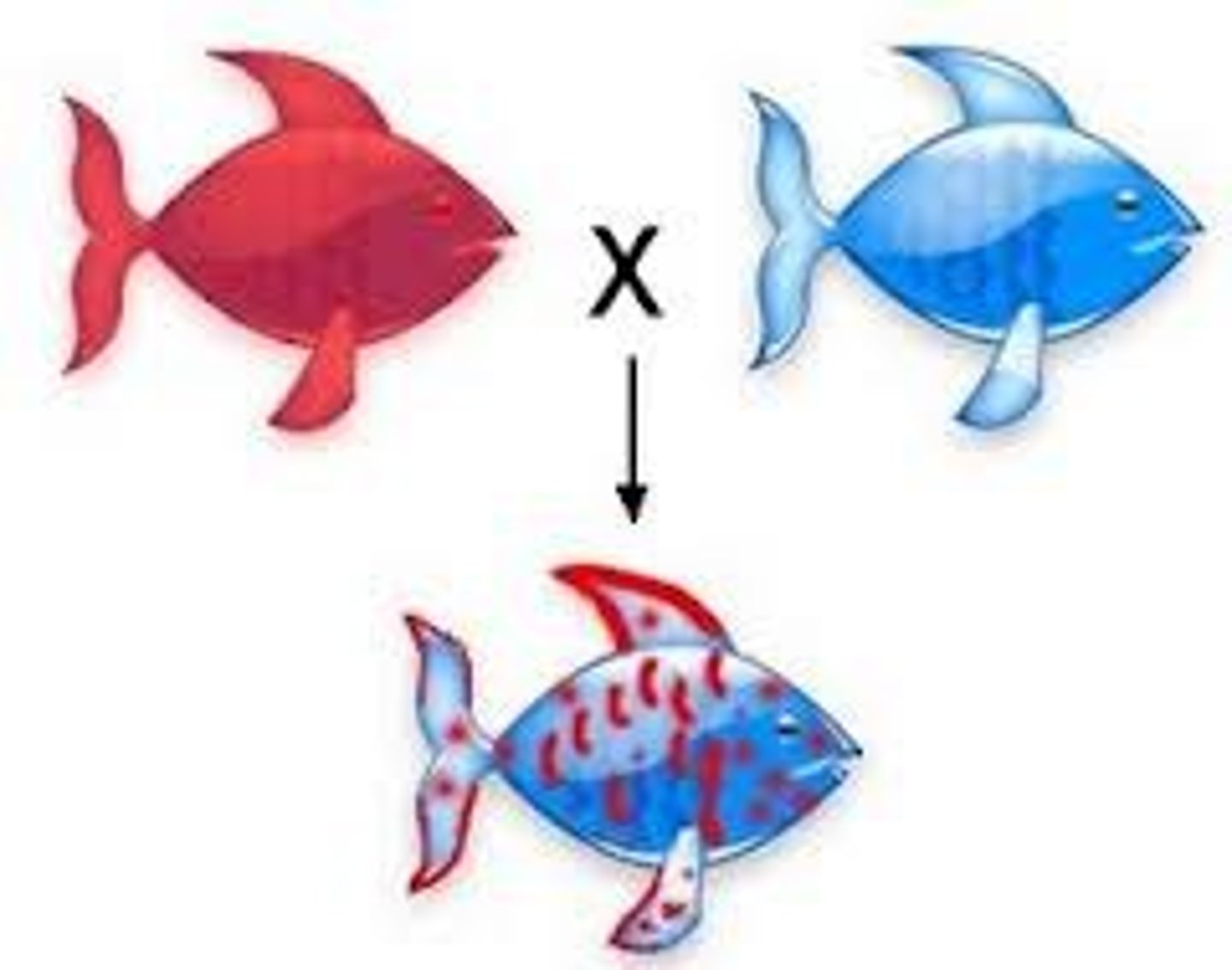
Genes and Chromosomes Overview
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Genome
The complete set of an organism's DNA, including all of its genes and noncoding sequences.
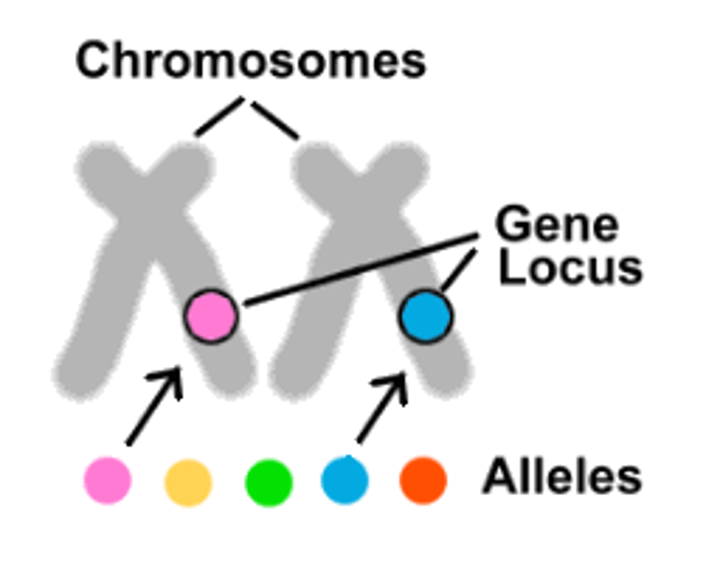
Locus
A specific position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located.
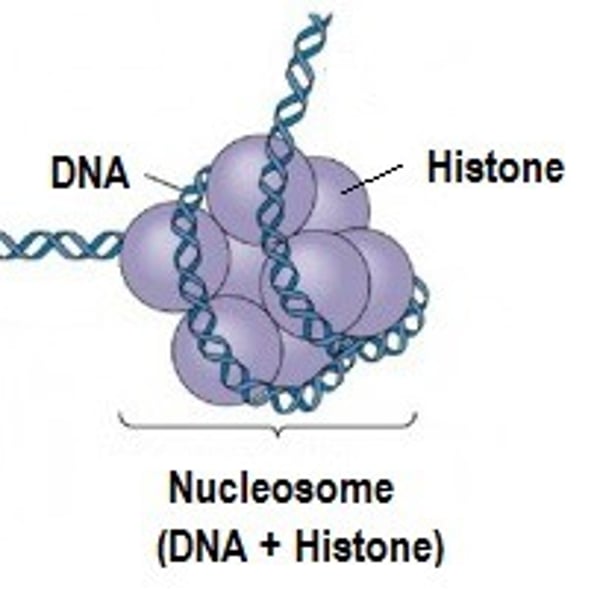
Histone protein
A simple protein bound to DNA, involved in the coiling of chromosomes
Chromosome
A thread-like structure made of DNA and proteins, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
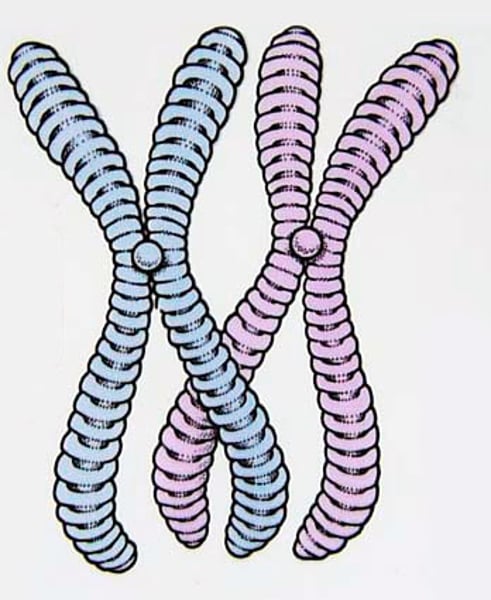
Somatic cell
Any cell of a living organism other than reproductive cells, containing a full set of chromosomes.
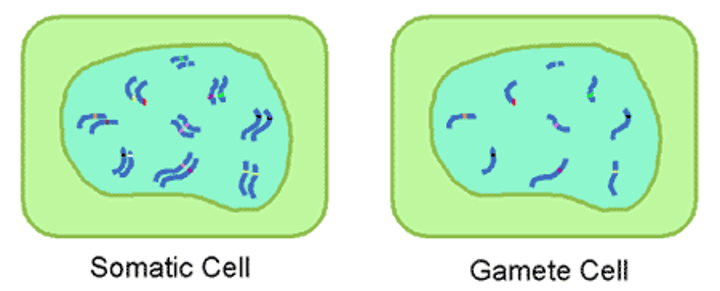
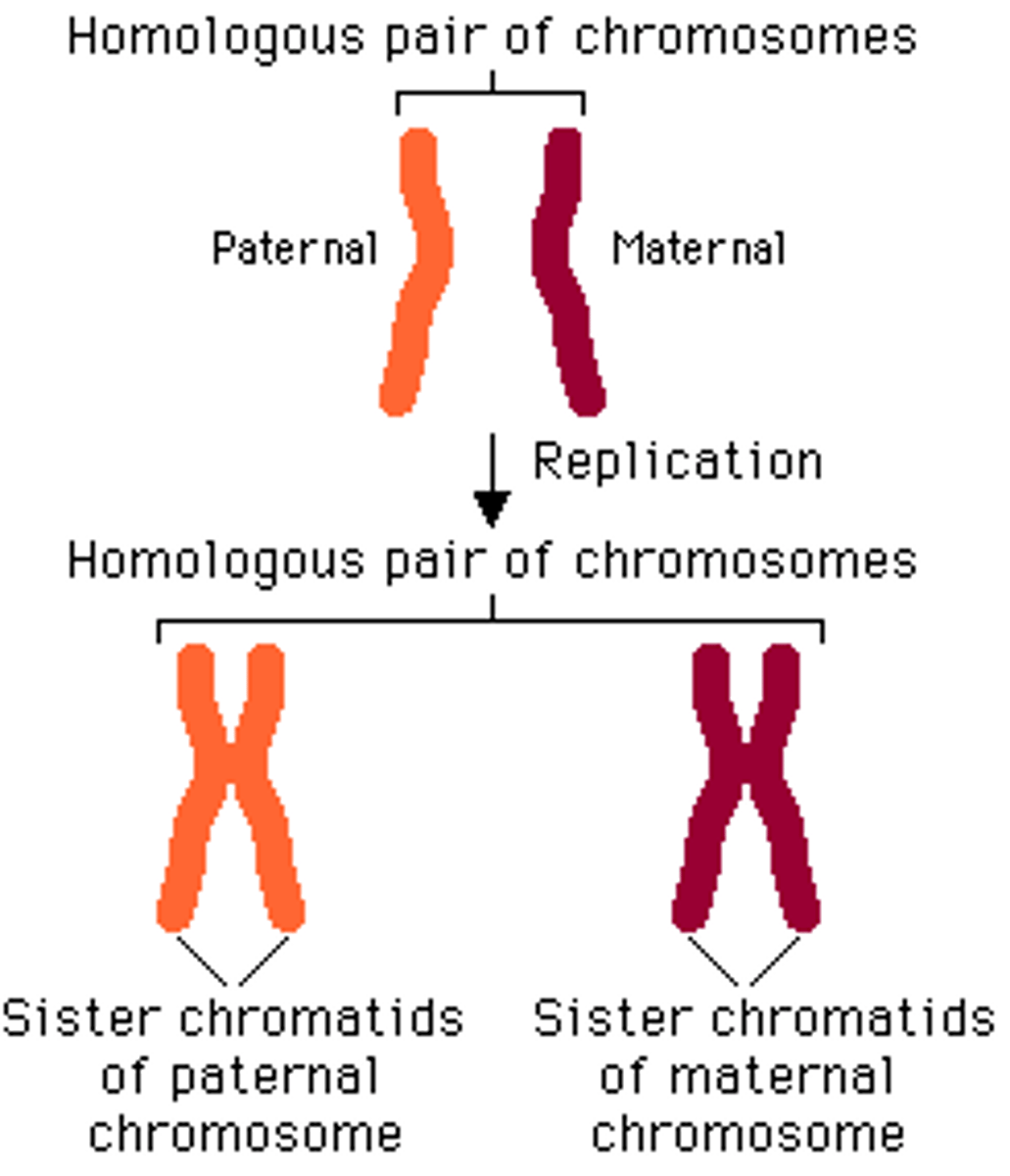
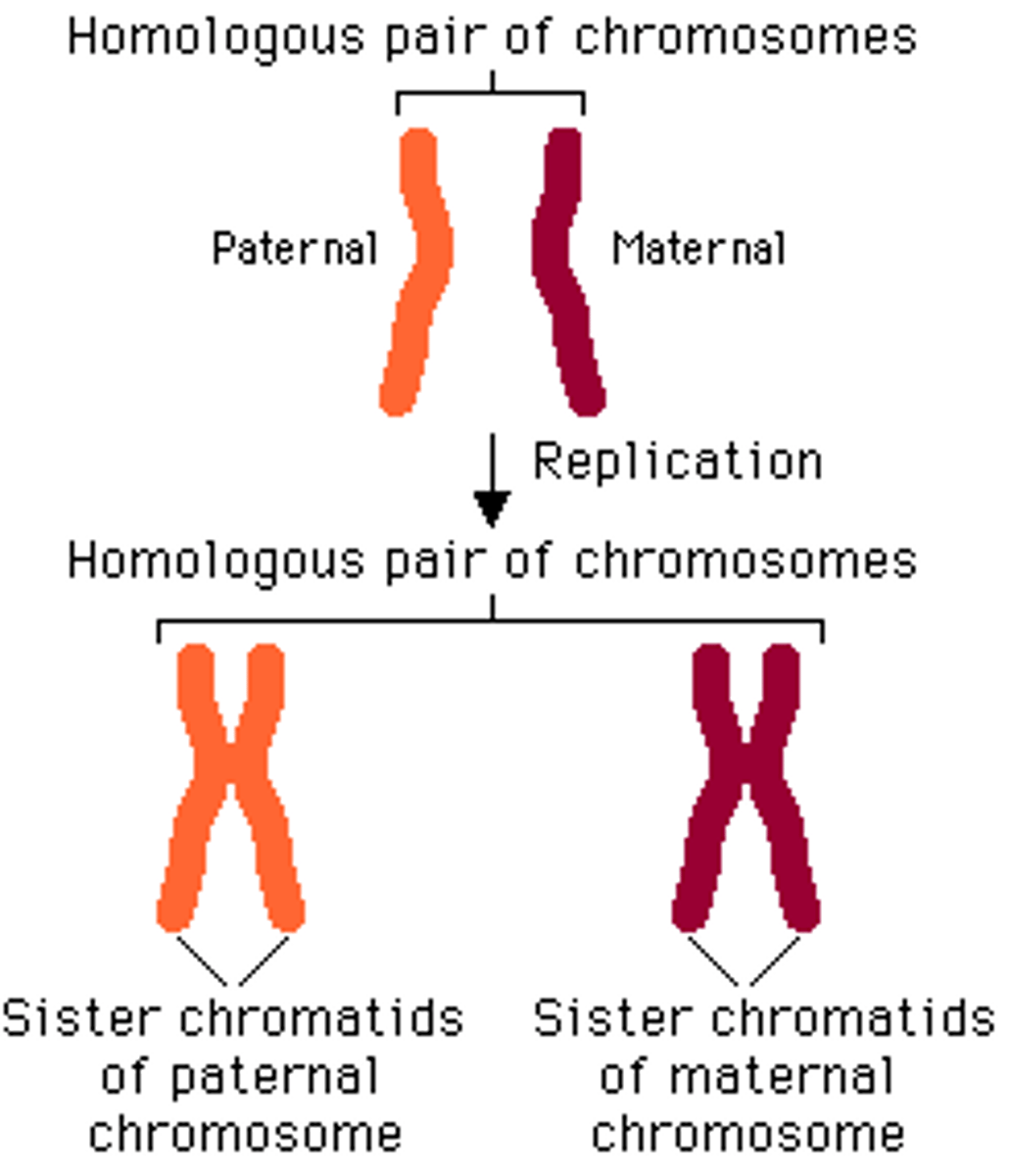
Homologous chromosome
A pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, one inherited from each parent.
