Material science - 1
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
metals & alloys characteristics
strong, tough, heavy + expensive
What is a polymer
Typically organic materials made of non-metallic elements such as C, H, O, N, S, Cl.
➢ Consisting of very large molecules that are composed of many repeating units.
polymer characteristics
light, cheap, soft & biofriendly
Ceramics
inorganic, non-metal solids
Ceramics characteristics
hard and usually brittle,
They have very high melting points → heat-resistant.
They have excellent chemical stability → oxidation-resistant
usually composed of oxides, carbides & nitrides
Glass characteristics
Stiff, quite strong, brittle & low toughness
Composites
Made by combining materials from the other three classes, To mix the properties of different materials.
Semiconductors
A material with
electrical conductivity between
that of a conductor (like metals)
and an insulator (like plastics)
Nanomaterials + examples
Have at least one dimension in the nanometre scale.
Eg. Graphene- A flat layer of carbon atoms.
• Carbon nanotube- A rolled-up layer of carbon atoms
Natural materials
Found in nature, not significantly altered by human processes.
Isostatic pressure
occurs when a solid is subjected to equal compressive
stresses (or pressure) on all sides
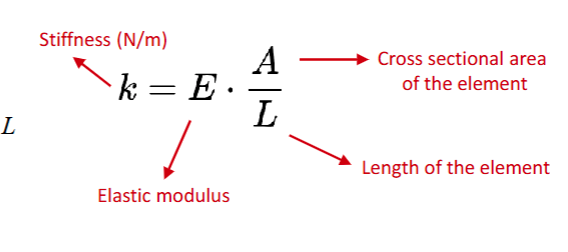
Stiffness
The stiffness of a material is its ability to return to its original shape after
an applied force is removed
Youngs modulus (E)
Slope of stress-strain graph during elastic region
E is an intrinsic property, independent of
the size or shape of the sample.
E is associated with stiffness of a material.
relationships between engineering stress/strain and true stress/strain

What is barrelling & how can it be minimised
Barrelling is the generation of a convex surface on the exterior of a
cylinder under compression. This happens due to friction between the
sample and the anvil that applies the load.
✓ This problem can be minimized by lubricating the anvils and the end
surfaces of the specimen.
what is hardness
Hardness is resistance to localized plastic deformation induced by either
mechanical indentation or abrasion
Hardness testing
Brinell test → steel sphere
o Rockwell test → steel sphere
→ diamond cone
o Vickers test → diamond pyramid
characteristics of tough materials
1) They fail only after absorbing
a lot of energy.
2) They strain a lot before failing
(i.e. they are ductile)
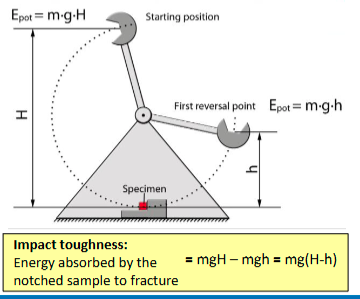
Notch toughness test
A material's ability to absorb energy and resist fracture when subjected to a
sudden impact or shock load.
The energy absorbed in fast fracture of a specimen that contains a notch
fracture toughness
Fracture toughness describes the ability of a
material containing a crack to resist fracture
under tensile stress.
(i.e. material's resistance to crack propagation)
fracture toughness vs crack length
fracture toughness is inversely proportional to square root of crack length.
Q is a constant, called the geometrical factor (usually ~ 1.0 )
Kc is called the critical stress intensity factor
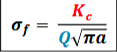
What is necking
In a ductile material under tensile loading, after reaching the ultimate tensile strength (UTS), the specimen no
longer deforms uniformly.
Instead, a localized deformation point (a “neck”) forms, usually at some weak point along the gage length.
From that point, further deformation is concentrated in the necked region rather than distributed uniformly.