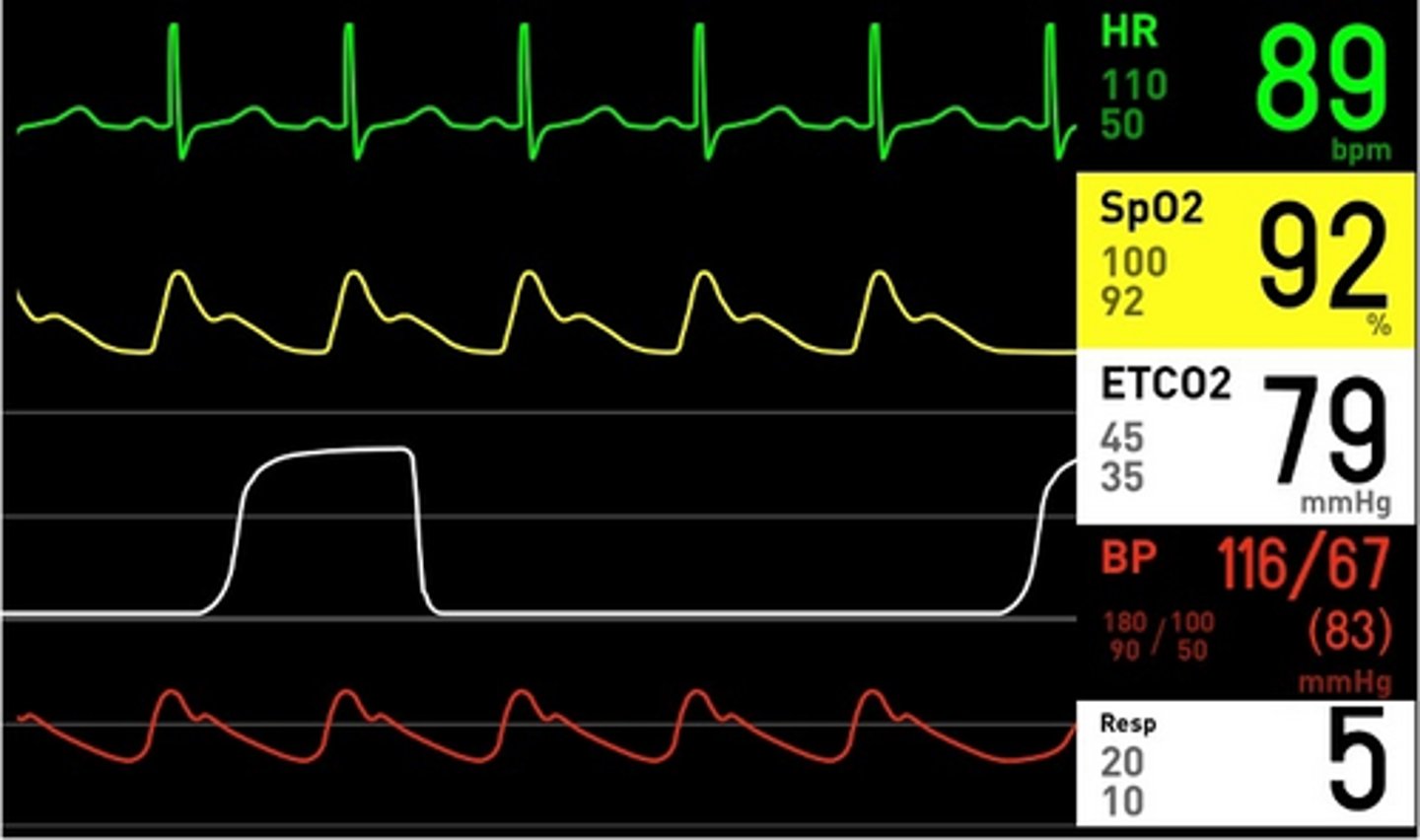
You have moved the horse into the recovery box. The horse is in lateral recumbency and has just swallowed so you removed the endotracheal tube. You notice the horse is making a noise and struggling to exhale, no airflow is detected at either nostril. What do you do?
