Chapter 5: Parenting Styles and Children's Socialization
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
first time parents
rely on a mixture of trial-and-error, intuition, personal experience, advice from family and friends, and information gleaned from articles and/or online sources
warm, loving, and consistent
positive emotional relationships are established when parents respond to young children in a manner that is _______
emotional attachment
there is an intense human need for what that is vital for survival, brain development, and social competence?
what children need from parents
attention, support, to be nurtured, and dependent to teach them skills needed to assume a productive role in society
educational background, available resources, cultural and religious norms, family structure, and geographical differences
a parent’s ability to recognize and successfully satisfy a child’s needs is influenced by what factors?
no it is bidirectional or transactional
is child-rearing a one direction process?
effective communication
requires that both the sender and receiver have a shared understanding of the intended message
verbal communication
refers to the words that are used to convey information
nonverbal communication
includes a person’s tone o voice, body language, emotional expressions, and active listening skills
active listening
involves not only hearing what a child is saying but also noting body language, tone of voice, and emotional expressions
also requires that an adult keep an open mind and restrain themselves from making a preconceived judgement until all of the information has been obtained
I-messages
effective for parents to use when they are angry or upset and likely to say something that they would later regret
consists of three statement components: how the parent feels, the behavior in question, and why the parent finds this behavior upsetting
the child’s age, behavior, the parents’ concern, and the context or situation
what factors influence the nature of parent-child communication?
baumrind’s classification model
how parents’ responsiveness influenced children’s socialization
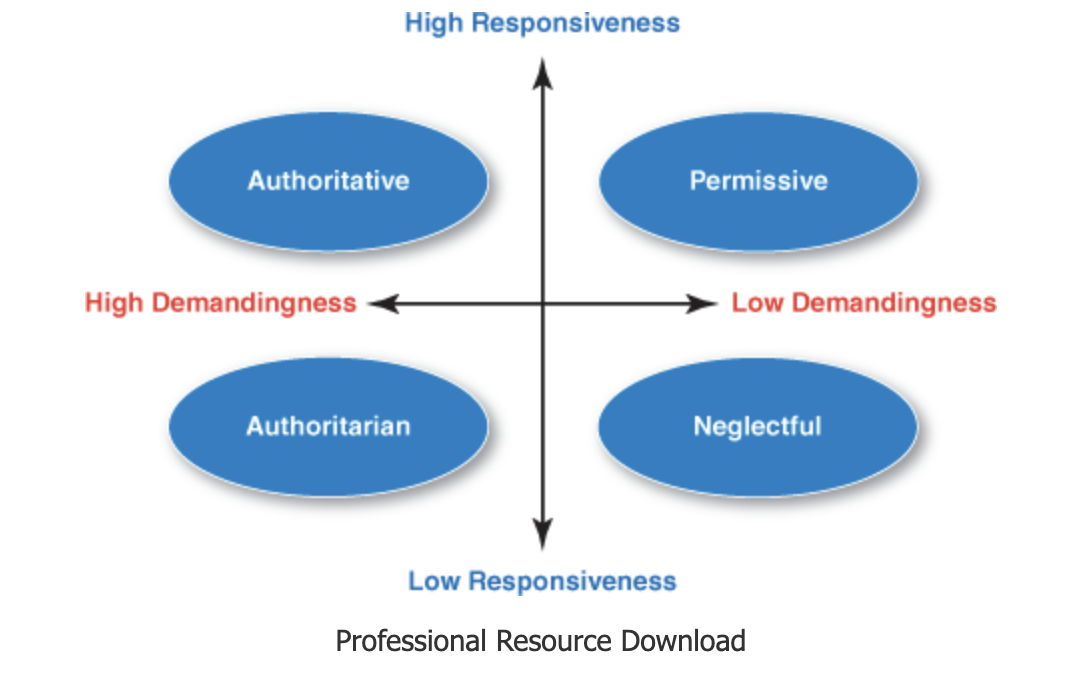
authoritative parenting style
is often referred to as democratic parenting, and is recognized for achieving the most positive developmental outcomes for children
parents maintain an ideal balance of demandingness and responsiveness
they value two-way communication, provide rationales for rules and limits, use discipline for teaching purposes, and willingly listen to children’s perspective when they disagree
involve children in decision-making and relinquish parental control as a child ages and matures. they grant children limited freedom as long as the child’s actions don’t interfere with, or cause harm to, others. they are also successful in creating a warm, supportive parent-child relationship while maintaining respect, limits, and high standards
children with authoritative parents
self esteem, problem solving skills, empathy, trust, and self-control
better social-emotional skills and achieve a higher level of academic success
present fewer behavior problems, and are less likely to engage in delinquent, high-risk, or bullying behaviors
authoritarian parenting style
tend to be extremely rigid, directive, and demanding. have significant need for control and are disinterested in children’s involvement
set high behavioral standards for their children and expect unquestioning obedience. nonnegotiable rules are established to maintain order, no explanations are offered for why they are needed, and strict compliance is demanded
“because i told you so”
verbal interactions with children are more likely to be negative and critical and there is harsh discipline
children with authoritarian parents
difficulty learning impulse control and self-regulation and become dependent upon others for behavioral control
susceptible to rebellion and risky behavior and risk of childhood obesity and eating disorder
tend to be average in school, and high rate of anxiety, fear, and depression
permissive parenting style
are nurturing, caring, and exceedingly tolerant. their relationship with children resemble one of equals or friends, and not one in which they are a respected authority figure. make few demands on children
generous with gifts and privileges to gain a child’s favor and the establish few rules or limits
children are relatively free to do as they please and are left to self-regulate their own behavior and children will learn from their behavior
children of permissive parents
do not learn how to control their behavior or conform to social expectations
act impulsively, make poor decisions that may place them at risk, and make demands without regard to others’ feelings
