Lecture 36: IVDD
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What are the chondrostrophic breeds?
Dachshund, Beagale, Pekingese, French Bulldog, Cocker Spaniel
Fibrocartilaginous lamellae, thicker ventrally
Annulus fibrosis
Amorphous gels, absorbs compressive loads
Nucleus pulposus
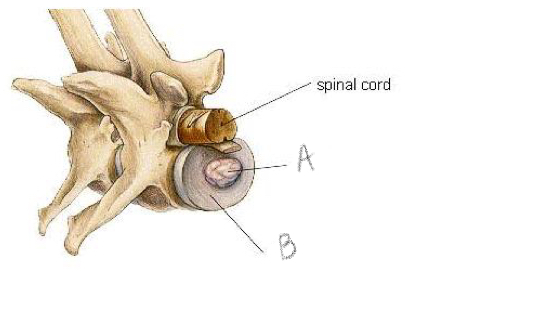
A- Nucleus pulposus
B- Annulus fibrosis
Cartilaginous end plates
Hyaline cartilage
Permeable outer and inner zones
Primary supplies of disk nutrition
Intervertebral disk
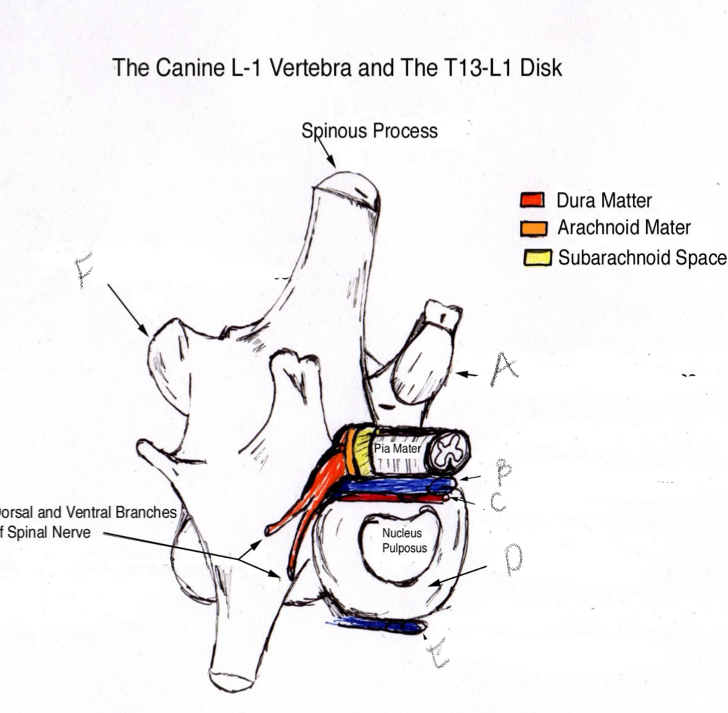
A- Cranial articular process
B- Dorsal longitudinal ligament
C- Vertebral venous plexus
D- Annulus fibrosus
E- Ventral longitudinal ligament
F- Caudal articular process
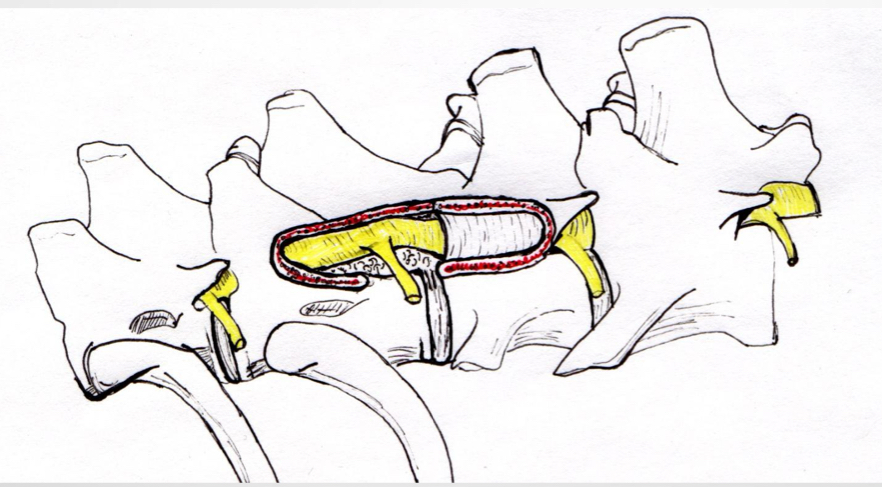
What makes up the spinal meninges?
