Flow Down Gradients
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is the definition of flow down gradients?
Transportation of "stuff" is a central process of all levels of organization in the organism, and a simple model describes such transport
What is the "stuff" that moves?
- Ions
- Molecules
- Blood
- Gas
How do flow down gradients move?
High to low
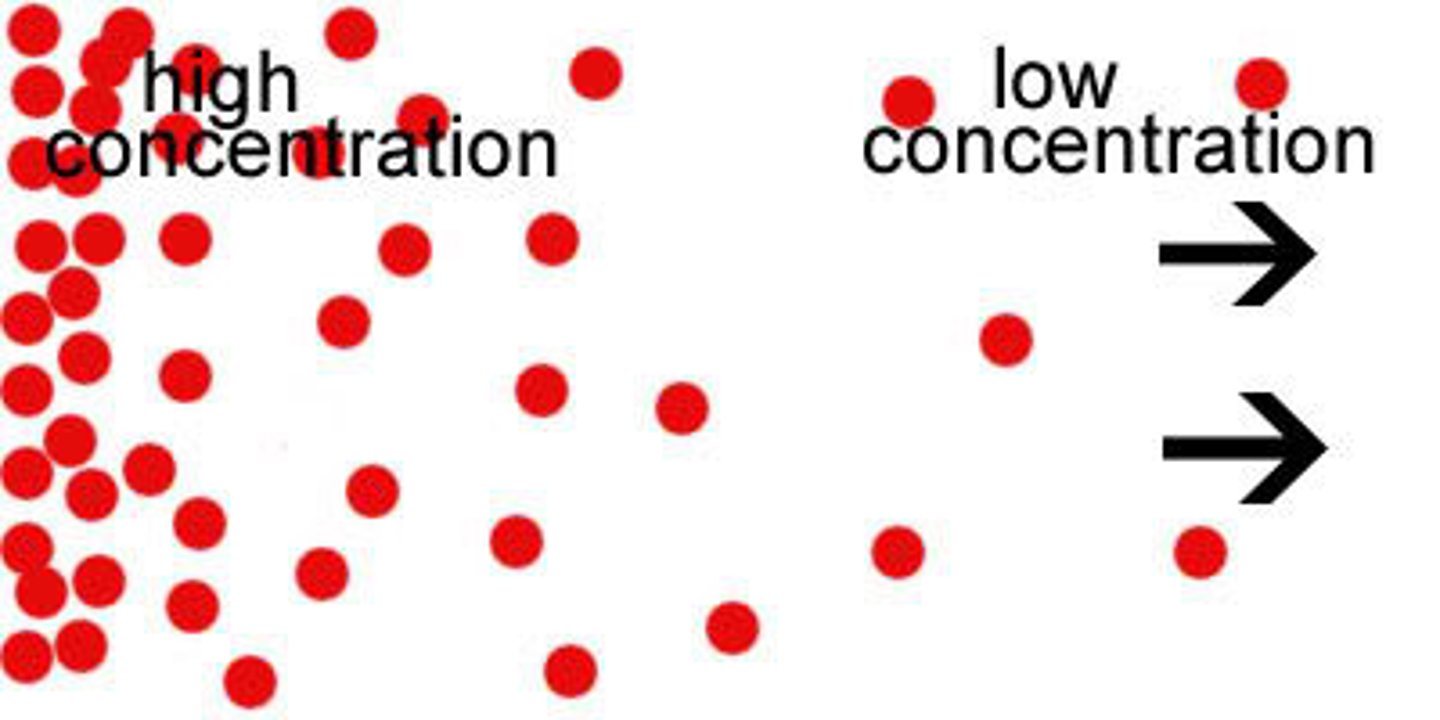
What is a gradient?
Quantitative difference in some value between two points
What are the four major gradients?
