Phys Rad Tech Exam 3
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
NMR stands for
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
MRI stands for
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI uses what types of waves
Radio Waves (NON-ionizing)
Electromagnetic Spectrum
In order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength—-
Radio Waves
Microwaves
Infrared waves
Visible Light
Ultraviolet light
X rays
Gamma Rays
Formula for photon energy
E =hf
What are the three types of magnetic materials?
-Ferromagnetic material: strongly attracted by a magnet (examples: iron, nickel)
-Paramagnetic material: weakly attracted by a magnet
-Diamagnetic material: weakly repelled by a magnet (examples: water and most biologic
tissues)
What is precession?
The magnetic moment of a particle with spin, such as an electron, precesses around an external magnetic field due to the torque exerted by the field on the magnetic moment.
The detected signal in MRI is called an…
Echo
SI unit for magnetic Field
Tesla (T)
Why hydrogen in MRI?
hydrogen gives largest signal per atom - relative sensitivity = 1
T1 and T2 weighting do what to fat and CSF+water
T1 weighting: Fat is bright / CSF and water are dark
T2 weighting: Fat is dark / CSF and water and bright
A transducer does what
detects and produces sound waves
A = decay constant * N
A = activity
N = number of atoms
most commonly used radionuclide in the world
Tc-99m
What is used as a Grid in nuclear imaging to reduce scatter?
collimator
What are the names of the
three pulse sequences that are used for the “bulk of” MRI
imaging?
spin echo
inversion recovery
gradient echo
formula for power
power = SAR(mass)
formula for energy
Energy = power (W) * Time (sec)
What are the four types of collimators in Nuclear imaging?
Parallel multihole collimator
Pinhole collimator- for imaging small objects
Converging collimator- image larger than object
Diverging collimator - image smaller than object
A positron is made up of antimatter (T/F)
True
PET uses positron emitting isotopes
TRUE- does not use a grid/collimator
FDG
Fluorodeoxyglucose - used in PET
Formula for Acoustic Impedance
Z = density of material * speed of sound
(Z= ρc)
Normal range of hearing
20 Hz- 20 kHz (low to high pitch)
Units for frequency
Hz
units for speed
m/s
units for wavelength
meter
MRI scanners are cooled by what
liquid helium
Faradays Law
changing magnetic field creates electrical field
SAR stands for
Specific Absorption Rate = power absorbed per kg of tissue
formula for SAR
SAR = c ∆T/ ∆t
Whats the most common compound contrast agent used in MRI?
Gadolinium (PARAMAGNETIC MATERIAL)
What does GBCA mean
Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent
Gadolinium-diethylenetriamine
pentaacetic acid (Gd-DTPA)
MEMORIZE- a paramagnetic material given by injection as contrast in MRI
What is the piezoelectric effect
Generating an internal electric charge from mechanical stress from certain materials (or vice versa)
What are the X and Y scales for A and B Ultrasound display modes
A mode: X- Time Y- echo amplitude
B mode: X- location of echo Y- location of echo
What are the four different types of ultrasound wave interactions?
Reflection, Refraction, Scattering, Absorption
Compare the peak sound pressure used in Ultrasound Imaging to the Earth’s atmospheric
pressure
Peak pressure in Ultrasound imaging is 10x the earths atmospheric pressure
What do the letters “HVT” stand for
Half Value Thickness
The thickness of tissue necessary to attenuate the incident intensity by 50%
What do the letters “PZT” stand for?
What is PZT used for?
lead-zirconate-titanate
can be used as a source of sound and also as a detector of sound
What are the two types of wave interference
constructive and destructive interference
What does a Photomultiplier Tube detect?
light
What are the two main functions of a Photomultiplier Tube?
detects light and amplifies the signal
What is SAR?
power absorbed per kg tissue
Power is measured in…
Watts (W)
1 W = 1 J/sec
What are the differences between the A mode and B mode ultrasound imaging displays
(Amplitude modulation): single transducer (Brightness modulation): transducer array, 2D scan
what is a radioactive isotope called?
radionuclide
Radioactive Decay
process by which an unstable nuclide becomes more stable
• Emits particles and energy
T
time for half of the radioactive
particles to decay; after a time T,
half are left.
What does HVT stand for and what it does mean
half-value thickness.
The thickness of tissue necessary to attenuate the incident intensity by 50%
piezoelectric materials do what
creates an internal electric charge from an applied mechanical stress
What are the names of the three basic types of radiation detectors as classified by detection
method
Gas Filled Detector, Scintillation detector, semiconductor detector
How does a Geiger counter work?
counts almost every particle that reaches the interior of the detector
How does a scintillation detector work?
Consists of a scintillator and a device, such as a PMT, that convert the light into an electrical signal
Spin-Echo Pulse Sequence
(memorize these steps)
Start at t = 0
Transmit 90 degree radiofrequency (RF) pulse
At t = TE/2, transmit 180 degree RF pulse.
At t = TE, detect signal.
At t = TR, start the process all over again
What causes the loud knocking noises in MRI?
a large force is being applied to the coils, these forces change directions, causing shifting of the coils in their mountings. This movement causes noise.
Units of Activity In SI and Traditional system
SI: becquerel (Bq)
Traditional: curie (Ci)
What is acoustic impedance used for
a measure of tissues stiffness and flexibility. in rayls (kg/m2/sec)
Average US radiation dose (yearly)
360 mrem/year
Units for Acoustic Impedance
Rayl (kg/m²s)
Radiation simply refers to…
energy that propagates through space or matter
Roentgen discovers x-rays on what day
November 8, 1895
three types of ioinizing radiation and what they are
Alpha particles - Helium nucleus
Beta particles - electron
Gamma rays- high energy photon
SI unit for radiation dose/absorbed dose
Gray (Gy)
SI unit for dose equivalent/equivalent dose
Sievert (Sv)
In words, what is the equation that defines radiation dose
the energy absorbed per unit mass
The Auger process produces..
an electron
what is the adult dose to the lungs for PA Chest radiography
1 mrad
What does GCF stand for? and formula?
Grid Conversion Factor = patient dose WITH grid / patient dose W/O grid
In CT what do the letters SFOV stand for
Scan Field of View
In MRI, T1 is the…
longitudinal relaxation time, AKA spin-lattice relaxation time
In MRI, T2 is the….
transverse relaxation time, AKA the spin-spin relaxation time
What is a typical gantry rotation speed in CT
1 revolution/sec
In order to improve contrast in mammography, what do we do with the kVp setting compared to conventional radiography?
decrease
What are the two types of contrast materials in x-ray imaging?
iodine compounds
barium sulfate (used for imaging digestive tract)
What x-ray interaction is most important for CT imaging?
Compton scattering
what xray interaction is most important for mammography
Photoelectric Effect
Does CT or conventional radiography have better contrast resolution?
CT images
Does CT or conventional radiography have better spatial resolution?
conventional radiography
formula for CT #
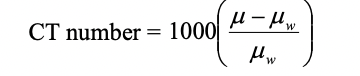
formula for grid ratio
grid ratio = h/d
pixel size formula
pixel size = field of view / # of pixels