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Subarachnoid space
Piamater
What layer of spinal meninges do we collect CSF from and inject contrast into?
Subarachnoid space
What makes up the spinal vasculature?
Paired vertebral venous sinuses, more lateralized in the thoracolumbar spine compared to cervical spine
What does degeneration of the nucleus pulposus cause?
Loss of water and proteoglycan molecules, increased collagen, calcification
Who does fibroid degeneration occur in?
Non-chondrodystrophic breeds
Disk degeneration of chondrodystophic breeds that occurs at first year of life
Chondroid metaplasia
Herniation of nucleus pulposus thru the annulus w/ extrusion into the spinal canal
Acute onset
Young chondrodystrophic breeds
Hanon type I
What is the most common areas?
T10-L1
Protrusion of the annulus into the spinal canal
Slow progressive onset
Older nonchondrodrodystrophic breeds
Hanson Type II
Forceful extrusion of small volume of nucleus pulposus thru the annulus w/ contusion of spinal cord
Acute onset
Young, chondrodystrophic breeds
Hanson Type III
What does primary trauma cause to the spinal cord?
Inflammation
Focal hemorrhage
Spinal cord swellling
Initiation of secondary mechanisms of injury
What are the secondary mechanisms of injury?
Vasoconstrictive substances (ischemic injury)
Increased in intracellular calcium (impaired metabolism)
Formation of lipid perioxidases (chemical damage)
Proprioception
Large, mylinated
voluntary muscle control
Intermediate, mylinated
Superficial pain
Smaller, mylinated
Deep pain
Small, unmylinated
When are surgery rads essential?
For differential diagnosis
What can you see with surgery rads?
narrowing/wedging of disk space
Alteration of intervertebral foramen shape
Presence of mineralized disk material
What is the seizure risk of myelography?
0-10%
Where do you perform a lumbar puncture?
L5-L6 or L4-L5 disk space
Where do you take cistern puncture?
Ceremedulary cistern
What should you do during a neuro exam for suspected IVDD dog?
Observe gait
Assess CP’s
Test patella reflexes
Palpate entire spine
Assess superficial pain
Assess deep pain
Differential diagnosis for IVDD
FCE
Spinal fracture/ luxation
Neoplasm
Diskospondylitis
Meningitis/myelitis
Single or occ. Episode of mild to moderate back pain ± CP deficits, no motor weakness
Conservative treatment
Favorable prognosis
Stage I thoracolumbar disk disease
Second episode or persistent and marked back pain, ± CP deficits
Dogs are able to stand and walk but may be ataxic
Conservative or surgical decompression
Favorable to guarded prognosis
Stage II thoracolumbar disk disease
Uncontrolled sever back pain, ± CP deficits
Dog are ataxia and ambulation is difficult
Surgical decompression
Excellent prognosis
Stage III thoracolumbar disk disease
No hindlimb motor function but deep pain sensation is present
Surgical decompression
Excellent prognosis
Stage IV thoracolumbar disk disease
No hindlimb motor function, no deep pain sensation
Surgical decompression <48 hrs
Unfavorable prognosis
Stage V thoracolumbar disk disease
What occurs during conservative therapy?
Strict immobilization
Minimum 3 weeks
Resolution of inflammation
Resorption
Fibrosis
What drugs are used in medical therapy?
Methylprednisolone, prednisone, methocarbamol, carprofen
Hemilaminectomy
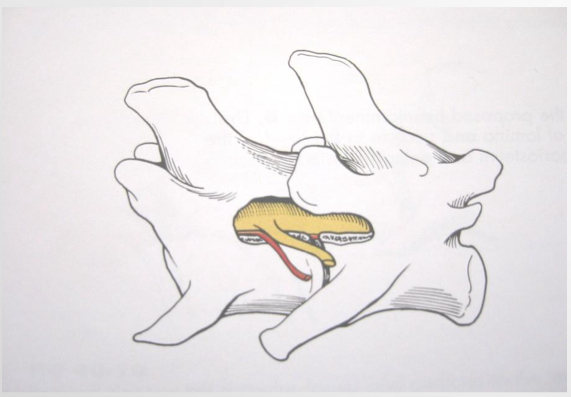
Pediculectomy
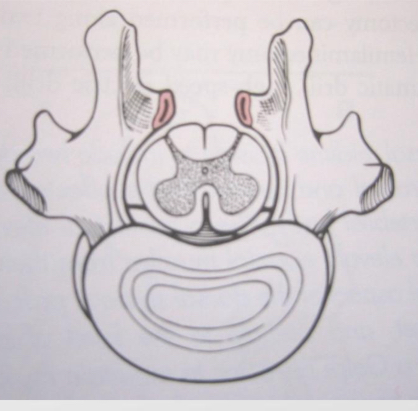
Modified dorsal laminectomy
When can you perform fenstration/laser ablation?
