vitreous physiology
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
vitreous volume, what percentage is water
4 ml
•Comprised of 99% H20
vitreous comprises ___% of the globe
80 --> largest structure in eye
2 zones of vitreous
cortex = outside
medullary = inside
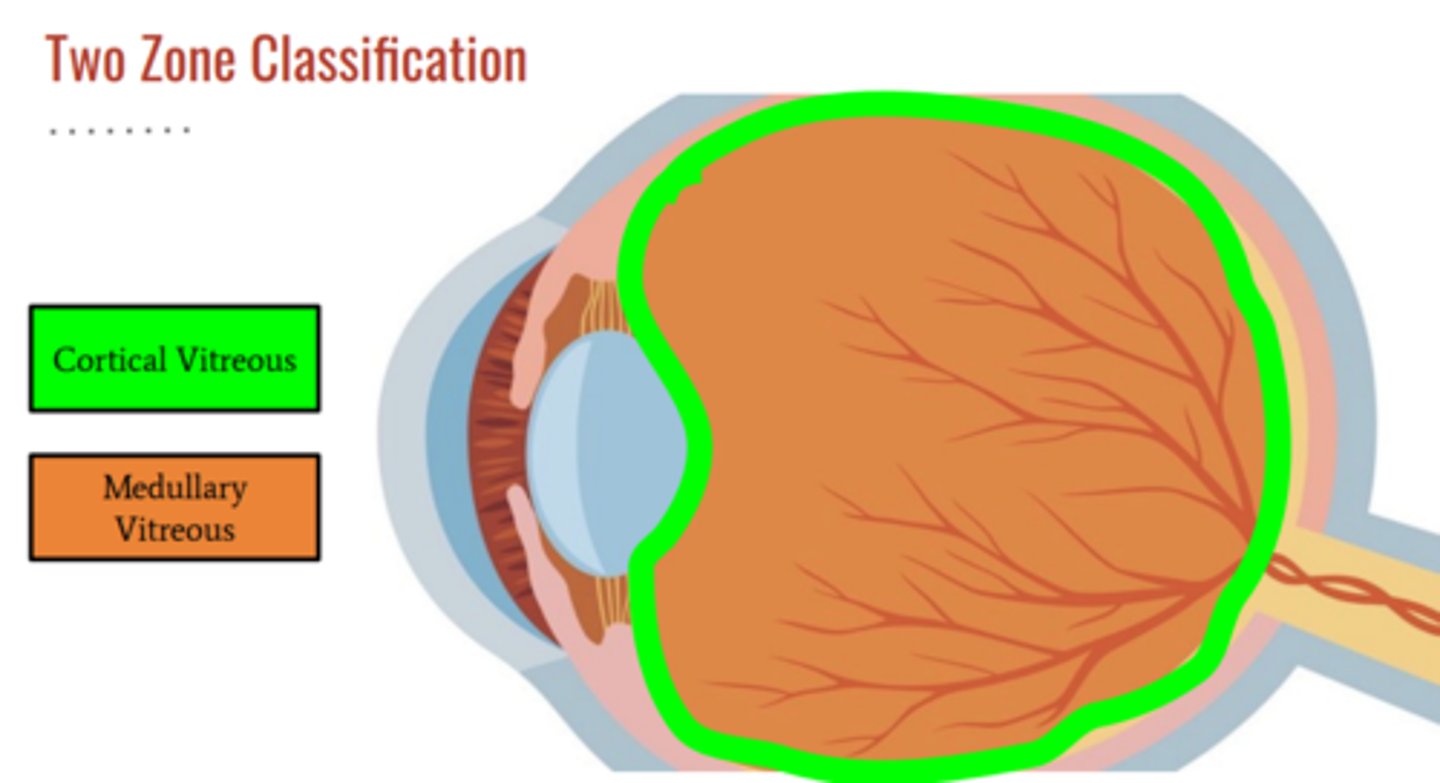
what portion of vitreous contains hyalocytes
cortical vitreous
what portion of vitreous contains anterior and posterior hyaloid
cortical vitreous
what zone of vitreous has aging changes first?