lack a sense of purpose, connectedness, and self-worth due to years of parental overindulgence and lack of involvement
neglectful parenting style
is sometimes referred to as uninvolved child-rearing. these parents make few if any demands on children and show minimal interest in their welfare other than meeting the basic needs for food and shelter
are often depressed, under considerable duress, or simply lack the time or energy to care
children are basically left to provide for themselves and to make their own decisions. in extreme form, this approach to parenting represents maltreatment or neglect
children with neglectful parents
typically not interested in academics and tend to perform poorly in school
get along with peers but are more likely to experiment with dangerous behaviors due to a lack of impulse control
free-range
a current phrase describing a permissive parenting style is known as _________ parenting
factors that influence parenting style
personal philosphy and experiences, goals and objectives for a child’s behavior, child’s age, gender, and temperament, family size, parent’s education, ethnicity and culture, and social class, and stress
familiarity and personal choice
what are the two most common reasons why parents may adopt a particular parenting style?
survival, health, and happiness; financial independence and self-sufficiency; and adherence to cultural values and traditions
parents may use a particular parenting style or a combination of styles to help their children achieve what goals?
factors that influence parenting style
familiarity, children’s age, gender, temperament, family size, stress, and when parents don’t agree
interpretive
instilling family values is associated with which of galinsky’s six stages of parenting?
no
does a child’s gender affect one’s parenting style?
anticipate the child’s needs and likely reactions
when there is a difference in parent and child temperament, parents should do what?
fewer children
families with fewer or more children are able to devote more quality attention to each child, respond more quickly to their individual needs, and provide greater economic and emotional resources?
characteristics of an effective family education program
availability of, and access to, classes, providing parents with feedback, delivery over several weeks, being inclusive of participant diversity, and focus on specific skills
with a disability
recent research by woodman was the first to investigate how raising a child _________________ influenced parents’ expectations and response to their behavior
no
do the majority of new parents receive formal educational training about effective child-rearing practices?
adolescents
________ are particularly vulnerable to inconsistent or conflicting parenting styles
no, researchers have expressed concern about the subjective nature of the terms used and the lack of cultural relevance in the model
is baumrind’s model of parenting styles widely accepted among researchers in the field?
practices
children’s behavior has an impact on parenting _____
effective communication
both the sender and receiver provide a clear message and use active listening
authoritative
high demand and high response
both listen, and mutual respect both ways
better social-emotional skills
achieve higher levels of academic respect
authoritarian
high demand and low response
strict compliance
set high behavioral standards and expect unquestioned obedience
children have difficulty learning impulse control and self-regulation
average students in school
permissive
low demand and high response
children are more friends with their parents and have an equal relationship
expect more from children
few rules and think children will learn from their own mistakes
do not learn how to control their behavior or conform to social expectations
lack a sense of purpose, connectedness, and self-worth
neglectful
low demand and low response
lack of concern and emotional connection with children
children have to provide for themselves
parents may be depressed or have health issues
few demands but minimal interest
typically not interested in academics and tend to perform poorly in school
lack of impulse control
people may be a mix of a few parenting styles and they may not look at other cultures
what are some possible criticisms of baumrinds classification model?
concerted cultivation
for middle class (more money)
foster skills, utilize more structured activities (like after school sports), and closely monitor children
emerging sense of entitlement
accomplishment of natural growth
for lower class (fewer resources and less money)
set limits for children, love their children, let kids grow spontaneously, no structured activities (encourage outside play), use directives (tell kids what to do with no explanation), distrustful of schools
emerging sense of constraint