In combination with spinal cord decompressive surgery
Prognosis if deep pain is present?
80-96% with 4 week recovery time
What is needed for recumbent nursing care?
Keep clean, dry, well padded
Check and express bladder three to four times a day
Physical therapy
What does prognosis if deep pain is absent?
Depends on duration of time between loss of deep pain and surgical treatment (38-50% success if 12-48 hrs after loss of deep pain)

Cervical disk disease
Differential diagnosis for cervical disk disease
FCE
Spinal OA
Wobbler’s
Spinal fracture/luxation
Neoplasm
Atlantoaxial instability
Meningitis/myelitis
Diskospondylitis
Single or occ. episode of mild to moderate neck pain
Conservative
Favorable prognosis
Stage I Cervical disk disease
First episode of severe neck pain, or second episode of mild to moderate neck pain
Conservative treatment, surgical decompression
Favorable to execellent
Stage II cervical disk disease
Uncontrolled neck pain, or repeated episode of neck pain
Surgical decompression
Excellent
Stage III cervical disk disease
Ambulatory tetraparesis
Conservative and surgical decompression
Guarded to excellent
Stage IV cervical disk disease
Nonambulatory tetraparesis w/out forelimb sensory deficits
Surgical decompression
Excellent
Stage V cervical disk disease
Nonambulatory tetraparesis w/ forelimb sensory deficits
Surgical decompression
Guarded prognosis
Stage IV cervical disk disease
What is seen with conservative management of cervical disk disease?
Strict cage confinement
± medical therapy
NO neck leads
Very minimal risk of tetraparesis
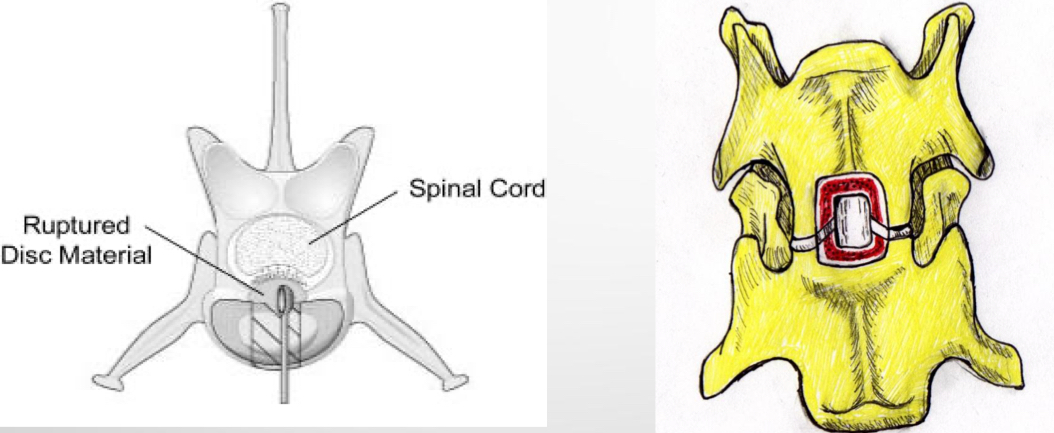
Ventral slot
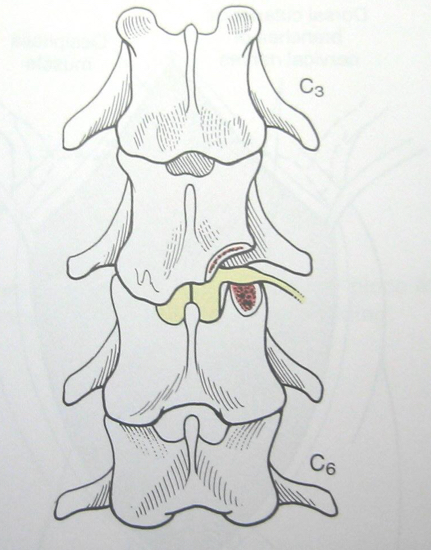
Dorsal hemilaminectomy
prognosis of cervical disk disease
Excellent for dogs with neck/forelimb pain only
Non-ambulatory dogs w/ good forelimb sensation 75% success rate
Non-ambulatory dogs with loss of forelimb sensation have a guarded prognosis
Which of the following breeds is commonly affected by IVDD? a) Labrador Retriever b) German Shepherd c) Dachshund d) Golden Retriever
c) Dachshund
Which of the following is a typical Physical Exam (PE) finding associated with Thoracolumbar (TL) IVDD? a) Decreased range of motion in the neck b) Ataxia in the hindlimbs c) Pain upon palpation of the cervical spine d) Forelimb lameness
b) Ataxia in the hindlimbs
Hanson Type I IVDD is characterized by: a) Slow, progressive protrusion of the annulus. b) Typically affecting older, nonchondrodystrophic breeds. c) Acute herniation of the nucleus pulposus through the annulus. d) A forceful extrusion of a small volume of the nucleus pulposus causing contusion.