medullary --> becomes liquified
acellular vitreous zone
medullary vitreous
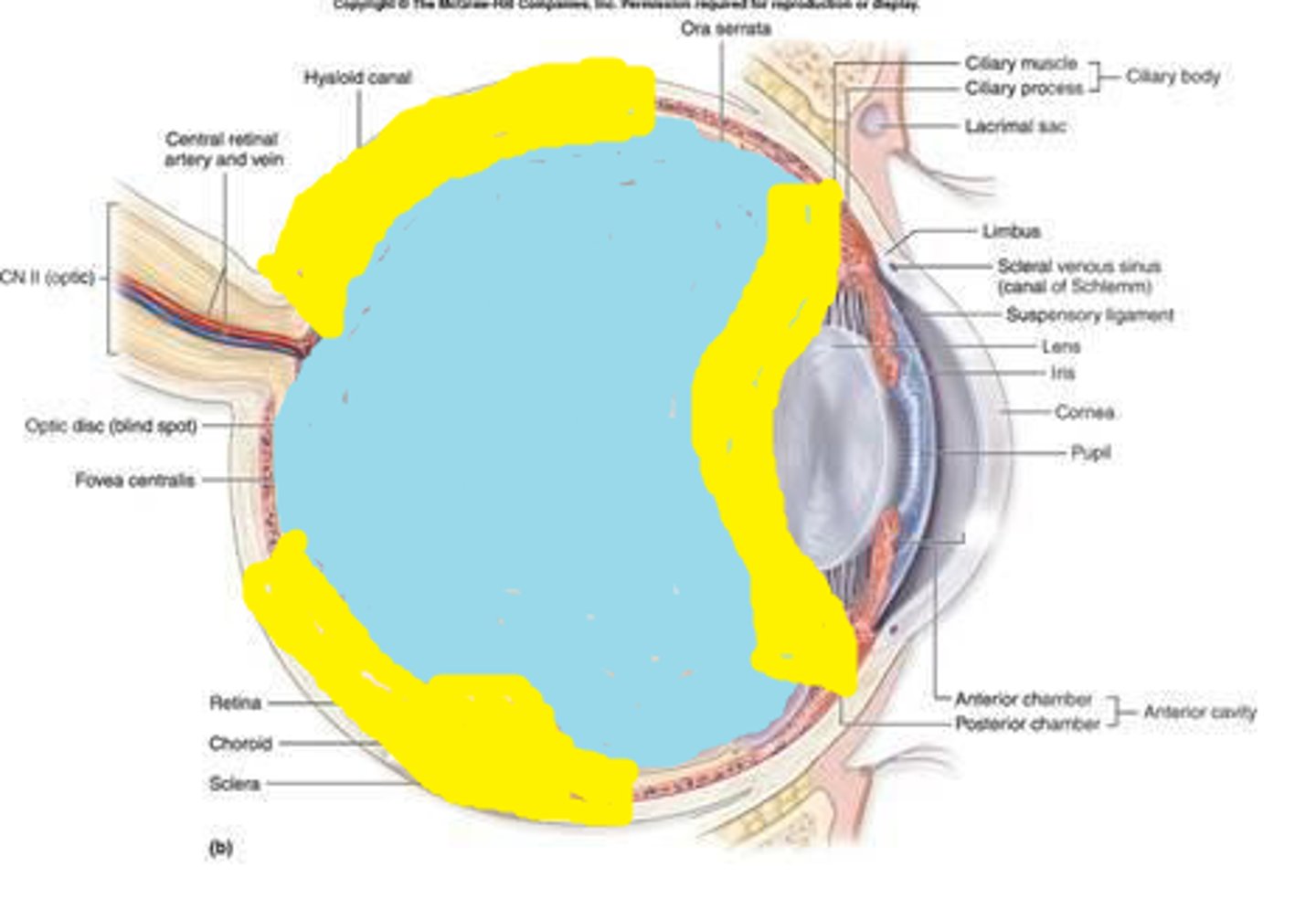
what keeps outer vitreous attached?
