Clinical Medical Assistant – Comprehensive Vocabulary Review
1/252
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering essential terms, regulations, procedures, anatomy, pharmacology, laboratory, and patient care concepts for Clinical Medical Assistant exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
253 Terms
Scope of Practice
The procedures, actions, and processes a healthcare practitioner is permitted to undertake, based on professional training, licensure, or certification.
Within Scope of Practice (CCMA)
Educating patients, health promotion, performing EKGs, taking vitals, urinalysis, throat cultures, and general patient education.
Outside Scope of Practice (CCMA)
Diagnosing, administering narcotics, interpreting lab results, identifying pathogens, performing arterial blood gases.
Assault
An open threat of bodily harm against another person.
Battery
Any action that causes bodily harm to another person.
Fraud
Deception intended to deprive a person of rights or property.
Invasion of Privacy
Unauthorized intrusion into a patient’s private affairs or disclosure of private information.
Malpractice
Negligent delivery of professional healthcare services.
Negligence
Failure to do what a reasonably prudent individual would do under similar circumstances.
Tort
A civil wrong committed against a person or property.
Chain of Custody
Chronological documentation showing custody, control, transfer, analysis, and disposition of evidence; specimen must be sealed in front of the patient.
CLIA (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments)
Federal legislation that sets quality standards and issues certificates for human clinical laboratories.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
Federal law protecting privacy of health information and ensuring continuity of insurance coverage.
The Joint Commission
Accrediting body emphasizing correct patient identification to improve safety.
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration)
Federal agency that regulates workplace safety; provides free training to employees.
Quality Control (QC)
Procedures that promote accurate laboratory test results.
Patient Identification
Most important patient-safety step; always ask for full name and date of birth.
Implied Consent
Permission inferred by patient actions, e.g., extending an arm for phlebotomy.
Informed Consent
Patient agreement after being told risks, outcomes, and alternatives.
Written Consent
Formal permission documented by patient signature.
Patients’ Bill of Rights
Guarantees such as access to records, fair treatment, and autonomy over medical decisions.
Problem-Oriented Medical Record (POMR)
Charting method organized chronologically around patient problems.
CMS-1500 Form
Standard claim form used to request reimbursement from Medicare/Medicaid and other insurers.
Encounter Form (Superbill)
Itemized list of services for insurance reimbursement and patient checkout.
Release of Information Form
Document allowing a patient to access or direct disclosure of their medical records.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
Managed-care network offering reduced rates to insured clients.
Medicaid
State-federal health insurance program for the medically needy.
Medicare
Federal insurance for individuals 65+ or disabled; funded through payroll taxes.
Tricare
Healthcare coverage for military personnel and their dependents.
Workers’ Compensation
Insurance providing wage replacement and medical benefits for job-related injuries.
Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN)
Waiver informing Medicare patients they may be responsible for payment if service isn’t covered.
Coinsurance
Percentage of costs a policyholder must pay after deductible is met.
Copay
Fixed amount due at time of service per insurance policy.
Deductible
Set amount a patient pays out-of-pocket before insurance begins coverage.
Explanation of Benefits (EOB)
Statement detailing what an insurer paid, denied, or reduced.
Preauthorization
Insurer’s advance decision that a service or device is medically necessary.
Precertification
Process of verifying eligibility and obtaining authorization before admission or procedures.
Referral
Directing a patient to a specialist or facility for definitive care.
Verification of Eligibility
Confirming a patient’s insurance coverage before providing care.
CPT (Current Procedural Terminology)
Code set that describes medical, surgical, and diagnostic services for billing.
ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
Diagnostic code system for reporting diseases and conditions.
Modifier (Coding)
Two-digit code indicating a procedure was altered or repeated.
Advance Booking
Scheduling an appointment well ahead of the visit date.
Clustering (Scheduling)
Grouping similar patient appointments in blocks.
Double Booking
Assigning two patients the same appointment time.
No Show (NS)
Patient who misses a scheduled appointment without notice.
Wave Scheduling
Three or four patients booked every 30 min and seen in arrival order.
Aerophagia
Swallowing air.
Alopecia
Sudden or excessive hair loss.
Anthropometric
used to assess the size, shape, and composition of the human body; e.g. BMI or a growth chart.
Chief Complaint (CC)
Primary symptom or concern for seeking medical care.
Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease
Cholecystectomy
Surgical removal of the gallbladder.
Dysuria
Painful or difficult urination.
Dextrocardia
Heart positioned to the right side of the chest.
Electronic Health Record (EHR)
Patient health information accessible across multiple organizations; must be backed up.
Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
Digital record within a single organization; requires backups.
Hemostasis
Process that stops bleeding and promotes clot formation (coagulation)
Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar; treat with orange juice.
Ischemia
restriction of oxygen-rich blood to a portion of the body.
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
hormone secreted by the parathyroid gland that is important in bone growth. Associated with the regulation of calcium in the body.
Patient-Centered Care
Care model involving patient and family in decision-making.