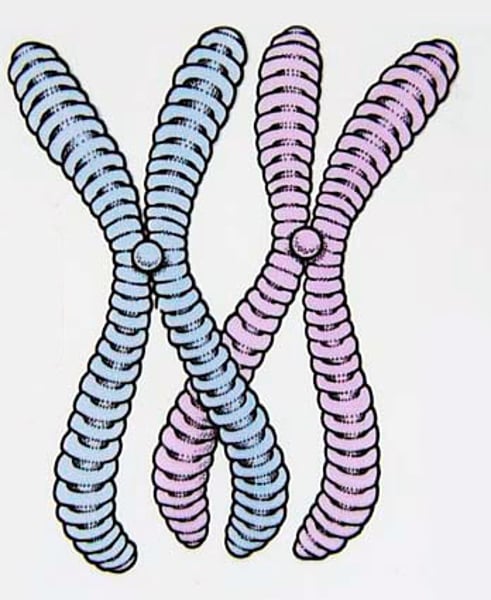
germline cells
cells that produce gametes
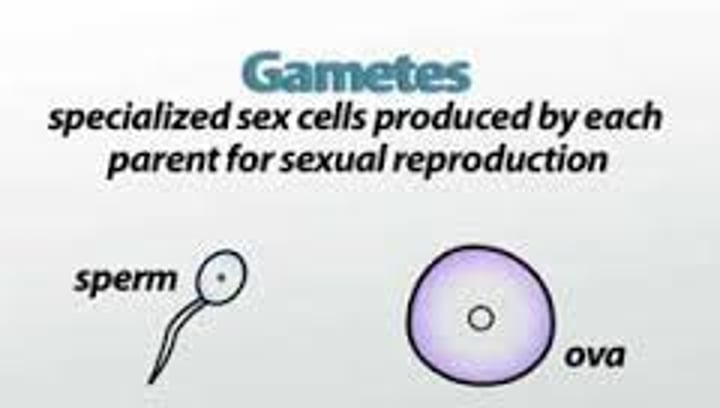
Gonads
sex glands
chiasma
The microscopically visible site where crossing over has occurred between chromatids of homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis.
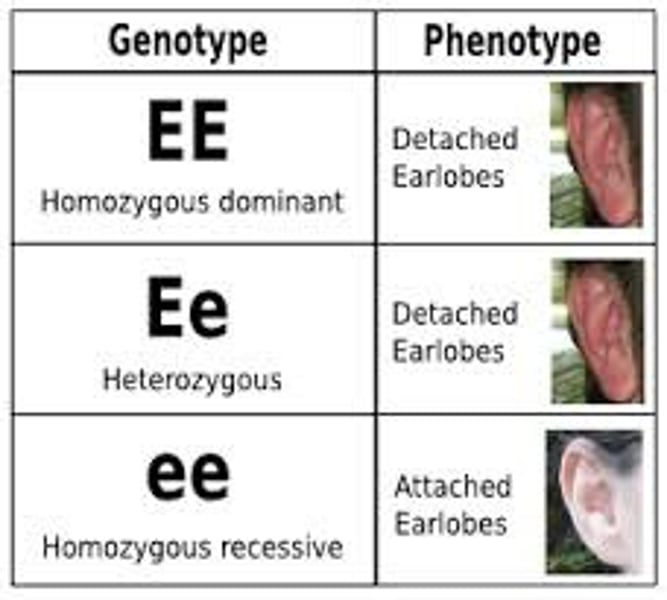
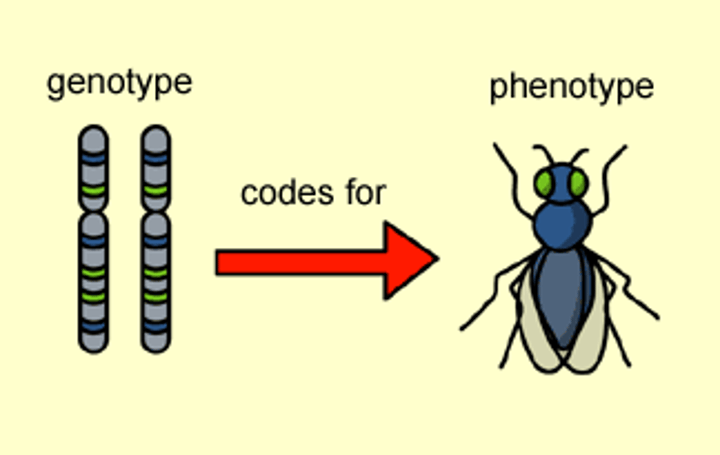
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
carrier
A person whose genotype includes a gene that is not expressed in the phenotype.
sex linked genes
Genes located on the sex chromosomes.
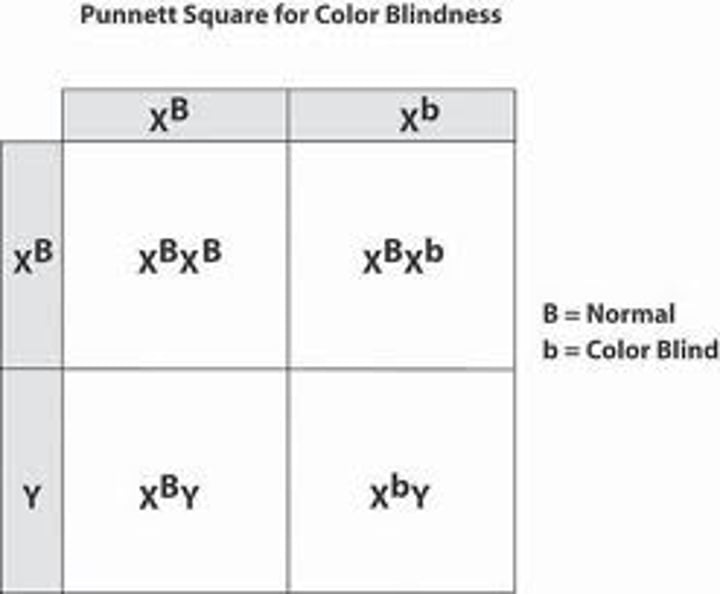
x-linked traits
a phenotype determined by an allele on an X chromosome
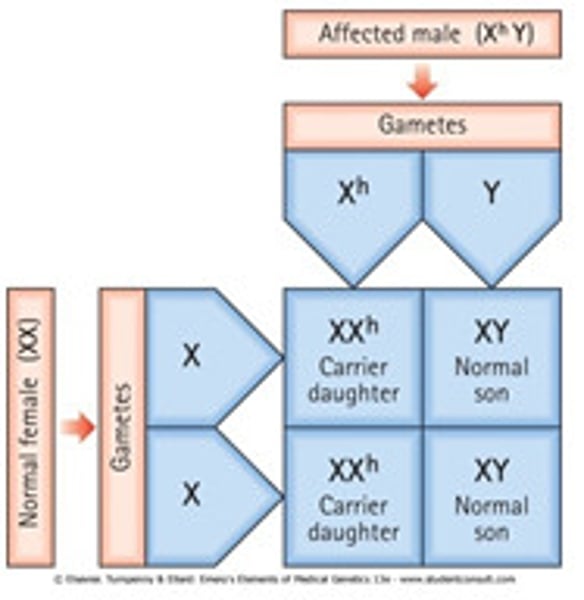
Y-linked traits
only males are affected, passed from father to all sons, does not skip generations
environment
the surroundings or conditions in which a person, animal, or plant lives or operates.
proportionate heritability
the amount of phenotypic variance that can be explained by genes in a given population