vitreous fibers Blend within basal lamina of CB epithelium and retinal Müller cells of ILM
Firmest attachment of the vitreous & retina in the region of the____
ora serrata
___ divides anterior hyaloid from posterior hyaloid
vitreous base (firmest attachment at ora)
strongest to weakest vitreous attachements
vitreous base (ora)
•Posterior Lens
•optic disc
•macula
•weakest - retinal vessels
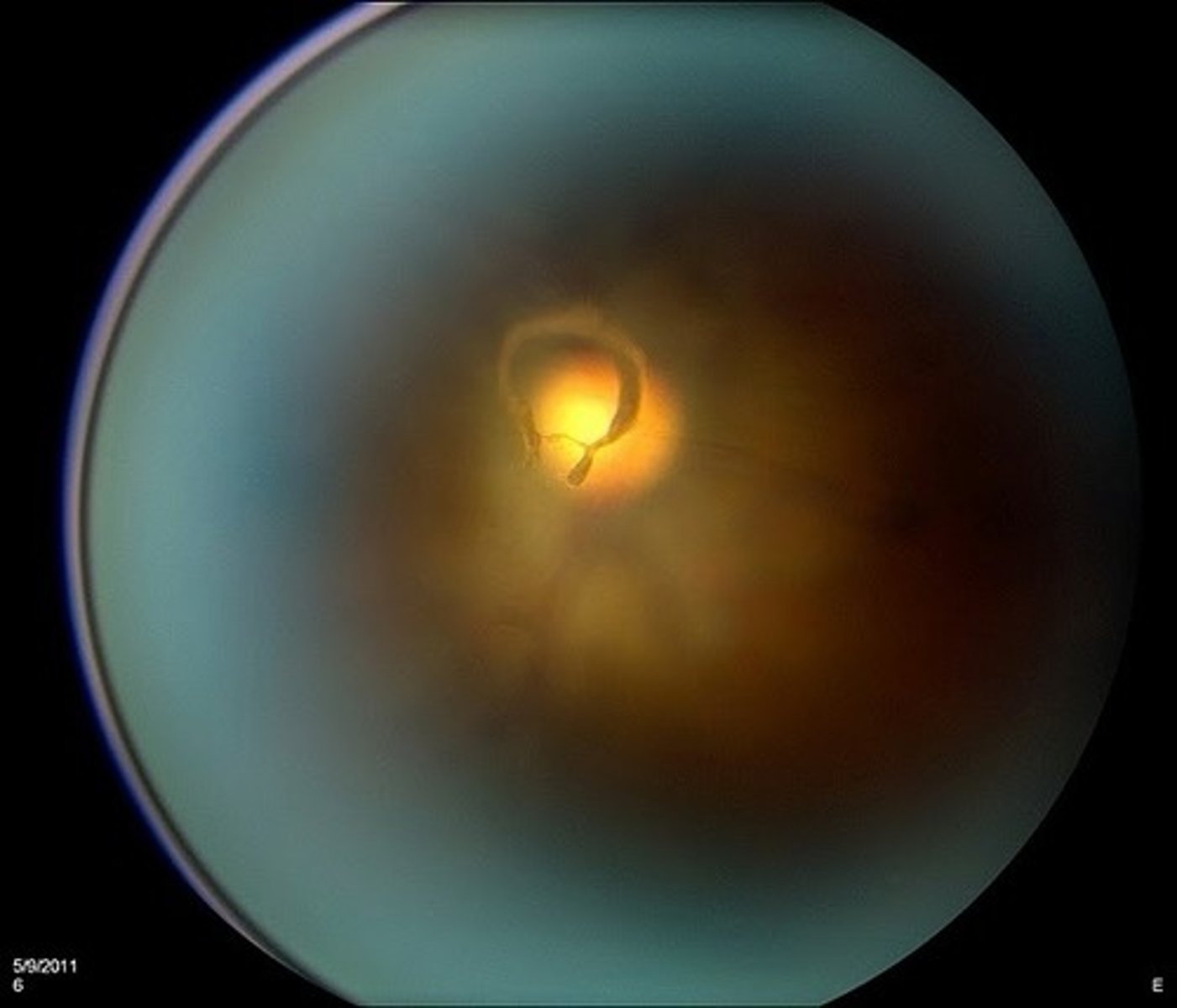
what causes weiss ring
vitreous detachment at optic disc
soluble and insoluble components of vitreous
solube (vitreous humor) = HA, ascorbic acid, sugar, electrolytes
insoluble (residual proteins) = collagen
Vitreous has a gel structure due to
long, thick, nonbranching collagen fibers suspended in hyaluronic acid (HA)
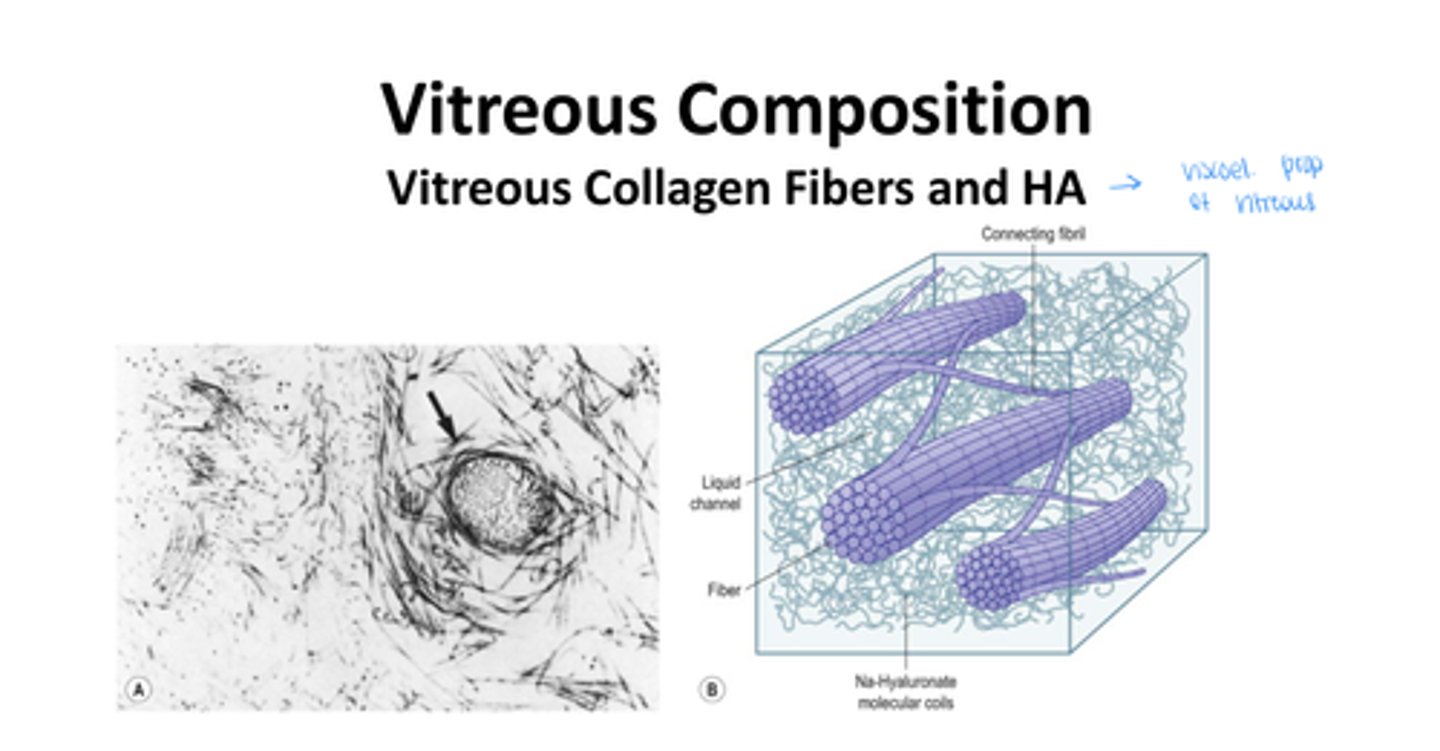