- Thermal
- Electrical
- Pressure (fluids)
- Chemical/Concentration
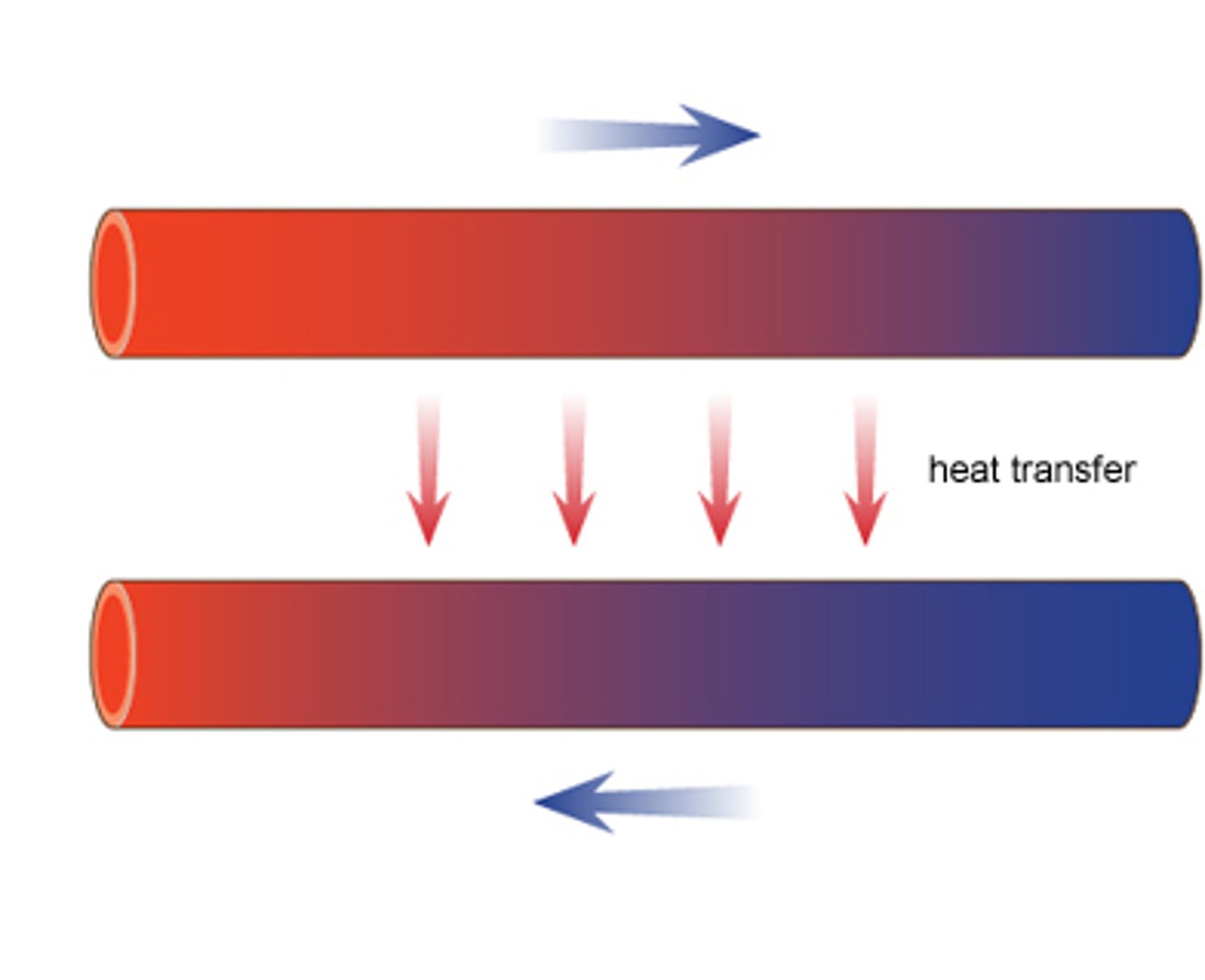
What is a thermal gradient?