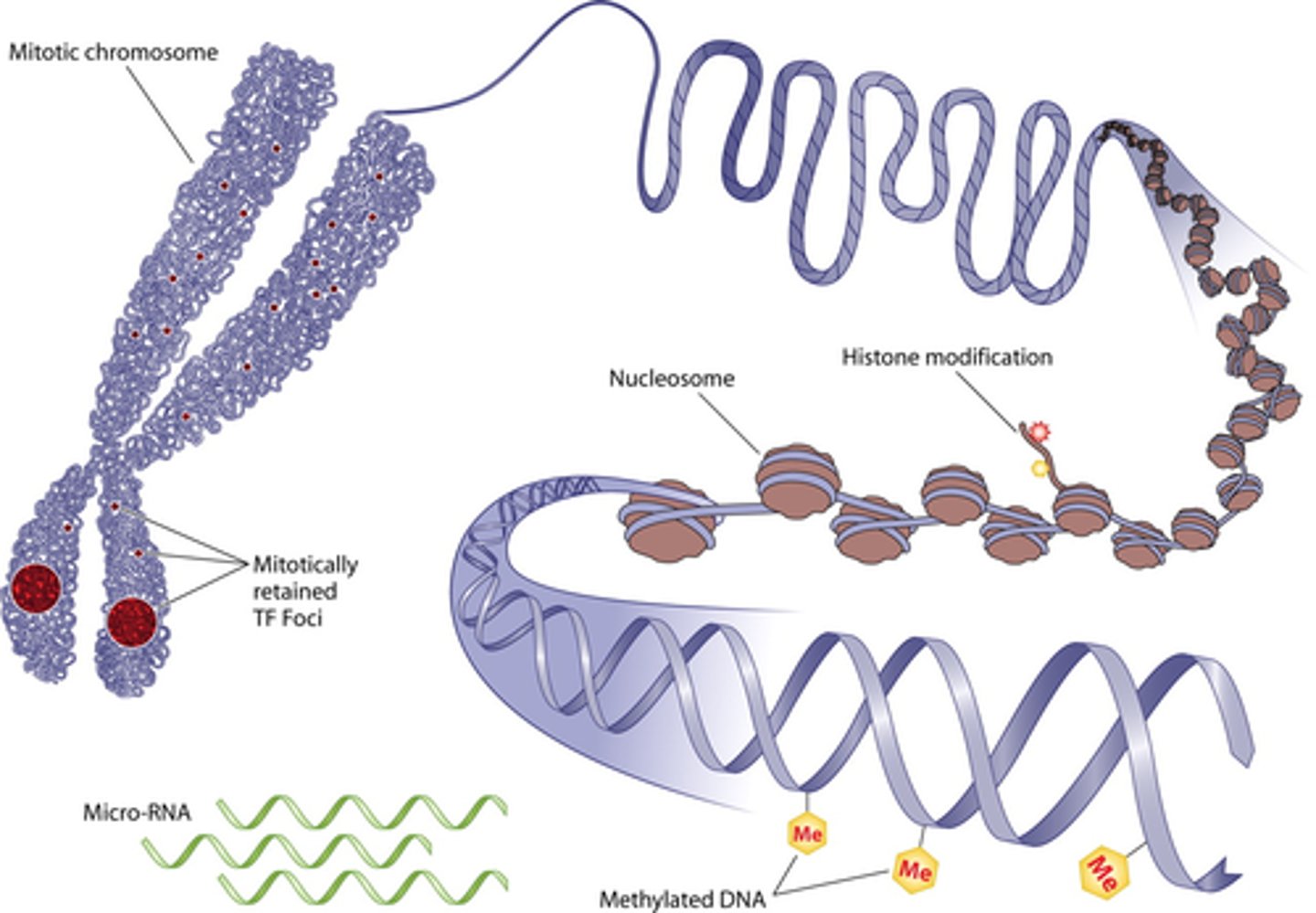
Epigenetics
Nature Vs Nurture
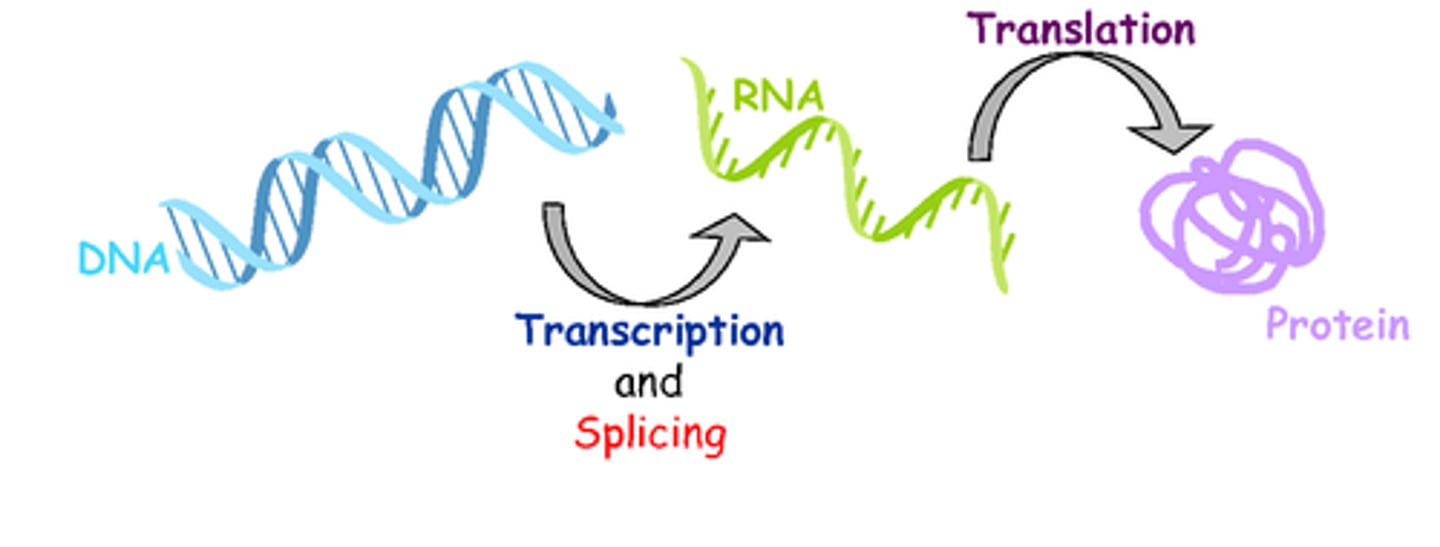
gene expression
process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out its function
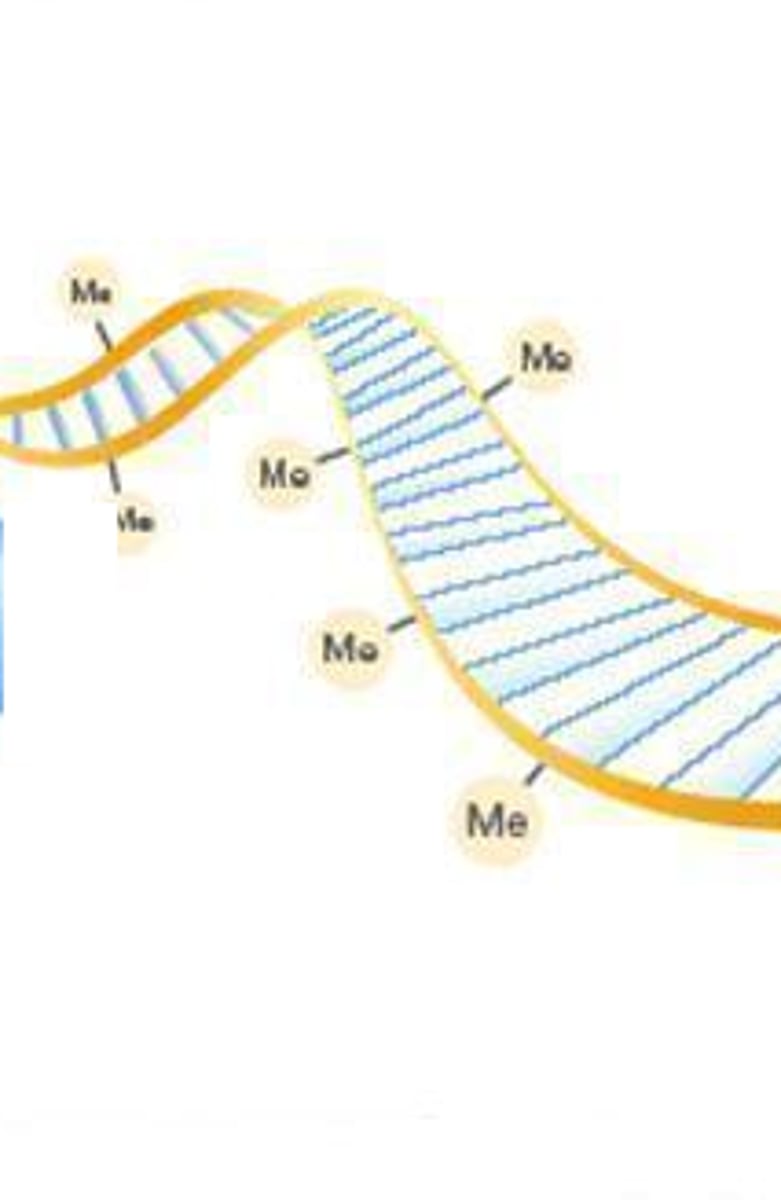
DNA methylation
a meyth group attaches to a nucleotide and stops the gene from being read/ expressed in the phenotype
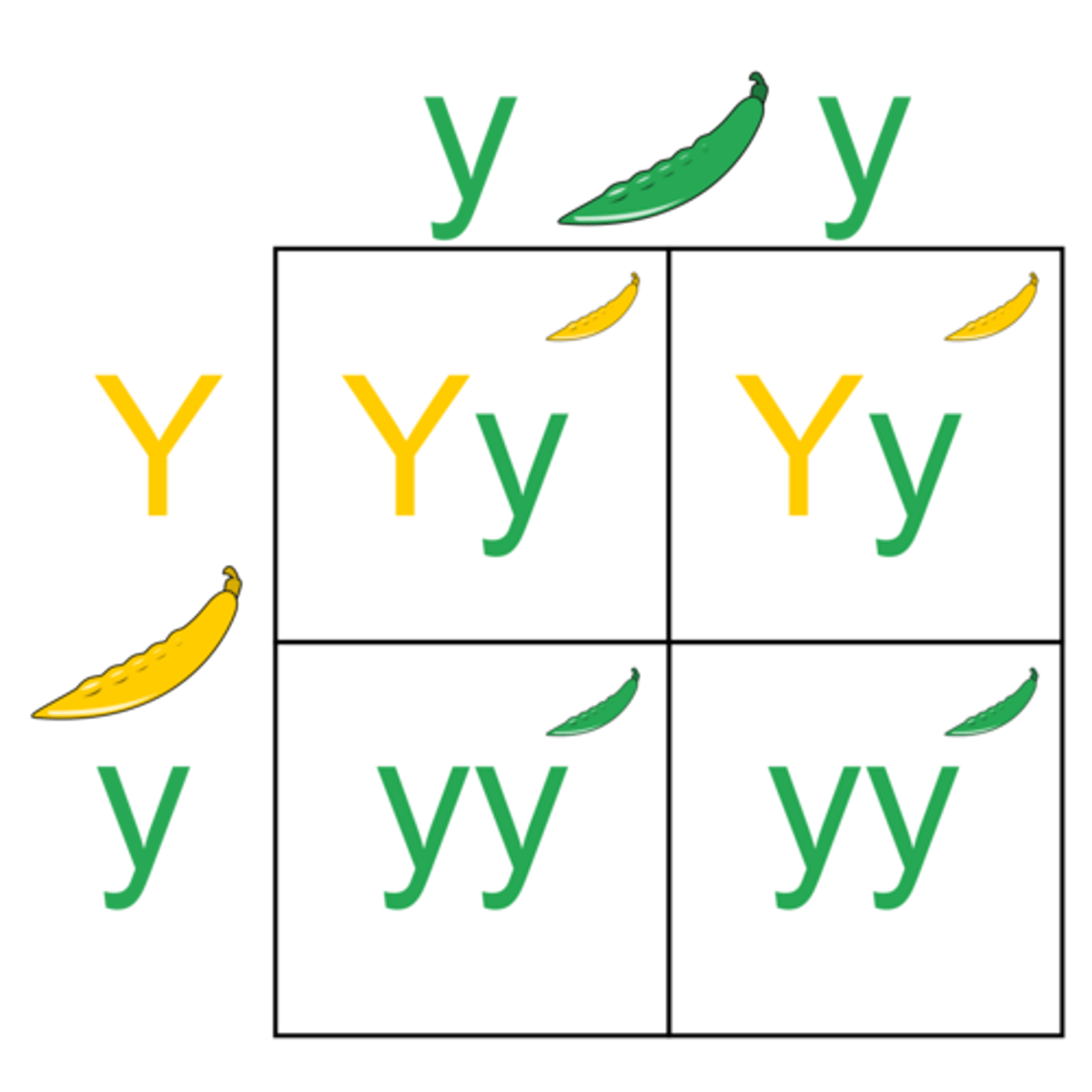
monohybrid cross
A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits
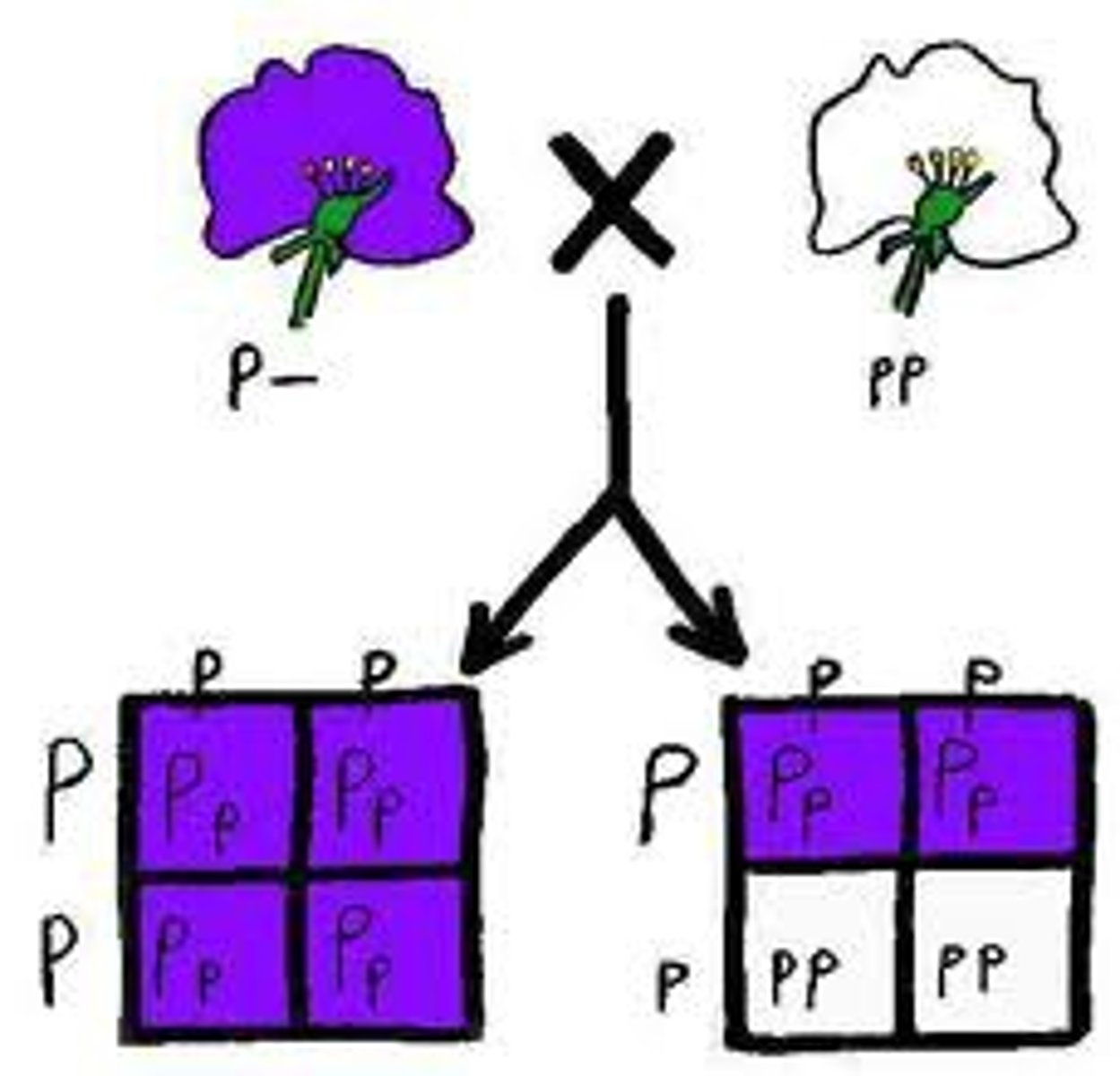
test cross
the crossing of an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the unknown genotype
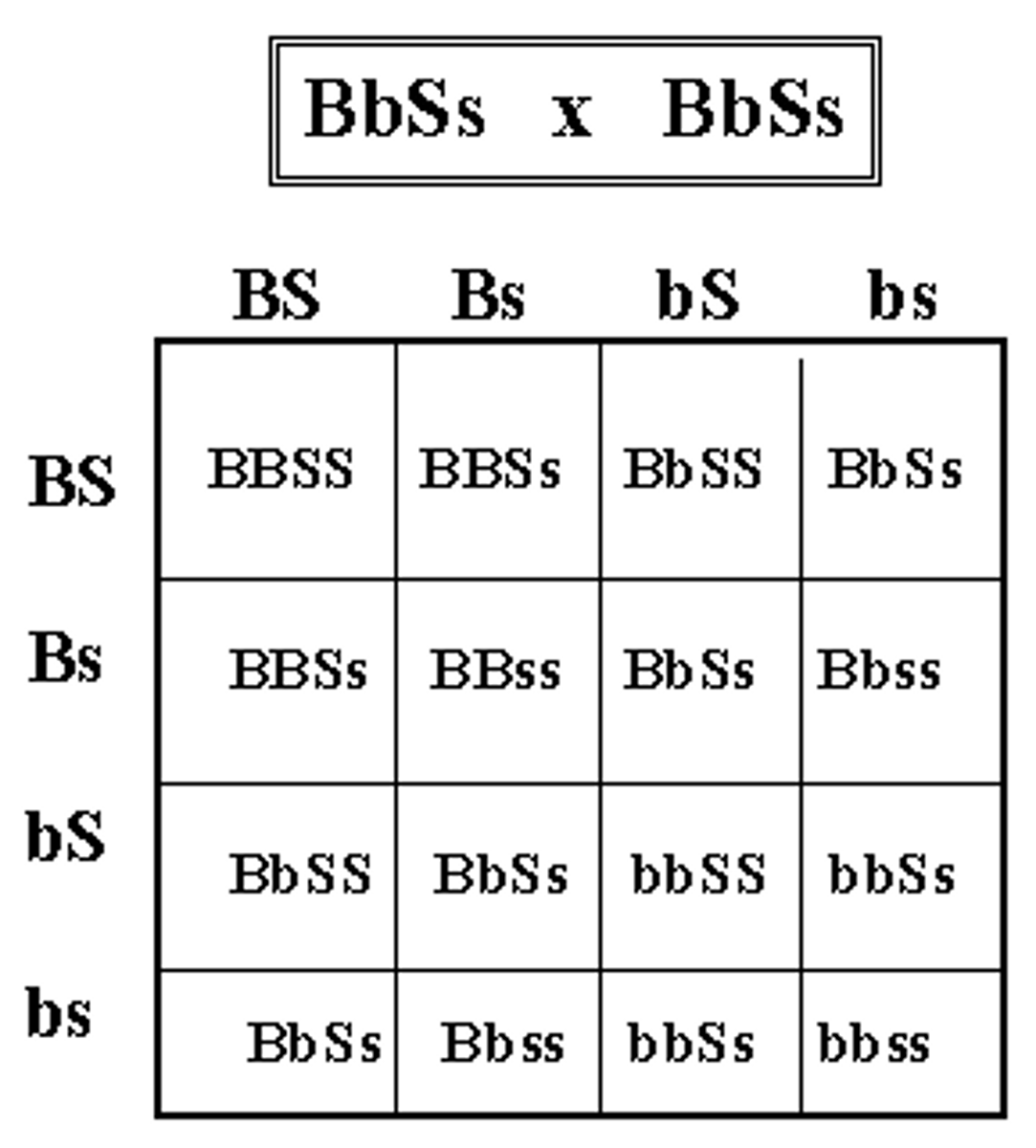
diybrid cross
a cross between individuals that involves two pairs of contrasting traits
unlinked genes
genes that are found on different chromosomes
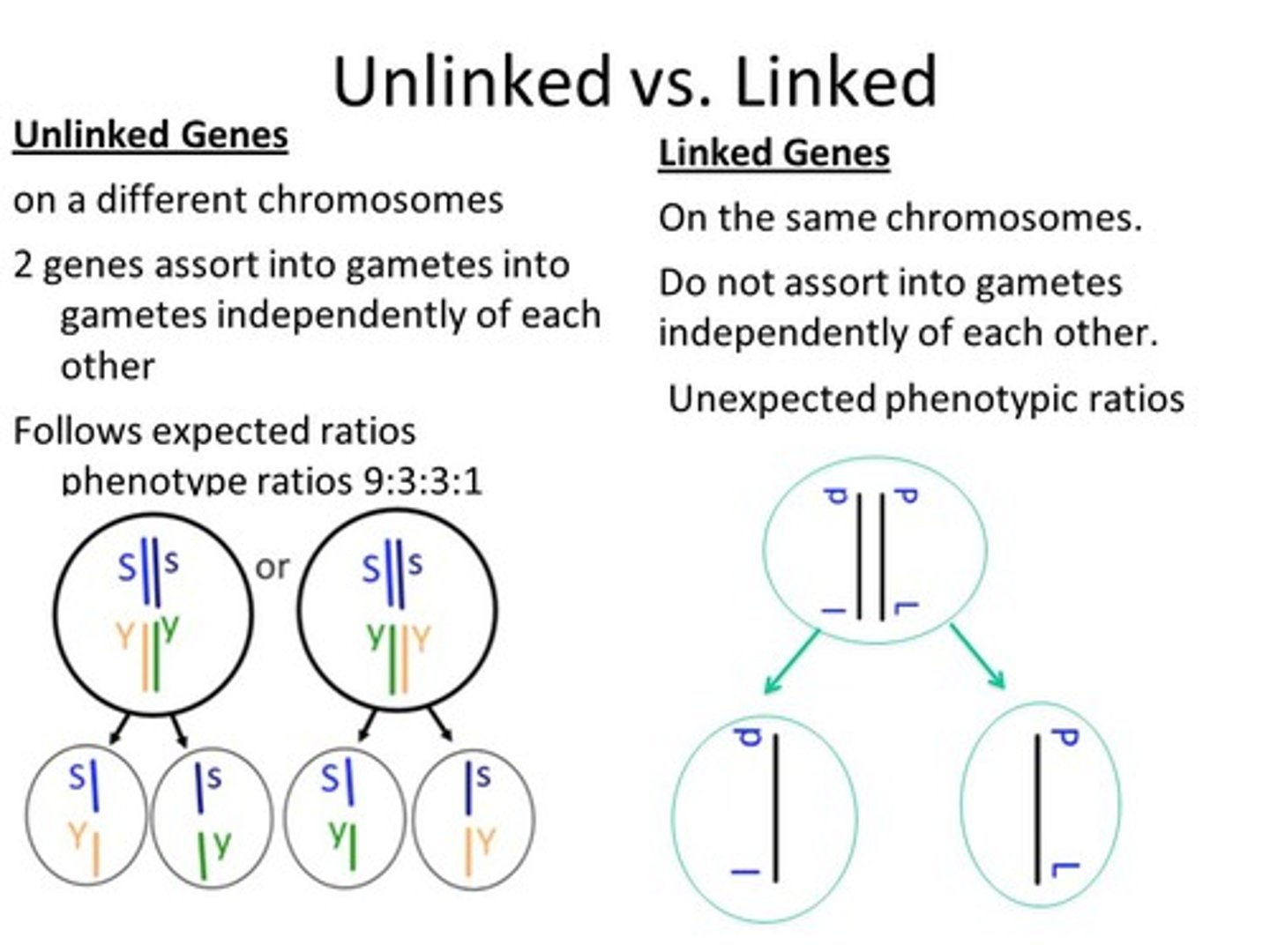
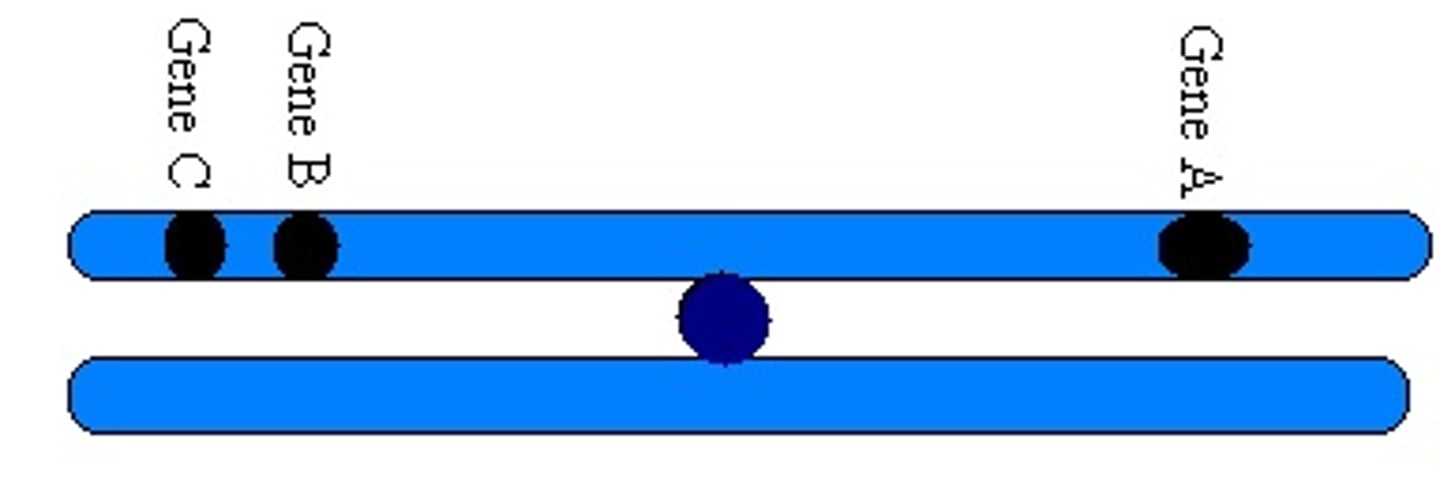
linked genes
Genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together in genetic crosses.