•Viscoelastic properties of vitreous =
HA + Collagen fibrils
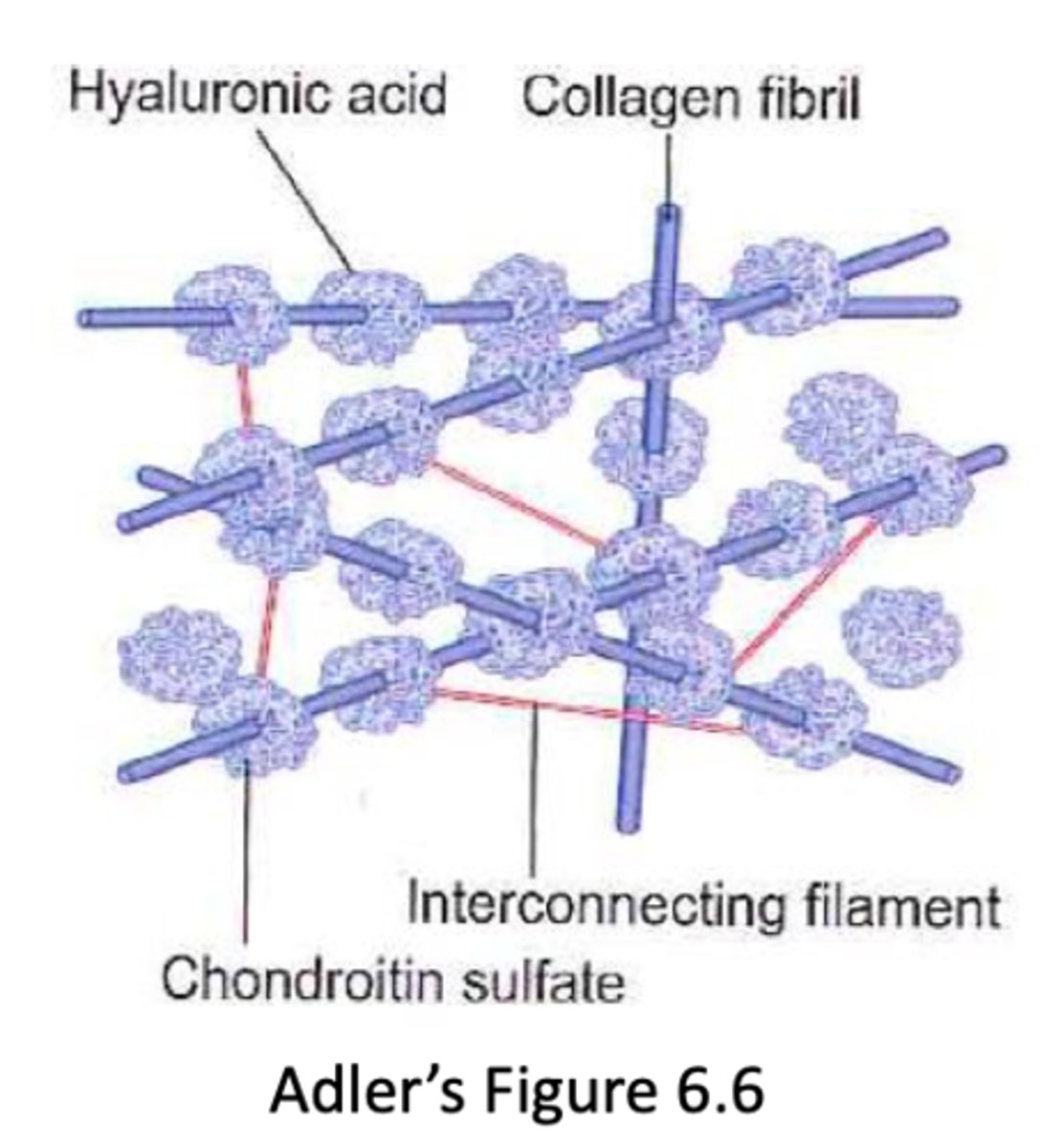
hyalocytes functions
synthesize HA and collagen type II
highest concentration of collagen is in the
cortex (where hyalocytes are)
describe HA
highly hydrophilic --> retains water
•MAIN VISCOSITY REDUCING AGENT IN VITREOUS
ascorbic acid --> Increases HA depolymerization
•Vitreous volume ___ from birth to adulthood
DOUBLES
Gel-Sol Transformation
liquefaction of vitreous associated with aging (from gel to soluble material)
Liquefaction of vitreous due to
depolymerization (loose water) of HA and collapse/structural changes of collagen framework
collagen Molecular weight ____ with age due to ___
-Molecular weight increases with age due to the formation of new covalent cross-links between peptide chains (less spacing btw them bc HA looses water)
____ vitreous is the first to liquefy (lacunae/water pockets)
Central (Medullary)
as medullary vitreous liquifies there is simultaneous ___ of collagen fibrils
Simultaneous syneresis/shrinkage/ collapse of collagen fibrils
describe the steps that lead to PVD
1. vitreous liquifies: HA depolymerization --> water molecules detach
2. water pooling in meullary vitreous
3. partial PVD --> vitreous fibers and ILM muller cells detach at weakest attachemnt (retinal BVs)
4. complete PVD --> detach up to vitreous base (ora)
•Factors contributing to breakdown of HA-collagen complex:
-Normal aging
-High axial myopia
-Aphakics
-Intraocular Inflammation
PVD is separation of posterior vitreous from the ___
ILM of the retina muller cells
complete PVD occurs where?
