Tableau Questions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is Data Mining?
It is the process of finding meaningful patterns/knoweldge from large datasets
What are Descriptive Tasks in Data Mining?
Looking at past data to find patterns and relationships on why that happened
What are some Discriptive Data Mining techniques?
Clustering and Association Rules
What are Predictive Tasks in Data Mining?
use past data and current data to make predictions on the future
What is an exmaple of a predicitve data mining technique?
Classification
What is Clustering in Data Mining?
grouping similar data together. like grouping all fruits together and all vegetables together
What is the Association Rule in Data Mining?
it shows relationships between variables for example a grocerys tore could look and see that when people buy peanut butter they often by jelly.
What is Classification in Data Mining?
uses past data to predict which group new incoming data should be placed into.
Group Identification or Data Segmentation is ___________
Clustering!
What is the most common way to measure distance between two points?
Euclidean Distance, this is just the straight line distance between two points
Formula for Euclidean Distance is what?
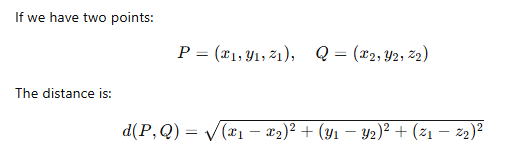
Two types of clustering:
Divisive Clustering
Agglomerative Clustering
Divisive Clustering: all items start in one large group and keep splitting into smaller clusters until each group is on its own (Big group to small group)
Agglomerative Clustering: Each item starts in their own cluster and the clusters gradually merge together until its all just one cluster. (Small group to big group)
Single Linkage CLustering (Nearest Neighbor Technique)
look at the groups with the closest distance and then merge them into one group
Complete Linkage Clustering means what?
the farthest points from each other and then you combine them
Average Linkage means what?
You find the average distance between your points and then you will start combining the groups together until you have comabined them all
What is a Dendrogram or what is its purpose?
tree-like diagram used to show the results of hierarchical clustering. It is the tree diagram stuff. Stuff that is at the bottom and low on the tree diagram are more similar while the boxes at the top of the tree disgram are not so simlar.
When looking at a physical Clustering Representation and you want to split the data into four clusters what would you do?
You decide how many clusters you want and then you draw a line horiztonal between the lines. However many lines you go throguh are the amount of groups you will have.
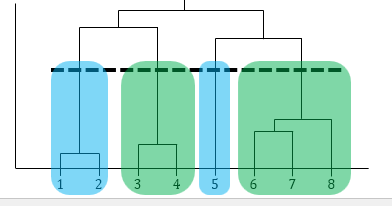
When dealing with a Dendrogram and you want to know where to split it what is a rule of thumb you can use?
find the largest verticle jump in the tree. Once you found that then draw a line in the middle of this jump/gap
What is the Association Rule Mining?
you are finding patterns of items that occur together in large data setsso one example would be a grocery store findng out people buy peanutbutter and jelly together. You are finding Dependency Rules
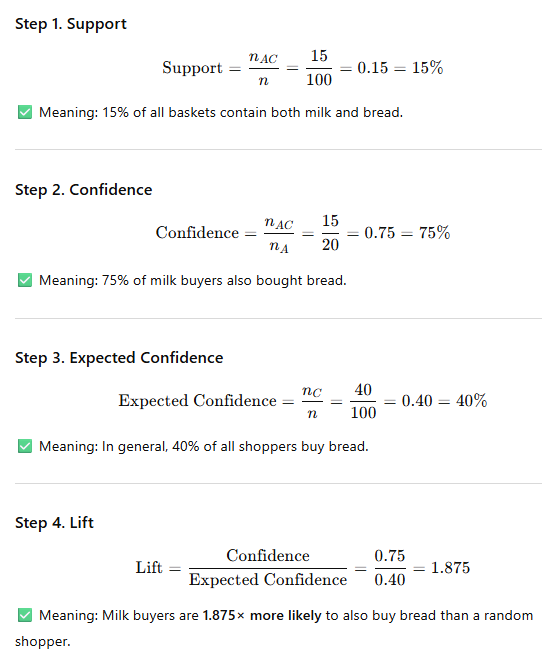
If you wanted to measure the strength of Association what are the two measurements?
Support = (amount of items that contain the antecedent and consequent) / (Total number of transactions)
Confidence = (amount of items that contain the antecedent and consequent) / (number of transactions that have the antedecent)
Strength of Association example
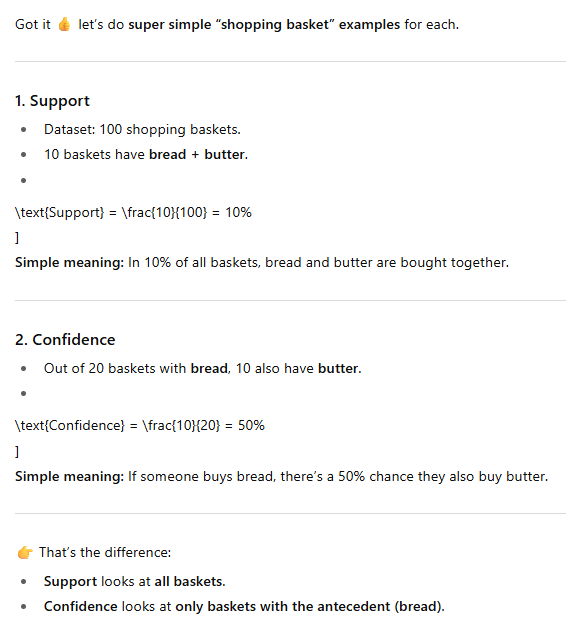
When we say this is the “Antecedent” of the problem what does that mean?
the group we are further analyizing. For example if we want to see how many people buy bread after they buy milk the milk group is our antecdent.
When we say this is the “Consequent” of the problem what does that mean?
Consequent is the outcome we test so we want to annalyze how many people buy bread after they have bought milk. Bread is the consequent becuase it is the thing we are testing for. It is the consequence of buying milk (not actually but a good way to remeber)

Example Problem