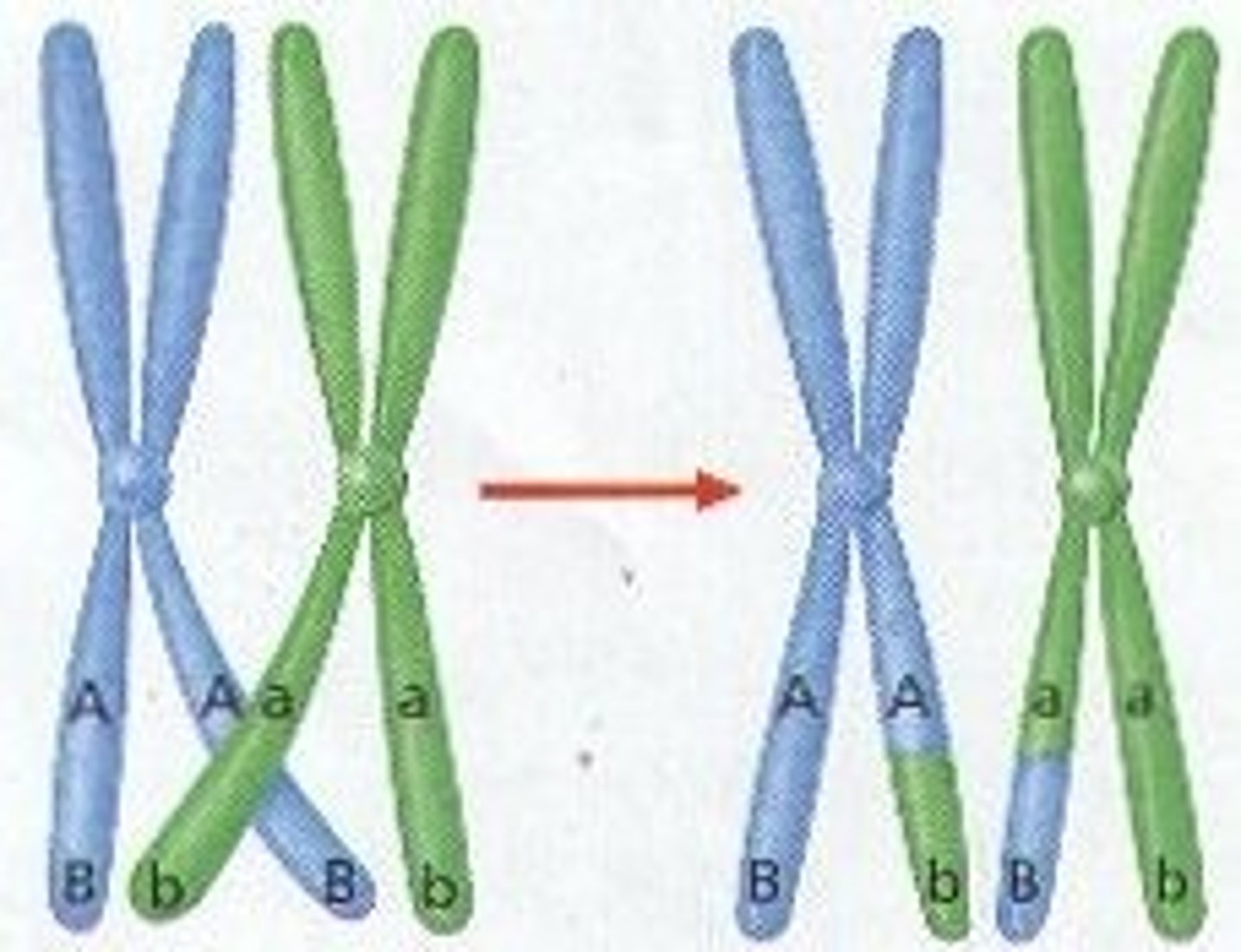
crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
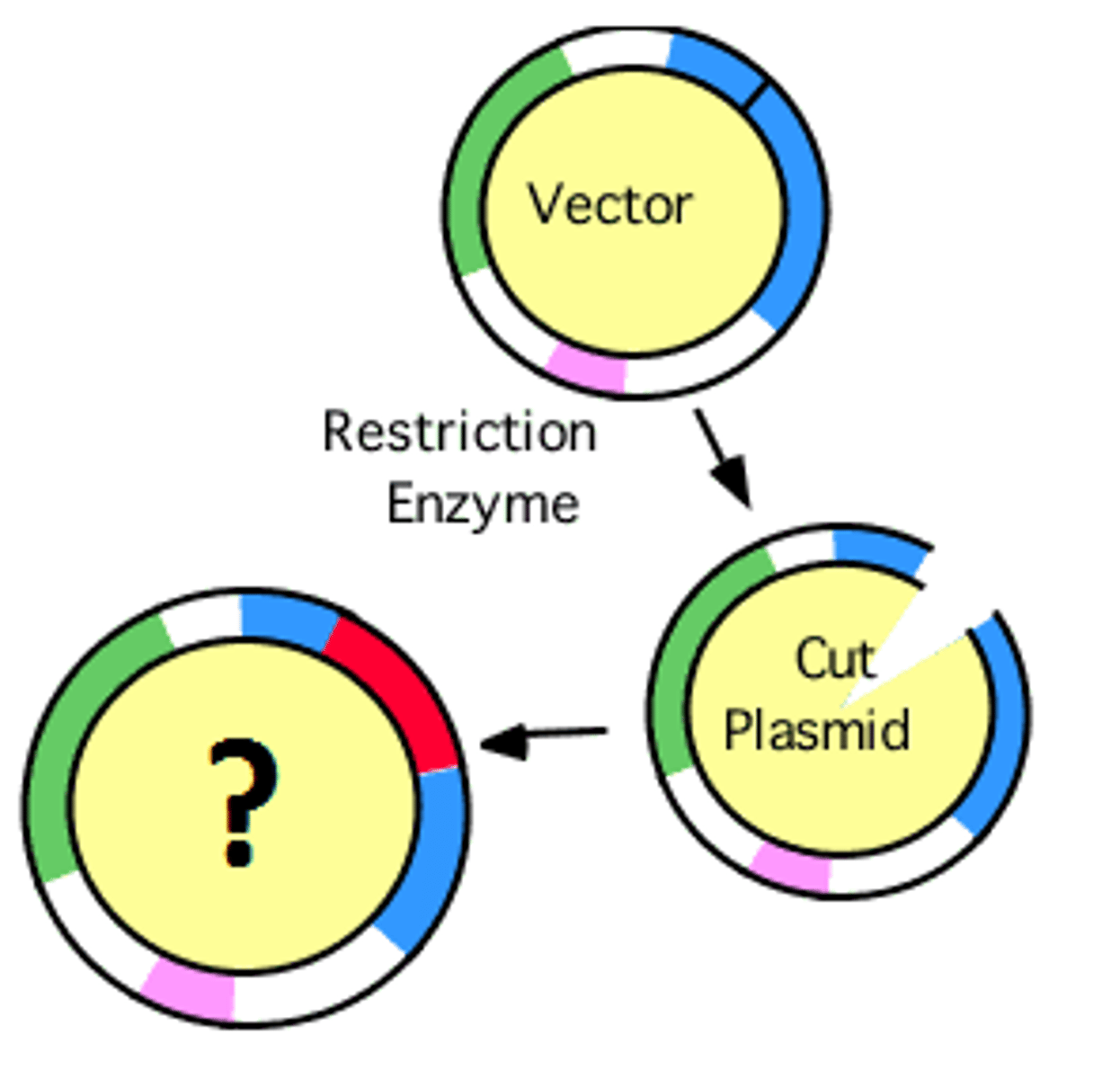
Recombinant DNA
DNA produced by combining DNA from different sources
parental chromosomes
retain the allele combinations from each parent
DNA
DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule that contains the genetic code that is unique to every individual
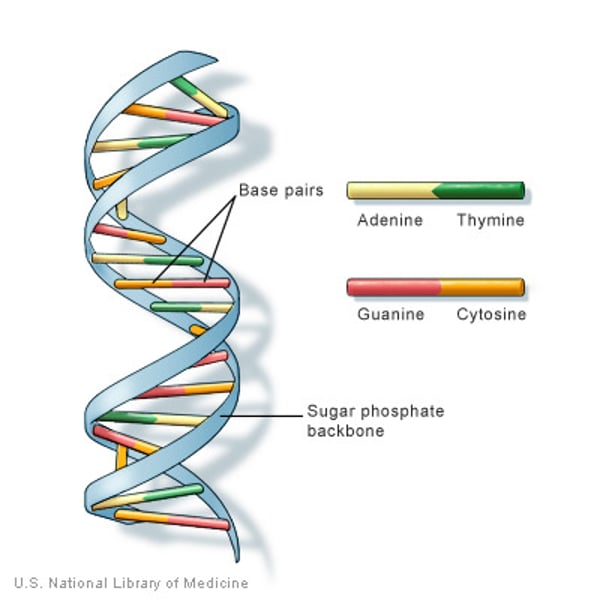
Nucleic acid
DNA and RNA
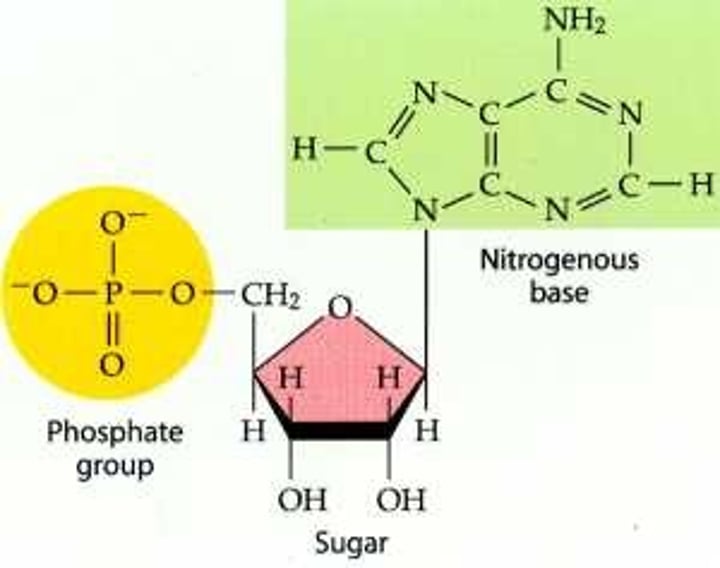
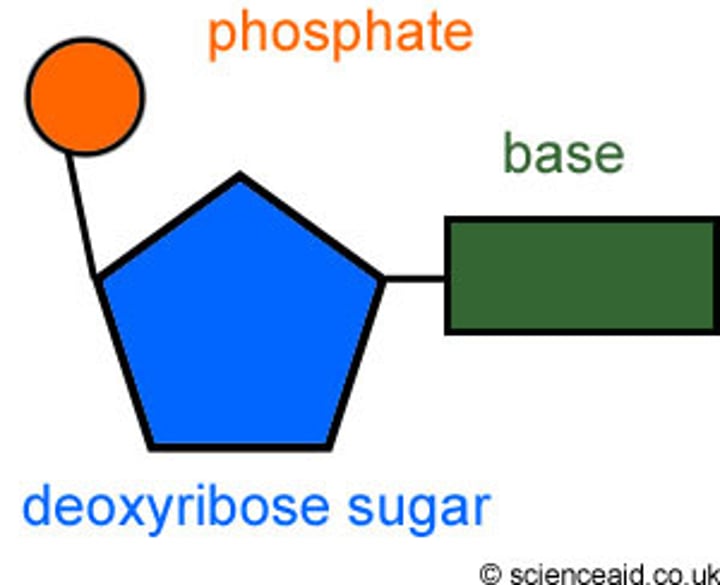
Nucleotide
A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
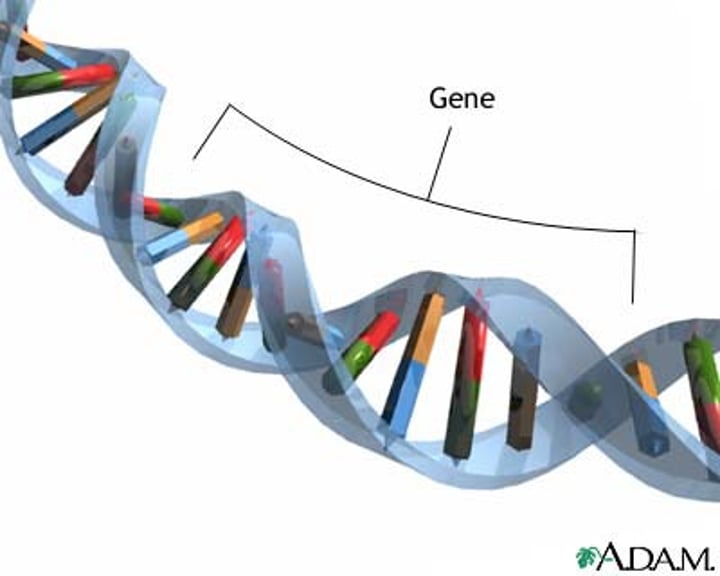
Gene
A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the offspring.
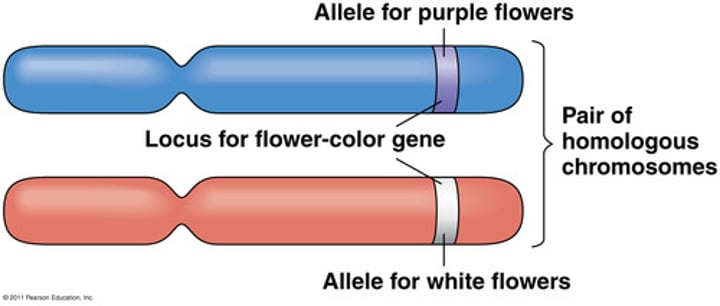
Allele
A variant form of a gene, which can result in different phenotypic traits.
Inheritance
The passing of genetic information from parents to offspring, determining the traits of the offspring.
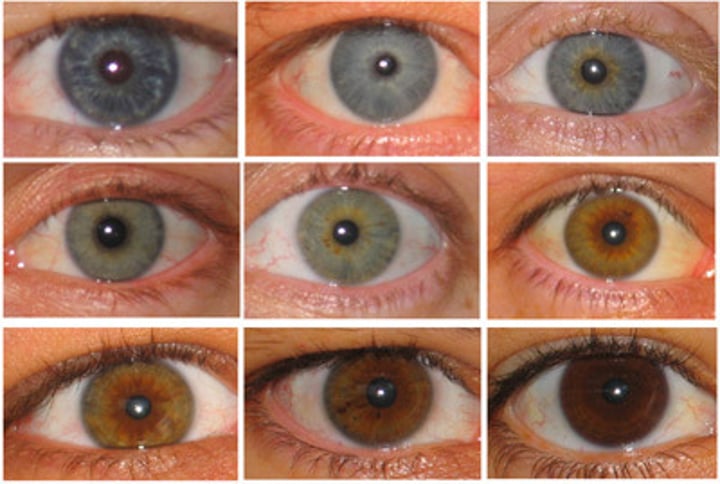
Phenotype
The observable characteristics or traits of an organism, resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment.