posterior to vitreous base (ora), anterior to vitreous base = anterior vitreous
___% of aphakic eyes have PVD
100
who gets PVD more:
female vs male
intracapsular cataract extract vs extracapsular
female > male
ICCE > ECCE
how does ILM aging changes contribute to PVD
ILM thickens with age and does not adequately hold inserted collagen fibers
•As vitreous pulls away from retina, it can also cause:
-Floaters
-Flashes (vitreoretinal traction)
-Retinal hemorrhage
-Vitreous hemorrhage
-Retinal tear
-Potential for retinal detachment
order of PVD locations
1. retinal BV (weakest attach)
2. macular
3. ONH
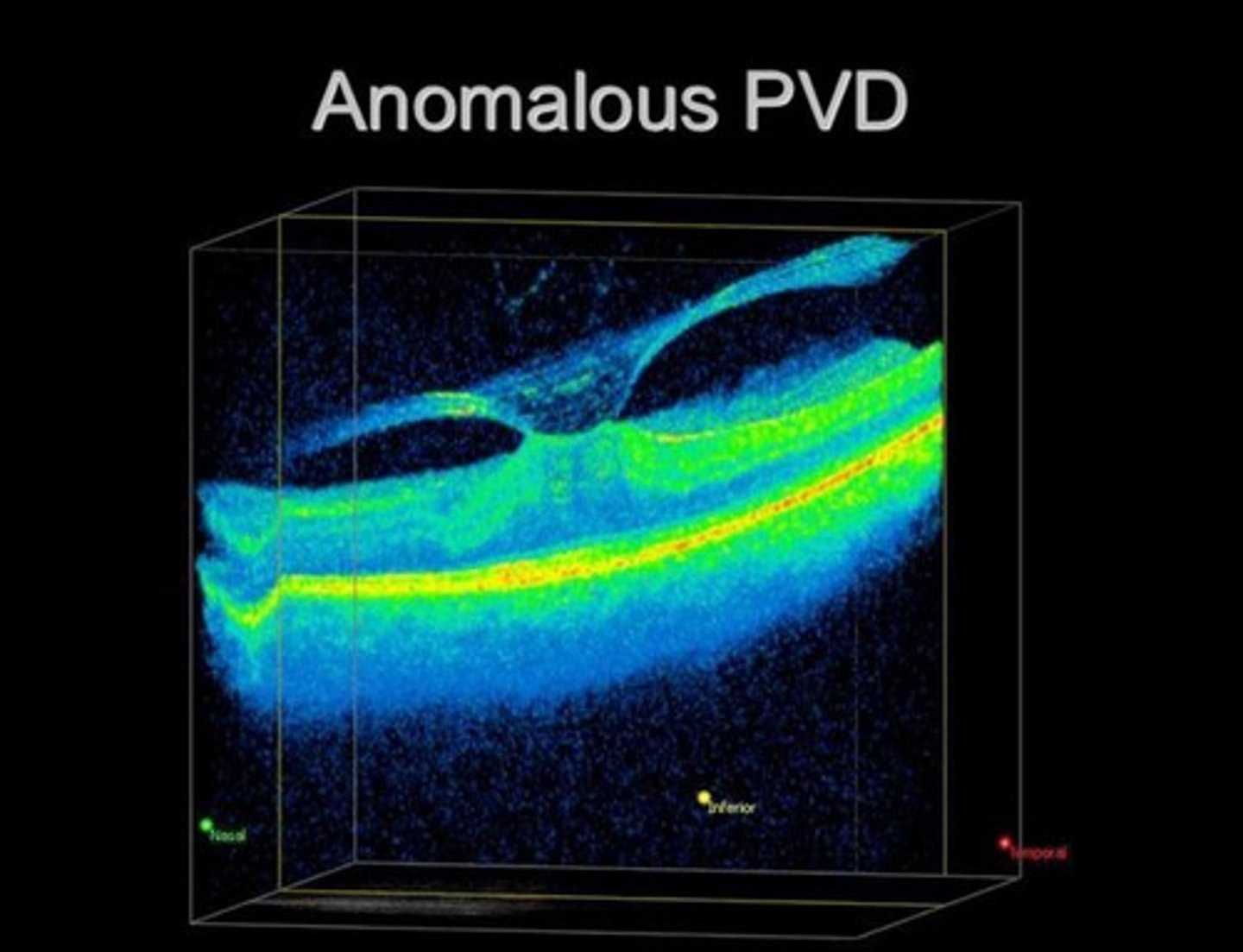
anomalous PVD
vitreous stays attached at macula --> can cause macular hole
vitreous base detachment most often occurs in ___
inferior temporal quadrant
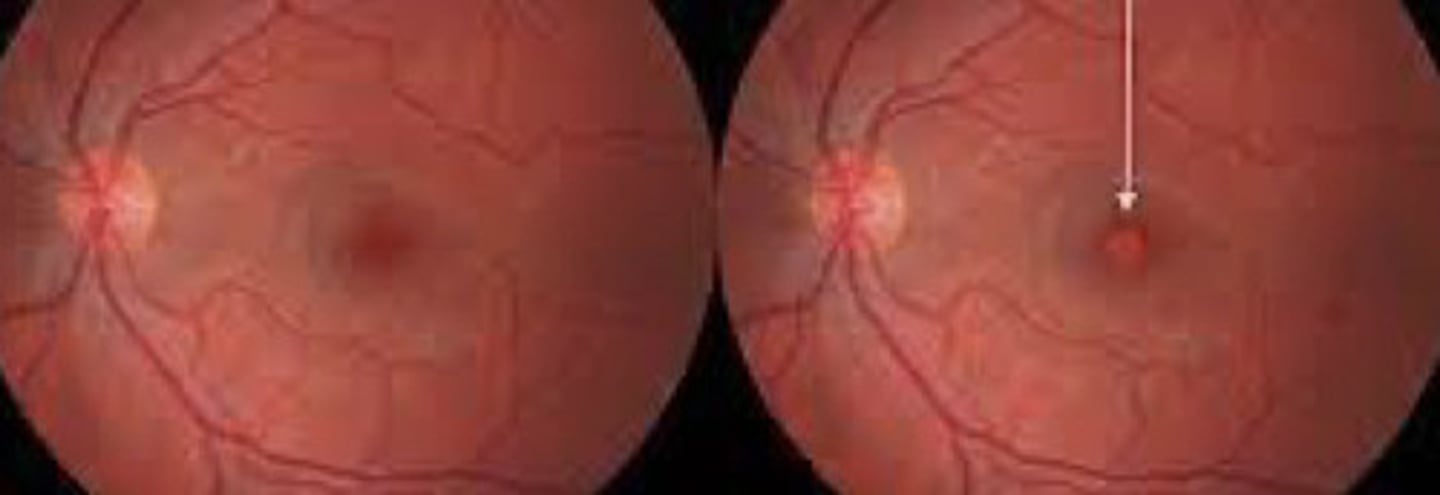
macular hole formation is the result of
foveal attachment plaques
•Strong areas of adhesion b/t vitreous cortex & ILM
PVD stays attached at macula and pulls off
