Disease Detectives
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Scioly Disease Detective events
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Epidemiology
The study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states or events in specified populations, and the application of this study to the control of health problems.
Frequency
The number of health events and its relationship to the size of the population
Pattern
The occurrence of health-related events by time, placement and person.
Determinants
Any factor, whether event, characteristic, or other definable identity that brings about a change in a health condition or other defined characteristic
Endemic
Regularly occurring in an area or community
Public health surveillance
Ongoing, systematic collection, analysis, interpretation, and dissemination of health data to help guide public health decision making and action. Essentially equivalent to monitoring the community
Field investigation
Results from surveillance. It may be limited, like a phone call, or could be coordinated efforts of many people to characterize the extent of an epidemic and its cause.
Analytic studies
Designing, conducting, analyzing, and interpreting a study to investigate an outbreak further
Effectiveness
The ability of a program to produce the intended or expected results in the field
Case definition
A set of standard criteria for classifying whether a person has a particular disease, syndrome, or other health condition.
Case classifications
Suspected, probable, confirmed
Rate
# of cases/size of population per unit of time
Descriptive epidemiology
Covers time, place and person
Secular (long-term) trends
Graphed over years or long periods of time
Epidemic period graph
y axis: # of cases
x axis: time period
Displayed as a histogram with boxesS
Spot map
A map used for clusters or outbreaks with limited case numbers. An x or dot is marked on the location most relevant to the disease of interest (ex: John snow’s cholera investigation)
Personal characteristics
Are analyzed because they can affect illness. The two most common are age and gender at birth, but ethnicity, race and socioeconomic status may also be considered
Analytic epidemiology
Uses observations made by descriptive Epidemiology to create and test hypotheses
Experimental studies
The investigator controls and manipulates variables, uses a controlled process of exposure, and then tracks the individuals or community over time to detect the effects of the exposure
Observational study
Observation of the exposure and disease status of each study participant (ex: John Snow cholera outbreak)
Cohort studies
Epidemiologist records whether or not a person was exposed or not, and then follows up to see if they developed the disease
Follow up or prospective cohort study
The participants are enrolled as the study begins and then followed over time to identify outcomes of interest
Retrospective cohort study
The exposure and outcomes have already occurred
Case-control study
A type of observational study where a group of people with the disease is compared to a group without the disease to compare previous exposures between the two groups. They can then estimate what exposure caused the disease based on the differences between the two groups.
Cross sectional study
A type of observational study that measures exposure and disease status at the same time. It is often used to assess the prevalence of a disease without considering the duration.
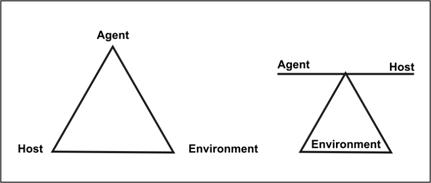
Epidemiologic triad
A traditional model for causation of infectious disease. It consists of an agent, a susceptible host, and an environment that brings the host and the agent together
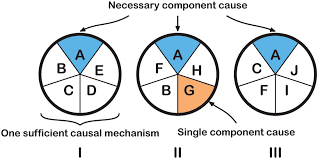
Causal pies
Individual factors that contribute to the diseases make up the pie, called component causes, build up to make a full pie that might be a causal pathway, called a sufficient cause. A component that occurs in every pathway is known as a necessary cause
Natural history of a disease
The progression of a disease process in an individual over time in the absence of treatment
Incubation period (infectious diseases) or latency period (chronic disease)
The time between exposure to the disease and onset of disease symptoms. It is harder to detect diseases during this period, but treatments are often more effective if administered.
Subclinical disease
A condition where the diseased state has begun, but no symptoms have yet occurred
Clinical disease
A condition in disease where symptoms have begun
Spectrum of disease
The range in severity of an illness from being hidden (subclinical) to being severe or fatal.
Infectivity
The proportion of people exposed to an infectious agent that become infected
Pathogenicity
The proportion of infected individuals who develop clinically apparent disease
Virulence
The proportion of clinically apparent cases that are severe or fatal
Carriers
People who are infectious but have subclinical diseases
Chain of transmission
When an agent leaves its reservoir or host through a portal of exit, is conveyed through some mode of transmission, and enters through an appropriate portal of entry to infect a susceptible host
Resevoir
The habitat in which the agent normally lives, grows, and multiplies. May be human, animal, environmental
Portal of exit
The path by which the a pathogen leaves its host
Direct transmission
An infectious agent is spread from a reservoir to a susceptible host via direct contact or droplet spread
Indirect transmission
The transfer of an infectious agent from a reservoir to a host by suspended air particles, inanimate objects (vehicles), or animate intermediaries (vectors)
Vehicles
May indirectly transmit an infectious agent and include water, food, biologic products (blood), and other inanimate objects
Vectors
May carry an infectious agent through purely mechanical means or may support growth or changes in the agent, and include mosquitoes, fleas, ticks, and other organisms.
Portal of entry
The manner in which a pathogen enters a susceptible host
Interventions
Aimed at controlling or eliminating agent at the source of transmission, protecting portals of entry, or increasing host’s defenses
Endemic level
The amount of a disease that is usually present in a community
Sporadic
a disease that occurs infrequently or irregularly
Hyperendemic
When there is a high and persistent level of disease in an area
Epidemic
An often sudden increase in the number of cases beyond what is usually expected for a population in that certain area
Outbreak
Carries the same definition as epidemic, but usually used for a more limited area
Cluster
An aggregation of cases grouped in a place and time that are suspected to be greater than the number expected
Pandemic
An epidemic that has spread over several countries or continents, usually affecting a large number of people
Common source outbreak
An outbreak in which a group of people are all exposed to an infectious agent or toxin from the same sourve
Point-source outbreak
A type of common-source outbreak where the group is exposed over a brief period, so everyone becomes ill within one incubation period. The graph of this has a steep upslope and a gradual downslope
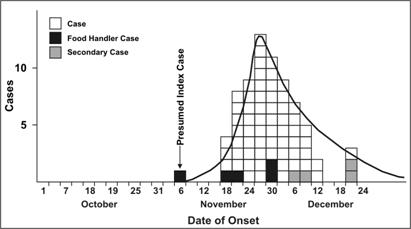
Continuous outbreak
A type of common-source outbreak where case-patients are exposed over a period of days, weeks, or longer
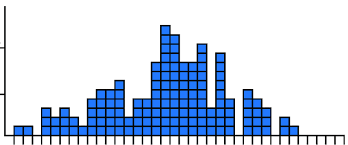
Intermittent outbreak
A common-source outbreak where the exposure to the disease is intermittent
Propogated aoutbreak
Results in transmission from one person to another. Cases here occur over multiple incubation periods
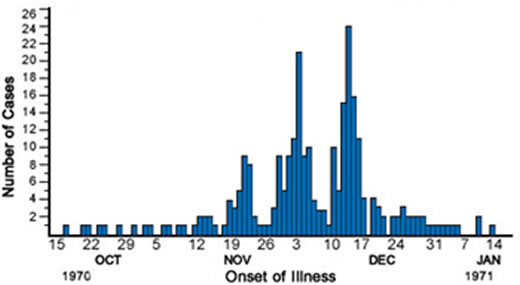
Mixed epidemics
Have features of both common-source epidemics and propagated epidemics. Occur often when a common-source outbreak is followed by a person-to-person spread.