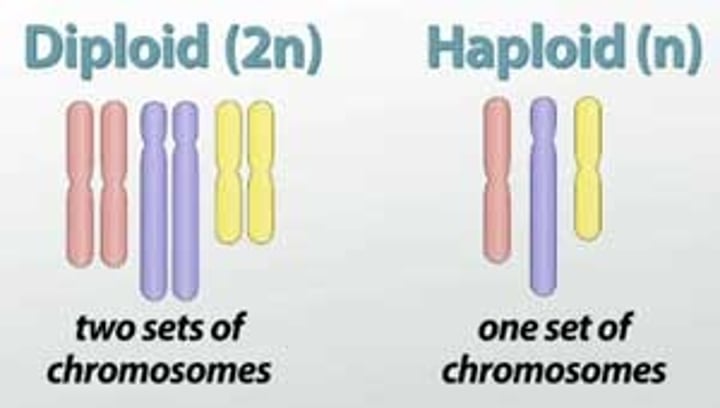
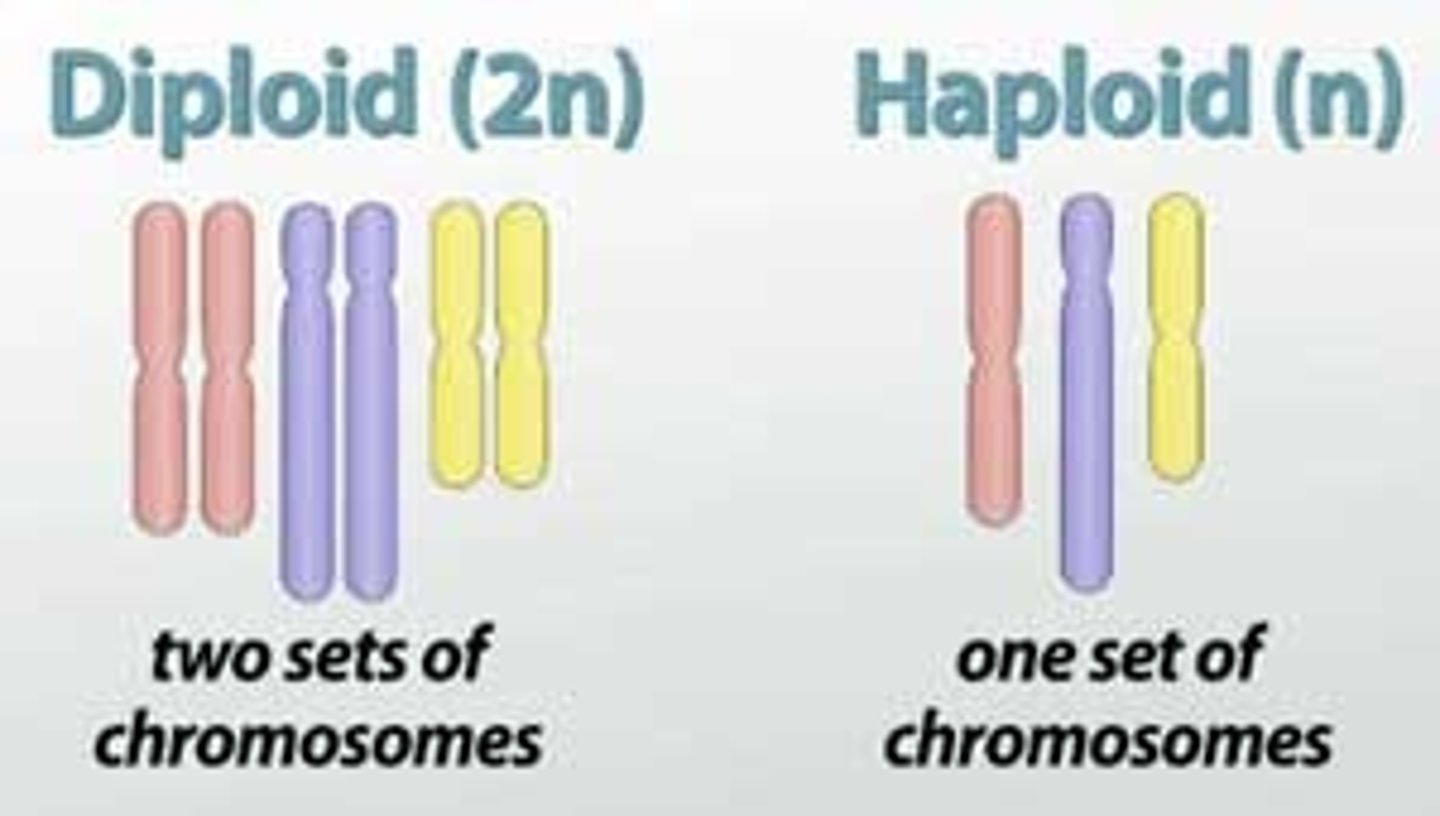
Haploid
Having a single set of unpaired chromosomes, typically found in gametes (sperm and egg cells).
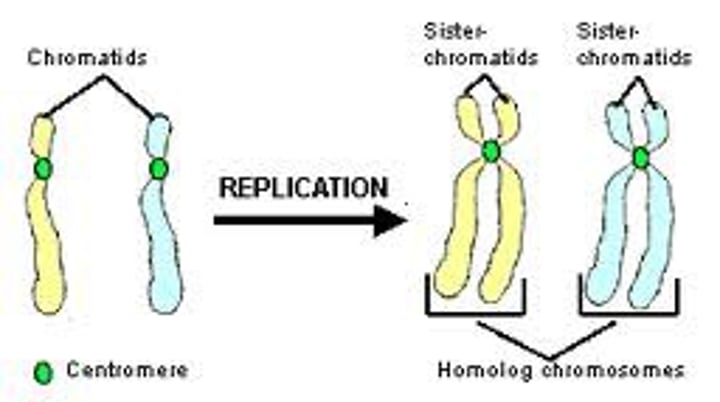
Chromatid
One of the two identical copies of a replicated chromosome, joined by a centromere.
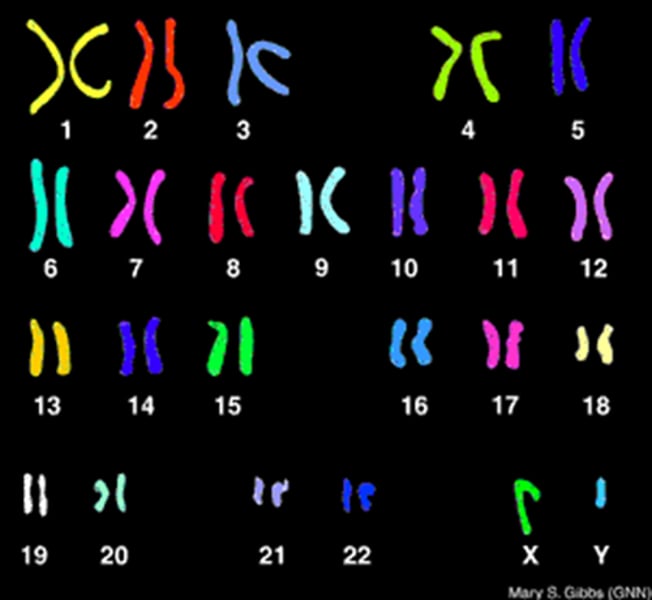
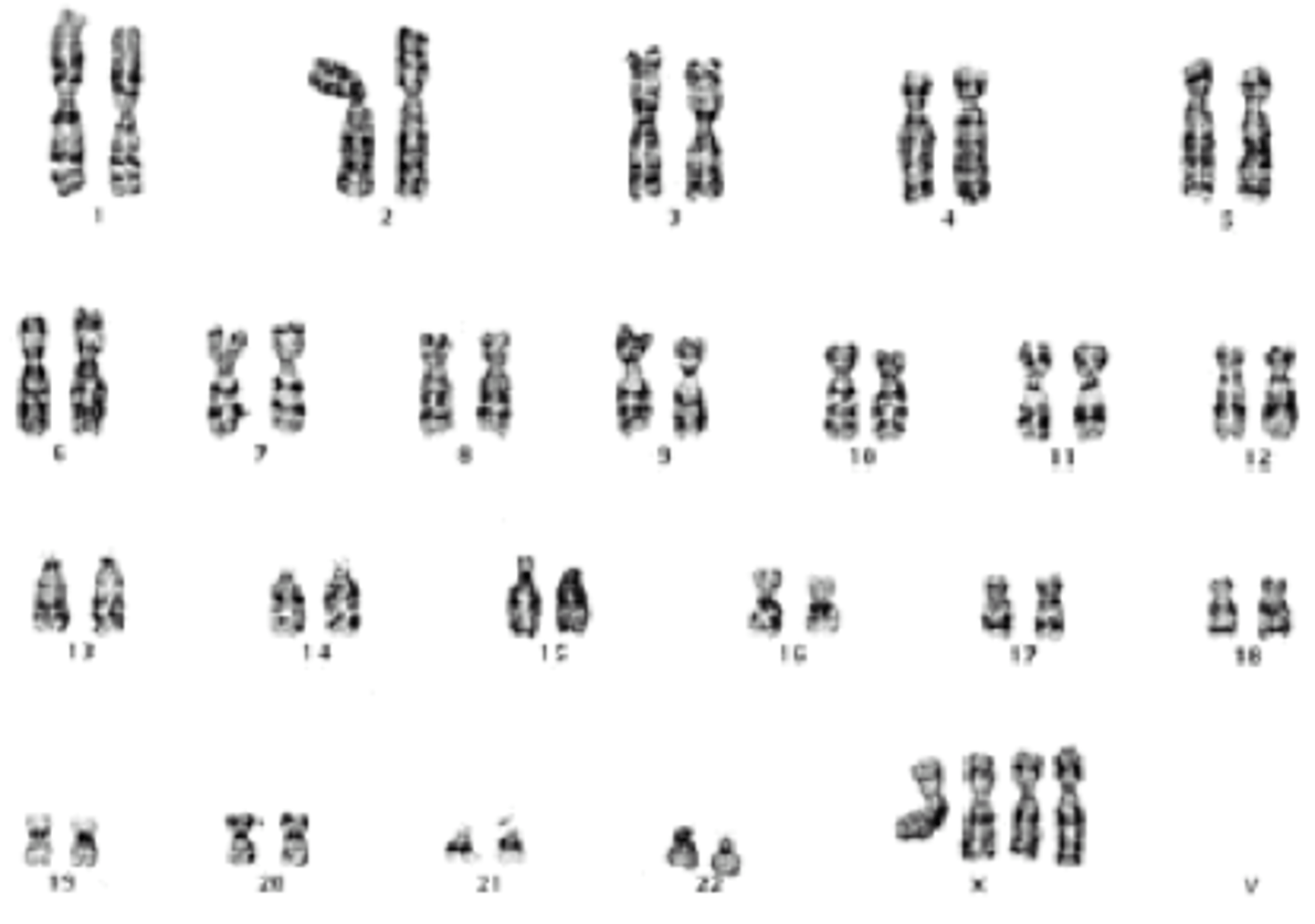
Karyotype
The number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, used to detect genetic disorders and chromosomal abnormalities.
Autosome
A chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, responsible for the inheritance of most traits.
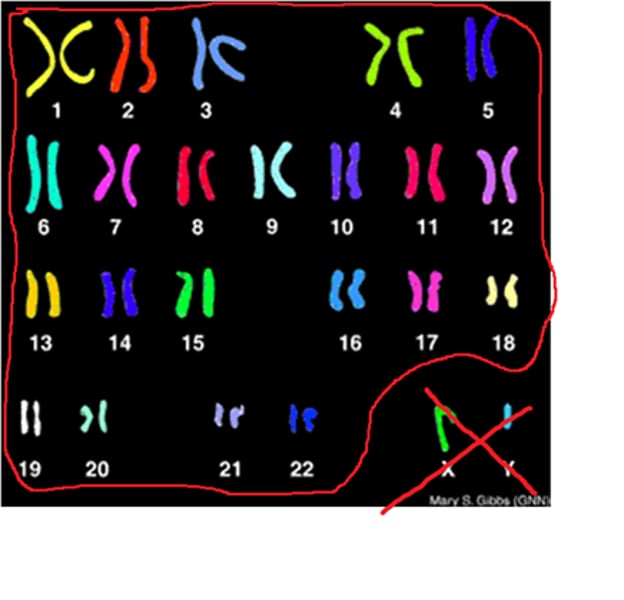
Sex chromosome
A chromosome involved in determining an individual's sex, such as the X and Y chromosomes in humans.
Aneuploidy
The presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, often leading to genetic disorders.