epiretinal membrane cause
-PVD causes disruption of ILM
-Retinal glial cells migrate through ILM
-Glia proliferate on retinal surface
•Stimulates RPE migration/proliferation
-Glia & RPE give macula a shiny/puckered appearance
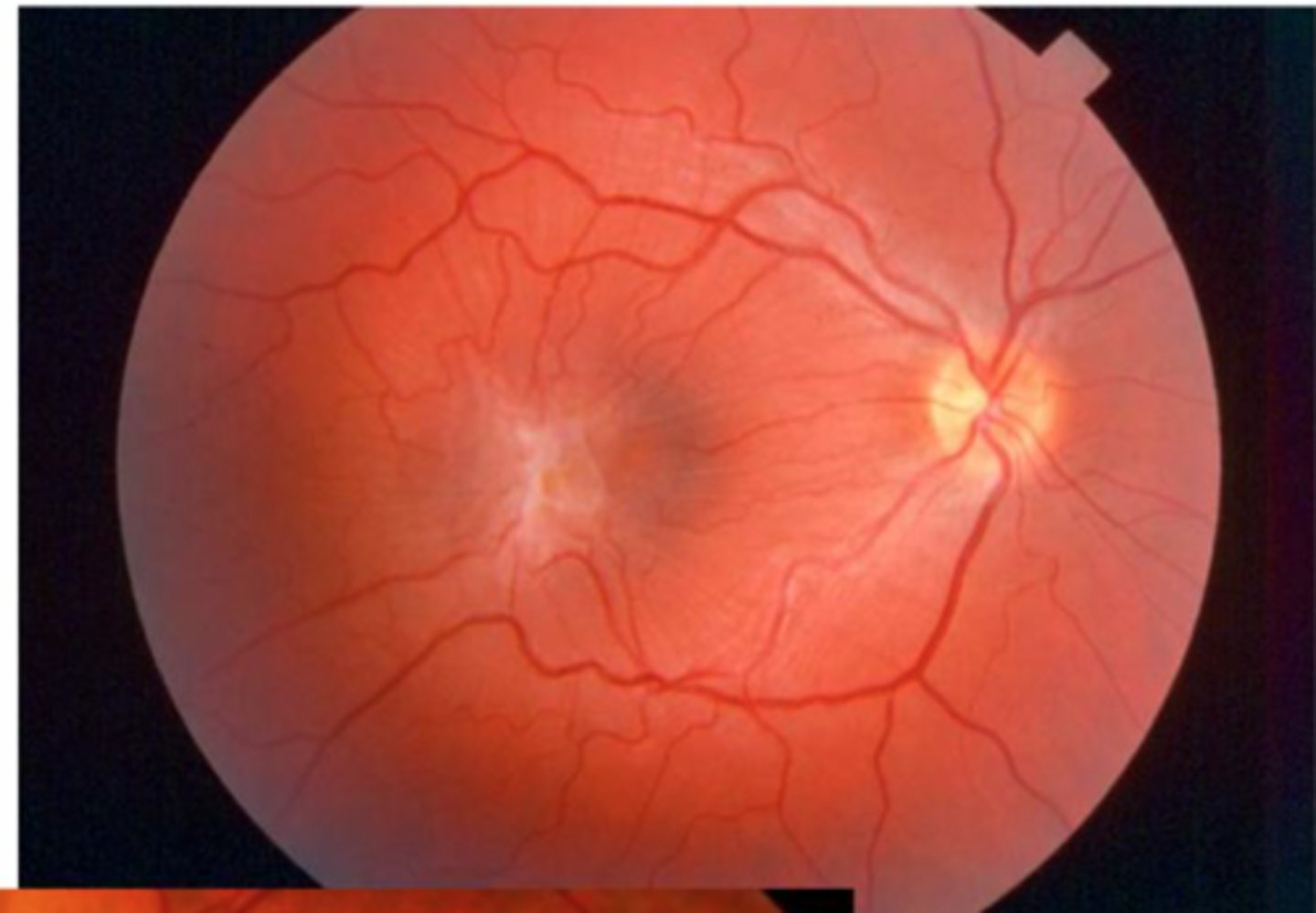
what causes asteroid hyalosis
•white or yellowish-white bodies (calcium soaps) that are tightly adherent to vitreous collagen strands
cholesterol crystals that are free flowing in vitreous occur in
Synchysis Scintillans