c) Acute herniation of the nucleus pulposus through the annulus.
Which type of breed is most commonly affected by Hanson Type I IVDD? a) Large breed dogs b) Giant breed dogs c) Young, chondrodystrophic breeds d) Older, non-chondrodystrophic breeds
c) Young, chondrodystrophic breeds
The annulus fibrosis of the intervertebral disk is described as: a) An amorphous gel that absorbs compressive loads. b) Fibrocartilaginous lamellae, thicker ventrally. c) Hyaline cartilage responsible for disk nutrition. d) Composed of paired vertebral venous sinuses.
b) Fibrocartilaginous lamellae, thicker ventrally.
The nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disk primarily functions to: a) Provide the main source of disk nutrition. b) Form the outer layer of the disk. c) Absorb compressive loads. d) Protect the spinal meninges.
c) Absorb compressive loads.
Which of the following is NOT a layer of the spinal meninges? a) Dura mater b) Arachnoid mater c) Pia mater d) Periosteum
d) Periosteum
Degeneration of the nucleus pulposus involves: a) Increased hydration and proteoglycan molecules. b) Decreased collagen content. c) Reduced calcification. d) Loss of water and proteoglycan molecules.
d) Loss of water and proteoglycan molecules.
Which diagnostic technique has limited accuracy in localizing disk extrusions? a) Myelography b) CT scan c) MRI d) Survey Radiographs
d) Survey Radiographs
What contrast agent is commonly used in myelography for diagnosing IVDD? a) Barium sulfate b) Iohexol or iopamidol c) Propofol d) Ketamine
b) Iohexol or iopamidol
What is a potential risk associated with performing myelography? a) Bradycardia b) Hypertension c) Seizures d) Hypothermia
c) Seizures
Assessment of which neurological function is crucial in determining the prognosis for Thoracolumbar IVDD? a) Palpebral reflex b) Pupillary light reflex c) Deep pain sensation d) Patellar reflex
c) Deep pain sensation
According to the staging chart for Thoracolumbar Disk Disease, a dog with no hindlimb motor function but with deep pain sensation (Stage IV) typically has what treatment recommendation? a) Strict confinement b) Medical management only c) Surgical decompression d) Euthanasia
c) Surgical decompression
What is the most common surgical procedure performed for Thoracolumbar IVDD? a) Fenestration b) Hemilaminectomy c) Laminectomy d) Pediculectomy
b) Hemilaminectomy
For Thoracolumbar IVDD, conservative therapy primarily involves: a) Moderate exercise b) Short walks on a leash c) Strict immobilization d) Hydrotherapy
c) Strict immobilization
Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) is sometimes used in the medical management of IVDD to: a) Provide long-lasting pain relief. b) Inhibit oxygen free-radical lipid peroxidation. c) Stimulate appetite. d) Prevent urinary tract infections.
b) Inhibit oxygen free-radical lipid peroxidation.
Which of the following is NOT a differential diagnosis for Thoracolumbar Disk Disease? a) Spinal fracture/luxation b) Neoplasm c) Atlantoaxial instability d) Diskospondylitis
c) Atlantoaxial instability
In Cervical Disk Disease, a surgical treatment option includes: a) Dorsal laminectomy b) Ventral slot c) Hemilaminectomy (primarily TL) d) Fenestration (not sole treatment)
b) Ventral slot
What is a critical aspect of conservative management for Cervical Disk Disease? a) Encouraging gentle neck exercises. b) Using a neck lead for walks. c) NO neck leads. d) Massaging the neck muscles.
c) NO neck leads
According to the prognosis for Cervical Disk Disease, dogs with only neck/forelimb pain undergoing surgical treatment typically have a(n): a) Guarded prognosis b) Fair prognosis c) Excellent prognosis d) Poor prognosis
c) Excellent prognosis