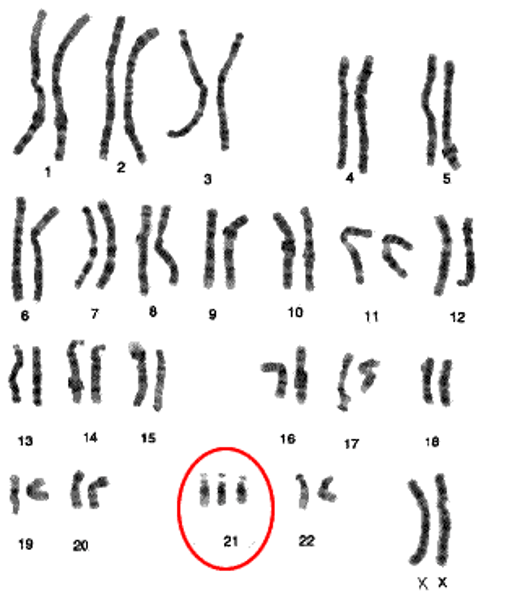
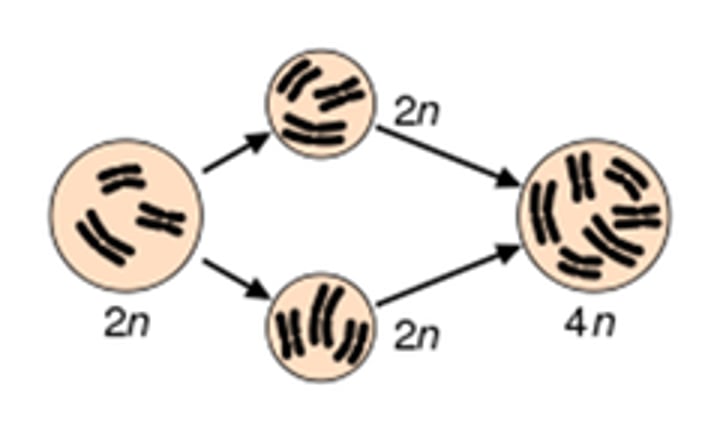
Polyploidy
(2)condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes
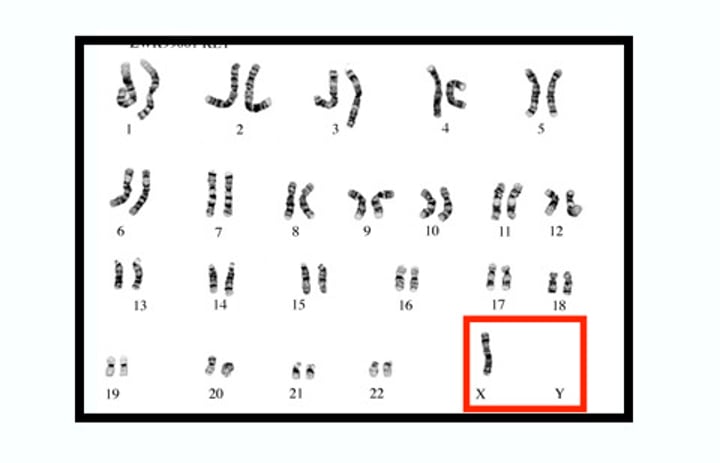
monosomy
Chromosomal abnormality consisting of the absence of one chromosome from the normal diploid number
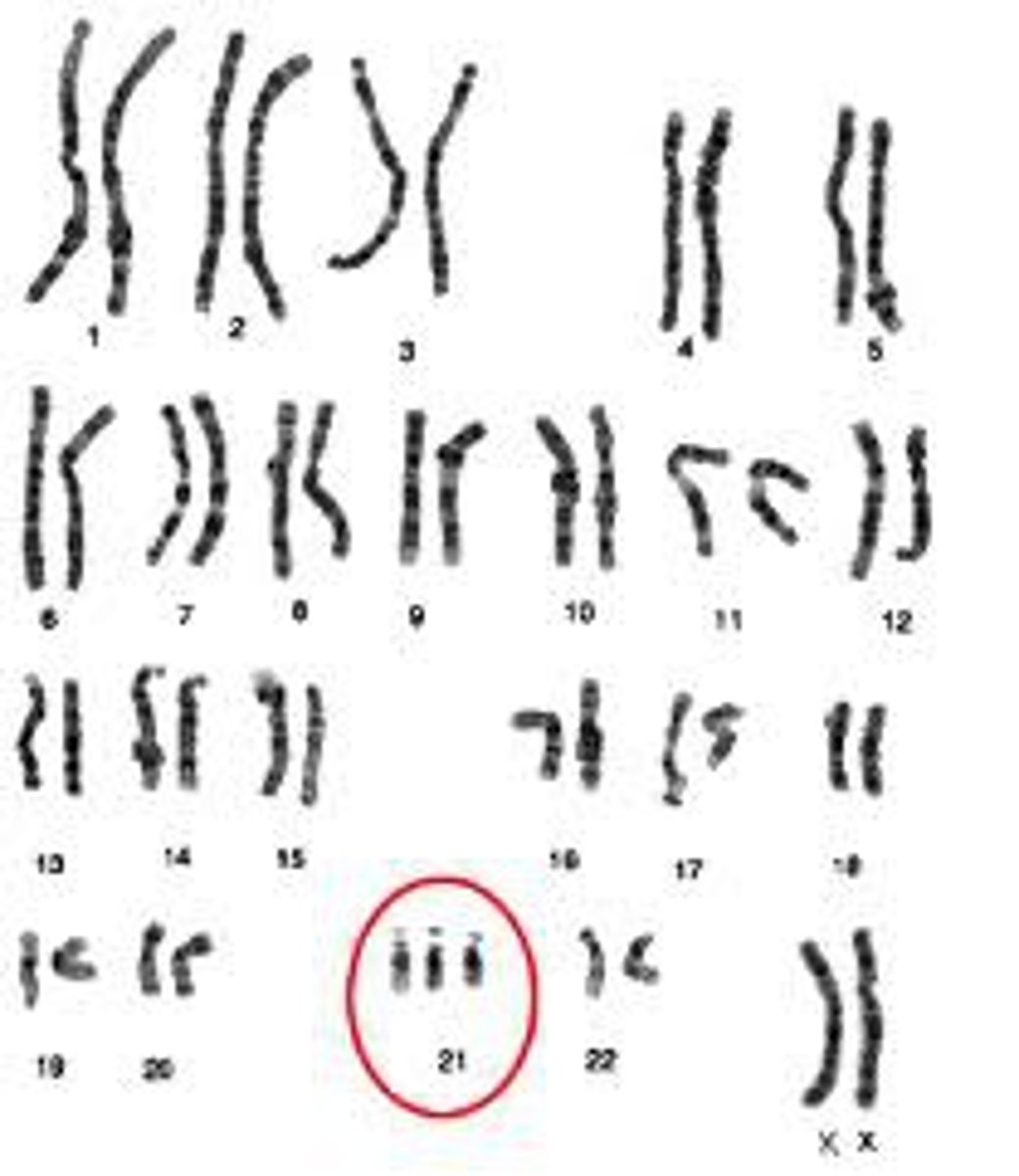
Trisomy
3 copies of a chromosome
Tetrasomy
gain of two homologous chromosomes (2n+2)
Homologue
One member of a homologous pair of chromosomes
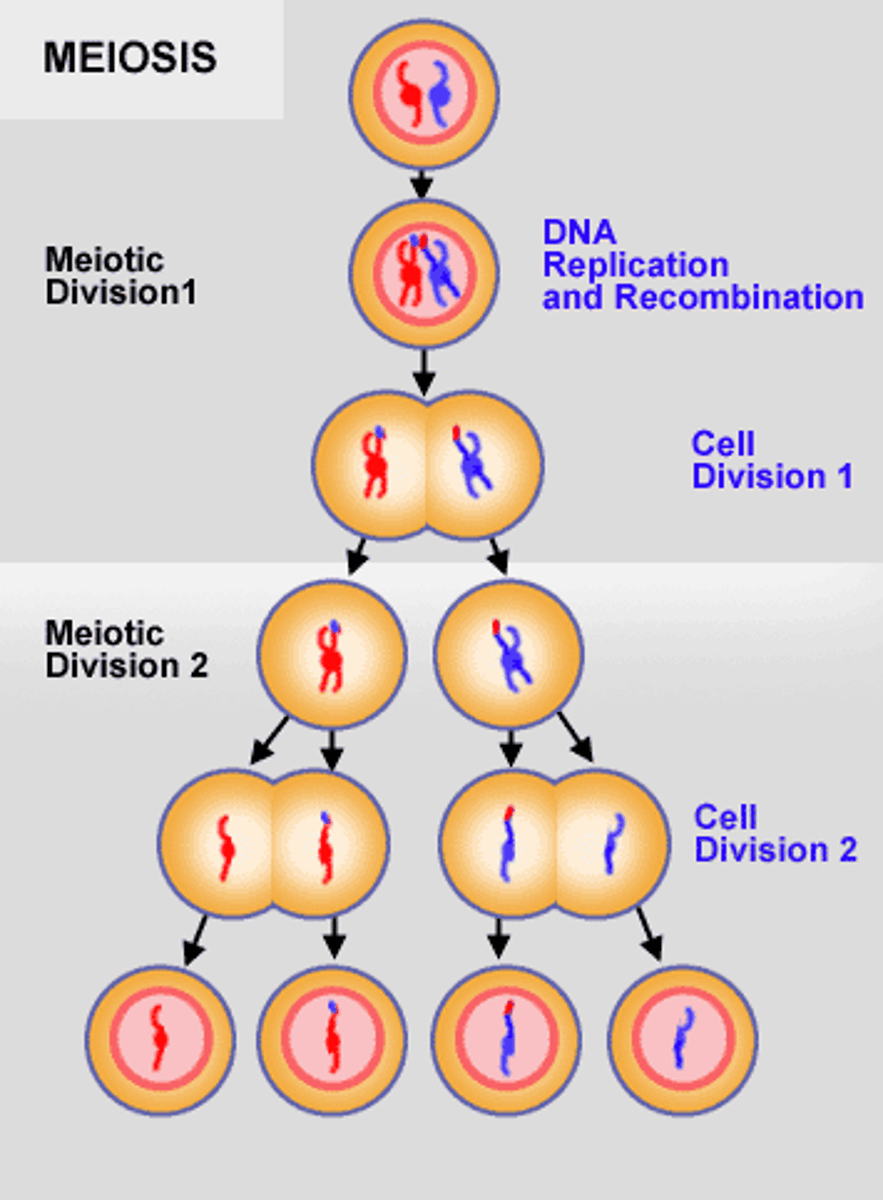
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
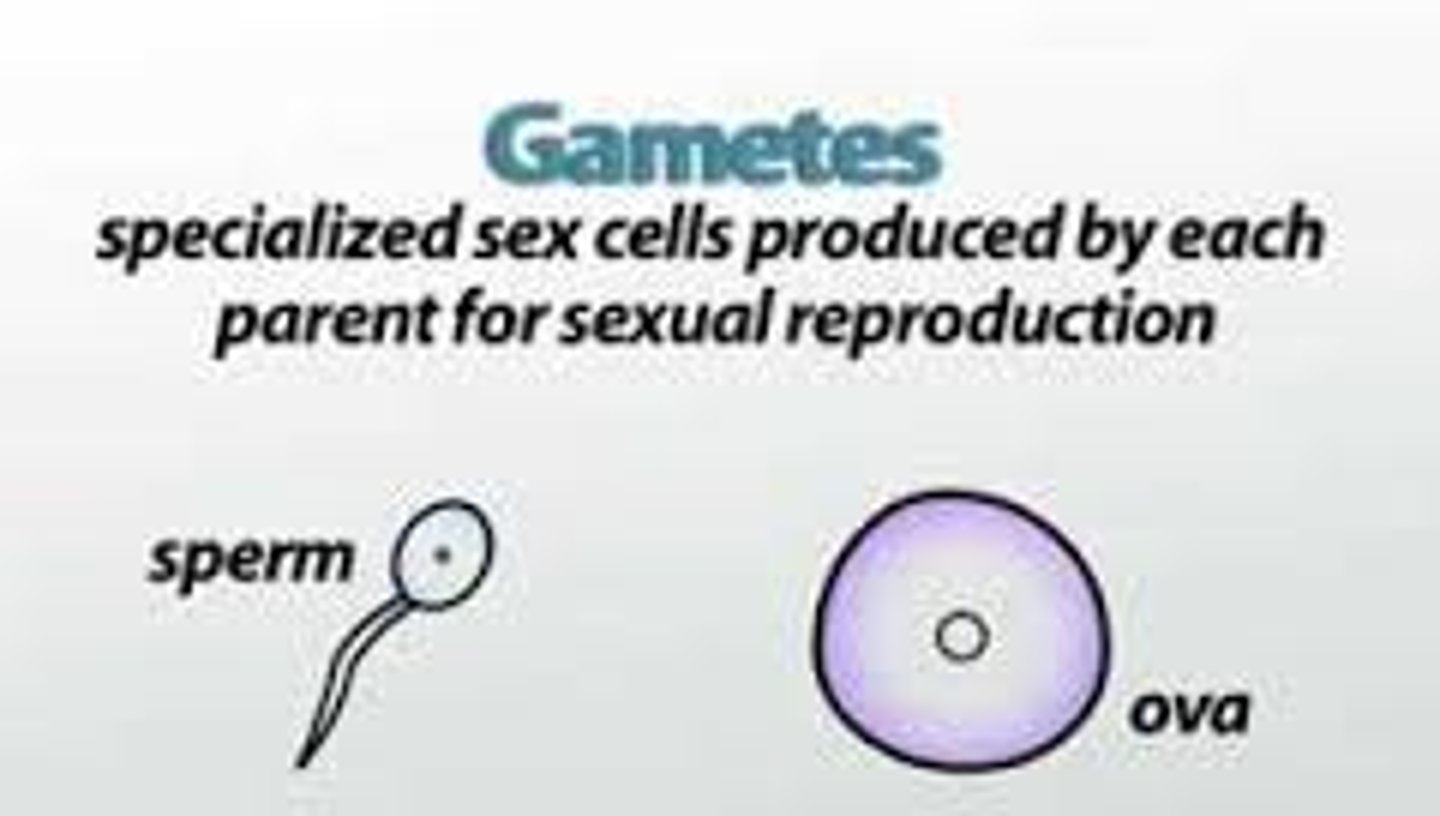
Gametes
sex cells
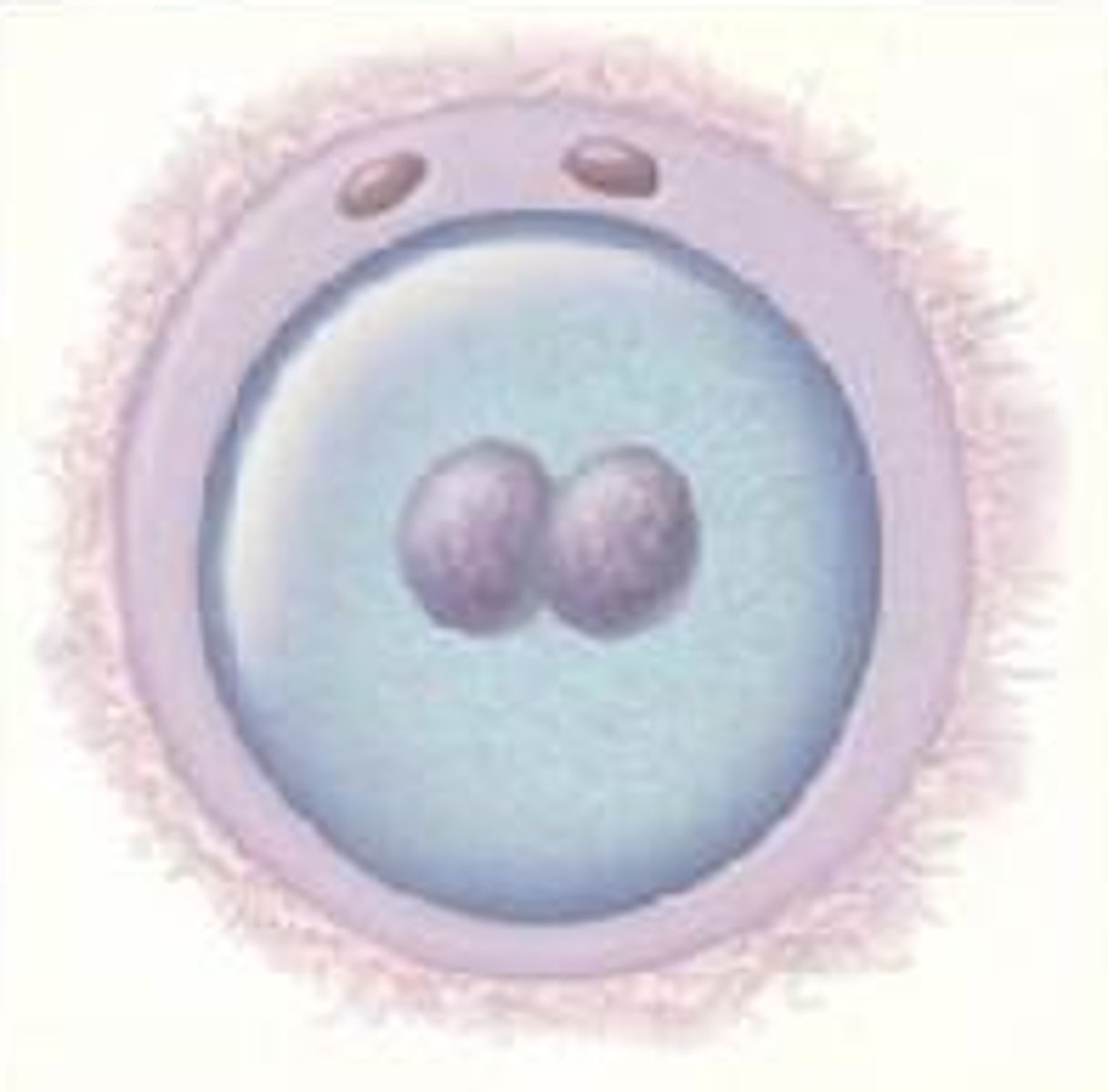
Zygote
fertilized egg cell that results from the union of a female gamete (egg, or ovum) with a male gamete (sperm)
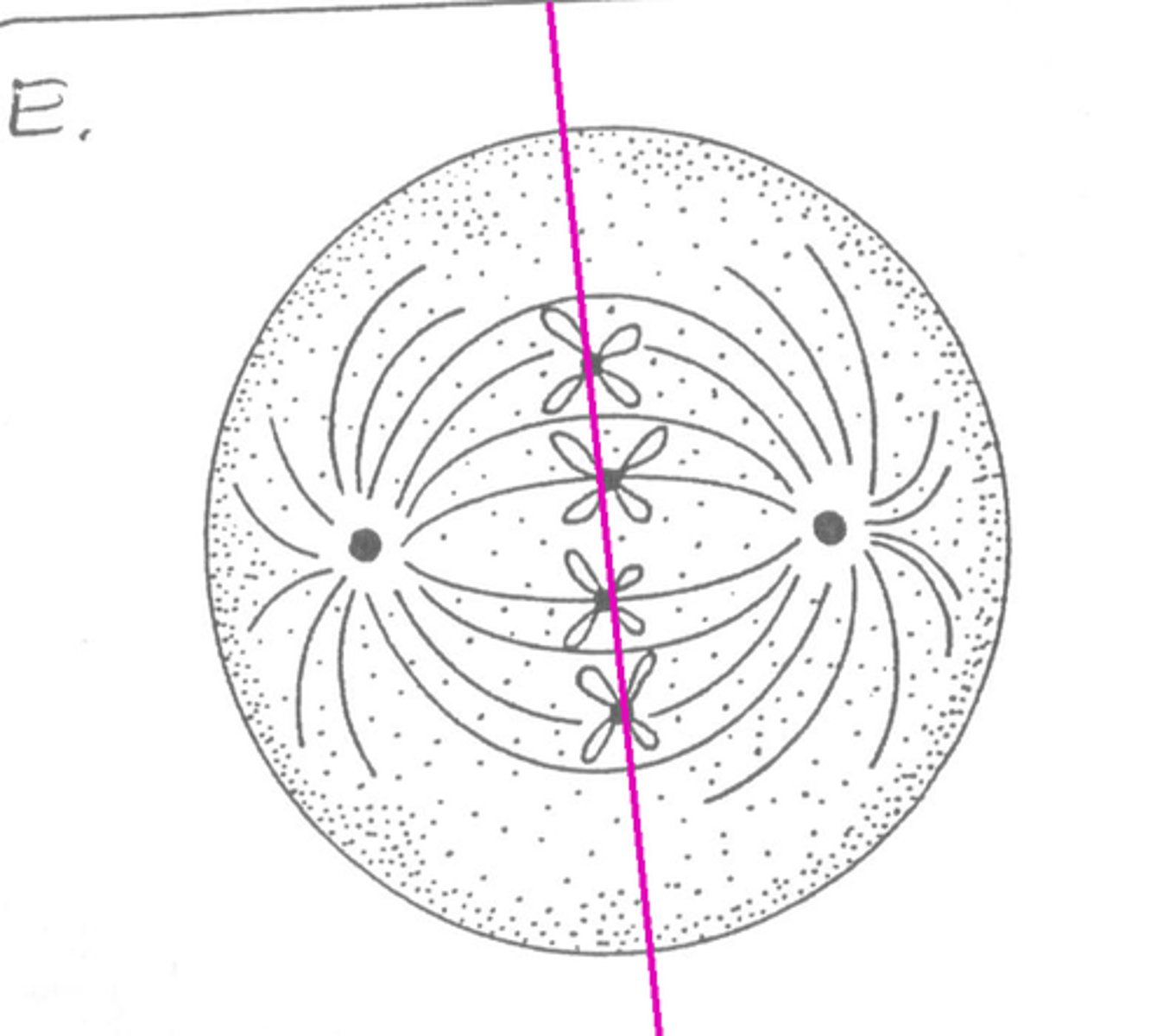
metaphase plate
Plane midway between the two poles of the cell where chromosomes line up during metaphase.