Insert a nasal tube
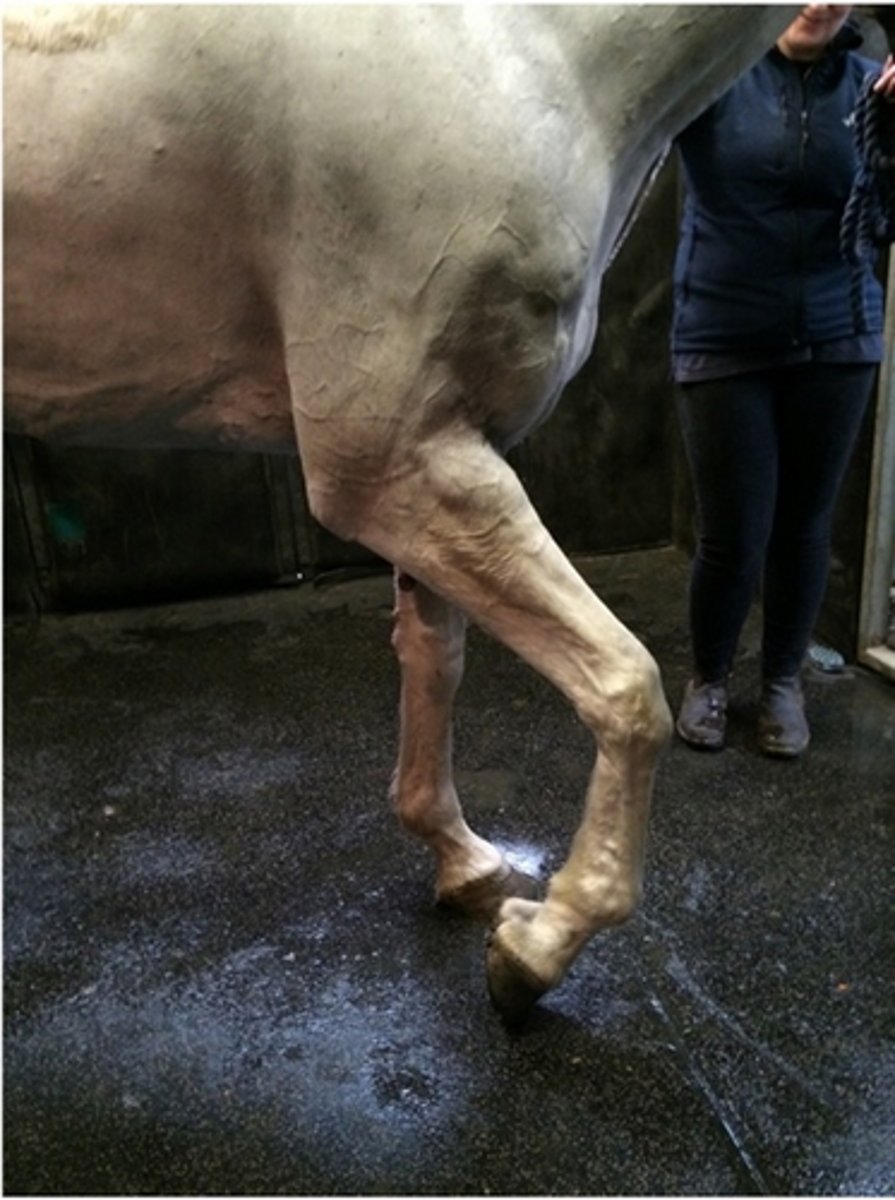
This horse has just recovered after a laryngeal tie back, recovery was a bit of a scrabble. He was in right lateral recumbency for 2 hours. You go into the recovery box and observe this. The shoulder musculature is hard. The horse's heart rate and respiratory rate is elevated and he is sweating. What do you suspect has happened?
Triceps myopathy
Which vasoactive drug is first choice in the face of hypotension in the horse?
Dobutamine
What mean arterial blood pressure would you try and achieve/exceed in horses?
70 mmHg
What does absence of a palpebral reflex, and a central, dry eye indicate in equine anaesthesia?
A deep plane of anaesthesia suggestive of anaesthetic overdose
Why does ventilating an anaesthetised horse have negative effects on the cardiovascular system?
It increases intrathoracic pressure
What would be the average amount of intravenous fluids an adult horse (e.g.450 - 500Kg) would receive intraoperatively per hour during anaesthesia?
5L
What is this?
Safety culture initiative
By how much did the WHO surgical safety checklist reduce deaths in human anaesthesia?
47%