Limbic System: Processing of Rewarding and Aversive Stimuli
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Processing of emotional cues and control of goal-directed behaviour. Limbus "border" in Latin. Cortex-like regions within the medial wall of the temporal cortex. 'Paul Broca - first description of limbic lobe in 1878.'
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Dorsal border of the limbic lobe
Cingulate cortex
Ventral border of the limbic lobe
Parahipocampal gyrus
James-Lang theory
Emotion is experienced through physiological or internal changes in the body
Cannon-Bard theory
Emotional experience can arise independently of physiological changes; found through severing the sensory inputs to the CNS and finding the presentation of emotions consistent
Papez circuit
The emotion system is synonymous with the limbic system; the precursor theory to the limbic system
Hypothalamus
Acts as a gate between the limbic system and the autonomic nervous system
Dimensional theories of emotion
Emotions may be represented by different features or dimensions, represented by different brain structures or patterns of activity across multiple brain regions
Amygdala
Involved in storage of emotional memories, appetitive conditioning, and necessary for fear conditioning and the extinction of fear; required for relating contextual cues to stimuli
Components of the amygdala
BLA: Basolateral amygdala
CEA: Central amygdala
MEA: Medial amygdala
Central amygdala
Controls autonomic and somatic responses to emotionally relevant stimuli
Basolateral amygdala
Involved in the formation of memories of emotional relevant stimuli; dependent on recognition of external emotion; neurons encode hedonic properties of a taste
Amygdala finding
Amygdala impairment lead to trouble discerning emotions in faces though no impairments in facial recognition
Fear conditioning
Results in responses of fight; somatic response in running; freezing; autonomic arousal; release of adrenocorticotropic hormone
Brain regions in fear response
Lateral amygdala: Receives conditioning stimuli via the thalamus
Central amygdala receives signals via the lateral amygdala
Central grey: Freezing behaviour
Lateral hypothalamus: Blood pressure
Periventricular nucleus of the thalamus: Release of hormones
Hippocampus
Required for contextual learning
Molecular basis of fear conditioning
Conditioned stimulus and unconditioned stimulus inputs converge onto the same cells in the lateral amygdala
Blockage of NMDA receptors
In the basolateral amygdala, fear learning is disrupted
Prefrontal areas consisting
Orbitofrontal cortex
Insula
Prelimbic cortex
Infralimbic cortex
Anterior cingulate cortex
Cortical areas functioning
Involved in decision-making, stimulus salience, contextual dependencies of relevant stimuli, and tracking of reward probabilities
Nucleus accumbens
Association of cues with rewards, not necessary for the approach to a reward; important for connection neutral stimuli to outcome of appetitive stimuli
Nucleus accumbens shell
Involved in feeding behaviour and responsible for representing value of predicted outcome; assessing value in a risky decision-making task; receives inputs from frontal cortex
Nucleus accumbens core
Pavlovian approach behaviour; receives inputs from frontal cortex and appears to be responsible for representing motivationally relevant events; GABA/neuropeptide; predictive for devaluation
Ventral pallidum
Processes the hedonic value of stimuli; GABA
Orbitofrontal cortex
Involved in value-based decisions; somatic marker hypothesis—decision making is influenced by physiological responses; necessary for outcome devaluation; lesions impair reversal stimulus learning
Cognitive map hypothesis
Orbitofrontal cortex represents abstract maps, proposing ‘hidden states’ to explain deficts in reversal learning and devaluation
Nucleus accumbens core and shell
Core: Incentive salience of a reward predictive cue
Shell: Tracking the value of the expected outcome
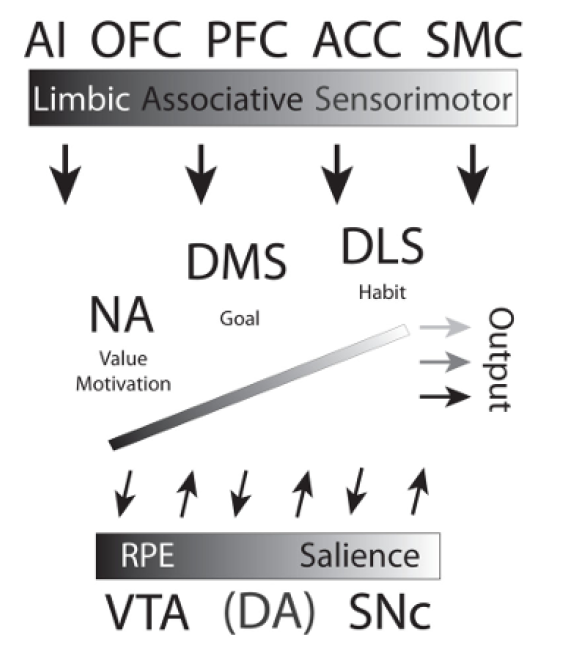
Ventral striatum
(Nucleus accumbens) ;inputs from limbic structures and the medial wall of the frontal cortex
Dorsomedial striatum
Inputs from associative cortices, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, lateral orbitofrontal cortex, and anterior insula
Dorsolateral striatum
Inputs from premotor, supplementary motor, and premotor cortex, as well as sensory areas
Limbic branch
Cortex: Amygdala, hippocampus, vmPFC, and omPFC
Striatum: Limbic
Midbrain: Ventral tegmental area
Associative branch
Cortex: Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
Striatum: Associative
Midbrain: Dorsomedial striatum
Sensorimotor branch
Cortex: Premotor/motor
Striatum: Sensorimotor
Midbrain: Ventrolateral striatum
Orbitofrontal cortex and striatum
Orbitofrontal cortex inactivation disrupts devaluation-sensitivity similar to dorsomedial striatum inactivation
Prevailing view of cortico-striatal function
Cognitive/limbic loops interact with the motor loops of the basal ganglia, controlling or interacting with the motor system