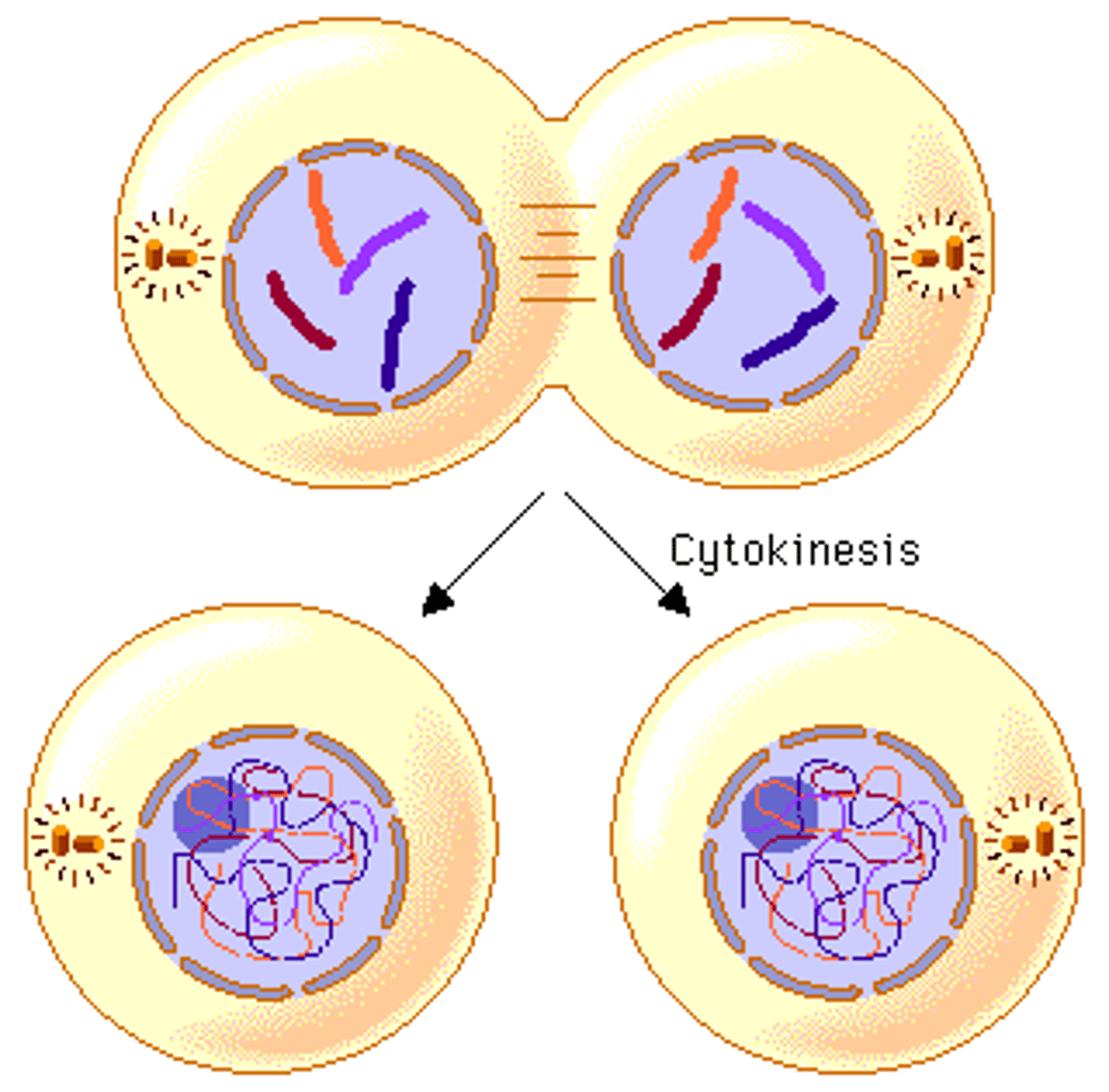
Cytokenis
The phase in the cell cycle that separates the cytoplasm forming 2 new cells
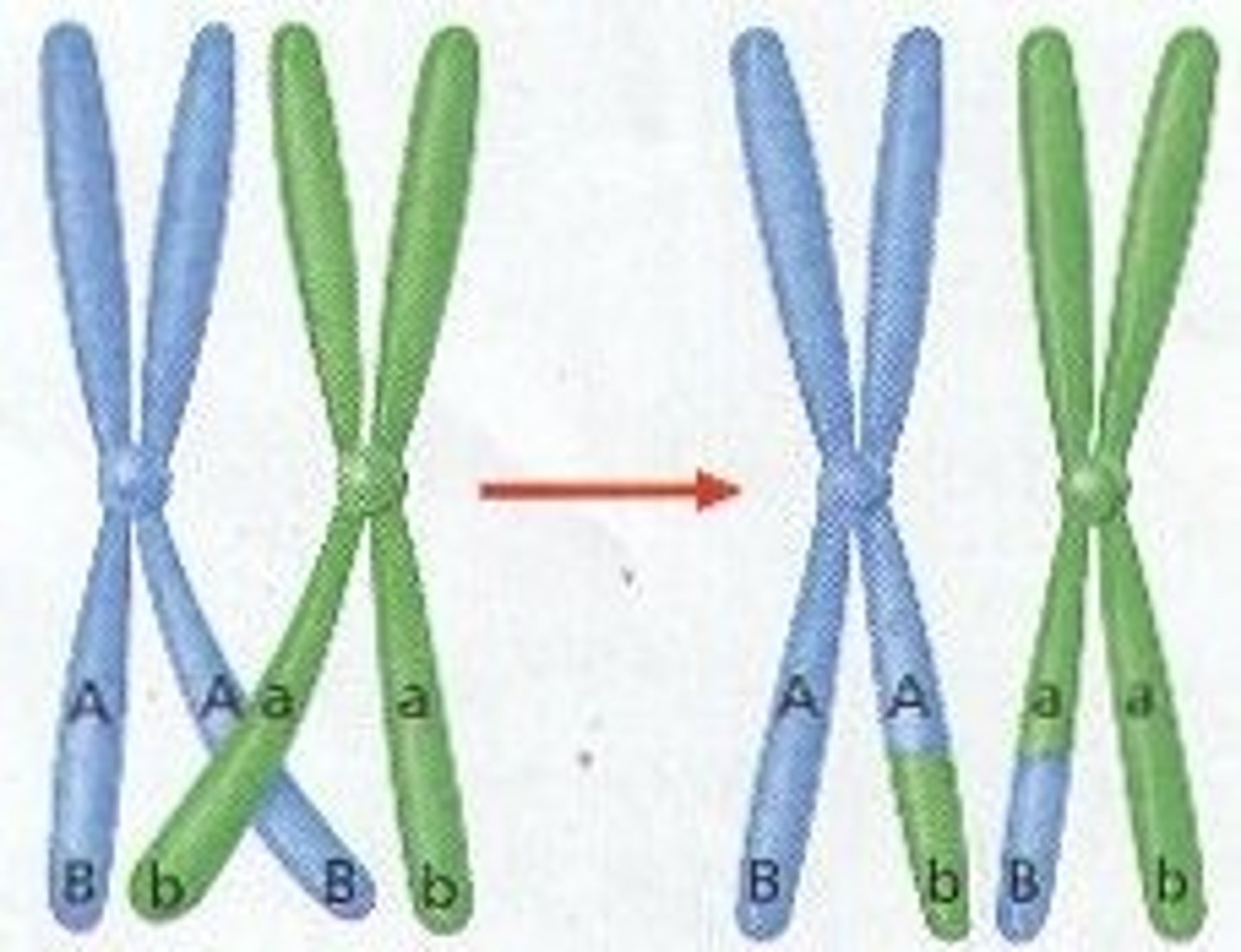
crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
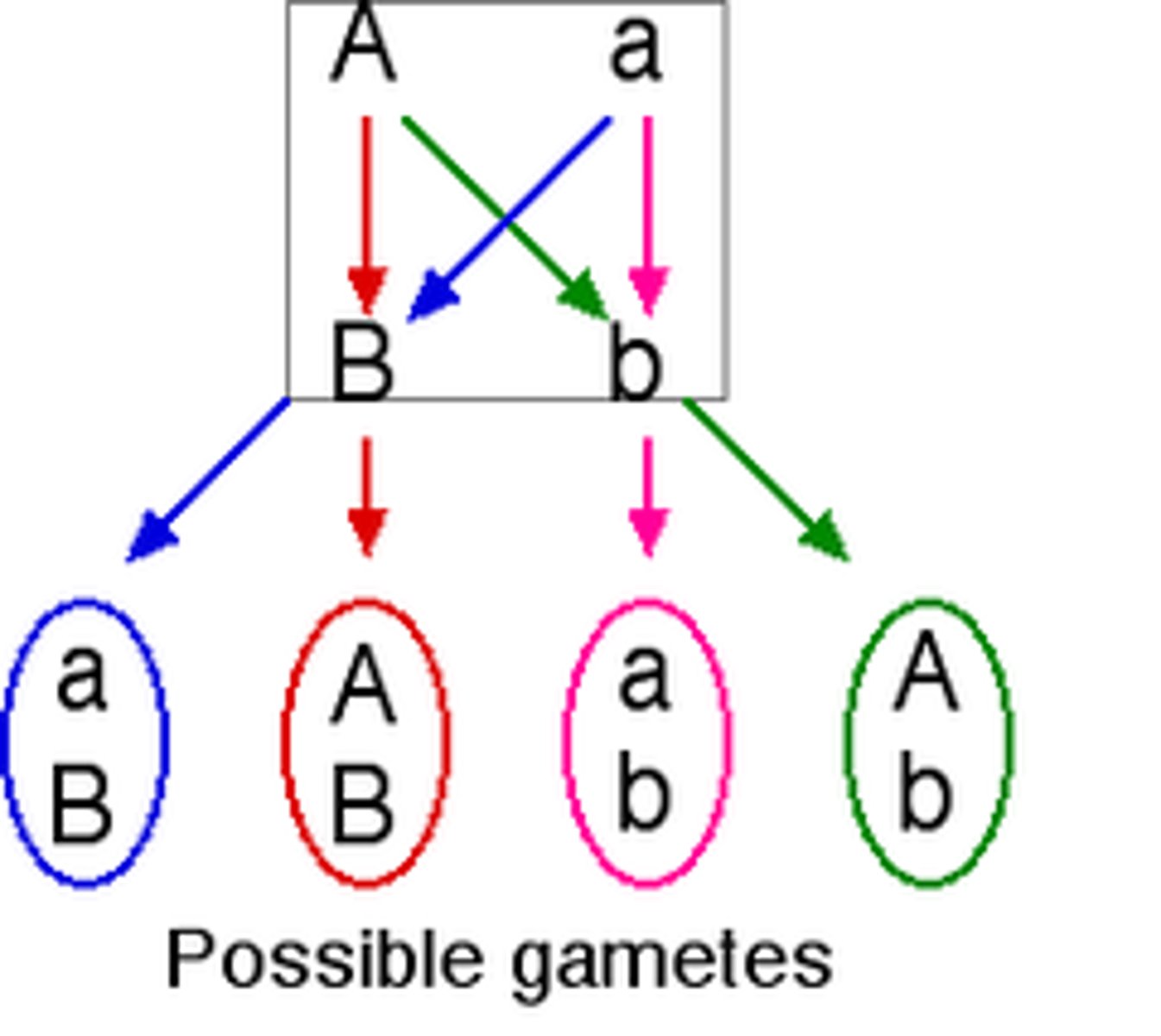
independent assortment
Independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes
dipolid
having two copies of each chromosome
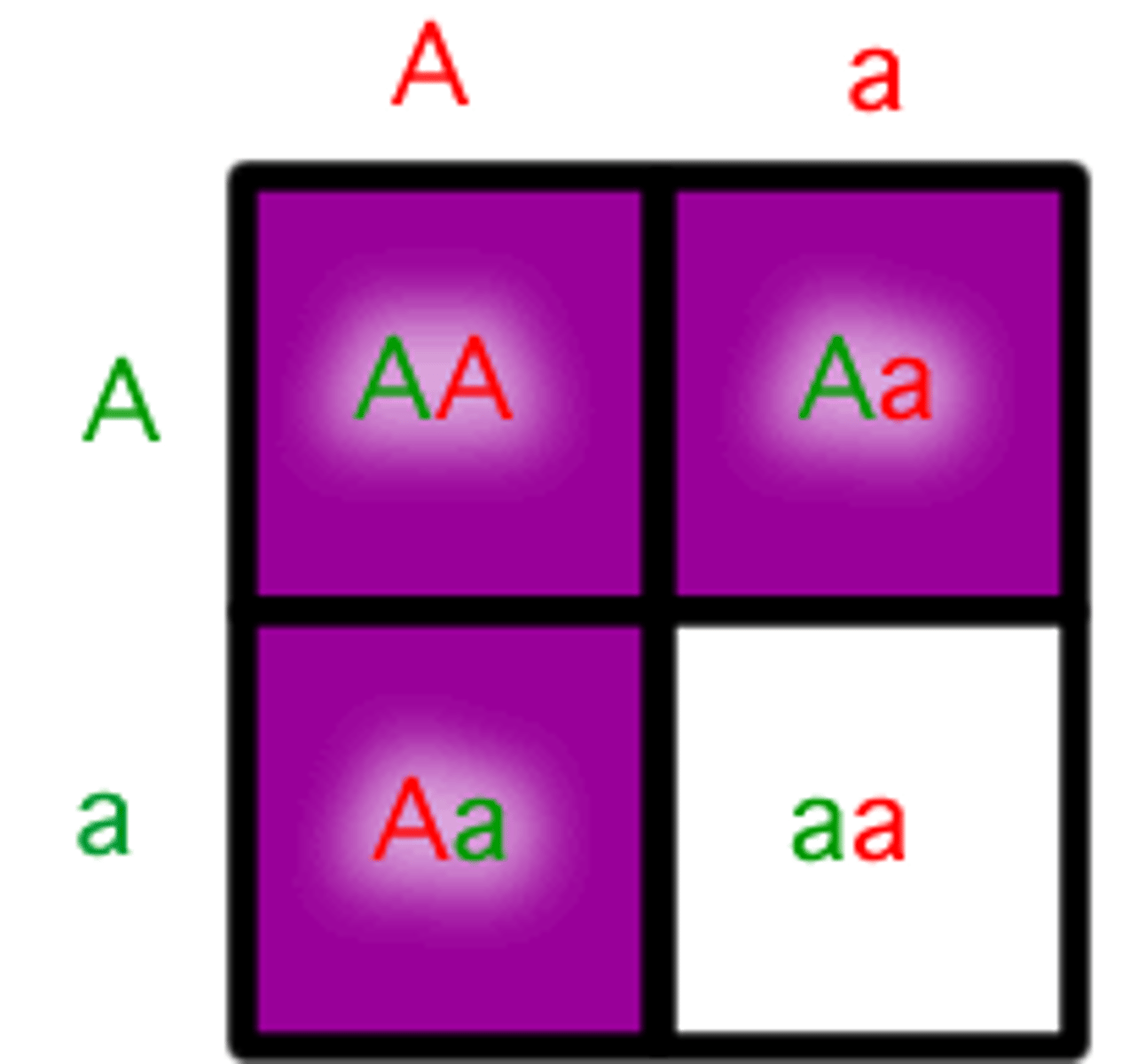
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait

Hetrozygous
individual that has two different alleles for a trait
dominant allele
An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present.
