HOC 7 transportation
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
transportation
the momevent of products from one location to another in the supplyy chain
significant supply chain cost (up to 20% pf total production cost)
major determinant of quick delivery service for some companies
modes of transportation
rail transportation
air transportation
waterway transportation
pipelines
road transportation
rail transportation : most suitable for
long distance transport of large quantities
products with low value and high density
rail transportation :
natural oligopoly due to high entry costs
low accessibility (prehaul and endhaul transport needed)
long transportation times due to consolidation
soorten rail transportation
traditional container train
piggyback transportation
double stack container transportation
air transportation : most suitable for
emergency shipments and perishable goods
products with high value to weight ratio
air transportation :
highly concentrated in limited number of carriers
low accessibility
fast but very expensive due to high variable costs
→ 65.6 million tonnes of cargo are transported by air every year
→1% of globally traded volume of goods, but 1/3 of the total global value
waterway transportation : most suitable for
long-distance transportation of large quantities
bulk products with low value, container transportation
waterway transportation :
inetrcontinental transportation, short-sea shipping or inland shipping
cost efficient mode thanks to large volumes, but very slow
low accessibility (prehaul and endhaul transportation needed)
pipelines : most suitable for
transport of products in liquid form (eg oil, gas)
pipelines :
high capital costs, but economical use and long lifetime
limited accessibility
road transportation : most suitable for
small point to poiont shipments
manufactured commodities with high value
road transportation :
competitive environment with many relatively small firms
high accessibility and reliability
flexible but expensive
transportation costs
fixed costs : infrastructure, terminals ect
variable costs : fuel, wages, maintenance
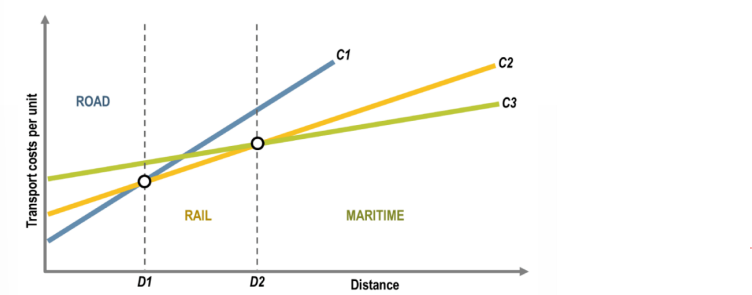
external costs
noise, congestion, global warming ….
heavy goods vehicle,
then containership
barge
goods train
intermodal transportation
at least two modes in a single transport chain
goods do not change container
the largest part by rail or waterway transportation
the shortest possible prehaul and endhaul by road transportation
intermodal transportation ; sustainability
reduces emissions, energy consumption, congestion ext
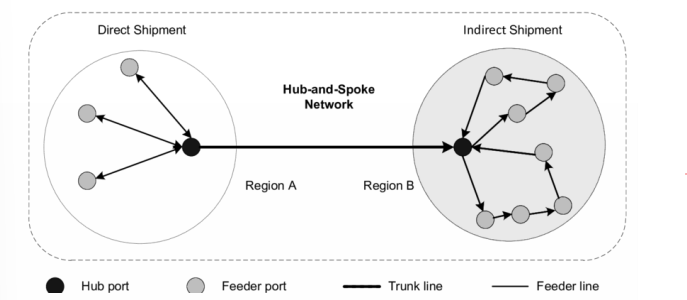
intermodal transportation
hub-and-spoke network with connected hubs
many stakeholders involved → requires coordination