Temperature differences. Heat flows down the thermal gradient
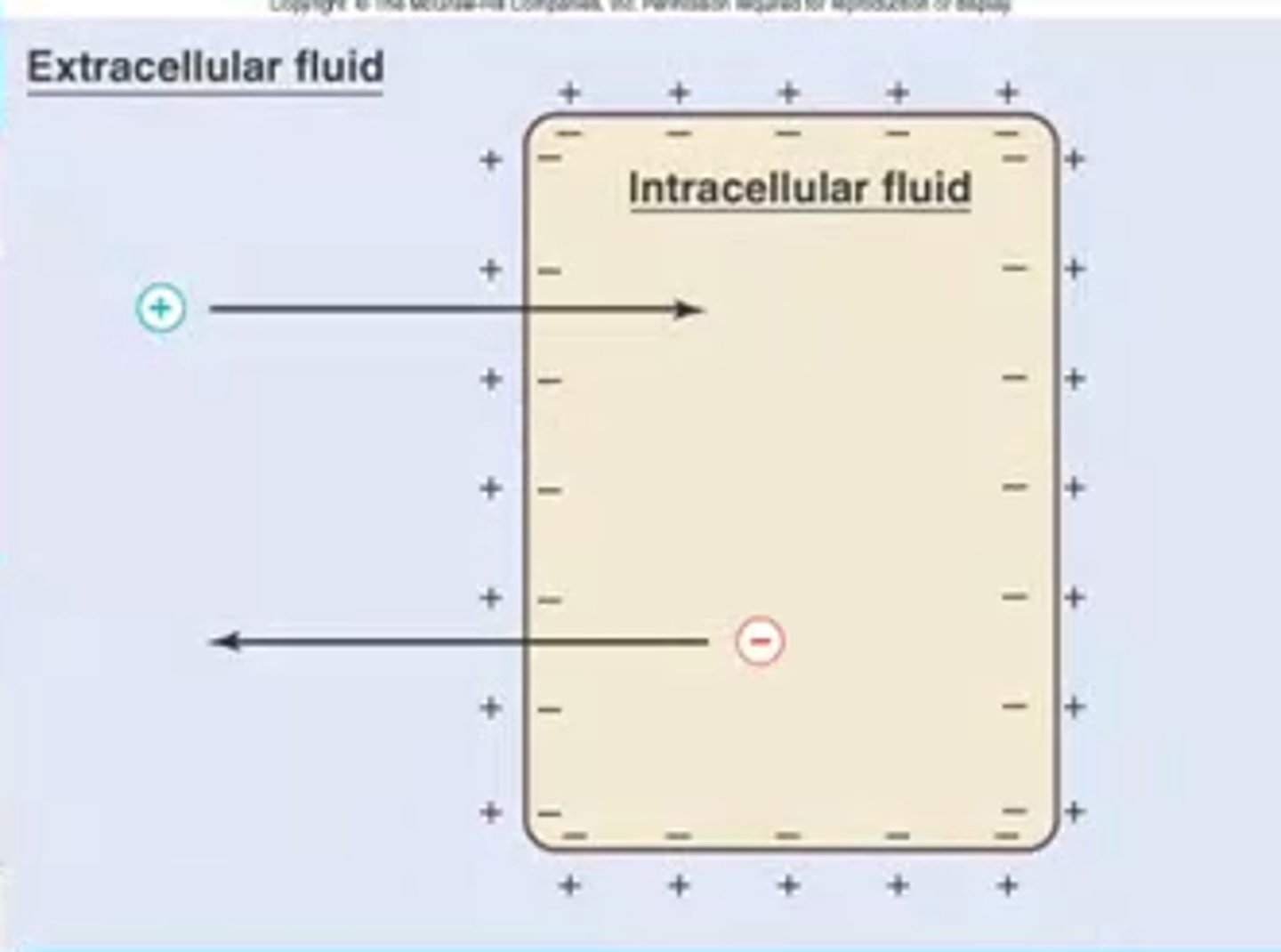
What is an electrical gradient?
The difference in the electrical charges between the inner surface and outer surface of the membrane
What is hydrostatic pressure?
- Vertical force against walls of chambers/tube
- Measured in mercury (mmHg)
What is a pressure gradient?
- Transport of fluids or gas through tubes
- Pressure has to drop in the lungs before air enters the lungs
What are the common features of gradients?
- Magnitude of gradient dictates magnitude of flow
- More than one gradient can dictate magnitude and net direction of flow
- Always a resistance opposing the flow
What is brownian movement?
Movement is random and & unpredictable
What is diffusion?
- Movement of solutes from regions of solute
- Process that happens to reach equilibrium
What is diffusion equilibrium?
- No gradient
- Become a state of equilibrium because of diffusion
- Stays in browian movement
What is osmosis?
- The movement of solvent
- Movement across a semipermeable membrane
What is tonicity?
Osmolarity of solution relation to ICF
Define hypotonic
LESS Osm than ICF
Define isotonic
SAME Osm as ICF
Define hypertonic
MORE Osm than ICF