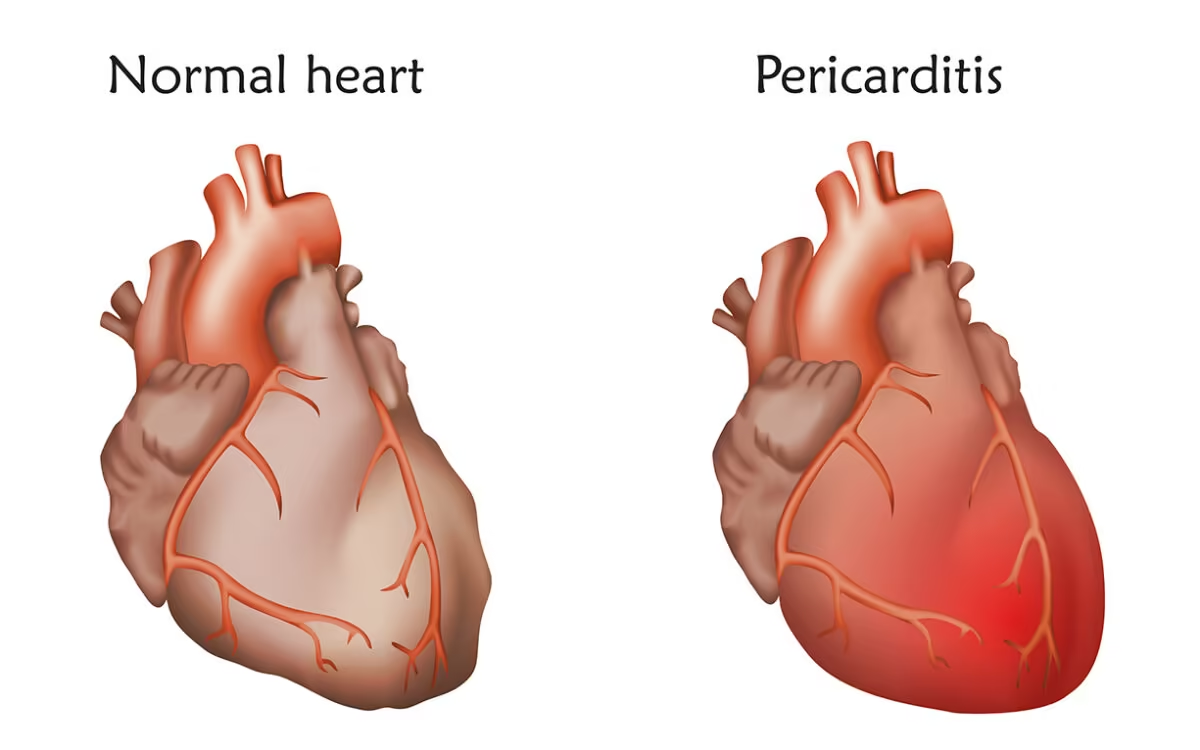
Pericarditis
Inflammation of the pericardial sac around the heart.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Items protecting workers from injury or infection; provided free under OSHA.
Petechiae
tiny spots of bleeding under the skin due to broken capillaries (tiny blood vessels). One reason is too tight a tourniquet.
Pyelonephritis
Kidney infection causing low-mid back pain. It’s specifically in the renal pelvis which collects urine hence the back pain. type of UTI
Retinopathy
Retinal disease causing vision loss, often due to diabetes.
Vertigo
episodes of dizziness and a sensation of spinning with certain head movements. Caused by an inner ear disorder. Can be caused by performing an ear irrigation on a patient.
SOAP Notes
a format for communicating important patient information in a chart in an organized manner.
Subjective = information the patient conveys.
Objective = measurable information about the patient (vitals, diagnostic findings, etc.).
Assessment = a detailed examination by the provider to determine health status.
Plan = a series of proposed interventions to improve health or treat disease.
Spirometry
common office test used to assess how well your lungs work by measuring how much air you inhale, how much you exhale, and how quickly you exhale. Requires two maneuvers.
Syncope
fainting, which can exhibit as dizziness, lightheadedness, and ringing in ears.
Transition of Care
refers to the coordination and continuity of health care during a movement of a patient from one healthcare setting to another or to home.
ABG
Arterial Blood Gas. Test measuring blood oxygen and carbon dioxide; outside CCMA scope.
BP
Blood Pressure. Force of blood against artery walls; normal ~110/70 mm Hg.
CBC
Complete Blood Count. Lab test enumerating blood cells.
CXR
Chest X-ray.
CC
chief complaint
Derm
skin
Dys
difficult, painful
CABG
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (Surgery improving blood flow to the heart.)
-ectomy
surgical removal.
I & O
Intake and Outputmeasures used to monitor fluid balance in patients.
-itis
Suffix meaning inflammation.
K
potassium
Nephr/o
Combining form meaning kidney.
-ology
study of
Ophth
Prefix relating to the eye.
Oto
Prefix relating to the ear.
-plasty
surgical reconstruction.
PE
physical exam
PO
by mouth
ROM
Range of motion.
STAT
Immediately, without delay.
STI
Sexually transmitted infection.
UA
Urinalysis
UTI
Urinary tract infection.
Cardiologist
Physician specializing in heart disorders.
Doctor of Osteopathy (DO)
Physician with holistic approach similar to MD.
Endocrinologist
Specialist in hormonal disorders such as diabetes or thyroid disease.
Nurse Practitioner (NP)
Registered nurse with advanced academic and clinical training.