recessive allele
An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present
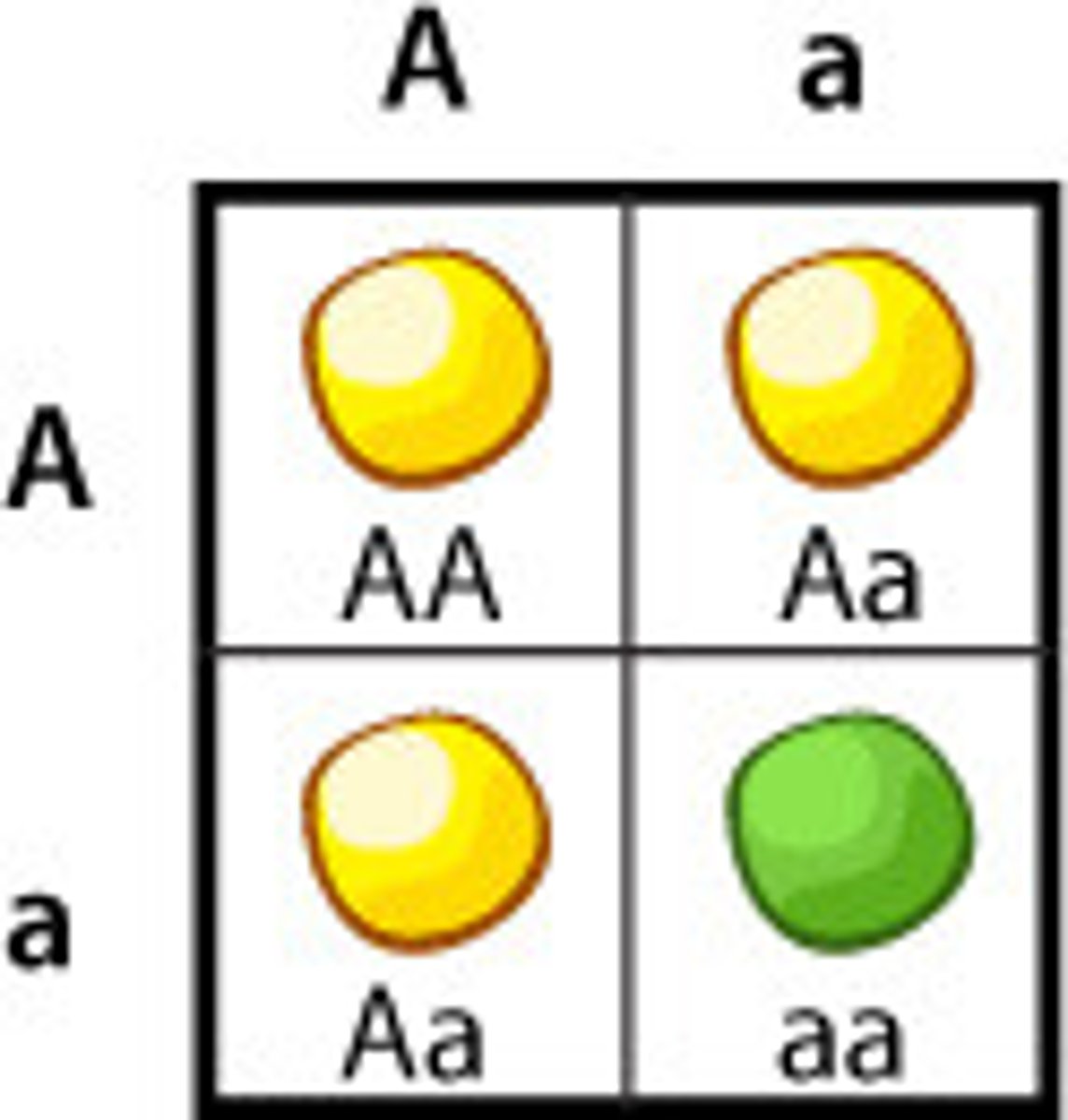
incomplete dominance
Situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele
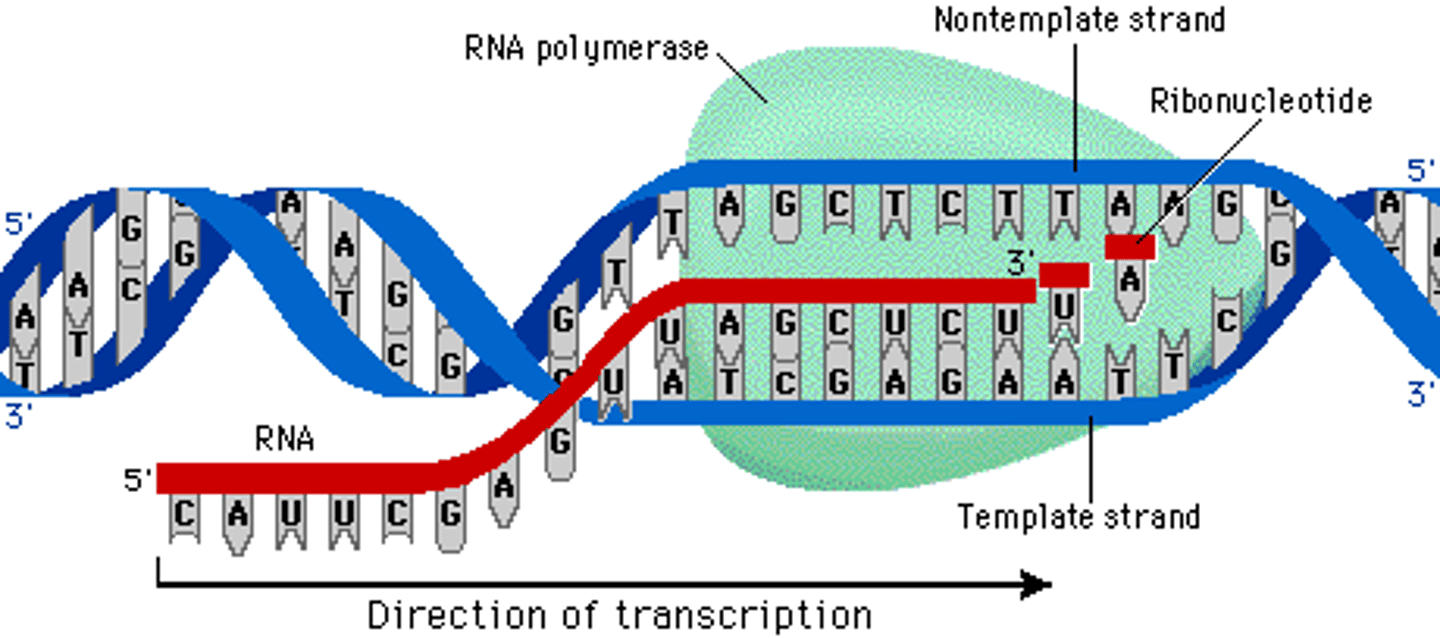
Transcrption
The first step of protein synthesis, in which the information on mRNA is "read" and translated into a sequence of amino acids, the building blocks of a protein
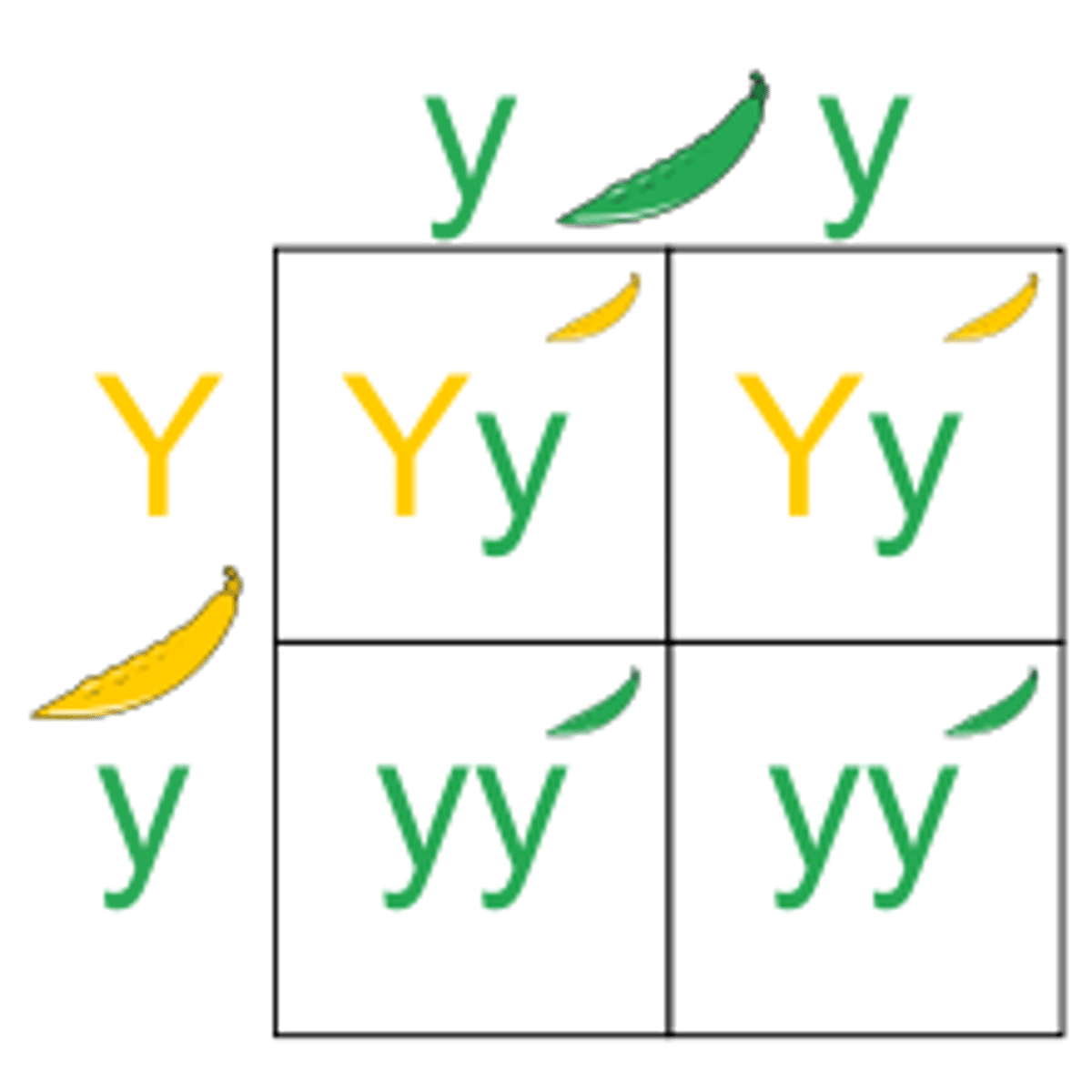
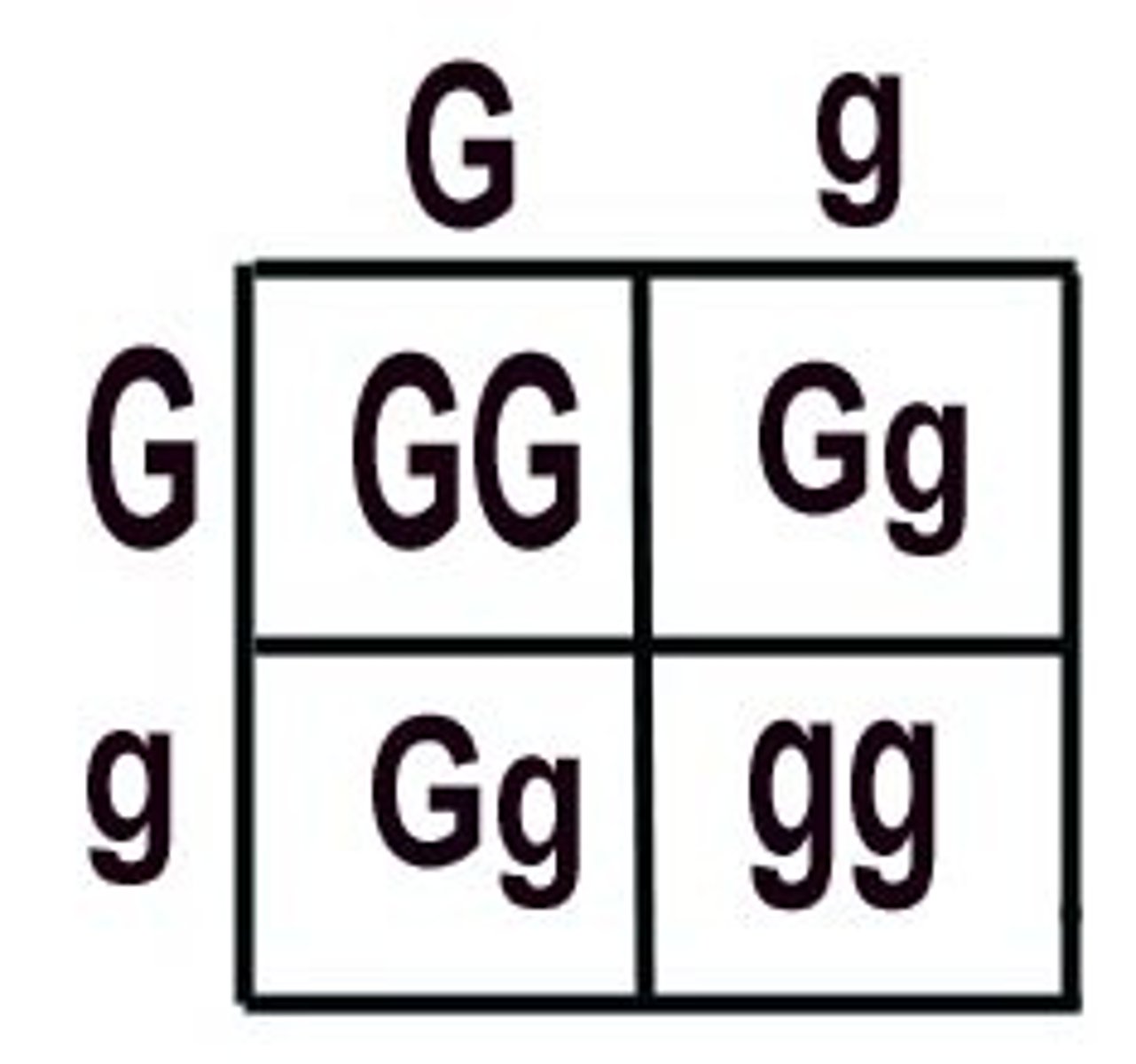
Punnett Square
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross
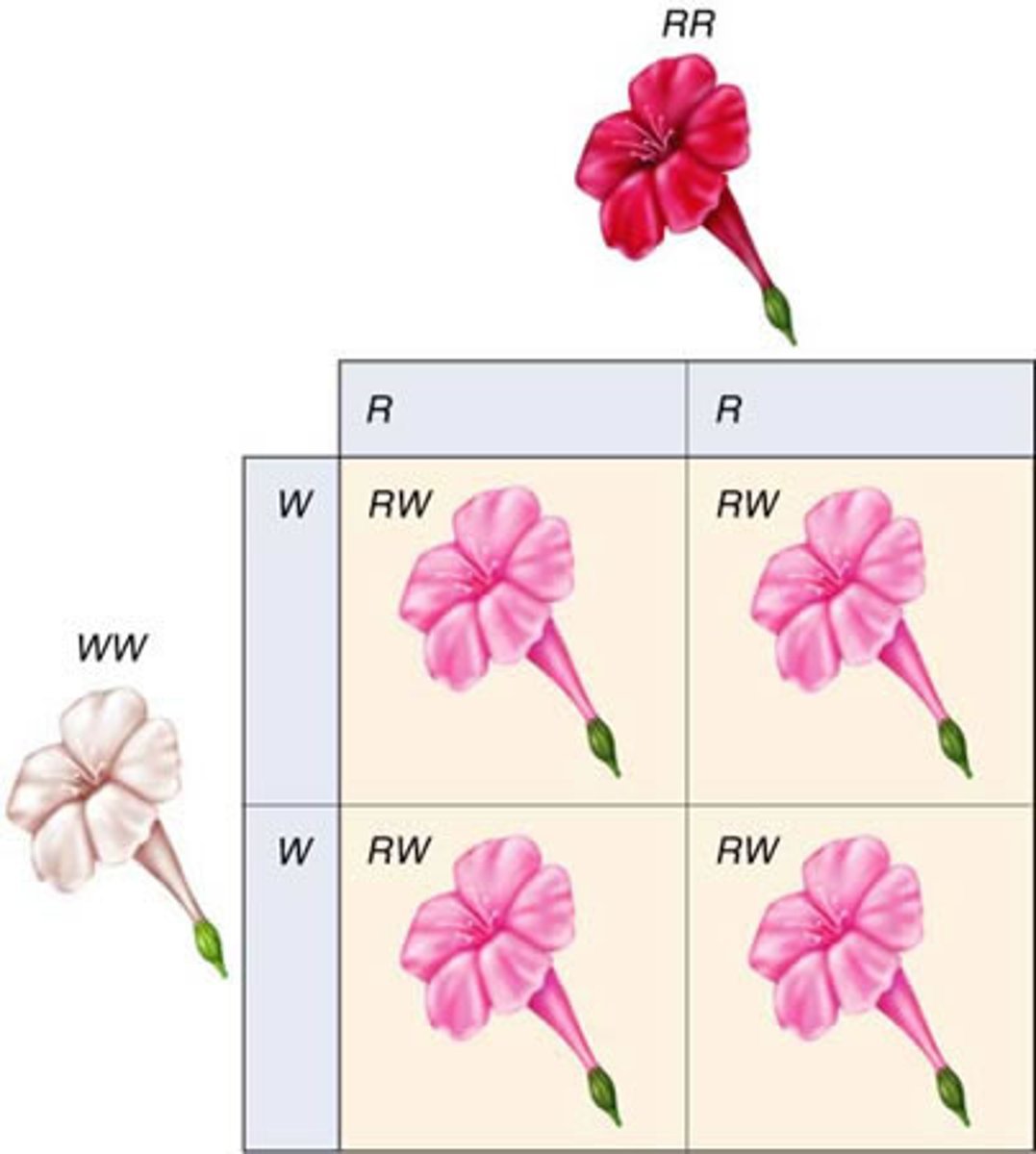
Codominance
A condition in which neither of two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive.